bio II exam 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/94
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1
New cards
FUNGI
* Domain?
* 6 monolithic groups? (CANBBG)
* Originated from which single-cellular flagellate protist group?
* Domain?
* 6 monolithic groups? (CANBBG)
* Originated from which single-cellular flagellate protist group?
eukarya, chytrid, asco, neo, basidio, blast, glomer, opisthokonts
2
New cards
what eukaryotic kingdom does this describe?
* chitin cell walls (in insects too hehe)
* filamentous or yeasts
* composed of hyphae (which may be separated by hypha)
* chitin cell walls (in insects too hehe)
* filamentous or yeasts
* composed of hyphae (which may be separated by hypha)
fungi
3
New cards
hyphae cells can (or cant) be seperated via septa
* _____- has 1 nucleus per septa
* _____ - no septa but hundreds of nuclei in continuous cytoplasmic mass
* _____- has 1 nucleus per septa
* _____ - no septa but hundreds of nuclei in continuous cytoplasmic mass
septa hypha, coenocytic hypha
4
New cards
FUNGI
____: single thread-like cell (but can house more than 1 nuclei separated by septa)
____: interconnected hyphae + main body of fungi
____: reproductive body, “mushroom part”types
____: the stalk/stem
____: dome top part
____: thin tissue that hold spores
____: single thread-like cell (but can house more than 1 nuclei separated by septa)
____: interconnected hyphae + main body of fungi
____: reproductive body, “mushroom part”types
____: the stalk/stem
____: dome top part
____: thin tissue that hold spores
hypha, mycelium, fruiting body, stipe, cap, gills
5
New cards
FUNGI
* 3 ways fungi reproduce asexually
* what is unique about the dikaryotic stage of reproduction?
* 3 ways fungi reproduce asexually
* what is unique about the dikaryotic stage of reproduction?
conidiospores, fragmentation, budding, plasmogamy/haploid nuclei cell
6
New cards
list order of fungal sexual reproduction
plasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis, release
7
New cards
are fungi autotrophs or heterotrophs? are they more closely related to plants or animals?
heterotrophs, animals
8
New cards
* which phylum are club fungi in?
* which phylum are sac fungi like yeast, mold, truffles in?
* which phylum is Rhizopus (bread mold) in?
* which phylum are sac fungi like yeast, mold, truffles in?
* which phylum is Rhizopus (bread mold) in?
basidiomycota, ascomycota, zygomycota
9
New cards
“Imperfect fungi” do not produce _____
(to our knowledge) and are in the phylum _____ and reproduce via this type of spore: ___
(to our knowledge) and are in the phylum _____ and reproduce via this type of spore: ___
sexually, deutermycota, conidiospore
10
New cards
* lichen: symbiotic mutualistic relationship formed between what 2 organisms?
* ____: symbiotic mutualistic relationship formed between plant roots and fungi
* ____: symbiotic mutualistic relationship formed between plant roots and fungi
fungi and algae, mycorrhizae
11
New cards
what 2 infections do parasitic fungi cause?
athletes foot and ringworm
12
New cards
3 types of fungi nutrition
1. ____: obtain nutrients from dead organisms
2. ____: absorbs nutrients from live host’s tissue
3. ____: symbiosis that is beneficial to both fungi and host
1. ____: obtain nutrients from dead organisms
2. ____: absorbs nutrients from live host’s tissue
3. ____: symbiosis that is beneficial to both fungi and host
saprophytes, parasites, mutualistic
13
New cards
* In lichens:
a. ____ receive nutrients and energy
b. ____ receive protection and moisture
\
* mycorrhizae have a special penetration mycelium called ____
* __% of plants have mycorrhizae
a. ____ receive nutrients and energy
b. ____ receive protection and moisture
\
* mycorrhizae have a special penetration mycelium called ____
* __% of plants have mycorrhizae
fungi, algae, arbuscules, 90
14
New cards
PLANTAE KINGDOM
* are green algae include in the plant kingdom?
* are fungi included in the plant kingdom?
* what do algae and plants have in common?
* are green algae include in the plant kingdom?
* are fungi included in the plant kingdom?
* what do algae and plants have in common?
yes, no, photosynthetic, cellulose, starch, chlorophyll a and b
15
New cards
plant adaptions for terrestrial life:
* **___:** coating that prevents zygote from drying
* **___:** waxy layer prevents water loss
* **___**: openings for gas exchange and prevent water loss
* ___: root-like structure for anchor and absorption
* ___: xylem and phloem for water/food transport
* ___: life cycle alternated between haploid + diploid generations (haplodiplontic)
* ___: root fungi mutualistic symbiosis
* **___:** coating that prevents zygote from drying
* **___:** waxy layer prevents water loss
* **___**: openings for gas exchange and prevent water loss
* ___: root-like structure for anchor and absorption
* ___: xylem and phloem for water/food transport
* ___: life cycle alternated between haploid + diploid generations (haplodiplontic)
* ___: root fungi mutualistic symbiosis
sphoropollenin, cuticle, stomata, rhizoids, vascularity, alternation of generations, mycorrhizae
16
New cards
* as plants became better adapted to land, which phase of the life cycle became the most dominant generation?
* what part of the body plant is haploid?
* what part of the body plant is diploid?
* are spores haploid or diploid?
a. produced by process of ___ in ____
* what stage produces the gametes?a. produced by process of *___* in *____* (archegonia, antheridia)
* what part of the body plant is haploid?
* what part of the body plant is diploid?
* are spores haploid or diploid?
a. produced by process of ___ in ____
* what stage produces the gametes?a. produced by process of *___* in *____* (archegonia, antheridia)
sporophyte, gametophyte, sporophyte, haploid, meiosis, sporangium, gametophyte, mitosis, gametangia
17
New cards
which plant kingdom phylum is:
* **non-vascular** (ergo no specialized functions)
a. but untrue as root, stem, and leaves
* photosynthetic
* “amphibians of the plant kingdom.”
* both **asexual** and **sexual**
* require water for sexual reproduction (**bc flagellated sperm**)
* **dominant gametophyte** stage
* Liverworts, hornwarts, mosses
\*the worts came before moss\*
\
* **non-vascular** (ergo no specialized functions)
a. but untrue as root, stem, and leaves
* photosynthetic
* “amphibians of the plant kingdom.”
* both **asexual** and **sexual**
* require water for sexual reproduction (**bc flagellated sperm**)
* **dominant gametophyte** stage
* Liverworts, hornwarts, mosses
\*the worts came before moss\*
\
bryophytes
18
New cards
___: (in asexual reproduction) multicellular vegetative bodies/buds (lense shaped) that are in cups
gemma
19
New cards
which plant is a true byrophyte?
moss
20
New cards
how are bryophytes important to ecology and economics?
(when bryophytes die, forms a thin soil layer)
* ecology: helps prevent ____
* economics: used as ___or burned as ___
(when bryophytes die, forms a thin soil layer)
* ecology: helps prevent ____
* economics: used as ___or burned as ___
erosion, potting soil, fuel
21
New cards
which plant kingdom phylum is:
* **vascular** but **seedless** (so still restricted to moist habitat)
* **dominant sporophyte** stage
* **true** **roots**
* most are **homosporous**
* club moss, ferns
\
* **vascular** but **seedless** (so still restricted to moist habitat)
* **dominant sporophyte** stage
* **true** **roots**
* most are **homosporous**
* club moss, ferns
\
tracheophytes
22
New cards
2 tracheophyte clades:
1. ___:
* club mosses (not true moss)
* has **true roots** but **lycophylls**
* sporophylls + strobilus
* **microphylls**
2. ___:
* ferns, whisk ferns, horsetails
* has fronds, sori, fiddleheads
* **Euphylls**
* **macrophylls**
\
what do both clades have in common?
\
1. ___:
* club mosses (not true moss)
* has **true roots** but **lycophylls**
* sporophylls + strobilus
* **microphylls**
2. ___:
* ferns, whisk ferns, horsetails
* has fronds, sori, fiddleheads
* **Euphylls**
* **macrophylls**
\
what do both clades have in common?
\
lycophytes, ptedriophytes/monilophytes, seedless
23
New cards
____small leaf-like structure w/ single vein (only in lycophytes!!)
____: large leaf-like leaves with many veins (all other plant phylas)
____: bisexual spores; produces 1 spore type that can become male or female
____: spores are already male or female
____: large leaf-like leaves with many veins (all other plant phylas)
____: bisexual spores; produces 1 spore type that can become male or female
____: spores are already male or female
microphylls, macrophylls, homospores, heterospores
24
New cards
In tracheophytes (as a whole), which vascular organ evolved first? second? third?
stem, roots, leaves
25
New cards
FERN LIFE CYCLE
* sori contain the _____
* process of ____ releases its spores
* process of mitosis creates the ______ (heart shape)
* this gametophyte contains both the antheridium and archegonium!
* flagellated sperm uses water to ___ to ___ (female gametophyte)
* fertilize!
* zygote matures into embryo which then matures into ______
* sori contain the _____
* process of ____ releases its spores
* process of mitosis creates the ______ (heart shape)
* this gametophyte contains both the antheridium and archegonium!
* flagellated sperm uses water to ___ to ___ (female gametophyte)
* fertilize!
* zygote matures into embryo which then matures into ______
sporangium, meiosis, gametophyte, swim, archegonia, sporophyte
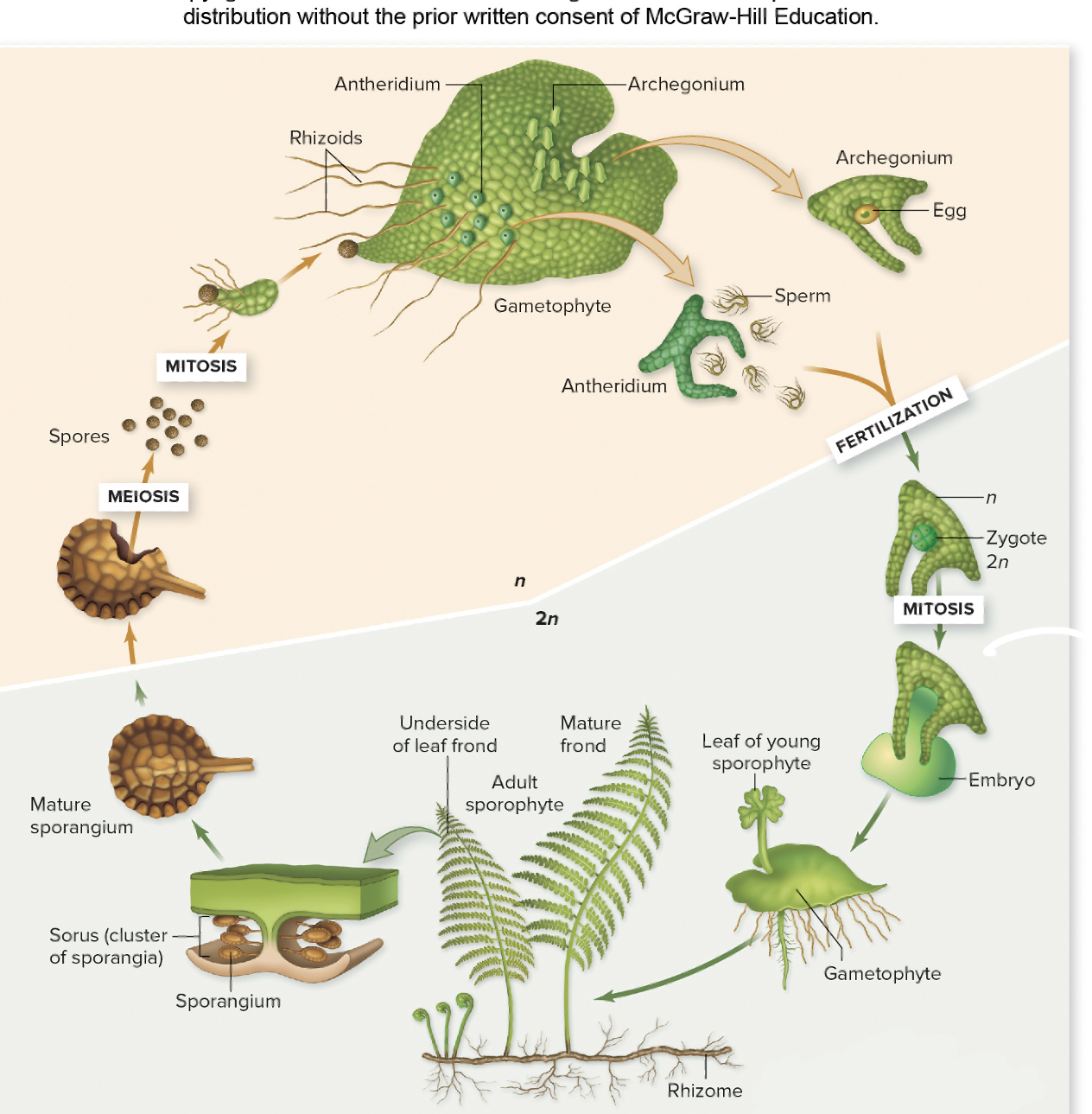
26
New cards
Note: Ferns are seedless but are closest living relative to ____
seed plants
27
New cards
club mosses have a cluster of microphyll-type leaves; these clusters form a cone. what is this cone called?
strobilus
28
New cards
FERNS CONTINUED
____: horizontal underground stem
____: tightly curled coils of young sporophyll leaf (emerges from rhizome)
____: sporangia clusters on back of sporophyll leaf
\
* fern’s germinating spore develops into a small __-shaped gametophyte anchored to the soil by ___.
____: horizontal underground stem
____: tightly curled coils of young sporophyll leaf (emerges from rhizome)
____: sporangia clusters on back of sporophyll leaf
\
* fern’s germinating spore develops into a small __-shaped gametophyte anchored to the soil by ___.
rhizome, fiddlehead, sori, heart, rhizoids
29
New cards
* _____:__ primary composition of cell wall synthesized by its _____
* _____: contents that makeup inside of cell (cytoplasm, organelles, etc)
* _____: contents that makeup inside of cell (cytoplasm, organelles, etc)
cellulose, protoplasts, protoplasts,
30
New cards
_____: undifferentiated cells that divide indefinitely and give rise to differentiated cells/specialized area for cell growth
* ____ meristems: located on tip of root/stems
a. primary growth (lengthens stem/roots)
b. produces leaves/flowers
c. protected by root cap and stored in primordia leaf
* ____ meristems: located on sides of root/stems
a. secondary growth (widens)
\
\
* 2 types
1. ____: APICAL; adds secondary xylem + phloem
2. ____: LATERAL; replaces epidermis into thicker periderm aka cork/bark (basically gives rise to cork/bark)
\
\
* Xylem produced inward, phloem produces outward; bc meristems produce xylem cells first then phloem cells
\
* ____ meristems: located on tip of root/stems
a. primary growth (lengthens stem/roots)
b. produces leaves/flowers
c. protected by root cap and stored in primordia leaf
* ____ meristems: located on sides of root/stems
a. secondary growth (widens)
\
\
* 2 types
1. ____: APICAL; adds secondary xylem + phloem
2. ____: LATERAL; replaces epidermis into thicker periderm aka cork/bark (basically gives rise to cork/bark)
\
\
* Xylem produced inward, phloem produces outward; bc meristems produce xylem cells first then phloem cells
\
meristems, apical, lateral, vascular cambium, cork cambium
31
New cards
3 types of vascular tissue
\
1. _____: protects plant; one cell thick layer
* ____: waxy and prevents water loss
* ____: open and close stomata for regulating gas exchange + transpiration (only found in epidermis cells containing chloroplasts)
* ____: hair-like outgrowths to reduce water loss, reflect light, and defense
2. _____:
* ____: transports water + minerals like PPN (phosphate, potassium, nit)
a. vessels and tracheids
* ____: transports water + organic material (multidirectional flow)
a. sieve plates and companion cells
\
3. _____: functions as storage, photosynthesis, support, short-distance transport
* its 3 cell types: ____
* \
\
\
1. _____: protects plant; one cell thick layer
* ____: waxy and prevents water loss
* ____: open and close stomata for regulating gas exchange + transpiration (only found in epidermis cells containing chloroplasts)
* ____: hair-like outgrowths to reduce water loss, reflect light, and defense
2. _____:
* ____: transports water + minerals like PPN (phosphate, potassium, nit)
a. vessels and tracheids
* ____: transports water + organic material (multidirectional flow)
a. sieve plates and companion cells
\
3. _____: functions as storage, photosynthesis, support, short-distance transport
* its 3 cell types: ____
* \
\
dermal tissue, cuticle, guard cells. trichomes, vascular tissue, xylem, phloem, ground tissue, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma
32
New cards
3 type of ground tissue cells
1. _____: (imagine like filler tissue) functions as storage, photosynthesis, secretion
* thin walls
* living protoplasts = so long life
2. _____: (imagine celery) functions as support bc really bendy/flexible
* thin flexible walls
* living protoplasts = long life
3. _____: (imagine wood) functions as structure and protection bc composed of lignin
* hard thick walls
* dead at maturity
1. _____: (imagine like filler tissue) functions as storage, photosynthesis, secretion
* thin walls
* living protoplasts = so long life
2. _____: (imagine celery) functions as support bc really bendy/flexible
* thin flexible walls
* living protoplasts = long life
3. _____: (imagine wood) functions as structure and protection bc composed of lignin
* hard thick walls
* dead at maturity
parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma
33
New cards
4 different zones of roots (top-→ bottom)
1. Zone of _____: cells mature into different types of tissue
* Zone of _____: cells increase in size (remember the vacuole expansion thing)
* Zone of ____: composed of apical meristems, active division going on in here
* _____: protects meristem and has gravity role
1. Zone of _____: cells mature into different types of tissue
* Zone of _____: cells increase in size (remember the vacuole expansion thing)
* Zone of ____: composed of apical meristems, active division going on in here
* _____: protects meristem and has gravity role
maturity, elongation, cell division, root cap
34
New cards
Different root types:
* ____: single large root with emerging smaller roots
* ____: system of smaller roots of similar diameter
* ____: any root that emerges out of stem/non-root place
a. ___ roots: thick roots that stick into ground and withstand wind (ex: corn)
b. ___ roots: roots extend into air and absorb water from air (ex: orchids)
c. ______: spongy outgrowth that sticks out of water in swamps/wet environments for oxygen intake
d. ___ roots: cork-screw root that spirals deeper into the ground each year (ex: lily flower bulbs)
e. ___ roots: peg-like roots of plants that lack chlorophyll; penetrates into plant stem (ex: dodder plant)
f. ___ roots: stores excess starch (ex: roots that grow from sweet potato, carrot, radish)
g. ___ roots: stores water, especially in arid regions (ex: pumpkins)
h. ___ roots: for extra structural support (ex: fig and tropical trees)
* ____: single large root with emerging smaller roots
* ____: system of smaller roots of similar diameter
* ____: any root that emerges out of stem/non-root place
a. ___ roots: thick roots that stick into ground and withstand wind (ex: corn)
b. ___ roots: roots extend into air and absorb water from air (ex: orchids)
c. ______: spongy outgrowth that sticks out of water in swamps/wet environments for oxygen intake
d. ___ roots: cork-screw root that spirals deeper into the ground each year (ex: lily flower bulbs)
e. ___ roots: peg-like roots of plants that lack chlorophyll; penetrates into plant stem (ex: dodder plant)
f. ___ roots: stores excess starch (ex: roots that grow from sweet potato, carrot, radish)
g. ___ roots: stores water, especially in arid regions (ex: pumpkins)
h. ___ roots: for extra structural support (ex: fig and tropical trees)
taproot, fibrous, adventitious, prop, aerial, pneumatophores, contractile, parasitic, food storage, water storage, buttress
35
New cards
* ___ point of attachment of leaf and stem
* ___: area of stem between 2 nodes
* ___: flat part of leaf
* ___: leaf stalk
* ___: develops into stems w/leaves or flowers
* ___: extends stem
* ___: area of stem between 2 nodes
* ___: flat part of leaf
* ___: leaf stalk
* ___: develops into stems w/leaves or flowers
* ___: extends stem
node, internode, blade, petiole, axillary bud, terminal bud
36
New cards
Growth rings on tree stumps
* light rings = _____
* dark rings = _____
* light rings = _____
* dark rings = _____
spring wood, summer wood
37
New cards
* ____: life cycle is 1 growing season (ex: marigolds and corn)
* ____: life cycle is 2 growing seasons (ex: carrots and parsley)
* ____: plants grow and produce year after year (ex: trees, shrubs, vines)
* ____: life cycle is 2 growing seasons (ex: carrots and parsley)
* ____: plants grow and produce year after year (ex: trees, shrubs, vines)
annuals, biannuals, perennials
38
New cards
Modified stems
* ____: swollen underground stem with fleshy leaves
* ____: resembles bulbs^ but no fleshy leaves
* ____: horizontal underground stem with adventitious roots
* ____: horizontal stems with long internodes that grow along the surface of ground
* ____: swollen tips of rhizomes ^ that contain carbs (ex: potatoes!)
* ____: twine around support and aids in climbing (looks like stretched out telephone cord)
* ____: swollen underground stem with fleshy leaves
* ____: resembles bulbs^ but no fleshy leaves
* ____: horizontal underground stem with adventitious roots
* ____: horizontal stems with long internodes that grow along the surface of ground
* ____: swollen tips of rhizomes ^ that contain carbs (ex: potatoes!)
* ____: twine around support and aids in climbing (looks like stretched out telephone cord)
bulbs, corms, rhizome, runners/stolons, tubers, tendrils
39
New cards
Leaf morphology
* ____: single blade
* ____: blade divided into leaflets
* ____: has parallel veins
* ____: has net-like veins
* ____: single blade
* ____: blade divided into leaflets
* ____: has parallel veins
* ____: has net-like veins
simple leaf, compound leaf, dicot, eudicot
40
New cards
_____: ground tissue found in leaves containing chloroplasts for photosynthesis
* has 2 types:
1. _____: contains air spaces for taking in CO2/releasing O2 process of photosynthesis
2. _____: column-shaped and located right under upper epidermis; where majority of chloroplast is (bc closer to sun duh)
* has 2 types:
1. _____: contains air spaces for taking in CO2/releasing O2 process of photosynthesis
2. _____: column-shaped and located right under upper epidermis; where majority of chloroplast is (bc closer to sun duh)
mesophyll, spongy, palaside
41
New cards
Recall that flowering is triggered by day and seasonal cues; photoperiods can be manipulated commercially
* Poinsettias (Mexican red xmas flower) can be manipulated by light in greenhouses, so it grows in time for holidays)
* Winter wheat cant flower without being chilled, then its seed will bloom in spring time
\
say yes
* Poinsettias (Mexican red xmas flower) can be manipulated by light in greenhouses, so it grows in time for holidays)
* Winter wheat cant flower without being chilled, then its seed will bloom in spring time
\
say yes
yes
42
New cards
Flower whorls
* ____: (whorl 4) _____
* ____: (whorl 3) _____
* ____: (whorl 2) collective term for the ___ and its structures
* ____: (whorl 1) collective term for the ____ and its structures
* ____: (whorl 4) _____
* ____: (whorl 3) _____
* ____: (whorl 2) collective term for the ___ and its structures
* ____: (whorl 1) collective term for the ____ and its structures
calyx, sepals, corolla, petals, androecium, stamen, gynoecium, carpals
43
New cards
* ____: flower has both stamens and carpals
* ____: flower lack either stamens or carpals (hence unisex flowers)
* ____: flower lack either stamens or carpals (hence unisex flowers)
perfect flower, imperfect flower
44
New cards
* ____ flowers → Bilateral symmetry
* ____ flowers → Radial symmetry
* ____ flowers → Radial symmetry
later evolved, primitive
45
New cards
Double fertilization process
1. Pollen grain (contains 2 cells: generative cell and pollen tube cell) adheres to stigma
2. Pollen tube penetrates into the style
3. Pollen tube cell grows deeper into style, whereas generative cell divides into 2 sperm cells
4. Pollen tube penetrates ovary in its hole called “micropyle”
5. 1 sperm fertilize with egg to make zygote, whereas other sperm fertilizes with 2 polar nuclei/central cell to make endosperm
\
say yes
1. Pollen grain (contains 2 cells: generative cell and pollen tube cell) adheres to stigma
2. Pollen tube penetrates into the style
3. Pollen tube cell grows deeper into style, whereas generative cell divides into 2 sperm cells
4. Pollen tube penetrates ovary in its hole called “micropyle”
5. 1 sperm fertilize with egg to make zygote, whereas other sperm fertilizes with 2 polar nuclei/central cell to make endosperm
\
say yes
yes
46
New cards
types of pollination
____: flower’s pollen pollinates stigma of same flower (in monoecious flowers)
____: flower A’s pollen pollinates flower B’s stigma (in diecious flowers)
a. Insects, birds, humans (artificial hybridization), and wind can do this
\
know that there was co-evolution: angiosperms evolved during Cretaceous period, and pollinating insects also evolved during this time and helped the angiosperms evolve
____: flower’s pollen pollinates stigma of same flower (in monoecious flowers)
____: flower A’s pollen pollinates flower B’s stigma (in diecious flowers)
a. Insects, birds, humans (artificial hybridization), and wind can do this
\
know that there was co-evolution: angiosperms evolved during Cretaceous period, and pollinating insects also evolved during this time and helped the angiosperms evolve
self pollination, cross pollination
47
New cards
Seedling parts
(remember – Seed = mature ovule\*)
* _____: embryonic leaf that forms the first leaf/leaves
a. Monocots and eudicots
* _____: embryonic root that forms the first root
* _____: forms the stem
* _____: has shoot apical meristem and tiny foilage leaf called ‘plumule’
(remember – Seed = mature ovule\*)
* _____: embryonic leaf that forms the first leaf/leaves
a. Monocots and eudicots
* _____: embryonic root that forms the first root
* _____: forms the stem
* _____: has shoot apical meristem and tiny foilage leaf called ‘plumule’
cotyledon, radicle, hypocotyl, epicotyl
48
New cards
_____: fruit that splits open at maturity
* Splits open to disperse seeds
* Ex: legumes
_____: fruit doesn’t split open at maturity
* Depends on decomposition or animal consumption to disperse seeds
* Ex: nuts
* Splits open to disperse seeds
* Ex: legumes
_____: fruit doesn’t split open at maturity
* Depends on decomposition or animal consumption to disperse seeds
* Ex: nuts
dehiscent, indehiscent
49
New cards
_____: a “pulling force” as water vaporizes from leaf stomata
_____: water molecules stick to each other
_____: water molecules stick to xylem walls
_____: water goes from high → low concentration through plasma membranes
_____: water molecules stick to each other
_____: water molecules stick to xylem walls
_____: water goes from high → low concentration through plasma membranes
transpiration, cohesion, adhesion, osmosis
50
New cards
___: if plant cell placed into ___ → cell expands
*___:* if plant cell placed into ____ → cell shrinks
*___:* if plant cell placed into ____ → cell shrinks
turgid, water, plasmolysis, sucrose
51
New cards
_____ deal with drought via morphological adaptions like:
a. Dormancy
b. Less leaves – deciduous plants (plants that shed leaves)
c. Cuticle
d. Reducing # of stomata
e. Having stomata in pits in the leaf
\
say yes
a. Dormancy
b. Less leaves – deciduous plants (plants that shed leaves)
c. Cuticle
d. Reducing # of stomata
e. Having stomata in pits in the leaf
\
say yes
leaves
52
New cards
Topsoil: a combo of what 3 things?
minerals, living organisms, humus
53
New cards
CARINIVEROUS PLANTS
* Grow in __ soils which lack ___
* Traps/eats insects to make up for their lack of ___
* Has modified ___ for luring/trapping
* Digests organisms via secreted ___
* Ex: venus fly trap, pitcher plant, sundew
* Grow in __ soils which lack ___
* Traps/eats insects to make up for their lack of ___
* Has modified ___ for luring/trapping
* Digests organisms via secreted ___
* Ex: venus fly trap, pitcher plant, sundew
acidic, nitrogen, nitrogen, leaves, enzymes
54
New cards
How are we dealing with food security issues?
* _____: focuses on increasing plants’ mineral uptake/storage
* GMO plants
a. Secrete ___ to solubilize ___
b. ____ plasma transport genes and transfer them into other plants
* _____: focuses on increasing plants’ mineral uptake/storage
* GMO plants
a. Secrete ___ to solubilize ___
b. ____ plasma transport genes and transfer them into other plants
food fortification, citrate, phosphate, clone
55
New cards
______:__ use to plants to concentrate and breakdown pollutants; 3 methods -
1. ____: Containment is broken down
2. ____: Contaminant is released via stomata
3. ____: Contanimant is concentrated in plant shoots
* All the pollutants are later harvested
1. ____: Containment is broken down
2. ____: Contaminant is released via stomata
3. ____: Contanimant is concentrated in plant shoots
* All the pollutants are later harvested
phytoremediation, phytodegration, phytovolatilization, phytoaccumulation
56
New cards
_____: divided into 4 eons > subdivided into eras > subdivided into periods
* what are the 4 eons in order? (HAPP)
* what are the 4 eons in order? (HAPP)
geological time, haeden, archean, protoerzoic, phanerzoic
57
New cards
meteor hit earth ___ BYA
* when this happened, oceans ____ and our mantle melted to ____ C degrees
* Earth began to change when ____ levels shifted
* ____ converted rock into soil
* CO2 then formed carbonic acid → decreased CO2 → lowers earth temperature
* when this happened, oceans ____ and our mantle melted to ____ C degrees
* Earth began to change when ____ levels shifted
* ____ converted rock into soil
* CO2 then formed carbonic acid → decreased CO2 → lowers earth temperature
4\.6, vaporized, 2000, co2, weathering
58
New cards
Crust created slabs of rock = **_____** (under continents + oceans)
* When it shifts, it creates **____**
* 2 supercontinents formed:
1. ____ (all continents)
2. ____ (all current southern hemisphere continents
a. ____ (formed from Gondwana)
* When it shifts, it creates **____**
* 2 supercontinents formed:
1. ____ (all continents)
2. ____ (all current southern hemisphere continents
a. ____ (formed from Gondwana)
plates, plate tectonics, rodinia, gondwana, pangea
59
New cards
life first emerged in which eon?
* ____: diversification of multicellular organisms
* animals appeared and plants transition to land
* ____: diversification of multicellular organisms
* animals appeared and plants transition to land
archean, cambrian explosion,
60
New cards
2 theories on how earth’s organic molecules formed
1. _____ theory: meteors/comets that slammed into earth possibly carried organic materials, but we discovered that meteor carbon isotopes didnt match with earth’s
2. ______ theory: although heavily debated, early atmosphere’s composition was thought to have CO2, nitrogen, water vapor, hydrogen
* This chemical makeup is called **reducing atmosphere** bc carbon availability and its electrons = don't require tons of energy to form life
1. _____ theory: meteors/comets that slammed into earth possibly carried organic materials, but we discovered that meteor carbon isotopes didnt match with earth’s
2. ______ theory: although heavily debated, early atmosphere’s composition was thought to have CO2, nitrogen, water vapor, hydrogen
* This chemical makeup is called **reducing atmosphere** bc carbon availability and its electrons = don't require tons of energy to form life
extraterrestrial, earth
61
New cards
CONDITIONS OF EARLY EARTH
* Did Haeden eon support life?
* Earth’s first organisms emerged + lived in ____ temperatures
* Did Haeden eon support life?
* Earth’s first organisms emerged + lived in ____ temperatures
no, high
62
New cards
* what process produced atmosphere’s O2?
* O2 atmosphere interacted with UV radiation = ___
a. this makes what possible?
* O2 atmosphere interacted with UV radiation = ___
a. this makes what possible?
oxygenic photosynthesis, ozone layer, life on land
63
New cards
Mitochondria and chloroplasts entered proto-eukaryotes via **____** (in this exact order)
endosymbiosis
64
New cards
evolution of endomembrane system caused by infolding of ______
* _____ accounts for eukaryotic complexity
1. Physical separation of translation/transcription adds levels of gene expression
2. Golgi apparatus and ER - facilitate transport and localizes specific _____ inside cell
* _____ accounts for eukaryotic complexity
1. Physical separation of translation/transcription adds levels of gene expression
2. Golgi apparatus and ER - facilitate transport and localizes specific _____ inside cell
cell membrane, nuclear membrane, proteins
65
New cards
4 plant phyla (in order)?
bryophytes, tracheophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms
66
New cards
4 types of growth in plants
1. ____: meristems continue to produce different tissues, similar to human STEM cells, can become anything!
2. ____: animal and plant organ growth only goes to a certain size
3. ____: lengthens root/shoot
4. ____: widens root/shoot
1. ____: meristems continue to produce different tissues, similar to human STEM cells, can become anything!
2. ____: animal and plant organ growth only goes to a certain size
3. ____: lengthens root/shoot
4. ____: widens root/shoot
indeterminate growth, determinate growth, primary growth, secondary growth
67
New cards
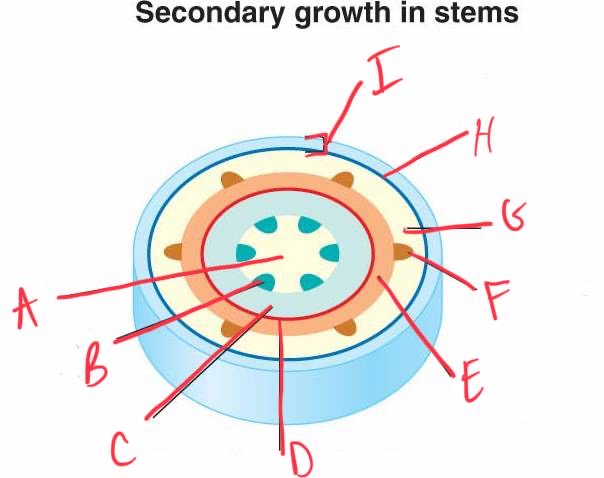
label accordingly
A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
F:
A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
F:
pith, primary xylem, secondary xylem, vascular cambium, secondary phloem, primary phloem, cortex, cork cambium, periderm
68
New cards
leaves grow from the ________
* they don’t really have secondary growth but can\*
* they don’t really have secondary growth but can\*
primadoria
69
New cards
Leaf vs leaflet
* ____: If its coming from an axil bud
* ____: If its not coming from an axil bud
Veination
* ____: all veins extend from midvein
* ____: veins intersect and come from a central point of the petiole
Shape types
* ____: no lobes
* ____: still 1 leaf but lobed (gravity falls leaf)
* ____: multiple leaflets
* ____: If its coming from an axil bud
* ____: If its not coming from an axil bud
Veination
* ____: all veins extend from midvein
* ____: veins intersect and come from a central point of the petiole
Shape types
* ____: no lobes
* ____: still 1 leaf but lobed (gravity falls leaf)
* ____: multiple leaflets
leaf, leaflet, pinnate, palmate, simple, lobed, compound
70
New cards
Shoot apical meristems create 3 types of primary-tissue making meristems:
1. _____: this meristem will make dermal tissue (→epidermis)
2. _____: this meristem will make vascular tissue (→primary xylem and phloem)
3. _____: this meristem will make ground tissue (→pith, cortex)
1. _____: this meristem will make dermal tissue (→epidermis)
2. _____: this meristem will make vascular tissue (→primary xylem and phloem)
3. _____: this meristem will make ground tissue (→pith, cortex)
protoderm, procambium, ground meristem
71
New cards
MOSS LIFE CYCLE
* spores ____ to make gametophytes
* male sporophyte’s antheridia will release its ____ to swim to ____ (female gametophyte)
* fertilize!
* zygote will mature into embryo which matures into _____
* sporophyte will release its ____
* spores ____ to make gametophytes
* male sporophyte’s antheridia will release its ____ to swim to ____ (female gametophyte)
* fertilize!
* zygote will mature into embryo which matures into _____
* sporophyte will release its ____
germinate, flagellated sperm, archegonia, sporophyte, sporangia
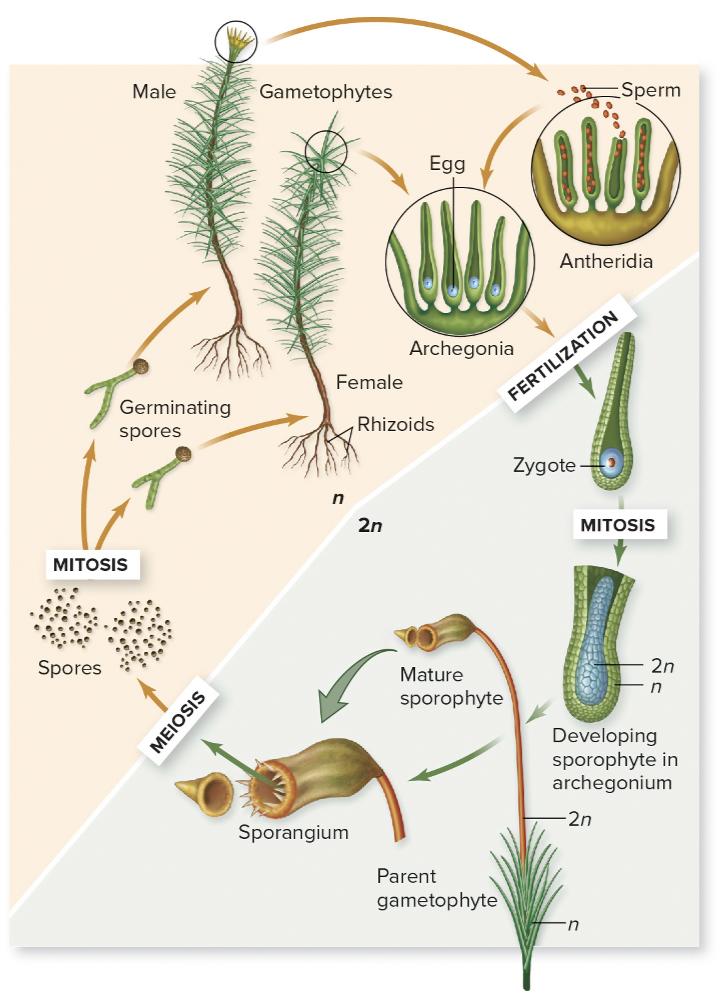
72
New cards
MANCHURIA LIFE CYCLE
* spores ____ to make gametophytes
* mature thallus (male gametophyte) will release its ___ to swim to the ___ (female gametophyte)
* fertilize!
* zygote will mature into embryo which matures into _____
* sporophyte will release its ___
* spores ____ to make gametophytes
* mature thallus (male gametophyte) will release its ___ to swim to the ___ (female gametophyte)
* fertilize!
* zygote will mature into embryo which matures into _____
* sporophyte will release its ___
germinate, flagellated sperm, sporophyte, sporangia
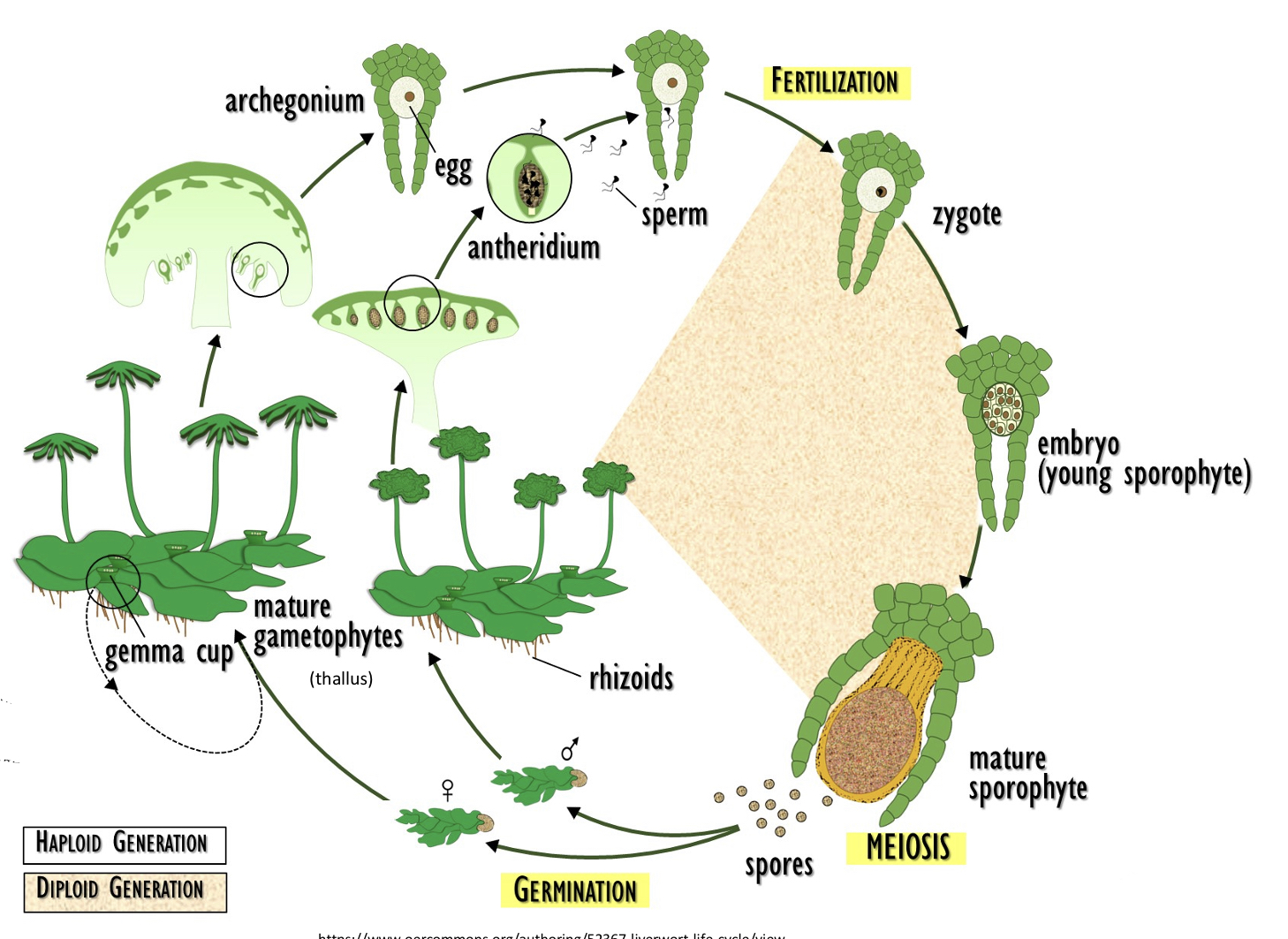
73
New cards
Order of terrestrial life adaptations?
(hint: put on covering, drink water and eat, get in the car, bloom in the shower)
(hint: put on covering, drink water and eat, get in the car, bloom in the shower)
cuticle, vascular tissue, seeds, flowers
74
New cards
know that 90% of absorbed water from roots is lost to atmosphere (hence why guard cells are saviors man!!)
\
say yes
\
say yes
yes
75
New cards
* integument develops into = ?
* ovule develops into = ?
* ovary develops into = ?
* ovule develops into = ?
* ovary develops into = ?
seed coat, seed, fruit
76
New cards
During the Mesozoic era (rise/fall of dinosaurs), what type of plants were dominant?
_____: Slow-growing tropical gymnosperms
_____: Slow-growing tropical gymnosperms
cycads
77
New cards
____: spore that produces female gametophyte
____: spore that produces male gametophyte
____: spore that produces male gametophyte
megaspore, microspore
78
New cards
* Do gymnosperms have flowers and fruits?
* Do they have cones?
* Are conifers monoecious or diecious?
a. commercial uses
* Do they have cones?
* Are conifers monoecious or diecious?
a. commercial uses
nom, yes, monoecious, timber, paper, resin, anticancer
79
New cards
What 3 adaptations enabled gymnosperms to thrive in cold, dry habitats?
seed, wind-blown pollen, wood
80
New cards
Are cycads (old house front yard plant) monoecious or dioecious?
Commercial uses?
Commercial uses?
dioecious, landscaping/ornamental
81
New cards
What is the only living species of Ginkgophytes?
Commercial uses?
Commercial uses?
gingko biloba, male plants used for landscaping
82
New cards
Phylum Anthophyta - What are 4 critical innovations that helped them be successful?
seed, flowers, fruits, endosperm
83
New cards
what does this describe?
* 1 cotyledon
* Long narrow leaves w/parallel veins
* Scattered vascular bundles
* Petal sets of 3
* Fibrous roots
* 1 cotyledon
* Long narrow leaves w/parallel veins
* Scattered vascular bundles
* Petal sets of 3
* Fibrous roots
monocot
84
New cards
what does this describe?
* 2 cotyledons
* Broad leaves w/network veins
* Ring vascular bundles
* Petal sets of 4-5
* Taproots
* 2 cotyledons
* Broad leaves w/network veins
* Ring vascular bundles
* Petal sets of 4-5
* Taproots
eudicot
85
New cards
* when mature, what structure forms fruit?
\
* Types of fruit:
1. _____ fruit: contains multiple ovaries (each containing a seed) but all comes from 1 flower
ex: strawberries
1. _____ fruit: contains multiple ovaries (each containing a seed) but each comes from multiple/its own flower; they all fuse
ex: pineapple
\
* _____: tomato
* _____: peas in a pod
* _____: has hard pit (peach/plum/cherries)
* _____: wing forms as outer structure (maple, elms, ashes)
\
* Types of fruit:
1. _____ fruit: contains multiple ovaries (each containing a seed) but all comes from 1 flower
ex: strawberries
1. _____ fruit: contains multiple ovaries (each containing a seed) but each comes from multiple/its own flower; they all fuse
ex: pineapple
\
* _____: tomato
* _____: peas in a pod
* _____: has hard pit (peach/plum/cherries)
* _____: wing forms as outer structure (maple, elms, ashes)
ovary, aggregate, multiple, berries, legumes, drupes, samaras
86
New cards
Pollinators and certain circumstances for germination
* Conifers dont open up until exposed to ___
* Nectar-loving bats are attracted to ____-smelling ___*/*___flowers
* ____ attracted to red/yellow flowers
* ____ attracted to ____-smelling yellow/blue/purple
* Conifers dont open up until exposed to ___
* Nectar-loving bats are attracted to ____-smelling ___*/*___flowers
* ____ attracted to red/yellow flowers
* ____ attracted to ____-smelling yellow/blue/purple
fire, sweet, pale, white, birds, bees, sweet
87
New cards
Commercial uses for seed plants?
* Food, Poacea (cereal wheat), rice, potatoes, roses, corn, cassava
* Wood used for lumber, paper, resin, etc
* Plant fibers (cotton) used for clothes
* 25% of medicine from angiosperms
* Illegal/legal drugs
\
say yes
* Food, Poacea (cereal wheat), rice, potatoes, roses, corn, cassava
* Wood used for lumber, paper, resin, etc
* Plant fibers (cotton) used for clothes
* 25% of medicine from angiosperms
* Illegal/legal drugs
\
say yes
yes
88
New cards
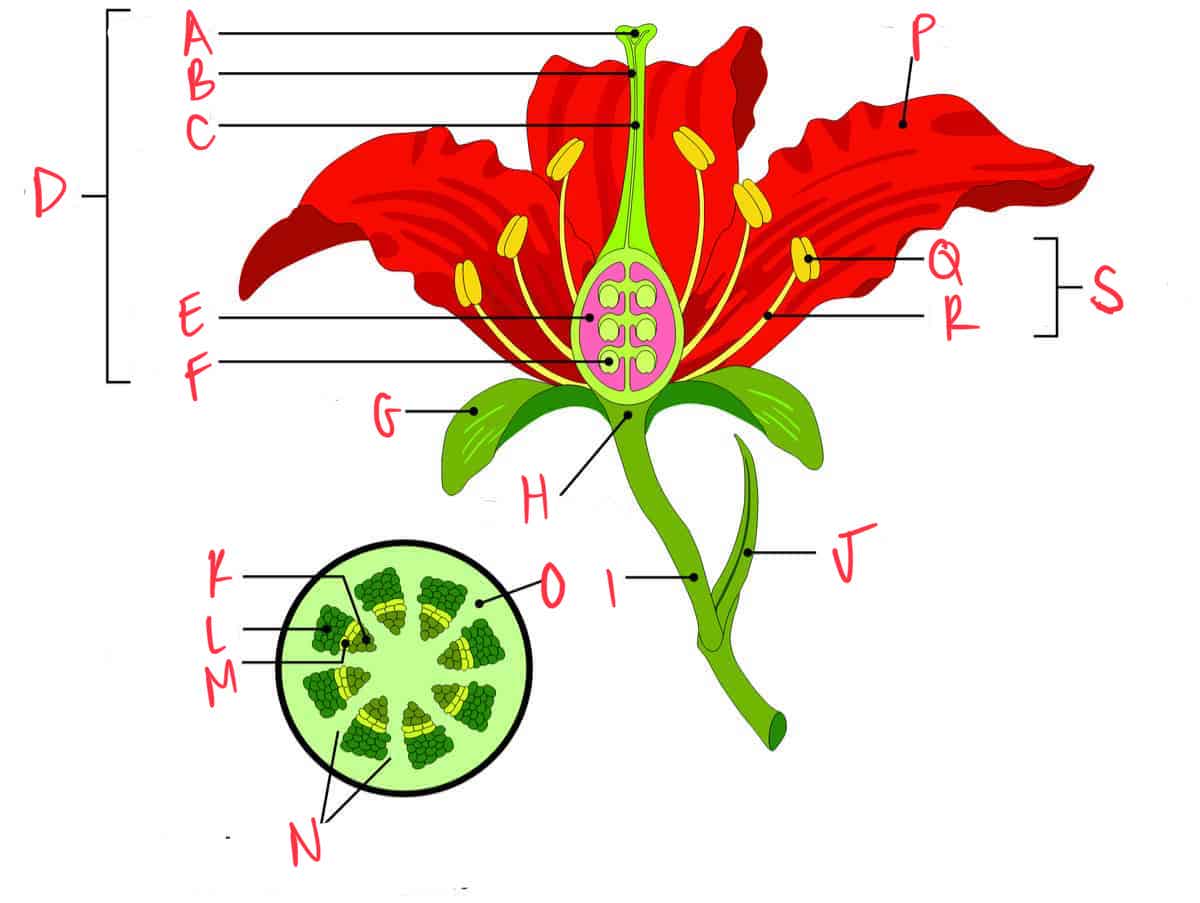
label flower accordingly
stigma, pollen, style, carpel, ovary, ovule, sepal, receptacle, stem, leaf, xylem, phloem, cambium, vascular bundle, cortex, petal, anther, filament, stamen
89
New cards
Angiosperm egg development (IMPORTANT)
ovary contains megaspore mother cell → meiosis → 4 megaspores → 1 survivor megaspore → 3x mitosis → 7 cells formed bc 2 fused into a single central cell , there are 3 antipodals, 2 synergids that surround the 1 egg
\
say yes
ovary contains megaspore mother cell → meiosis → 4 megaspores → 1 survivor megaspore → 3x mitosis → 7 cells formed bc 2 fused into a single central cell , there are 3 antipodals, 2 synergids that surround the 1 egg
\
say yes
yes
90
New cards
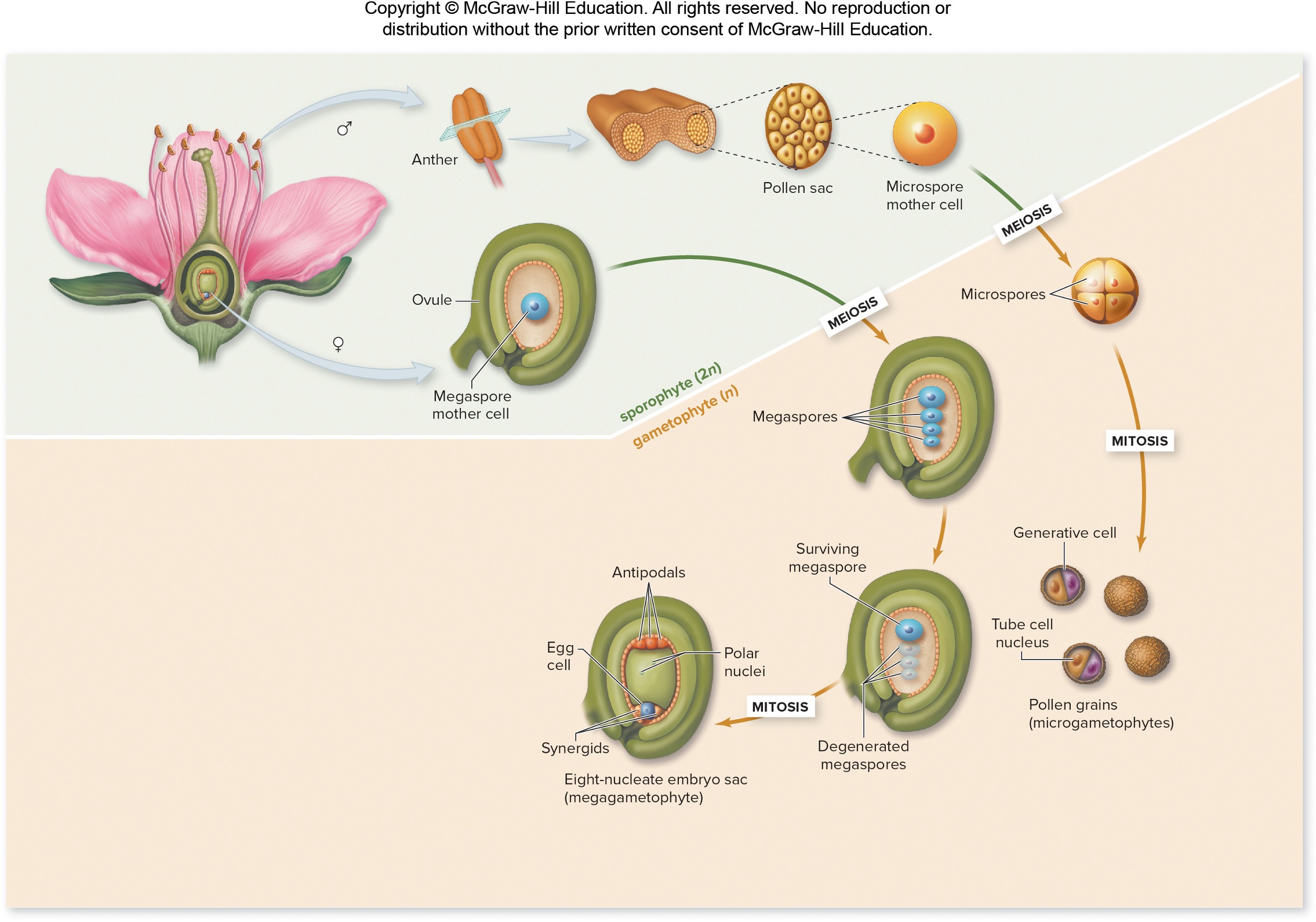
Angiosperm pollen development
(IMPORTANT)
anther contains pollen sack holding multiple microspore mother cells → 3x meiosis → 4 microspore pollen grains→ each one undergoes mitosis → now each pollen grain contains a generative cell + tube cell
\
say yes
(IMPORTANT)
anther contains pollen sack holding multiple microspore mother cells → 3x meiosis → 4 microspore pollen grains→ each one undergoes mitosis → now each pollen grain contains a generative cell + tube cell
\
say yes
yes
91
New cards
where else is lignin present?
inside walls of xylem
92
New cards
why would fungi switch to sexual reproduction?
undesirable environmental conditions,
93
New cards
what is a land plant that does not have these traits:
* apical meristems
* alternation of generations
* walled spores in sporangia
* multicellular gametangia
* multicellular dependent embryos
* apical meristems
* alternation of generations
* walled spores in sporangia
* multicellular gametangia
* multicellular dependent embryos
charophytes
94
New cards
which anthocerotophyta plant does this describe?
* live with cyanobacteria
* permanently opened stomata
* “horn” shaped gametophyte
\
which bryophyte plant does this describe?
* most abundant plants in arctic/ antarctic
* greatest moss diversity (bc withstands long droughts but ironically uncommon in deserts)
* prevents erosion, potting soils, burned as fuel
\
\
* live with cyanobacteria
* permanently opened stomata
* “horn” shaped gametophyte
\
which bryophyte plant does this describe?
* most abundant plants in arctic/ antarctic
* greatest moss diversity (bc withstands long droughts but ironically uncommon in deserts)
* prevents erosion, potting soils, burned as fuel
\
\
hornworts, mosses,
95
New cards
know that this is the order
* Apical meristem → procambium -→ vascular cambium/or cork cambium
* Apical meristem → procambium -→ vascular cambium/or cork cambium