9.1 mutations
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is a gene pool
a gene pools is the sum total of genes (genotypes, with all their variations, possessed by a particular species at a particular time (in a population)
what is allele frequency
how often each allele of gene occurs in the gene pool for that population.
what are factors that contribute to allele frequency and evolution
Mutation
Variation
Natural selection
Barriers to gene flow (isolation)
Random genetic drift
Migration and founder effect
Speciation
Genetic diseases
what is mutation
A mutation is a permanent structural alteration in a organism's DNA.
Mutations are the ultimate source of variation, introducing new alleles into a gene pool
Mutations can have no effect, be favourable, or unfavourable for a population.
Mutations in genes and chromosomes can result from errors in DNA replication, cell division or from damage caused by mutagens.
what are the two main types of mutations
gene or point mutations
chromosomal mutations
Gene or point mutation
changes in the base sequence of a single gene so that the traits normally produced by that gene are changed or destroyed
These usually occur before cell division - during the replication of the DNA molecule.
chromosomal mutations
in which all or part of a chromosome is affected
what are mutagenic agents/mutagens
agents that increase the rate at which mutations occur.
what are examples of biological mutagens
bacteria, viruses
what are examples of chemical mutagens
antibiotics
mustard gas
formaldehyde
sulfur dioxide.
what are examples of physical mutagens
radioactive wastes
atomic and nuclear explosions
x rays
uv radiation
what are the ways in which mutagens can cause damage to DNA
can trigger DNA replication errors
can cause DNA breakage/lengthening
can block DNA replication/damage DNA structure
can chemically react and modify DNA
what is an induced mutation
genetic alterations that occur as a response to specific environmental conditions, often as a survival mechanism for cells under stress
what are spontaneous mutations
mutagens in biological processes, causing error such as in meiosis and mitosis.
what is a somatic mutation
when the body cells, or somatic cells are involved with a mutation.
Only the individual with the mutation is affected and does not pass on the mutation.
what are germinal or Germline mutations
when reproductive cells are affected, and the mutation occurs in the gametes
the mutations then may be passed on
in this case, the individual is not usually affected but produces gametes with changed DNA.
what are the different effects of mutations
missense mutation
nonsense mutation
neutral mutations
silent mutations
what is a missense mutation
cause a change in the amino acid, and therefore in the protein produced.
non sense mutation
change the base sequence to the code to STOP. This means that the synthesis of the protein will stop, and so a shorter protein is produced that is unlikely to be able to fulfil it’s function
neutral mutations
cause a change in the amino acid; however the amino aid is of the same type and does not change the structure of the protein enough to change its function.
silent mutations
do not cause any change in the amino acid, and therefore in the protein produced. This is possible, as most amino acids are coded for by more than one base sequence.
what are the different ways point mutations can cause change in DNA.
can be due to a nucleotide being:
inserted
substituted
deleted
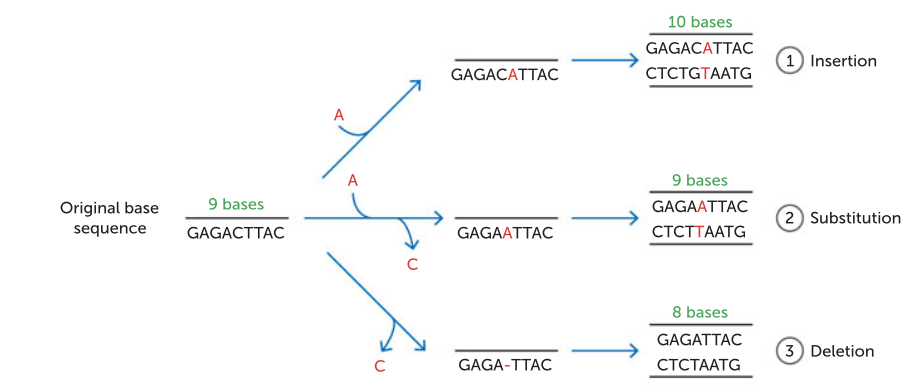
inserted
a new nucleotide is added to the DNA strand
substituted
a existing nucleotide is replaced with a another one, with a different base.
deleted
a nucleotide is removed from the DNA strand
what is a frameshift
a frameshift occurs when bases have been added or removed
results in the series of three bases that code for an amino acid starting at a different base
affect the outcome for all the DNA from that point on.
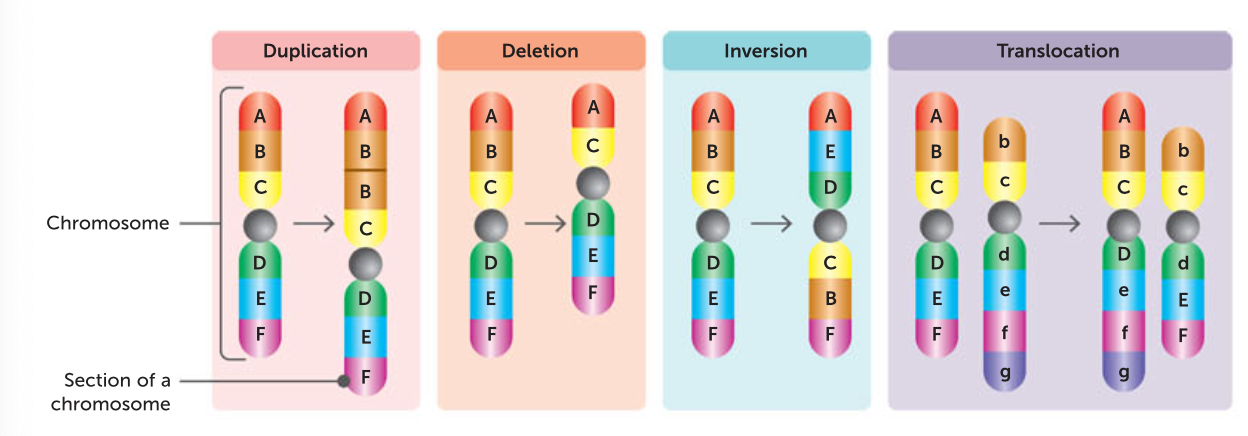
what are some chromosomal changes during a mutation
deletion - a piece of DNA is removed
duplication/insertion - a section of chromosome occurs twice
Inversion - breaks occur in a chromosome and the broken piece joins back in, but the way back around.
translocation - part of a chromosome breaks off and is rejoined to the wrong chromosome
non disjunction - during meiosis, chromosome pair does not separate and so one daughter cells has an extra chromosome and one has less.