Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis MedChem
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the characteristics of a prokaryotic ribosome?
Constructed from ribosomal RNA, located free in cytoplasm as 70s size
What subunits is the prokaryotic ribosome made of?
Small 30S subunit and large 50S subunit
What is in the 30S subunit?
16S rRNA and small subunit proteins, binds to mRNA
What is in the large 50S subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes?
23s rRNA and 55 rRNA and large subunit proteins, binds to 30S unit to complete the ribosome
Where is peptidyl transferase found?
23S subunit
What does every proteins code start with in bacteria?
Formyl methionine
How is protein translocation initiation completed in bacteria?
30S ribosomal subunit acted on by initiation factors (small proteins) to become 30S + subunits, energy is added along with the tRNA and mRNA to form the initiation complex of methionine
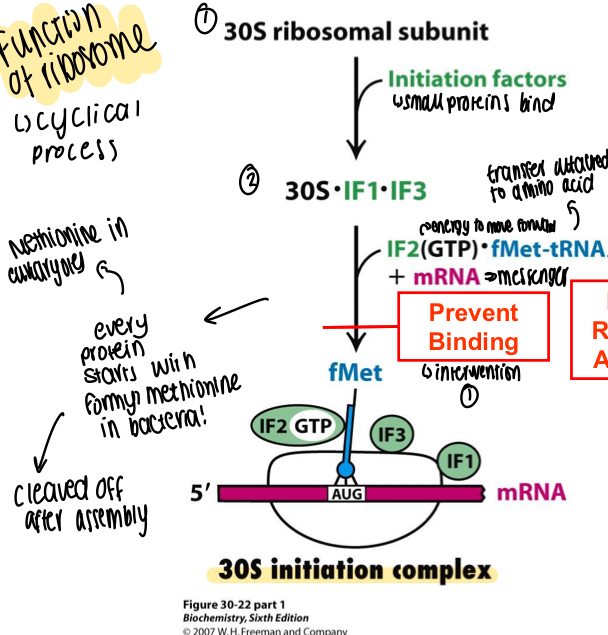
How is the 70S initiation complex made?
30S initiation complex joins to 50S subunit using water, the initiation complexes leave 30S and energy creates 70S complex with methionine in the binding site
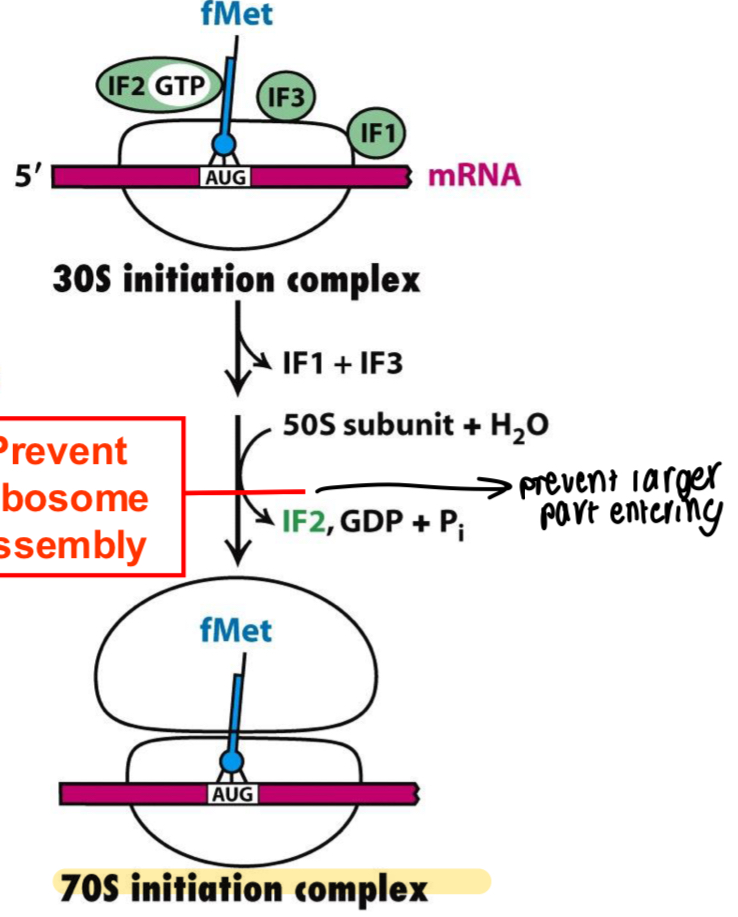
How can antibiotics act in protein translation to inhibit further proteins being made in the initial stages of translation?
Prevent binding of methionine or prevent ribosome assembly of 50S combining with 30s
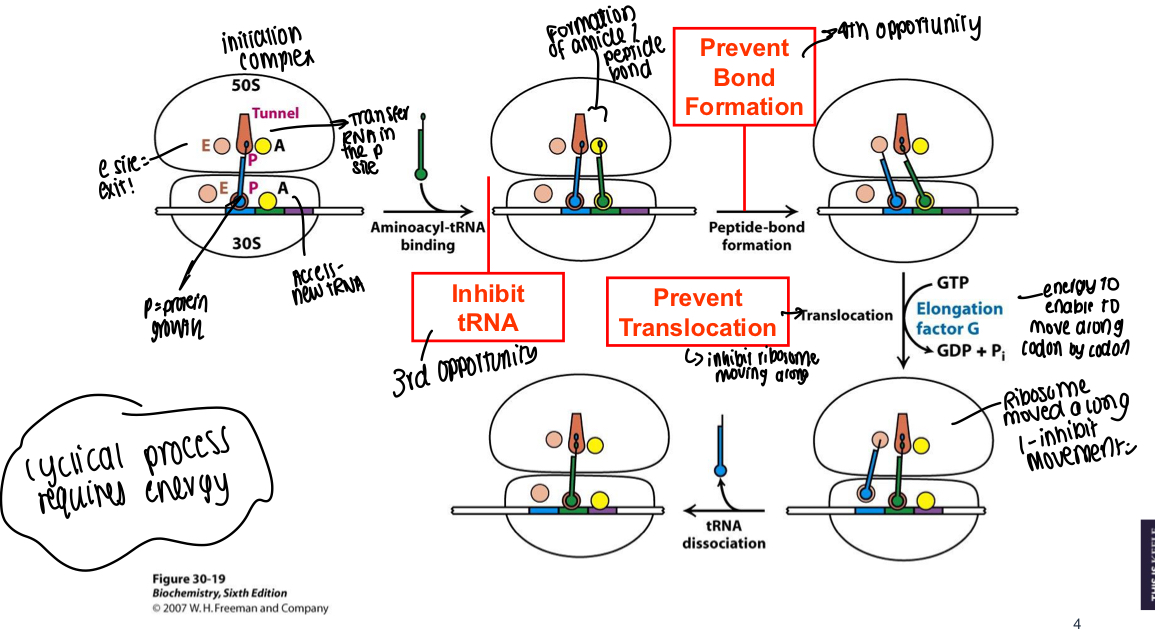
What are some other ways that protein synthesis can be inhibited, after the initiation phase, in bacteria?
Inhibit tRNA entering, prevent peptide bond formation, prevent translocation or inhibit the cycle by using elongation factors
How does protein synthesis occur after ribosome assembly is complete?
TRNA in P site, e site is where tRNA leaves and access site is where new tRNA enters
Amide/peptide bond formed between 2 mRNAs
Bond is formed between the molecules
Translocation occurs using energy to move along codon by codon - ribosome moves position e.g., molecule previously in P site moves to E
Cycle continues until end codon found
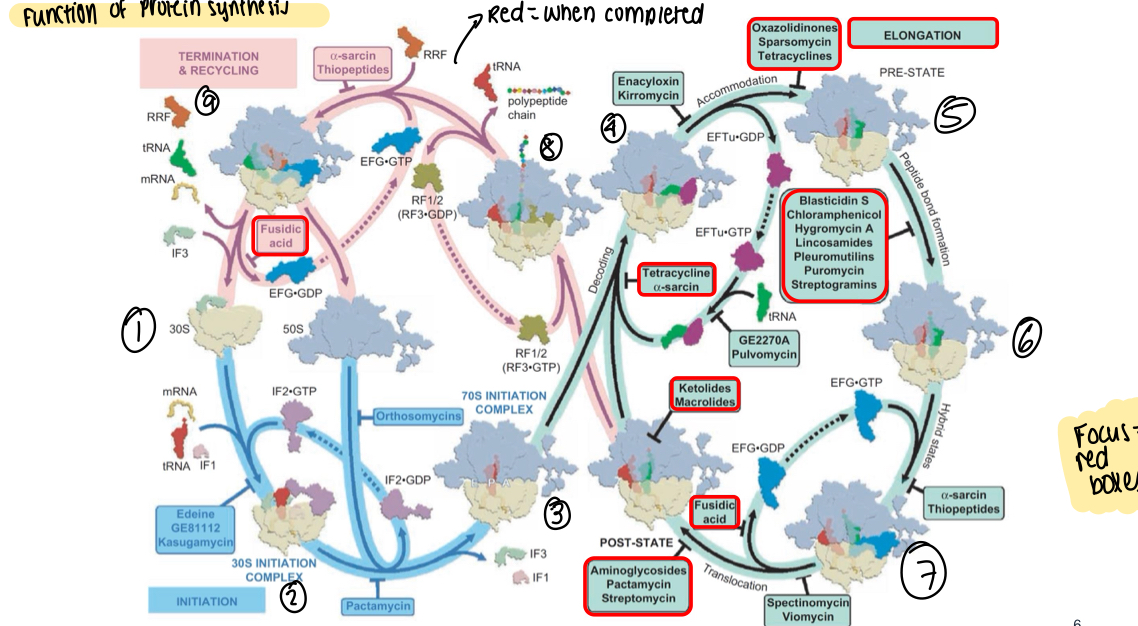
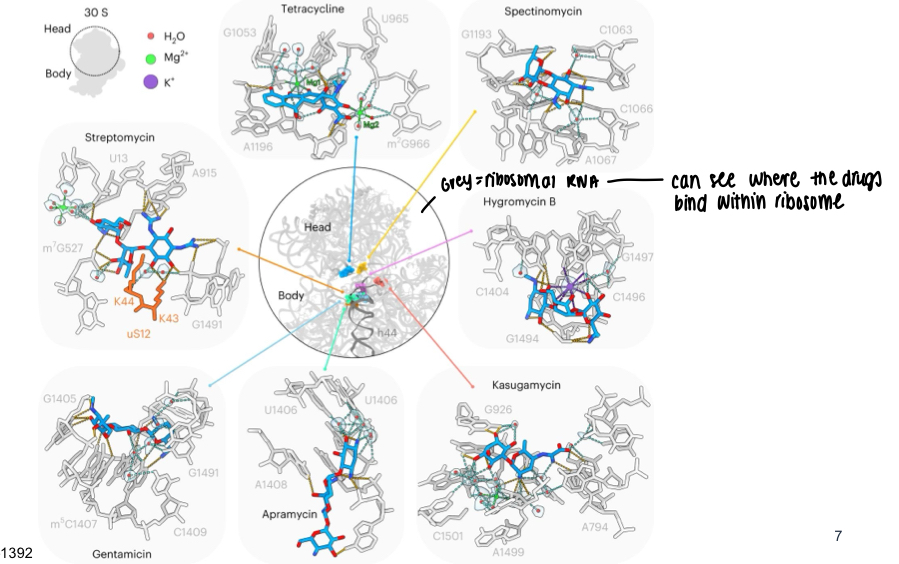
What is a diagram showing where many antibiotics act in protein synthesis?
What can be used to view how antibiotics bind to small subunit of bacterial ribosomes?
Cryo-electron microscopy - can be used to give a precise description of antibiotic-ribosome interactions
What is the basic SAR of tetracyclines?
All 4 rings essential, stereochemistry essential and basic motif must stay, substituents tolerated on D ring, ring B-C keto-enol essential and ring A MUST not be changed
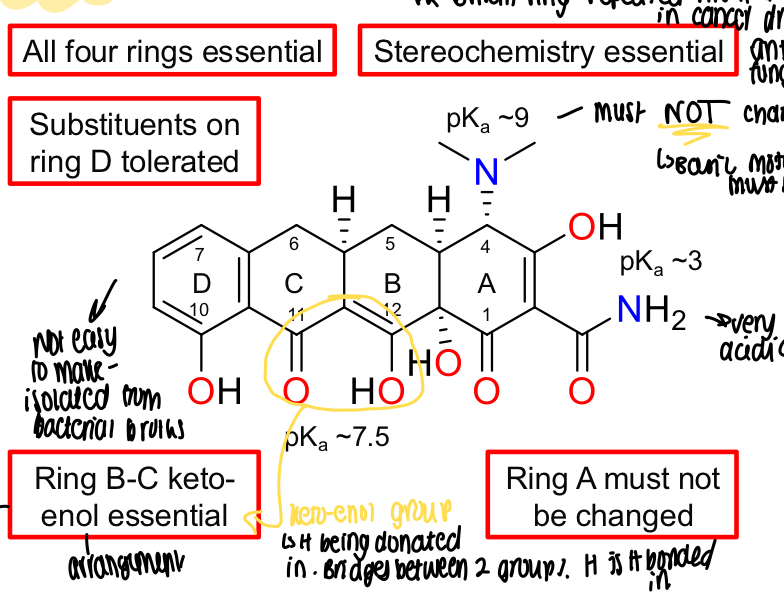
What happens in the keto-enol group in the B-C rings in tetracyclines?
H is donated in, bridges between 2 groups
What is a disadvantage of the keto-enol group in ring B-C in tetracyclines?
Can complex metal ions so shouldn’t be given to infants as it complexes with calcium and can stain teeth
Where are tetracyclines derived from?
Soil samples/bacterial broths
How do tetracyclines affect bacteria?
Bacteriostatic so prevent growth and spreading
What is the MOA of tetracyclines?
Bind reversible to 30S subunit and inhibit binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to active site in 70S ribosome, extremely broad spectrum
How was tetracycline resistance spread?
Transposons spread
What are the side effects of tetracyclines?
GI disturbances, modified gut flora that can lead to secondary infection, incorporation into bones and teeth, phototoxicity and hepatotoxicity
What are some examples of tetracyclines?
Doxycycline, minocycline, lymecycline
What amino acid residue does lymecycline contain?
Lysine residue
What are tetracyclines most commonly used for?
Skin infections
Which tetracycline is mostly used for skin infections e.g., acne?
Lymecycline
What is the advantage of lymecycline?
Absorbed greatly by the gut due to ability to exploit normal transport mechanisms used by peptides and carbohydrates
What other tetracycline is lymecycline a derivative on?
lysine derivative of minocycline
What drug class is novel derivative of tetracyclines?
Glycylcyclines
What are the benefits of glycylcylclines?
Exploit additional binding interactions, broad spectrum e.g.., MRSA, GRE and reserved for complex infections, delivered by infusion
What is the main structural difference from tetracyclines to glycylcyclines?
New substituents added onto the D ring e.g., glycine with butyl group added in tigecycline
What is an example of a glycylcycline?
Tigecycline
What are some examples of oxazolidinones?
Linezolid, tedizolid
What is the activity of oxazolidinones?
Active against gram positive including MRSA and GRE, not gram negative
When are oxazolidinones used?
When other Abx cannot treat the infection
What is the SAR of oxalozolidinones?
Stereochemistry essential, N-aryl group and oxazolidinones ring also key
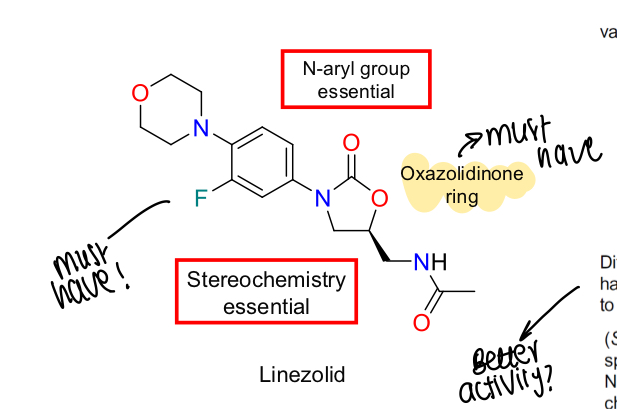
How does linezolid work (MOA)?
Binds into A site of the ribosome and blocks the movement of uracil (U2585) into the binding site, keeping it in inactive form
What stereoisomer of chloramphenicol is active?
1R, 2R
How many chiral centres are present in chloramphenicol?
2
What is chloramphenicol used for?
Eye infections - topically applied
How does chloramphenicol work?
Bacteriostatic - binds reversibly to 50S subunit and inhibits peptidyl transferase and the transfer of growing peptide to next AA residue
What are the drawbacks of chloramphenicol?
Potent CYP450 inhibitor, not for use in pregnancy as it can increase foetus mortality rates, severe bone marrow depression causing pancytopenia - NOT to be used systemically
What are aminoglycosides?
Aminated carbohydrates connected to a dibasic cyclitol by glycosidic linkages
What are examples of aminoglycosides?
Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin
What activity do aminoglycosides have against bacteria?
Kill bacteria - bactericidial, good spectrum of activity
What is the MOA of aminoglycosides?
Binds irreversibly to 16S rRNA and freezes the 30S initiation complex, binding to 16S rRNA increases A site affinity regardless of anticodon and also binding slows protein synthesis and induces mRNA misreading
What can aminoglycosides effects be enhanced by?
Peptidoglycan synthesis inhibitors e.g., B-Lactams
What type of bacteria are aminoglycosides not active against?
Anaerobic bacteria as oxygen needed for uptake
Why do aminoglycosides side effects occur?
Structural homology between bacterial ribosome and human mitochondrial/cytosolic ribosomes
What side effects are seen with aminoglycosides?
Ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity (especially when used with cephalosporins)
What is ototoxicity?
Progressive damage to and destruction of sensory cells in the ear, leading to vertigo, balance loss and deafness
What are examples of macrolides?
Erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin