Enthalpy change
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What kind of reaction is associated with bond breaking
Endothermic
What kind of reaction is associated with bond making
Exothermic
What do all chemical reactant shave a certain amount of
Stored chemical energy
Enthalpy definition
Thermal energy stored in a system
What is a system
Atoms and bonds involved in the chemical reaction
What can Enthalpy change be monitored by
Temperature change
Symbol for Enthalpy change
Triangle H
Exothermic reaction features
Products have less energy than the reactants, energy is given out to surroundings, temperature of surroundings increases
Endothermic reaction features
Products have more energy than the reactants, energy is taken in from surroundings, temperature of surroundings decreases
Endothermic energy level diagram
Products energy level is higher than the reactants as heat has been taken in

Exothermic energy level diagram
Energy level of products is lower than reactants as heat is given out
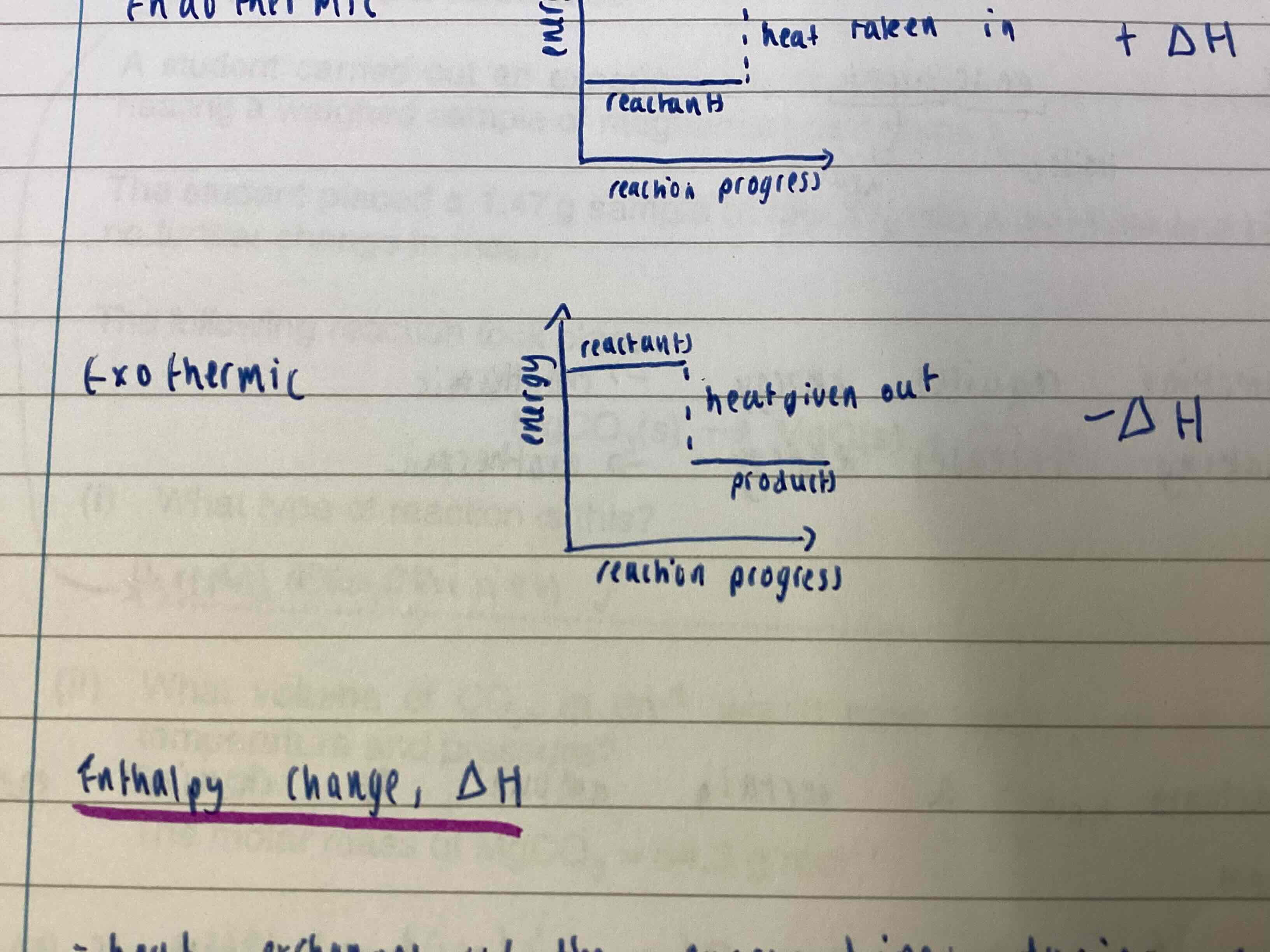
Enthalpy change definition
Heat exchanges with. He surroundings during a chemical reaction, is the difference between the energy of the products and the Enthalpy of reactants
Enthalpy change equation
Enthalpy change = Enthalpy products - Enthalpy of reactants
What does theta mean
Standard conditions
What is Enthalpy change measure in
KJ/ mol
Standard conditions
100 kPa, 298 Kelvin, 1 mol/dm³ concentration
Standard state definition
The physical state of that substance under standard conditions eg water = liquid
Activation energy
Ea = minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
Exothermic Enthalpy profile diagram
Products below reactants

Endothermic Enthalpy diagram
Enthalpy of products is higher than reactants
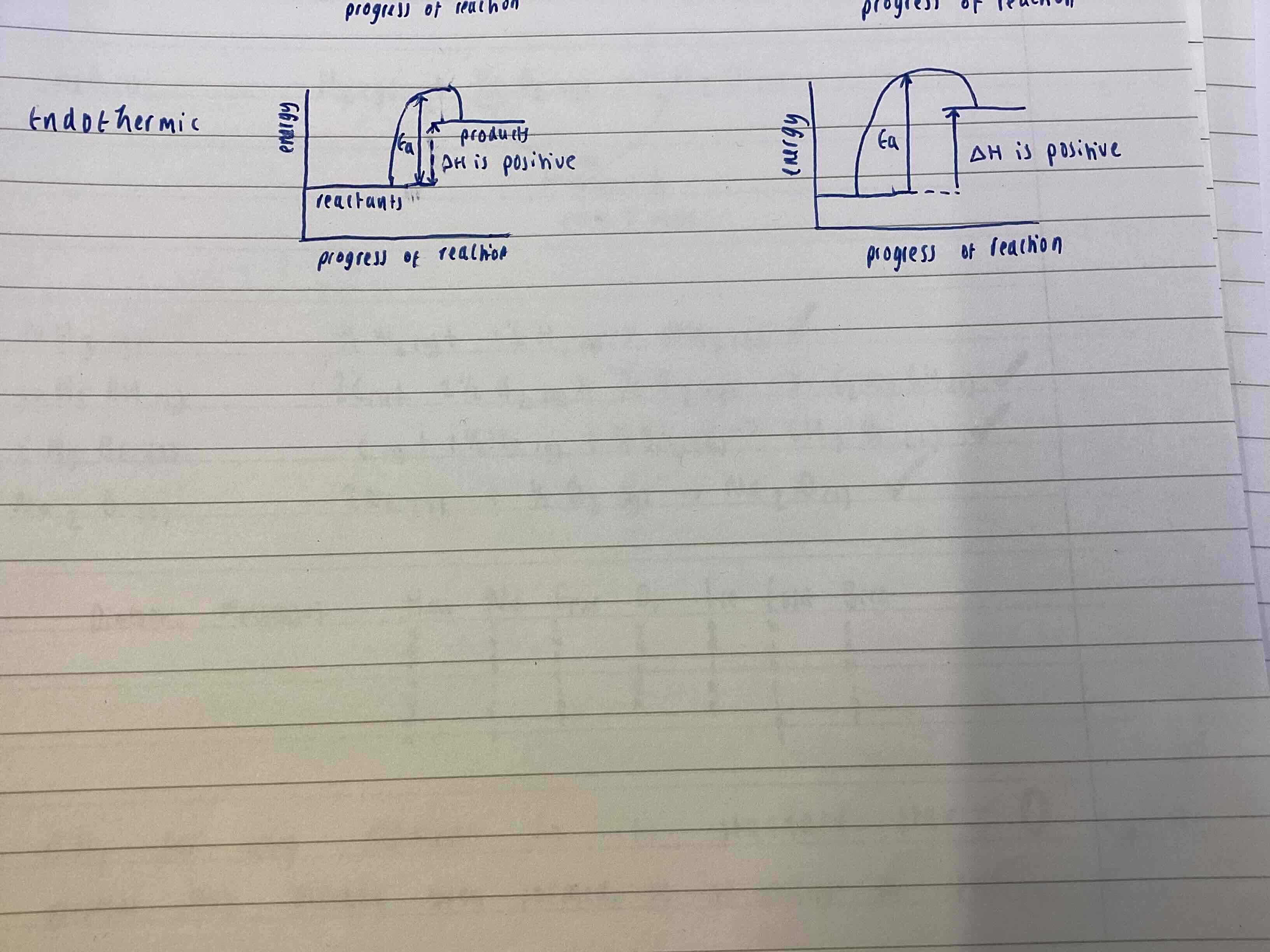
What do you need on Enthalpy profile diagrams
State symbols, all arrows point upwards
Enthalpy of formation symbol
Triangle H subscript f
Enthalpy change definition
When one mole of a substance is made from its constituent elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Enthalpy o formation of CH4
C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4 (g)
What do you need to do when writing Enthalpy of formation equations
Balance so you get one mole of product, use state symbols
What is the ^Hf for any element in its standard state
0 as the element has already been formed so there’s no change in energy
Diatomic molecules
Hydrogen, Nitrogen , Fluorine, Oxygen, Iodine, Chlroine, Bromine → Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
Enthalpy change of combustion symbol
Triangle ^ H subscript c
Enthalpy change of combustion definition
Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance us burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions
^Hc of CH4
CH4 (g) + 2O2(g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
What do you need in equations for ^Hc
State symbols, one mole of named compound eg chlorine
Enthalpy change of neutralisation symbol
Triangle ^ H subscript neut
^Hneut definition
Enthalpy change when one mole of water is formed during a neutralisation reaction under standard conditions with all reactants and products in their standard states
^Hneut of HCl
HCl (aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
What do you need in equations for ^Hneut
State symbols, one mole of water in products
Ionic equation for neutralisation ractions
H+ + OH- → H2O
Trick to work out equations for ^Hneut
Only need one lot of H+ ions so for things like H2SO4 you can quickly see you only need half eg ½ H2SO4 (aq) + NaOH(aq) → H2O (l) + ½ Na2SO4
Enthalpy change of reaction symbol
Triangle H subscript r
^Hr definition
Enthalpy change when the number of moles of reactants specified by the balanced equation react together
How can ^Hr, ^Hc, ^Hneut be measured
Through an experiment using a thermometer