HTHS 1110 Exam 1 Weber State
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
+2
+1
0
-1
-2
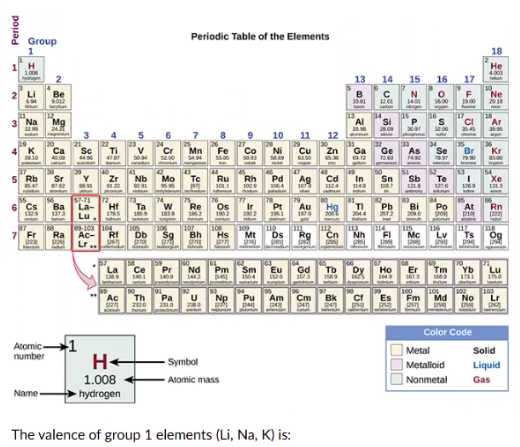
+1
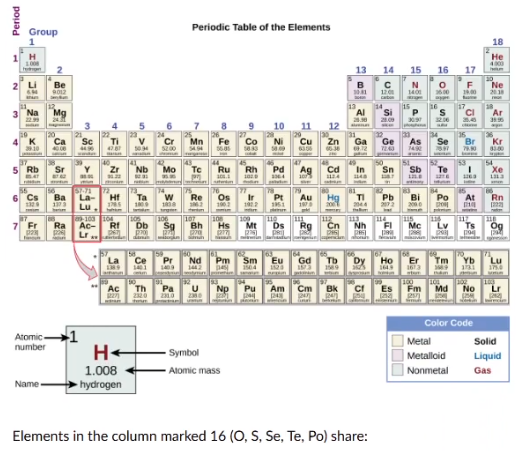
similar chemical proprties
the same number of electrons
thc same number of neutrons
the same number of protons
the same stuffed rabbit (fomite)
similar chemical proprties
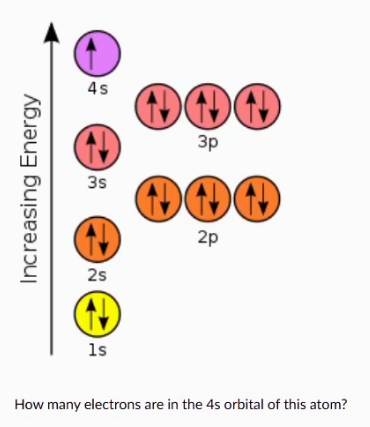
0
1
2
3
6
1
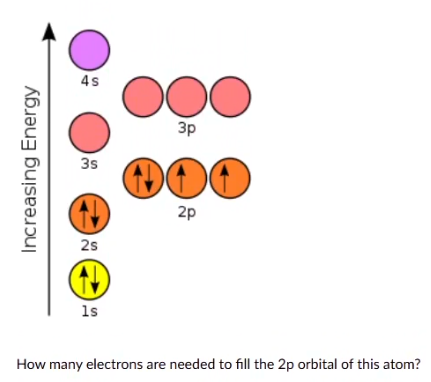
-2
-1
0
1
2
2
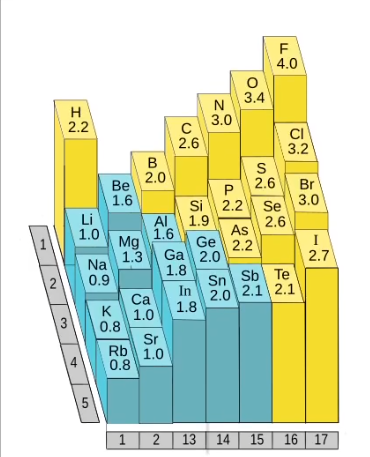
1.0
2.6
3.2
4.0
2.6
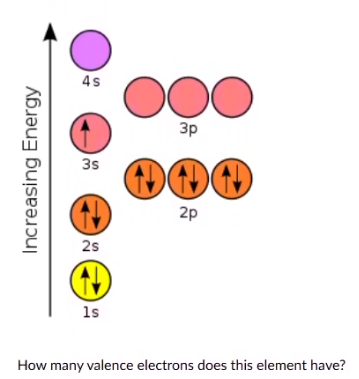
0
1
2
6
7
9
1
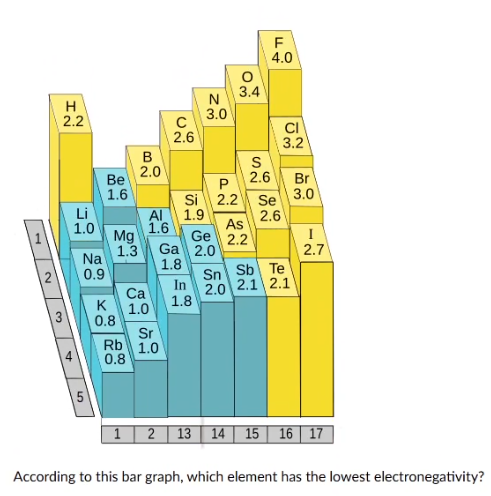
fluorine
hydrogen
krypton
potassium
potassium
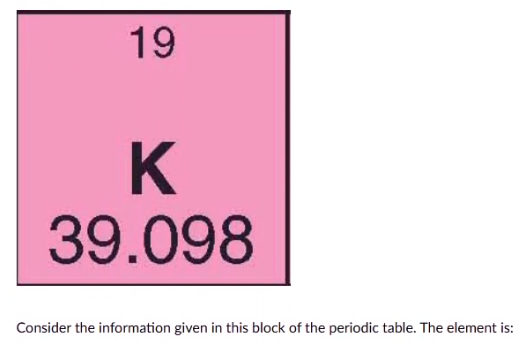
cadmium
calcium
krypton
potassium
potassium
Which of the following correctly lists the noble gases?
C, Sit Gc. Sn, Pb
E Cl. Br. I, At
H. Li. Na. K. Rb. cs. Fr
He, Ne. Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
N. P, As. Sb, Bi
He, Ne. Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
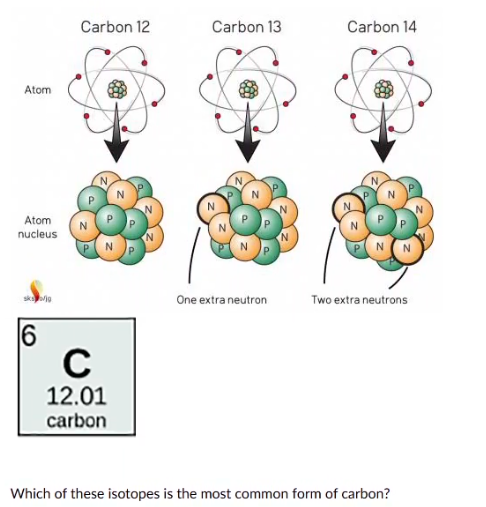
Which of these isotopes is the rnost common form of carbon?
12C
13C
14C
12C
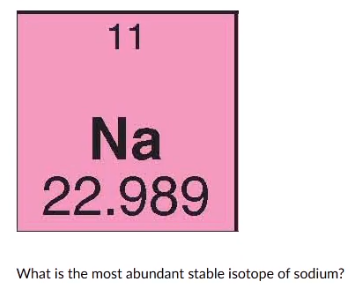
11Na
22Na
22.989Na
23Na
34Na
23Na
Entropy refers to the amount of _____ in a system.
disorder
heat
kinetic energy
motion
potential energy
disorder
Of the following list, the easiest bond to break would be:
double covalent bond
hydrogen
ionic bond
single covalent bond
triple covalent bond
hydrogen
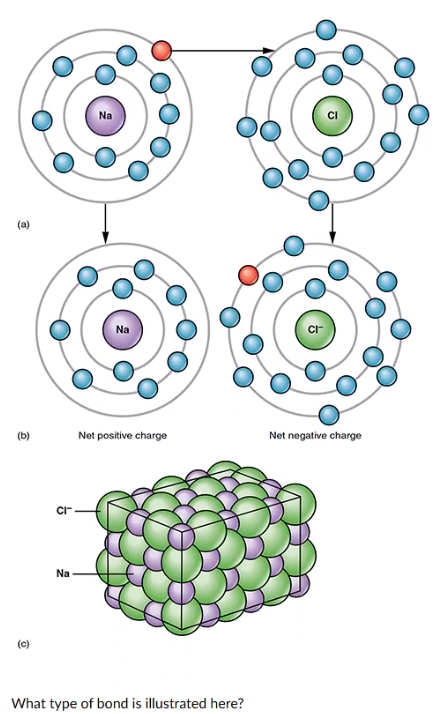
What type of bond is illustrated here?
hydrogen bond
ionic bond
non-polar covalent bond
polar covalent bond
ionic bond
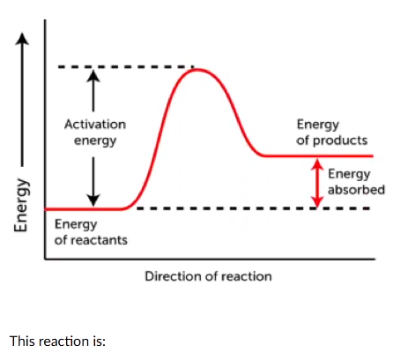
This reaction is:
endotherrnic or endergonic
exothermic or exergonic
kinetic
potential
endotherrnic or endergonic
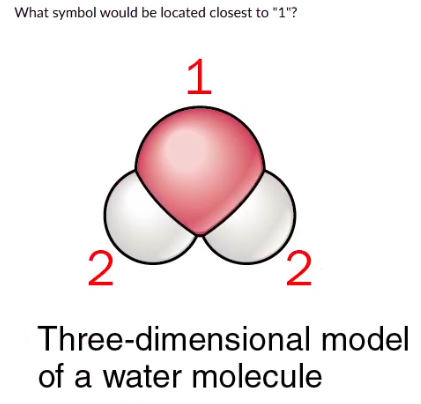
-
+
s-
s+
s-
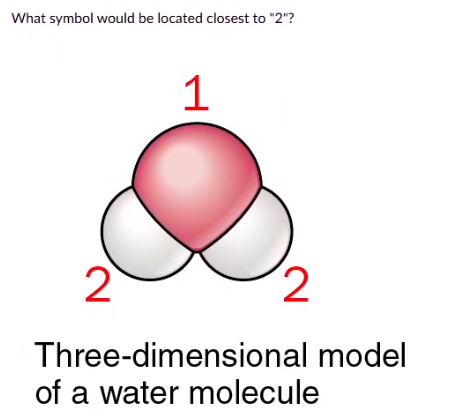
-
+
s-
s+
s+
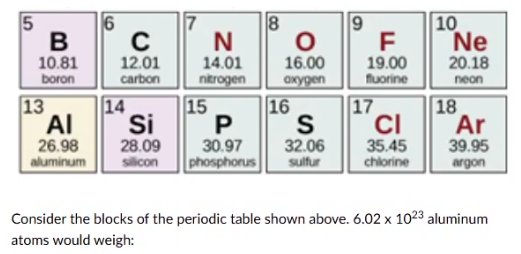
1 gram
26.98 grams
39.95 grams
6.02 x 10^23 grams
26.98 grams

22.99 grams
35.45 grams
58.44 grams
6.02 x 10^23 grams
58.44 grams
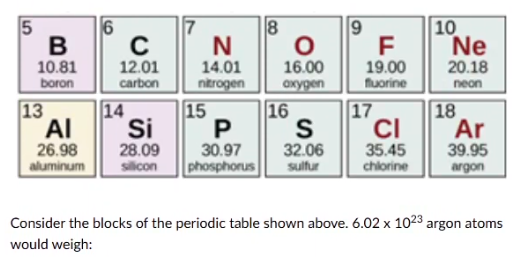
1 gram
26.98 grams
39.95 grams
6.02 x 10^23 grams
39.95 grams

amino
carboxyl
methyl
phenyl
methyl
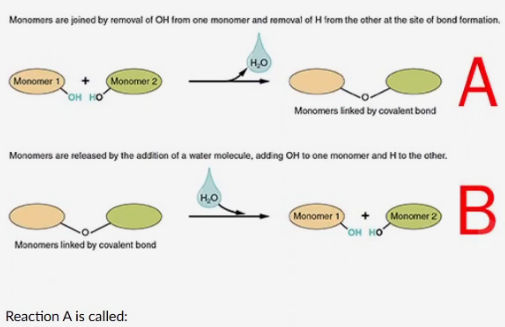
acid-base reaction
burning of hydrogen gas
dehydration synthesis
hydrolysis
dehydration synthesis

A
B
C
D
B
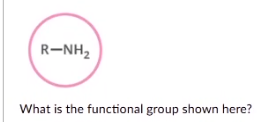
What is the functional group shown here?
alcohol
amine (amino)
carboxylic acid (carboxyl)
ether
amine (amino)
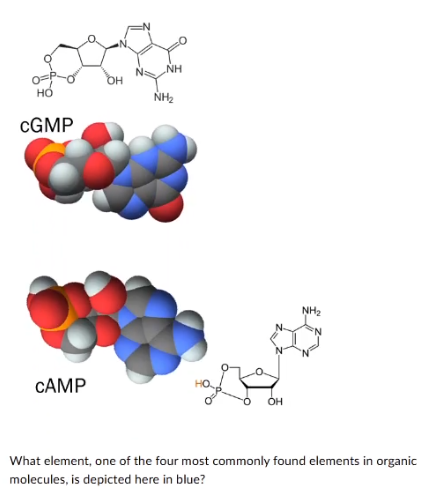
What element. one of the four most commonly found elements in organic molecules. is depicted here in blue?
carbon
nitrogen
oxygen
phospiwrus
sulfur
nitrogen
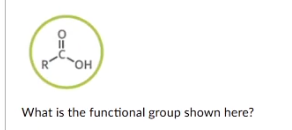
What is the functional group shown here?
alcohol
amine (amino)
carboxylic acid (carboxyl)
ether
carboxylic acid (carboxyl)
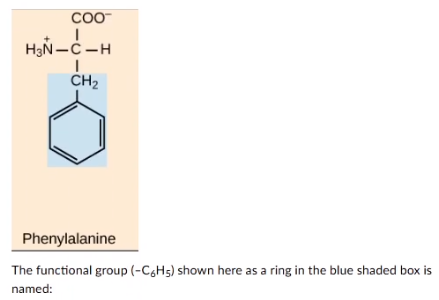
The functional group (-C6H5) shown here as a ring in the blue shaded box is named:
alcohol
ester
ketone
phenyl
phenyl
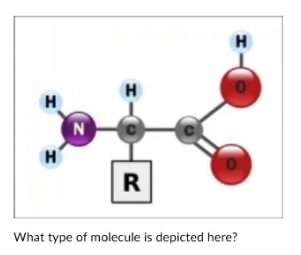
What of molecule is depicted here?
alcohol
amino acid
fatty acid
ketone
amino acid
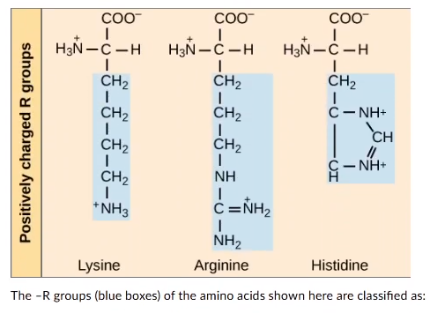
The -R groups (blue boxes) Of the amino acids shown here are classified as:
acidic
basic
non-polar
uncharged
basic
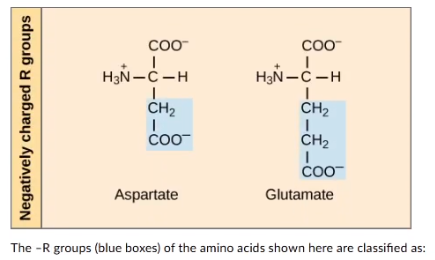
The -R groups (blue boxes) of the amino acids shown here are classified as:
acidic
basic
non- polar
uncharged
acidic
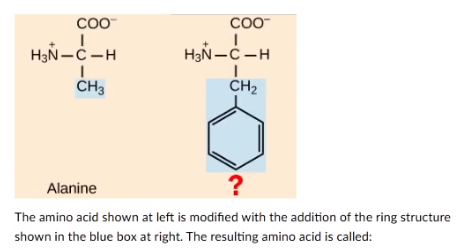
The amino acid shown at left is with the addition of the ring structure shown in the blue box at right. The resulting amino acid is called:
asparagine
glycine
leucine
phenylalanine
phenylalanine
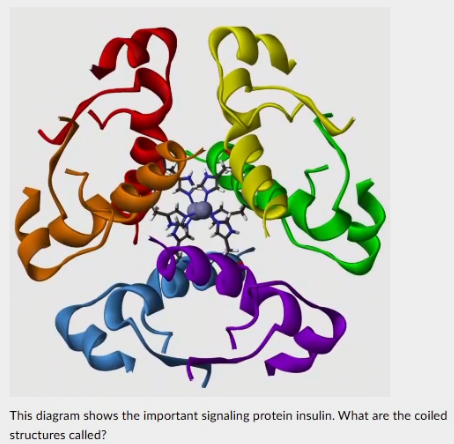
This diagram shows the important signaling protein insulin. What are the coiled structures called?
a-helices
ß-oleated sheets
heme groups
hydrogen bonds
peptide bonds
a-helices
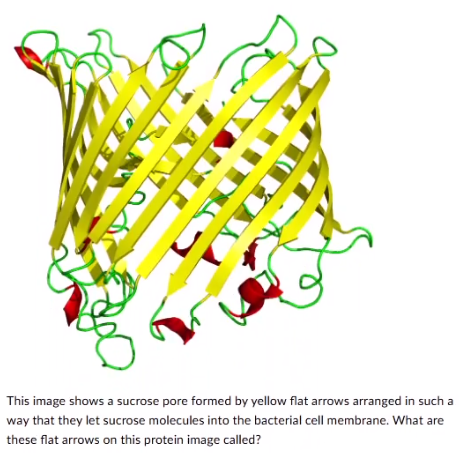
This image shows a sucrose pore formed by yellow flat arrows arranged in such a way that they let sucrose molecules into the bacterial cell membrane, What are these flat arrows on this protein image called?
a-helices
ß-pleated sheets
heme groups
hydrogen bonds
peptide bonds
ß-pleated sheets
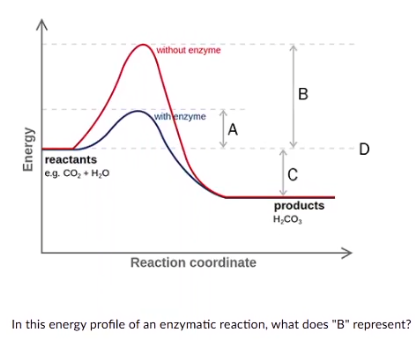
In this energy profile of an enzymatic reaction, what does B represent?
activation energy needed with catalyst
activation energy needed without catalyst
energy of products
energy of reactants
activatön energy needed without catayst
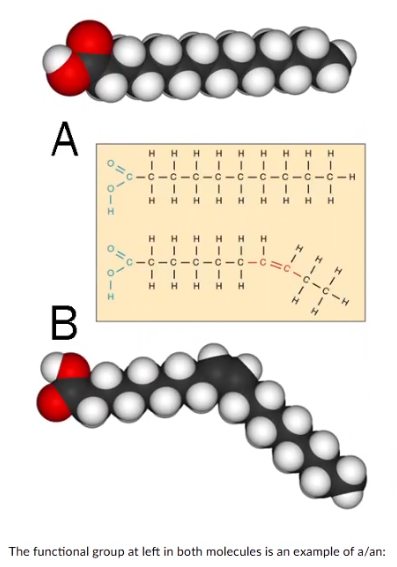
The functional group at left in both molecules is an example of a/an:
amino group
basic residue
carboyxlic acid group
disulfide bond
ester group
carboyxlic acid group
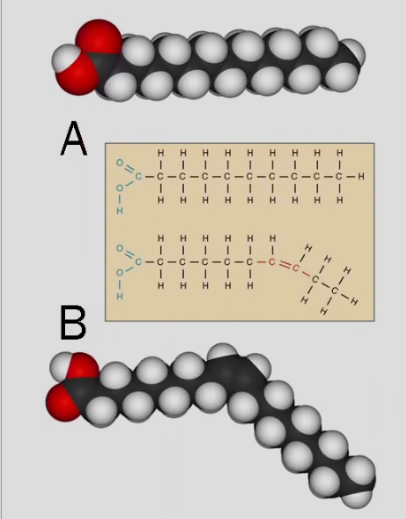
The red atoms in the molecules depicted here represent:
carbon
hydrogen
nitrogen
oxygen
oxygen
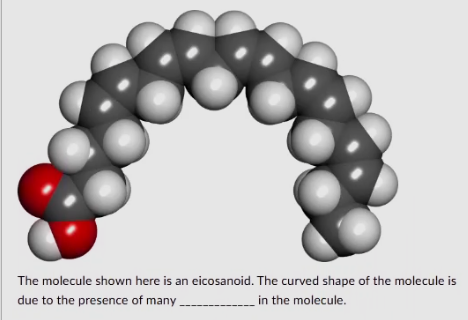
The molecule shown here is an eicosanoid. The curved shape of the molecule is due to the presence of many _____ in the molecule.
double bonds
nitrogens
prolines
sulfates
double bonds
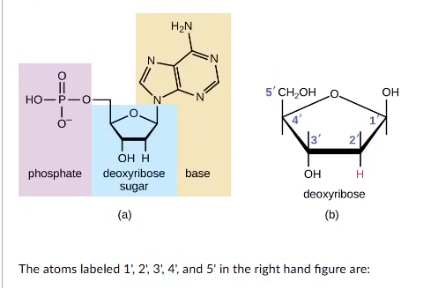
The atoms labeled 1', 2, 3, 4', and 5' in the right hand figure are:
carbons
hydrogens
nitrogens
oxygens
carbons
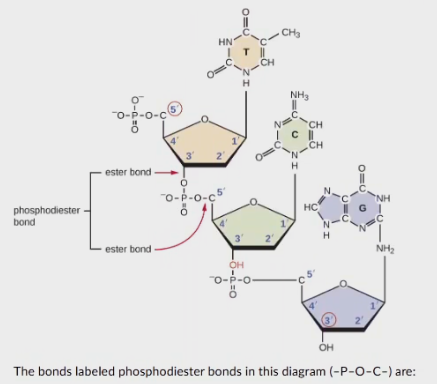
bonds labeled phosphodiester bonds in this diagram (-P-O-C-) are:
covalent bonds
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
peptide bonds
covalent bonds
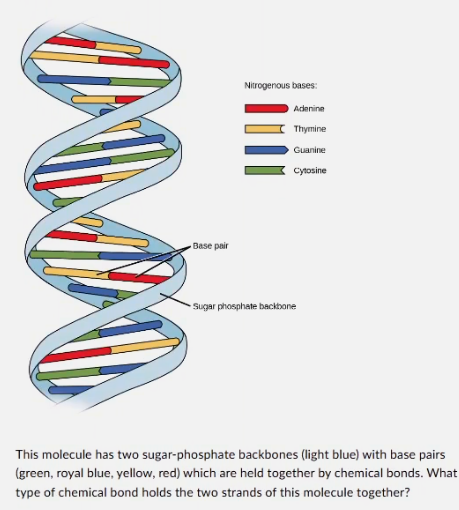
This molecule has two sugar-phosphate backbones (light blue) with base pairs (green, royal blue. yellow, red) which are held together by chemical bonds. What type of chemical bond holds the two strands of this molecule together?
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
non-polar covalent bonds
polar covalent bonds
hydrogen bonds
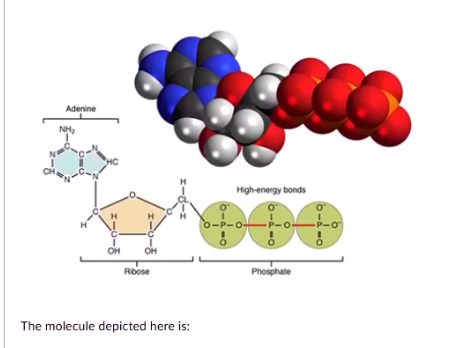
The molecule depicted here is:
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
anandamide
oleic acid
thymidine
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
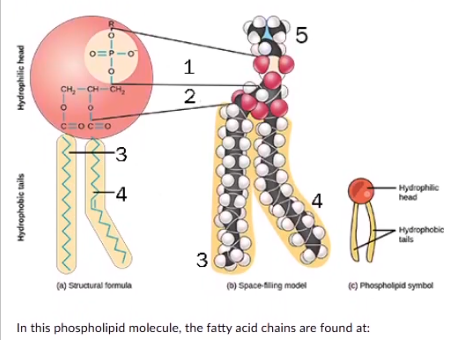
In this phospholipid molecule. the faty acid chains are found at:
1
2
3&4
5
A mixture of water, K+, Na+, Cl-, PO4–3, HCO3–, glycogen, proteins, and RNA would be called:
centrosomes
cytoplasm
cytoskeleton
cytosol
proteasomes
cytosol
Cilia and flagella are both organelles involved in cellular:
energy production
motility
storage and digestion
structure
synthesis
motility
These structures perform special functions in cellular growth, maintenance, and reproduction.
cytoplasm
cytoskeleton
cytosol
nucleus
organelles
organelles
Mitochondria:
generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
move the cell
oxidize organelles
produce proteins
synthesize glycolipids
generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
The "enzyme soup" enclosed by the highly-folded inner mitochondrial membrane is the:
crista
cytoplasm
intermembrane space
matrix
matrix
The terms exothermic, exergonic, and catabolic all refer to chemical reactions that:
create energy
destroy energy
release energy
require energy
release energy
The terms endothermic, endergonic, and anabolic all refer to chemical reactions that:
create energy
destroy energy
release energy
require energy
require energy
Which list contains only molecules that are reused and not altered in the process of cellular respiration?
acetate, FAD, NAD+
coenzyme A, FAD, NAD+
coenzyme A, glucose, pyruvate
glucose, pyruvate, acetate
coenzyme A, FAD, NAD+
In the formation of ATP, the stored energy is held in high-energy bonds between the:
adenine and ribose
adenosine and first phosphate group
phosphate groups
ribose and first phosphate group
phosphate groups
Which of the following molecules is broken into two 3-carbon sugars by the process of glycolysis?
ATP
FAD
glucose
pyruvate
glucose
Which of the following molecules involved in cellular respiration is not consumed by the process?
glucose
NADH
oxygen
pyruvate
NADH
Which list contains only molecules that are consumed in the process of cellular respiration?
acetate, FAD, NAD+
coenzyme A, FAD, NAD+
coenzyme A, glucose, pyruvate
glucose, pyruvate, acetate
glucose, pyruvate, acetate
Which of the following molecules involved in cellular respiration is not consumed by the process?
coenzyme A (CoA)
glucose
oxygen
pyruvate
coenzyme A (CoA)
Which of the following processes occurs in mitochondria?
digestion of unneeded proteins
electron transport chain
glycolysis
synthesis of protein
electron transport chain
As a result of anaerobic respiration, lactate can build up in cells, causing pain. This sensation occurs because increaded lactate causes an increase in:
acidity
alkalinity
solubility
tonicity
acidity
Which of the following molecules involved in cellular respiration has 3 carbons?
acetate
carbon dioxide
glucose
pyruvate
pyruvate
Which of the following molecules involved in cellular respiration has 3 carbons?
acetate
carbon dioxide
glucose
lactate
lactate
In the presence of oxygen, each glucose molecule produces a net of ____ ATP molecules.
2
4-6
20-26
26-38
26-38
Lactate is an end-product of:
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
lysosomal degradation of unneeded organelles
protein synthesis
anaerobic respiration
Acetyl-coenzyme A formation occurs in the:
cytosol
intermembrane space
mitochondrial matrix
nucleus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
mitochondrial matrix
Pyruvate is an intermediate in:
aerobic respiration
free radical formation
lysosomal degradation of unneeded organelles
protein synthesis
aerobic respiration
This organelle is filled with H2O2, and is common in liver and kidney where it plays an important role in the breakdown of toxins.
centrosome
cilia
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitochondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
peroxisome
By the end of the citric acid cycle, all six carbons from the original glucose molecule are "consumed" by pairing each one with oxygen to make:
bicarbonate
carbon dioxide
citric acid
pyruvate
carbon dioxide
After glycolysis, acetyl-coenzyme A formation, and the citric acid cycle, we have formed a net total of _______ per glucose molecule.
0 ATP
2 ATP
4 ATP
26-38 ATP
4 ATP
What is the location of the electron transport chain?
inner mitochondrial membrane
mitochondrial matrix
nucleus
plasma membrane
inner mitochondrial membrane
A proton gradient is critical for:
cellular respiration in mitochondria
cytoskeletal movements during mitosis
flagellar motility
processing of newly-formed proteins in the Golgi complex
cellular respiration in mitochondria
The water which is produced at the end of the electron transport chain is called:
alkaline water
heavy water
metabolic water
vitamin water
metabolic water
A cell without mitochondria (for example, a bacterial cell) can make ______ ATP molecules from each glucose molecule by glycolysis.
0
2
24
36
2
Approximately how many ATP molecules are made from one glucose molecule in the most efficient form of cellular respiration?
0
2
24
36
36
When the glycogen "tank" is full, excess carbohydrates not needed for metabolism are:
converted to amino acid and stored as protein
converted to cellulose and stored as complex carbohydrates
converted to cholesterol and stored as membranes
converted to triglycerides and stored as fat
converted to triglycerides and stored as fat
Some amino acids can be made in the body. Those that cannot, and must be obtained from the diet, are called:
alimentary
critical
essential
nutritional
essential
Triglycerides are lipid molecules in which a glycerol backbone is connected to three:
amino acids
fatty acids
glycogens
phospholipids
fatty acids
Glycogen is stored primarily in the liver and:
heart
kidney
pancreas
skeletal muscle
skeletal muscle
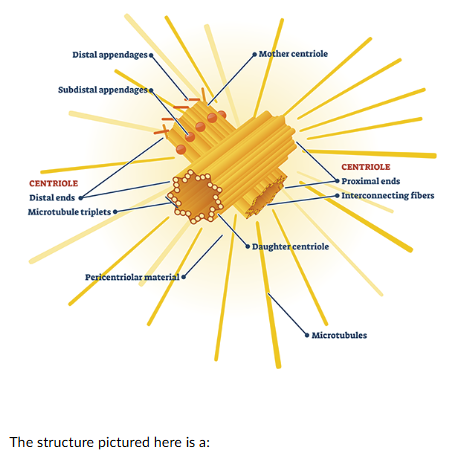
The structure pictured here is a:
centrosome
cilia
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitrxhondrion
gæroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
centrosome
The largest of the cytoskeletal elements is the:
intermediate filament
microfilament
microtubule
microtubule
Some cells increase their surface area by folding up the cell membrane into microvilli. At the core of each microvillus is a bundle of:
collagen
intermediate filaments
microfilaments
microtubules
microfilaments
Cilia and flagella have the same basic structure, with groups of ______________ running the length of the organelle in a regular pattern.
collagen fibers
intermediate filaments
microfilaments
microtubules
microtubules
The male sperm is the only human cell that possesses this organelle.
centrosome
cilia
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitochondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
flagellum
The organelles that move inhaled particles and mucus from the deeper parts of the lung to the oropharynx are the:
cilia
flagella
mitochondria
proteasomes
ribosomes
cilia
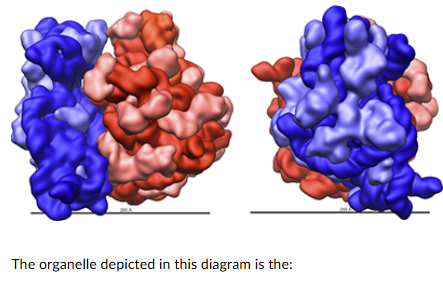
The organelle depicted in this diagram is the:
centrosome
cilia
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitrxhondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
ribosome
Glycosylation
Phosphorylation
Geranylgeranylation
Farnesylation
describe chemical modifications that are applied to:
carbohydrates
lipids
nucleic acids
proteins
proteins
This organelle is acidic, with a pH of about 5. Here, enzymes called acid hydrolases break down other organelles that are being recycled or that are no longer needed.
centrosome
cilia
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitochondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
lysosome
A protein destined for export from the cell passes through which organelles, in order?
Golgi complex > rough endoplasmic reticulum > secretory vesicle
Golgi complex > secretory vesicle > rough endoplasmic reticulum
rough endoplasmic reticulum > Golgi complex > secretory vesicle
rough endoplasmic reticulum > secretory vesicle > Golgi complex
secretory vesicle > Golgi complex > rough endoplasmic reticulum
rough endoplasmic reticulum > Golgi complex > secretory vesicle
Glycosylation
Phosphorylation
Geranylgeranylation
Farnesylation
are processes that occur in the:
centrosome
cilium
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitochondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi complex
This organelle can be found free-floating, or attached to a membrane network,
centrosome
cilium
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitochondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
ribosome
ribosome
Proteins are synthesized in the ______________________. Lipids are synthesized in the ______________________.
centrosome; lysosome
mitochondrion; peroxisome
proteasome; ribosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum; smooth endoplasmic reticulum
rough endoplasmic reticulum; smooth endoplasmic reticulum
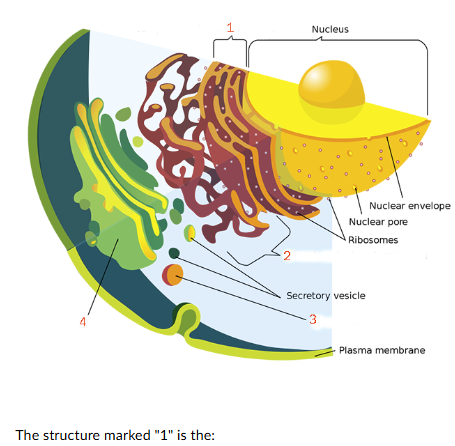
The structure marked "I" is the:
centrosome
cilia
cytoskeleton
flagellum
Golgi complex
lysosome
mitochondrion
peroxisome
proteasome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
rough endoplasmic reticulum
Newly-synthesized proteins arrive at the _________________ face of the Golgi complex.
cis
clown
Mt. Rushmore
trans
ugly
cis
Organelles needed for synthesis of new molecules include:
cytoskeleton
lysosome
peroxisome
proteasome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
rough endoplasmic reticulum