Chapter 11
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Large surface area, thin walls, good ventilation, and good blood supply.
What are the common features of gas exchange surfaces?
The alveolus.
What is the primary gas exchange surface in humans?
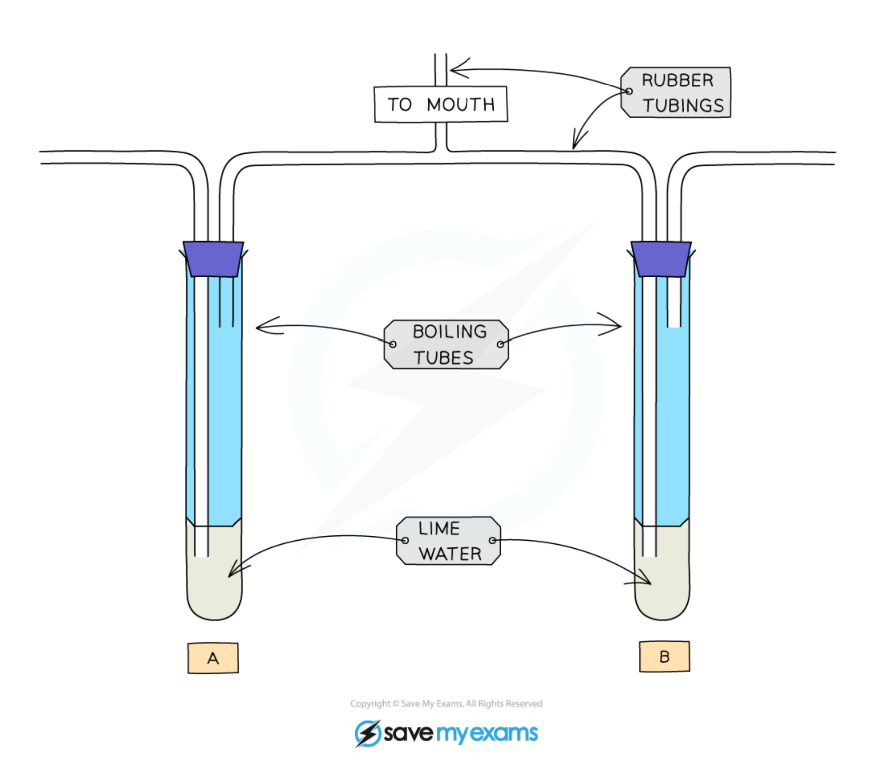
Limewater becomes cloudy when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it.
How does the limewater test indicate carbon dioxide levels in exhaled air?
Inspired air: 21%, Expired air: 16%.
What are the approximate percentages of oxygen in inspired and expired air?
The frequency and depth of breathing increase.
What happens to the breathing rate during exercise?
External intercostal muscles (outside rib cage) and internal intercostal muscles (inside rib cage).
What are the two sets of intercostal muscles?
To support the airways and keep them open during breathing.
What is the function of cartilage rings in the trachea?
The diaphragm contracts and flattens, increasing the volume of the chest cavity.
What physical changes occur in the diaphragm during inhalation?
They detect changes in blood gas levels and pH, sending signals to adjust breathing rate.
What is the role of chemoreceptors in breathing?
The process of removing lactic acid by combining it with oxygen.
What is the term for repaying the oxygen debt after exercising?
Cilia push mucus trapped with particles and pathogens up towards the throat for removal.
How do cilia protect the breathing system?
They produce mucus that traps dust and pathogens.
What do goblet cells do in the respiratory system?
Air pressure inside the lungs decreases, drawing air in.
What happens to the pressure in the lungs during inhalation?
Oxygen enters the blood, and carbon dioxide and water vapor leave the blood.
What are the primary gases exchanged in the alveoli?
Increased physical activity raises energy demand, necessitating faster gas exchange.
How does physical activity affect the need for gas exchange?
the alveoli.
The main purpose of ______________ is to facilitate gas exchange in the lungs.
inhalation.
During ______________, oxygen levels in the blood increase and carbon dioxide levels decrease.
mucus.
The ______________ in the respiratory system help to trap and clear dust and pathogens.
moist.
In order to maintain effective gas exchange, the respiratory surfaces must be ______________.
diaphragm.
The ______________ is a muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen and plays a critical role in breathing.
pressure.
The _________ of air in the lungs becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure during exhalation, pushing air out.
oxygen debt repayment.
The process of ______________ occurs after intense exercise to restore oxygen levels in the body.
remove.
Cilia are located in the respiratory tract and function to ___________ particles and pathogens from the lungs.
external.
The ___________ intercostal muscles assist in inhalation by expanding the rib cage.
carbon dioxide.
During exercise, increased levels of ______________ in the body stimulate deeper and more frequent breaths.
To lift the rib cage during inhalation, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
What is the primary role of the external intercostal muscles?
exhalation.
The internal intercostal muscles primarily aid in ______________ by pulling the rib cage downward.
21
Fill in the blank: Inspired air is made up of approximately _______% oxygen.
Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases.
What happens to the composition of air as it moves from inspired to expired air?
By contracting and relaxing, they change the volume of the thoracic cavity.
How do the intercostal muscles contribute to breathing mechanics?
carbon dioxide.
Fill in the blank: The volume of _________ in expired air is higher than in inspired air due to cellular respiration by the body.
During inhalation.
During which phase of breathing do the external intercostal muscles contract?
False.
True or False: Expired air contains more oxygen than inspired air.
They assist in increasing the rate and depth of breathing.
What role do the intercostal muscles play during physical activities like exercise?
lower.
Fill in the blank: The pressure in the lungs is _________ than atmospheric pressure during inhalation, allowing air to flow in.