9-Venus
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Which planets are ancient discoveries?
Venus (+ Mars, Jupiter, Saturn)
Venus observations from earth?
no surface features (seeing upper cloud)
same mass and size of earth
RETROGRADE orbit, backwards compared to other terrestrial planets
closer to sun, hotter
atmosphere first observed 1761
What was first mission to Venus?
Mariner 2 - Flyby Venus 1962
surface >400 C, no chance of ocean
no magnetic field
atmosphere mostly CO2, cool clouds
Other missions to Venus?
Mariner 5 (US)
flew by
measured atmosphere remotely
Venera 4 (USSR)
dropped into Venus’s Atmosphere
Pressure and temp increased until spacecraft destroyed
What about Mariner 10?
Mariner 10 - 1973.
flyby
first pictures of Venus
V-shaped structures visible in clouds in UV light
clouds contain sulphuric acid
What exploration techniques are there to see Venus’ surface?
Land on surface, take photos
e.g. Venera 4 falling as transmitting data until destroyed
Find some wavelength that penetrates the clouds
What about Venera 7?
Venera 7 - 1970.
Designed to withstand atmosphere pressure
first probe to return data from surface of another planet
discovered surface conditions. 93x earth pressure, 750K temp
What about Venera 8?
Venera 8 - 1972.
53 minutes on surface
confirmed temperatures and pressure of Venera 7
discovered enough light for photography
Venera 9?
Venera 9 - 1975.
first images from surface of Venus
rocks angular and noticeably not eroded
Venera 10?
Venera 10 - 1975.
compressibility of surface, for density
angular rocks, slabby
basaltic, lava flows.
What chemistry did Venera 13 and 14 use?
X-ray methods - touching surface.
Convert signal into chemical elements.
High error bars.
Low in silica, rich in MgO.
High levels of K2O.
Provided indication of volatile bearing basaltic lavas suggesting that we must have had partial melting going inside in the Venusian interior.
What were the Vega 1 and 2 spacecraft?
USSR. Vega1 failed in atmospheric descent.
Vega-2 landed in Aphrodite Terra.
last one hour on surface
discovered evolved rocks
balloon bots, tracked, survive 2 days then popped
What is the pioneer Venus mission?
Orbiter mission, 4 probes, 1978, NASA MISSION
lasted over 20 years
used radar to observe surface
topographic map
What colours indicate what on a topographic map?
Red and whites indicate highland areas.
Blue areas as lowland areas.
What about Venera 15 and 16?
Venera 15 and 16 - 1983.
mapped regions of Venus
revealed lava flows, volcanoes, heavily folded regions.
What about Megellan?
NASA Magellan 1990
space shuttle launch
mapping surface in high resolution
How does radar technique work?
send down pulse through atmosphere
interaction with surface
bounce back, backscatter radar pulse tells us about surface
Bright reflectance - rough surface, slopes
Smooth reflectance - smooth surface
Impact craters of Venus?
Very few impact craters on surface of Venus.
so very young surface.
What is the Venus Express?
atmosphere mission
recycled Mars express
CO2 96.5%, N 3.5%
atmosphere is DRY.
What about the Venus Climate Orbiter Mission?
Japan
4 UV and infrared cameras
mapping clouds
detecting lightning
observing the vertical structure of the atmosphere with radio science technique
What is the major rock type in the lunar mare?
BASALT - Black regions on moon, dominated on nearside of moon, represent volcanic eruptions.
What is the major rock type in the lunar highlands?
Anorthosite
What is a troctolite?
Volcanic rock: olivine and anorthite plagioclase
Coarse grain, intrusive rock
50% olivine 50% anorthite plagioclase
What Apollo mission visited the Descartes Highlands?
Apollo 16.
What are Tycho and Copernicus?
Young (post 800Ma) Impact
When did the Imbrium impact occur?
3.9Ga
Apollo 15 visited which landing site?
Hadley Rille
What is the name of the successful series of Russian missions sent to Venus?
Venera
The Magellan mission to Venus deployed what important detector system?
Radar
Why is Venus’s surface so hot?
450 degrees.
Greenhouse effect
So close to Sun
Why doesn’t Venus have a magnetic field?
Much slower rotation than earth.
Planet still can retain an atmosphere as it is large, and thus has a high gravity field.
Why do small asteroids never impact the surface of Venus?
Get crushed by atmosphere on way down to Venus’ surface.
What is Venus’s geology like?
High terrains display youthful features.
Max crust 300km.
Crust most likely 20-30km.
One or more major cycles of volcanism in the last billion years.
Time periods for Venus:
Last part where volcanism occurred. Widespread deformation giving large scale fault systems.
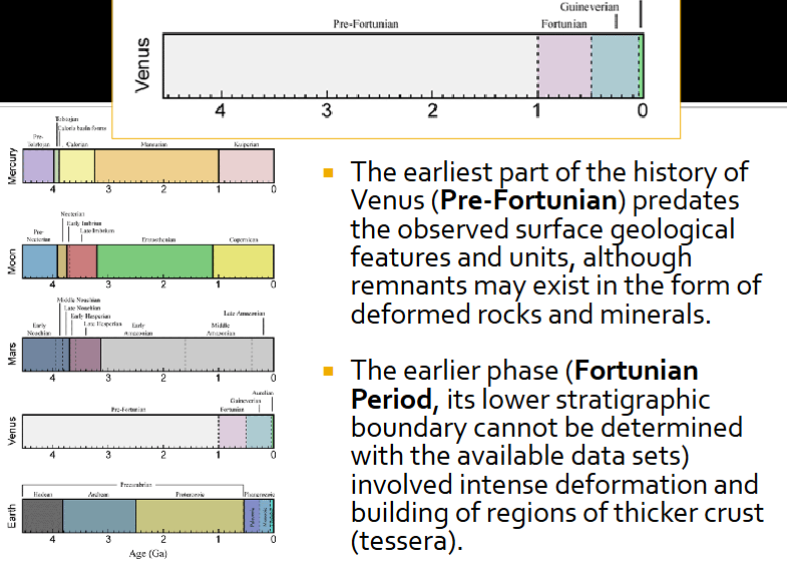


What are the drivers of magmatism?
Heat retained through INNER mantle convection.
Stagnant part of out mantle, no tectonics now.
Why are Venus volcanoes not that big compared to other planet volcanoes?
Stagnant lid. On Venus:
The crust is mostly one solid plate
Magma does not stay in one place long enough to build huge volcanoes
Instead, lava tends to erupt through many fractures and spreads out
What is the Chemistry of Venera 13 and 14?
X-ray spectroscopy methods.
Resemble basalts on earth.
Low in silica.
What is a pancake dome?
Implies viscous lava, lava with more SiO2.

If you wanted to test if Venus was volcanically active?
seismometer for earthquakes
visit suspected volcanic place
temperature measure
measure for gas emitted, Sulfur
What are novae and coronae?
Novae = starburst cracks from rising magma
Coronae = giant circular cracks and ridges from collapsing crust over hot mantle

Summary of Venus:

Habitability?

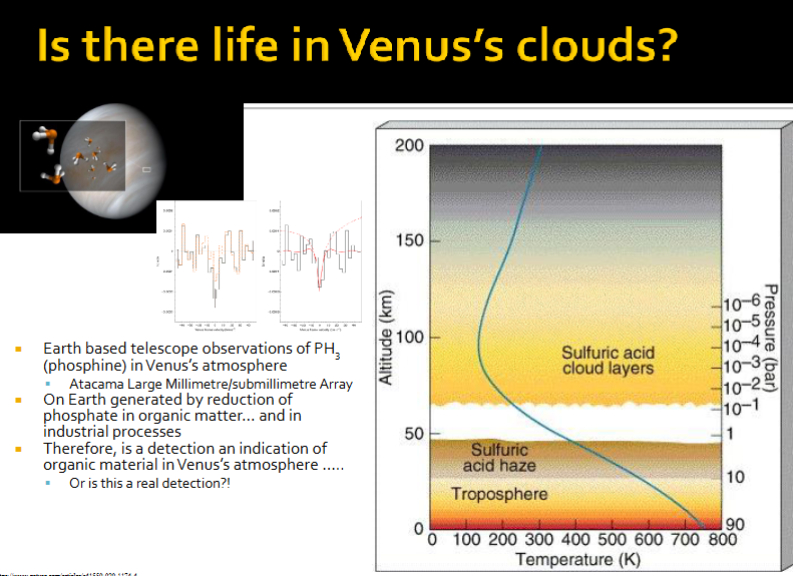
Is there life in Venus's clouds?
Phosphine in Venus’s atmosphere is interesting because on Earth it is mainly produced by living organisms under oxygen-poor conditions. MAYBE? probably not.
What new missions are going to Venus?
EnVision, European Space Agency, targeted observation for surface change detection, looking through thick atmosphere.

Reading Materials: Planetary Volcanism. What type of magma erupts at mid-ocean ridges?
Basalt, which is silica-poor and metal rich.
What volcanic landforms form over hotspots on Earth?
Shield volcanoes e.g. Hawaii
What type of eruption happens when silica, rich gas-rich magma?
Explosive eruptions (like Plinian or Vulcanian)
What creates a caldera?
Caldera - large crater formed when a volcano collapses after its magma chamber empties.
Collapse after large amounts of magma drain from a reservoir.
What are the dark ‘maria’ made of?
Flood basalt lava flows.
Dark maria - dark, fault areas on the Moon made of ancient lava.
Why are lunar lavas so long-flowing?
They have extremely low viscosity.
What are sinuous rilles on the Moon?
Long meandering channels carved by hot, turbulent lava.
Why are Martian volcanoes so large?
Low Gravity + no plate tectonics = volcanoes grow in one spot for a long time
What is the largest Martian volcano?
Olympus Mons
What do giant calderas on Mars indicate?
Very large, long-lived magma chambers.
What carved sinuous channels on Mars?
Extremely fluid, turbulent lava eroding the ground.
Why aren’t Venus volcanoes very tall?
No plate tectonics → magma spreads over the surface instead of building height. Also runny lava.
What are ‘fluctus’ on Venus?
Very long, flood, like lava flows.
What are coronae on Venus?
Large circular features with ring fractures, caused by upwelling magma beneath the crust.
What are novae on Venus?
Star-shaped radial fracture systems formed by rising magma.
What is the main type of volcanism on Mercury?
Vast basaltic lava plains (similar to lunar maria)
What do rimless depressions with bright deposits indicate?
Explosive volcanic activity with volatile-rich magma.
Why is Io the most volcanically active body in the solar system?
Strong tidal heating from Jupiter.
Celestial body is heated inside because gravity from Jupiter constantly stretches and squeezes it.
What drives Io’s gigantic eruption plumes?
Magma mixing with buried sulfur & SO2, causing explosive expansion.
What is cryovolcanism?
Eruption of liquid water or other volatiles instead of molten rock.
What moon shows active water-rich plumes today?
Enceladus (feeds Saturn’s E-ring)
What evidence shows some asteroids once had volcanism?
Meteorites with textures of solidified magma or mantle rocks.
What causes early asteroid melting?
Heating by short-lived radioactive isotopes like Al-26.
What is difference between effusive and explosive eruptions?
Effusive - flowing lava, flows gently e.g Hawaiian-style
Explosive - violent blast, thick magma, magma shatters into ash and rock, ash clouds, pyroclastic flows
What are Strombolian eruptions?
Bursting of large gas bubbles, causing small explosions.
What are Vulcanian eruptions?
Sudden blast when gas pressure builds and the rock above breaks open.
What are Hawaiian eruptions?
Continuous low-viscosity lava fountains + lava flows.
What is a Plinian eruption?
Powerful, sustained ash columns reaching tens of km into the atmosphere.
What are phreatomagmatic eruptions?
Explosions from magma interacting with water or ice.
Why do some lava flows stop even on a slope?
Lava cools → viscosity increases → flow stops even while still partly molten
What are lava levees?
Cool, stationary banks forming along the sides of a flowing lava channel.
Why are lava flows longer on other planets?
Higher eruption rate + lower gravity + low viscosity basalt
Planetary Impacts: What is a planetary impact?
When an asteroid or comet crashed into a planet or moon at very high speed.
What do impacts mainly create?
Craters and basins
Why are impacts important?
Shape surfaces and crusts, especially in early SS
When were impacts most common?
About 4 billion years ago.
What are the three stages of crater formation?
contact and compression
excavation
modification
What happens during contact & compression?
A shock wave forms and rock is highly compressed.
What happens in excavation?
Rock is blasted out, forming the crater cavity.
What happens in the modification stage?
Crater collapses and changes shape under gravity.
What is a simple crater?
Small bowl-shaped crater with smooth walls.
What is a complex crater?
Large crater with
central peak
terraces, step-like ridges along the crater walls formed when the sides of the crater collapse inward
flat floor, when melted rock and debris settle and level out
What causes the central peak?
The ground that rebounds upward after the impact.
What is an impact basin?
A huge crater hundreds to thousands of km wide.
What is ejecta?
Rock thrown out of the crater
What are ejecta rays?
Bright streaks of debris radiating from a crater
Why are rays brighter?
Fresher rock reflect more light
What is shock metamorphism?
Rock changes caused by extreme pressure from impact.
What evidence proves an impact crater?
shocked minerals
melt rock
shatter cones, cone-shaped cracks in rocks caused by the shock waves of a meteorite impact
Why does the Moon have many craters?
No atmosphere and no erosion.
Why does Earth have fewer visible craters?
Weathering, erosion, and plate tectonics erase them.
Why do Mars craters last longer than Earth’s?
Mars has weak erosion and no plate tectonics.
What famous impact affected like on Earth?
Dinosaur-killing impact 65 million years ago.
Cretaceous-Palaeogene
How often do large impacts hit Earth?
Roughly every 100 million years.