Piaget
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Schemas
In Piaget's theory, mental structures or programs that guide a developing child's thought

A mental process that modifies new information to fit into existing schemes
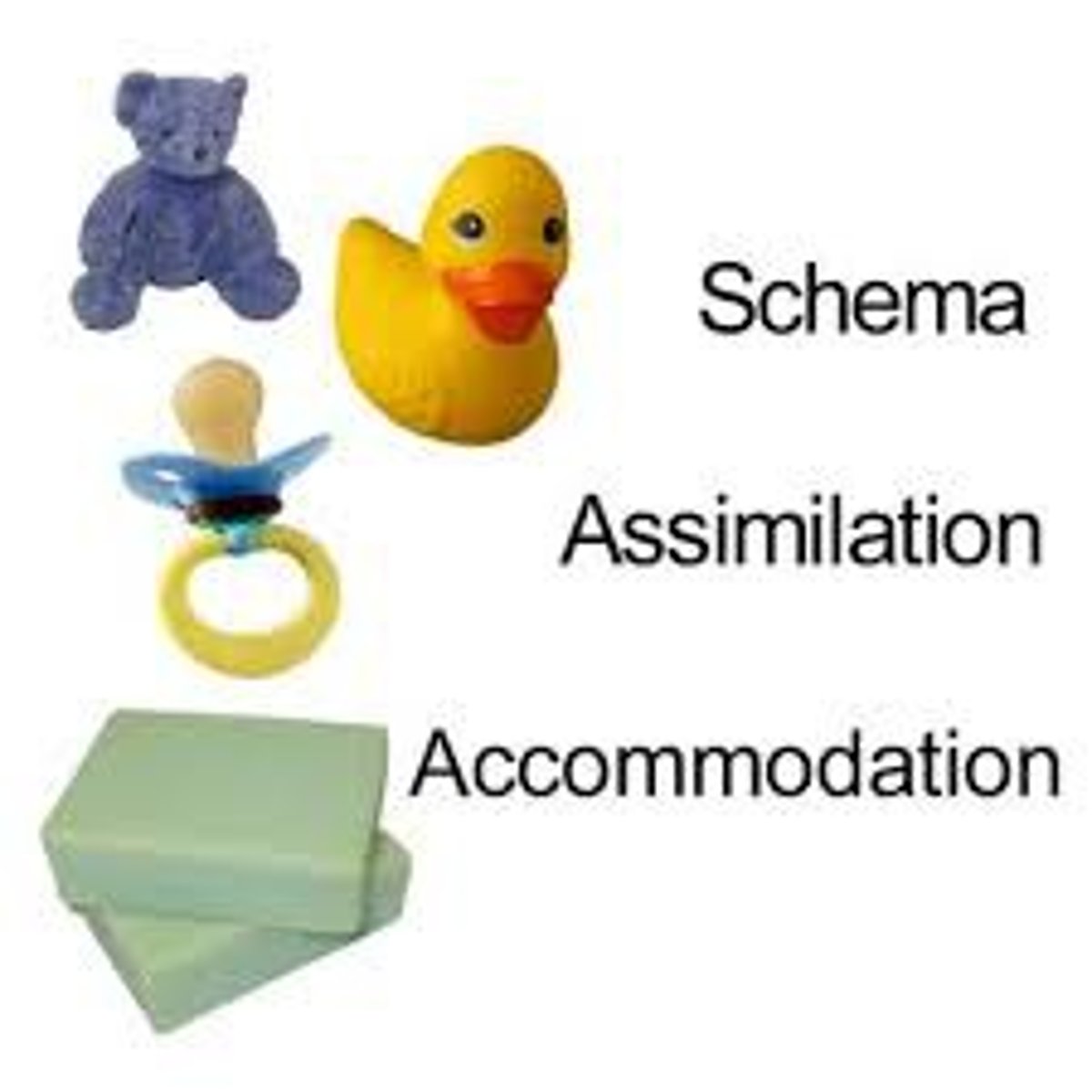

Accommodation
A mental process that restructures existing schemes so that new information is better understood
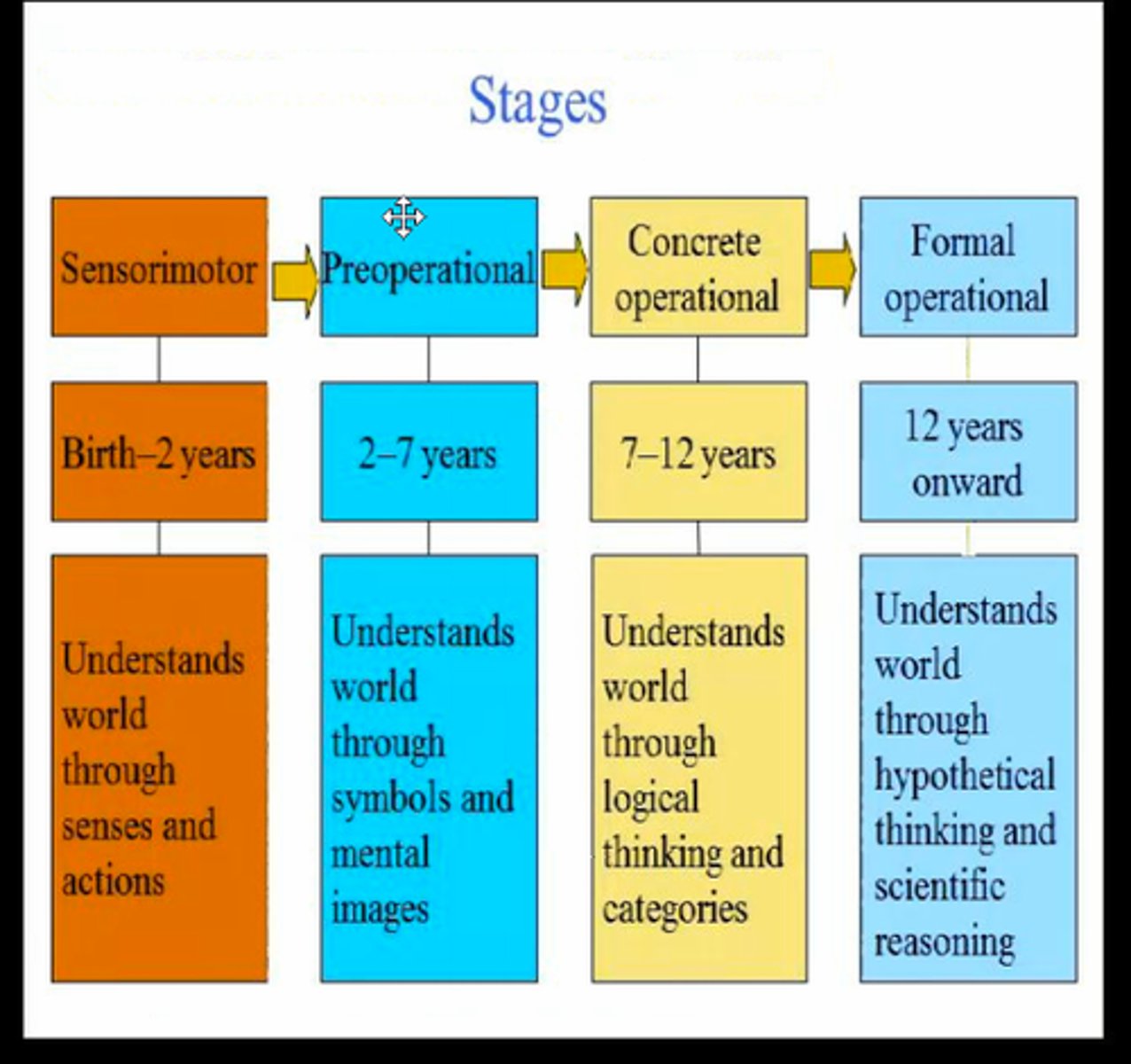
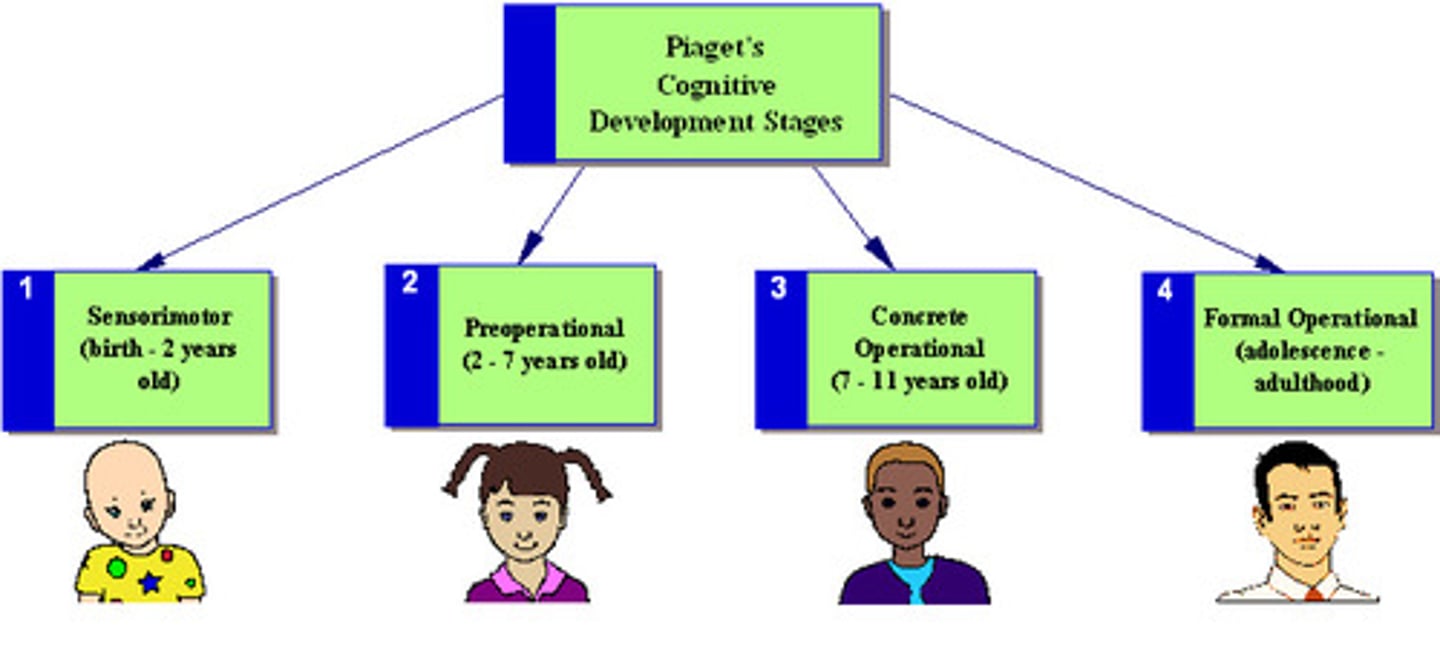
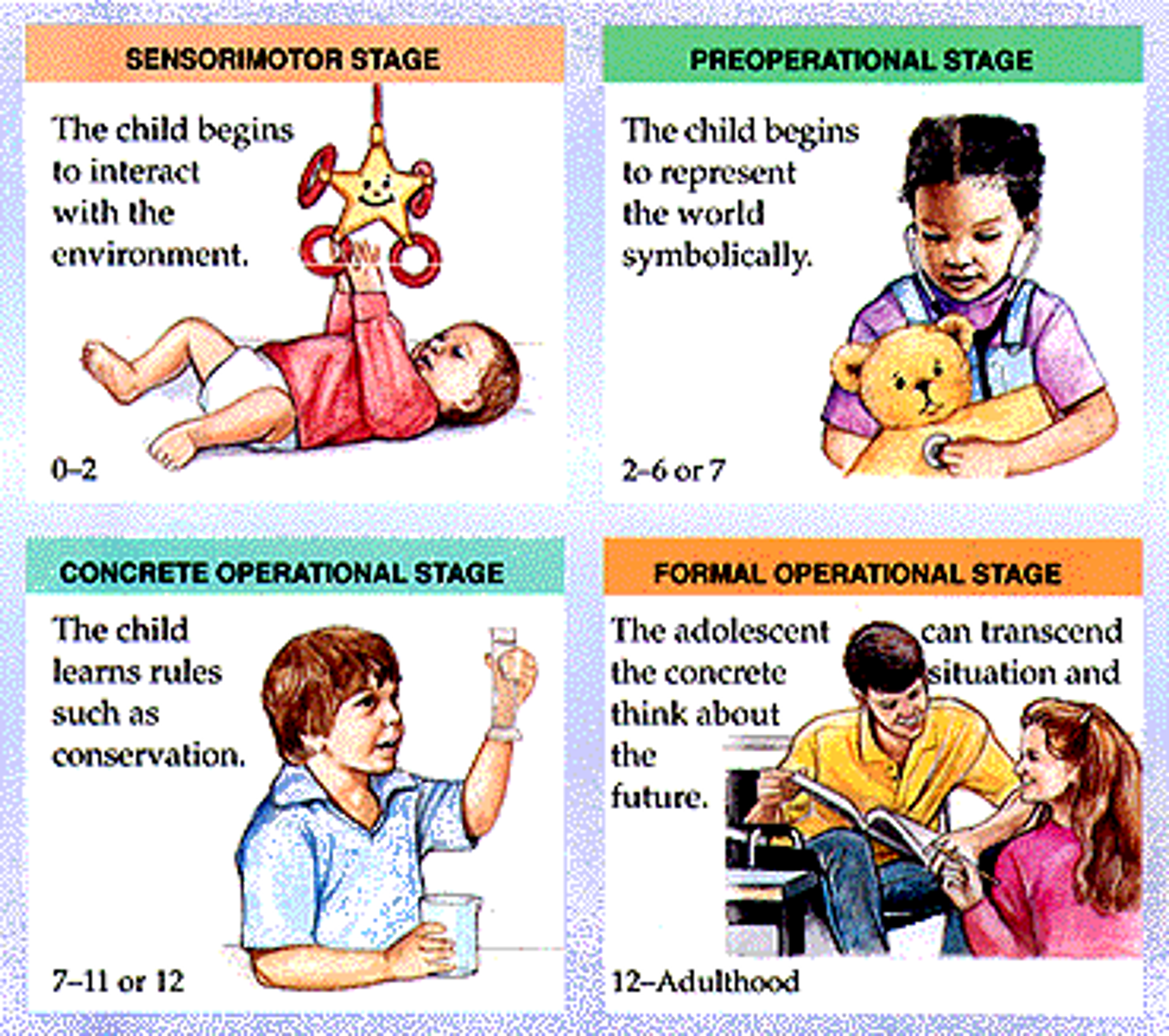
Sensorimotor stage
The first stage in Piaget's theory, during which the child relies heavily on innate motor responses to stimuli
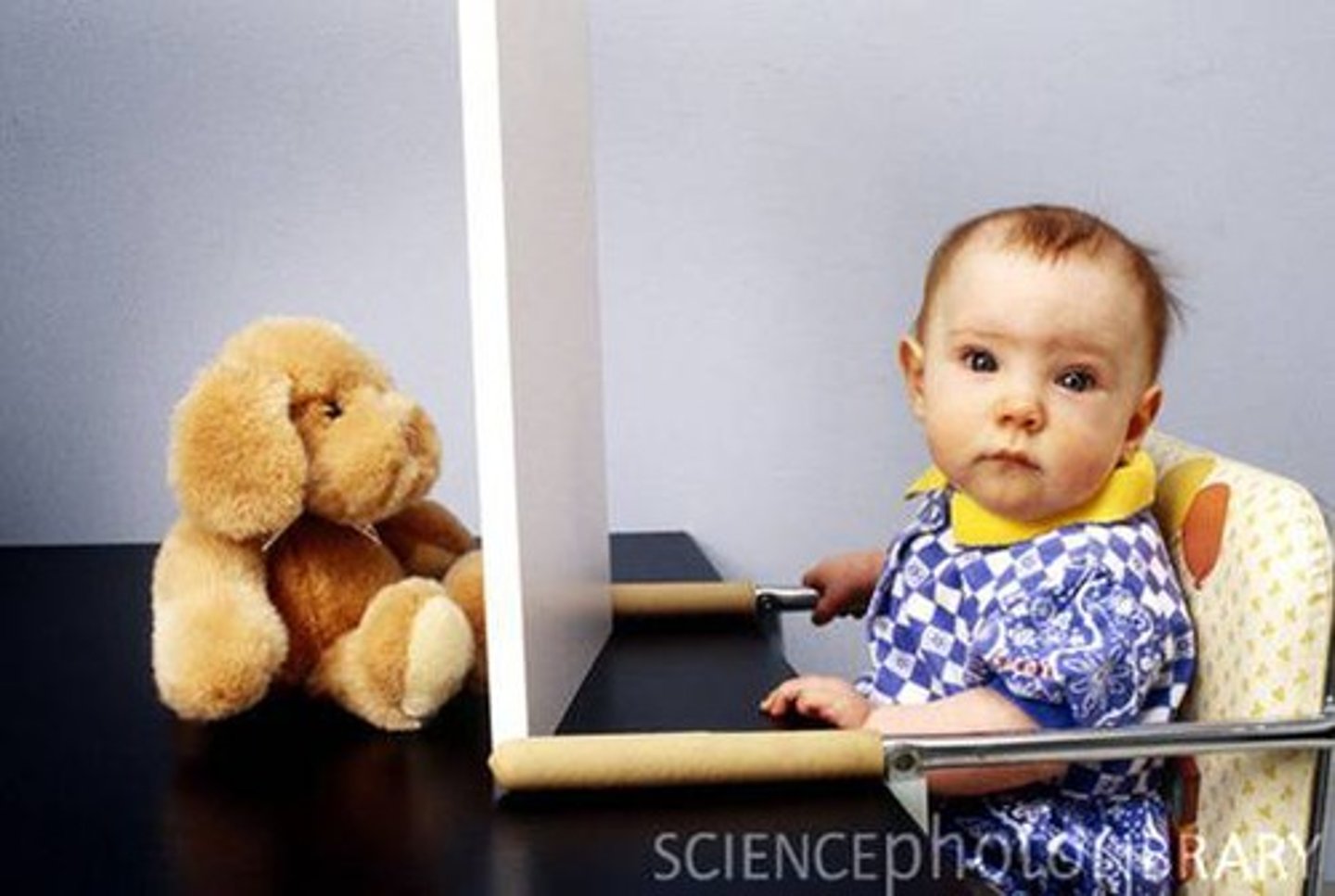
Object permanence
The knowledge that objects exist even if they cannot be seen or touched

Preoperational stage
The second stage in Piaget's theory, marked by well-developed mental representation and the use of language

Egocentrism
Having difficulty seeing or being unable to see things from another person's point of view

Concrete operational stage
The third of Piaget's stages, when a child understands conversation but still is incapable of abstract thought

Formal operational stage
The last of Piaget's stages, during which abstract thought appears
Abstract thinking
A way of thinking that does not rely on being able to see or visualize things in order to understand concept

Logical thinking
Ability to develop strategies to solve problems, identify a range of possible solutions to problems, develop hypothesis and systematically test solutions
