Unit 2: Introduction to Chemistry
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Standard notation (St. N)
Scientific notation (Sc. N)
Scientific notation expresses very large or extremely small numbers as a coefficient raised to a power of 10.
The exponent for 10 can be a positive number (large numbers) or a negative number (small numbers).
→ Ex: 123,456,000 is standard notation.
1.23456000 × 108 is scientific notation.
Conversion factor (CF)
A fractional expression relating or connecting two different units or prefixes.
A fraction with a value = 1
CF are used to change from one unit to another
Always include units in every step
Unit conversion
U = I x CF (x CF x CF… etc.)
Identify the Unknown amount and units
Identify the Initial amount and units
List the CF(s) that will relate or connect the I units to the U units.
Solve (the units of I must cancel with units of the bottom of the CF)
Multiple CF’s
Always create a plan:
Ex: L → gal → $ or mL → L → kL
Each “→” represents a CF.
Can be computed in separate steps or all in one step.
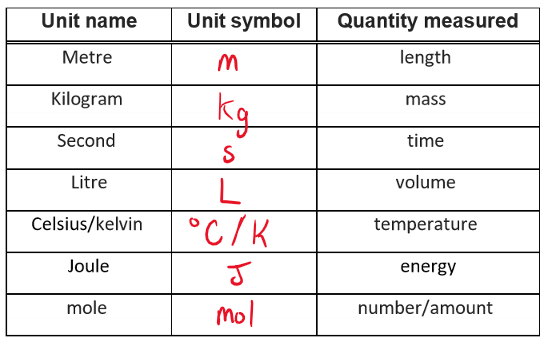
SI units
The International System of Units (SI) is the modern form of the metric system.
Devised around the convenience of 10.
World’s most widely used system.
Base (SI) units: a base unit of measurement, all other units are multiples of the base unit.
Metric prefixes
mega (M) = 106
kilo (k) = 103
deci (d) = 10-1
centi (c) = 10-2
milli (m) = 10-3
micro (µ) = 10-6
nano (n) = 10-9
pico (p) = 10-12
Converting Squared & Cubed Units
Convert 2.4 × 106 cm3 in m3?
2.4 × 106 cm3 × 106 m3 / 1cm3 = 2.4 m
Converting Derived Units
Derived Units are made by combining 2 or more other units.
→ Ex: Velocity (speed) is a derived unit made up of distance (km) and time (h).
Density
A derived unit consisting of mass (m) and volume (V).
Formula: d = m / V
The density of water is ~1.0 g/mL
Density depends on how tightly packed your particles are.
More tightly packed = more dense.
1cm3 = 1mL
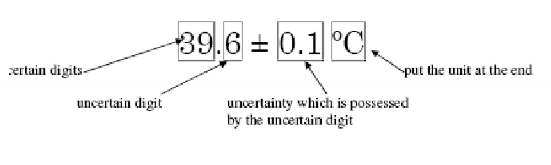
Significant figures (Sig Figs / SF)
Significant figures/digits include the digits that you are certain about.
All non-zero digits are significant
→ Ex: 123 has 3 SFs.
Trailing zeros with no decimal point after them are NOT considered significant.
→ Ex: 100 has 1 SF.
Trailing zeros after a decimal point are assumed to be significant. They show the precision of the measuring device.
→ Ex: 1.20 has 3 SFs.
Leading zeros are not significant.
→ Ex: 0.03 has 1 SF.
All zeros between non-zero digits are significant.
→ Ex: 5002 has 4 SFs.
Exact numbers (like conversion factors) have an infinite number of significant figures.
→ Ex: “37 people” has ∞ SF.
Calculations with Significant Figures
Multiplying and diving: The answer should have the same number of SF as the LEAST precise measurement.
Adding and subtracting: Line up the decimal place and round to the LEAST precise decimal place.
REMEMBER!
Don’t forget BEDMAS, determine SF in each step but do not round early.
SF applies to measured values, not defined values (like conversion factors).
Rouding rules
If your answer ends in a number that is greater than 5, increase the preceding digit by 1.
→ Ex: 2.346 can be rounded to 2.35.
If your answer ends with a number that is less than 5, leave the preceding number unchanged.
→ Ex: 5.73 can be rounded to 5.7.
If your answer ends with 5
Increase the preceding number by 1 if it is odd.
→ Ex: 18.35 can be rounded to 18.4.
Leave the preceding number unchanged it it is even.
→ Ex: 18.25 can be rounded to 18.2.
Precise vs. Accurate
Accurate = measure that is close to the correct or accepted value.
Precise = reproducible measurement, more significant digits / more decimal places.
Assume the CORRECT measurement of a pencil is 27.3200 cm.
27.3 is ACCURATE but not very PRECISE.
28.466 is PRECISE but not very ACCURATE.
27.3201 is both ACCURATE and PRECISE.
35.2 is neither ACCURATE nor PRECISE.
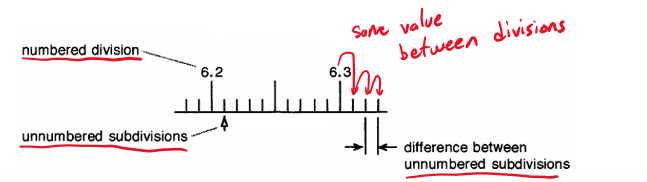
Uncertainty
To find uncertainty value for a measurement, take the difference between the smallest increment/ division and divide by 10. The uncertainty is always in the last digit (the one that was estimated).
This gives us a RANGE for the measurement.