Chapter 12: Nervous system- Glial cells , myelination Axon regeneration
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
function of glial cells
support and protect neurons
are glial cell excitable?
No
the quantity of glial cells is about the same number as the neurons
true, it is about the half the volume of nervous system
general characteristics of glial cells
-capable of mitosis
-protect and nourish neurons
-provide physical scaffolding for nervous tissue
-critical for normal function of neural synapses
glial cell of CNS
-astrocyte
-ependymal cell
-microglial cell
-oligodendrocyte
astrocyte characteristics and function
-most abundant in the CNS
-have processes that end in perivascular feet
-structural support
-assist neuronal development
-alter synaptic activity
-occupy the space of dying neurons
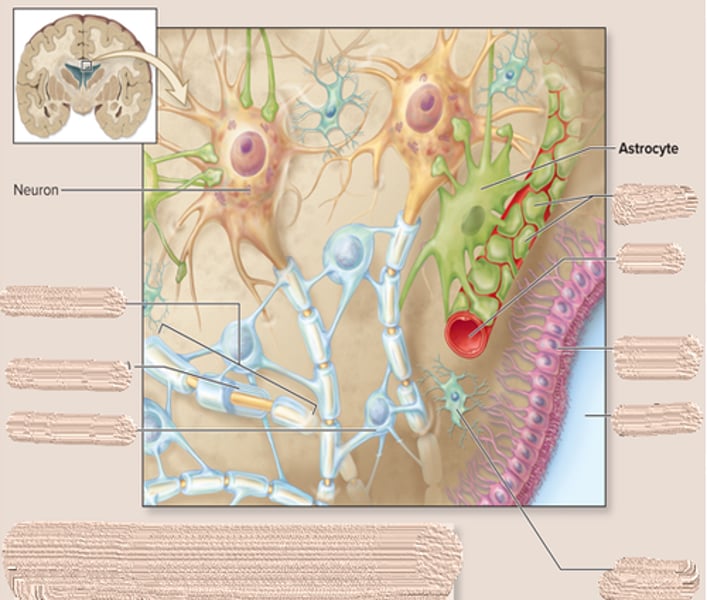
how does the astrocyte help to form blood brain barrier?
by wrapping feet around brain capillaries
- it controls which substance have access to brain
how does the astrocyte regulate tissue fluid composition?
- controls the chemical environment around the neurons
-Ex: can regulate potassium concentration
ependymal cells function and characteristics
-line cavities in the brain and spinal cord
-produces cerebral fluid
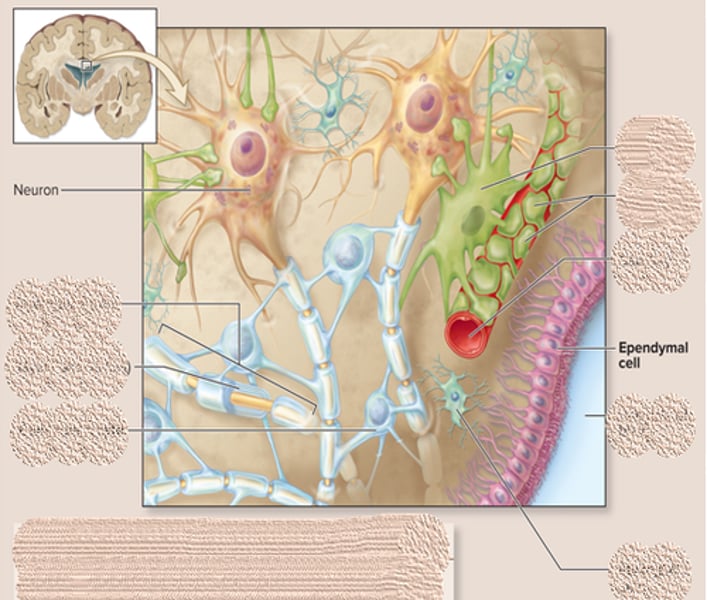
ependymal cells is part of ______which produces cerebral fluid
choroid plexus
microglia function and characteristics
-small cell that wander in the CNS and replicate during infection
-engulf infectious agent and remove debris
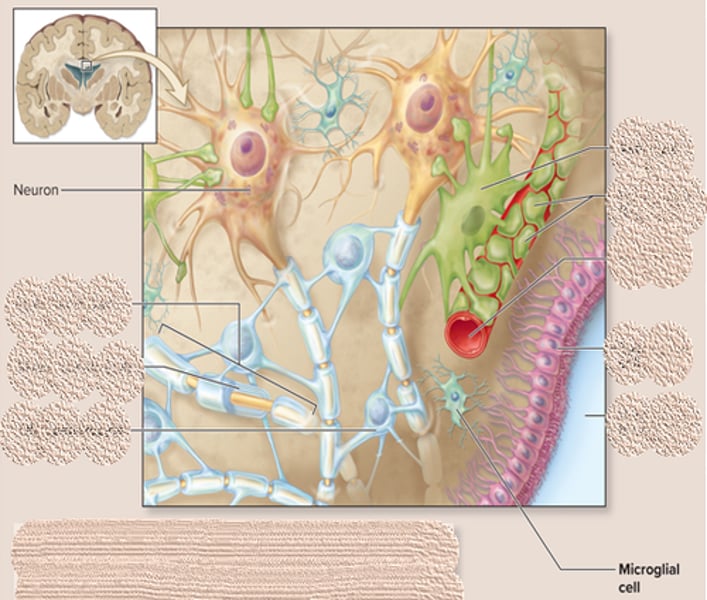
microglia can be characterized as
phagocytic cell of immune system
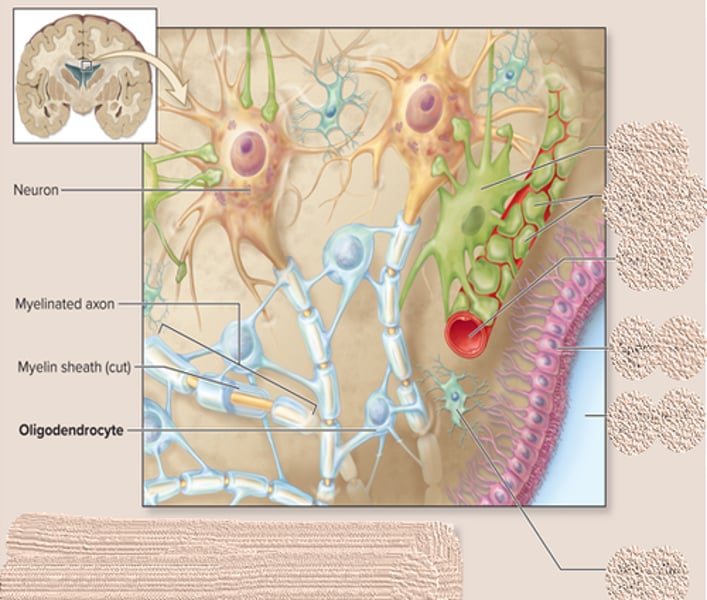
oligodendrocytes function and characteristics
-larger cell with slender extensions
-extensions wrap around axons of neurons forming the myelin sheath
glial cell in PNS
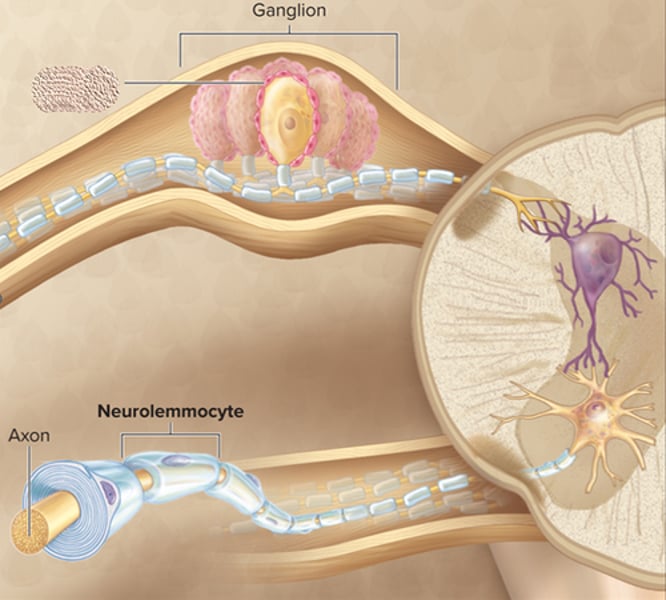
satellite cell
neurolemmocytes ( Schwann cells)
satellite cell function and characteristics
-arranged around neuronal cell bodies in ganglion
-electrically insulate and regulate the exchange of nutrients and waste
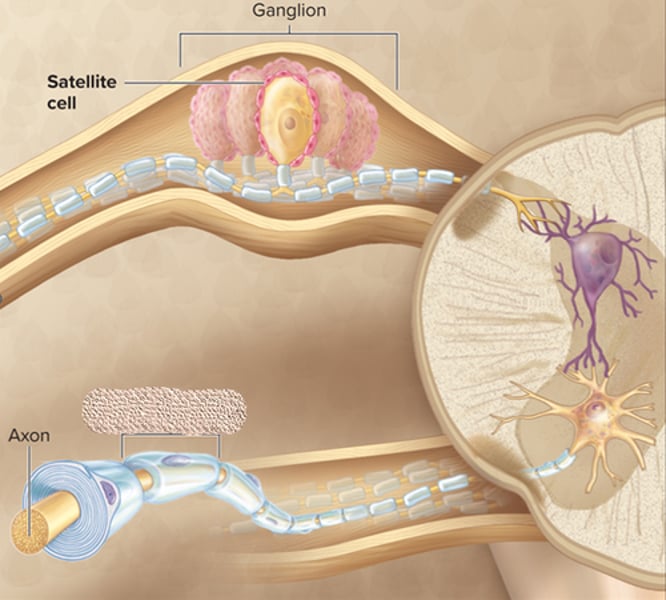
schwann cells
-Elongated, flat cells that ensheath PNS axons with myelin
-Allows for faster action potential propagation
neoplasm
-unregulated cell growth that happens in CNS
-primarily brain tumor
neoplasm usually happens to what type of tissue
-tissues with capacity to undergo mitosis
-meninges or glial cells
glioma
-glial cell tumors
-may be benign or malignant
what is myelination?
process of wrapping an axon with myelin
what is myelin?
several layers of membrane of glial cells
myelin content
high lipid content which it gives its glossy-white appearance and insulated axons
myelin formation on PNS: step 1
neurolemmocyte starts wrap around a 1mm portion of an axon
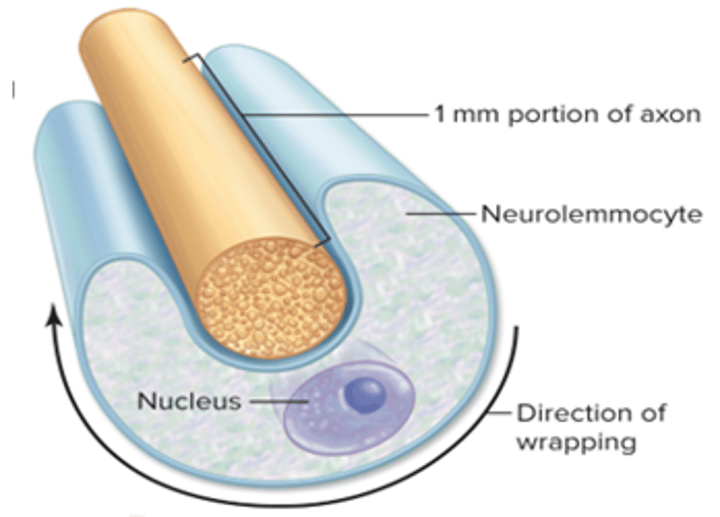
myelin formation on PNS: step 2
plasma membrane and cytoplasm of neurolemmocyte begin to form consecutive layers around the axon
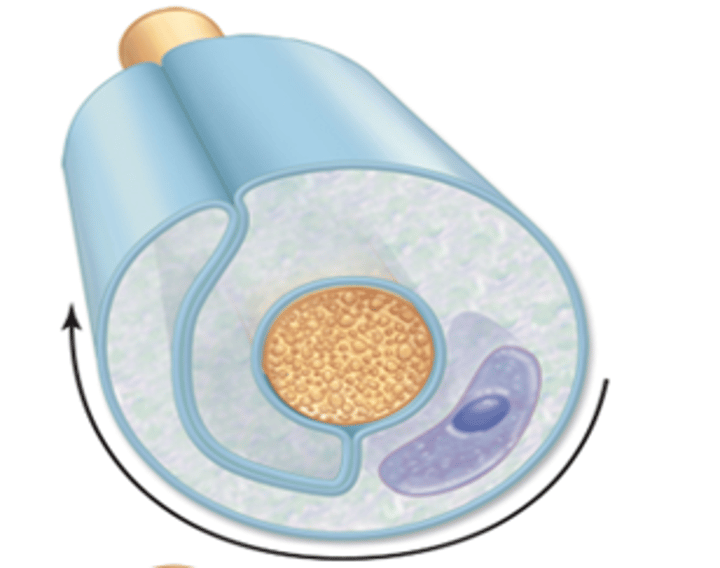
myelin formation on PNS: step 3
the overlapping layer of neurolemmocyte plasma membrane form the myelin sheath
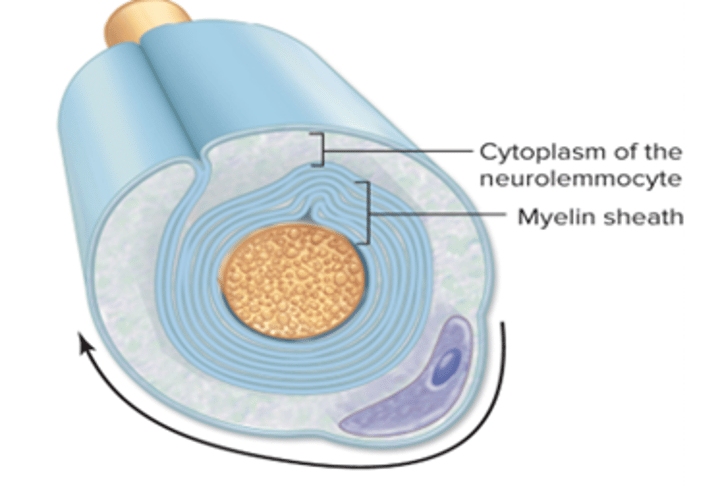
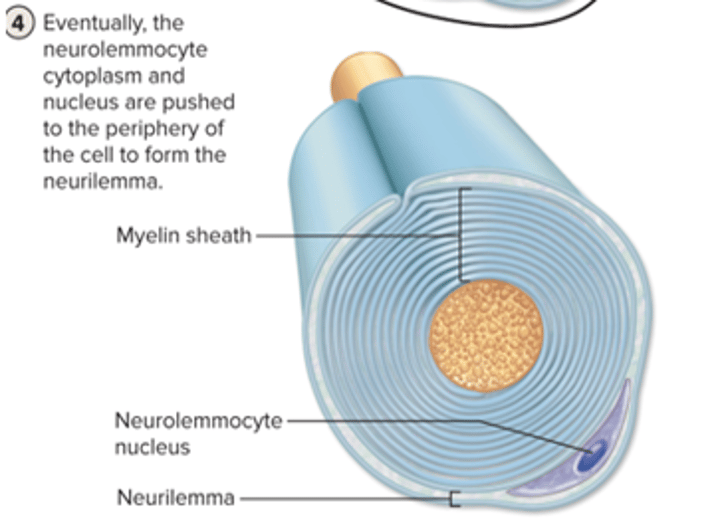
myelin formation on PNS: step 4
the neurolemmocyte cytoplasm and nucleus are pushed to the periphery of the cell to form the neurilemma
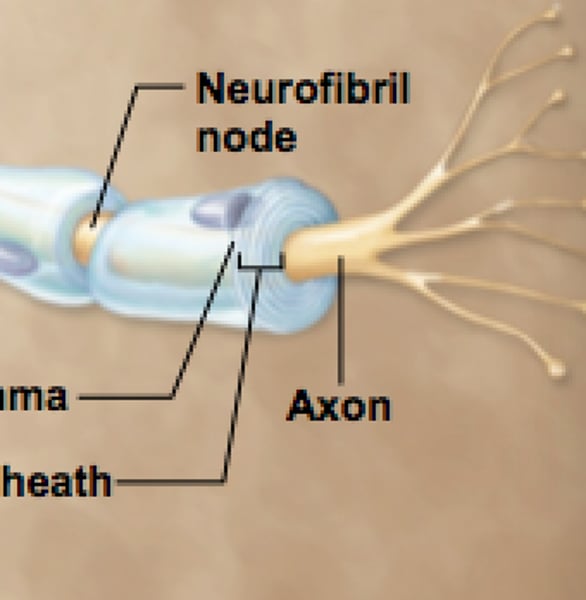
myelin sheath
overlapping layer of neurolemmocyte plasma membrane
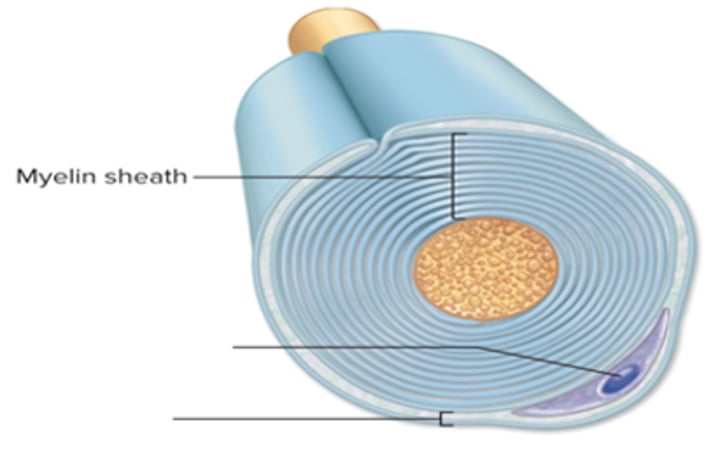
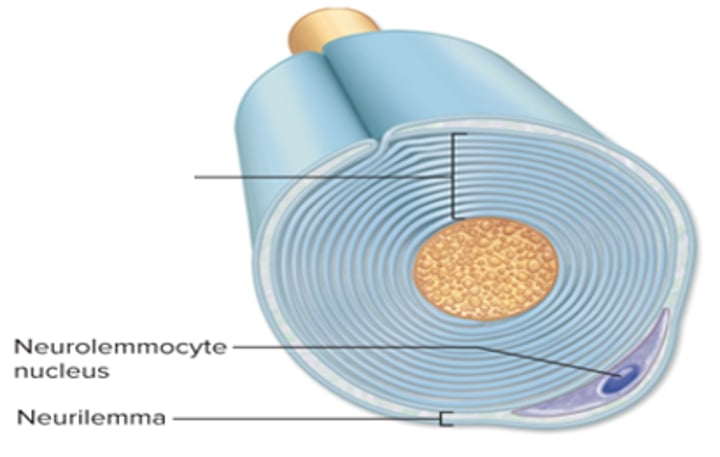
neurilemma
External part of myelin sheath
-includes neurolemmocyte nucleus
neurofibril nodes
-nodes of Ranvier
-gaps between myelin sheath
CNS myelin sheath is formed by
oligodendrocytes
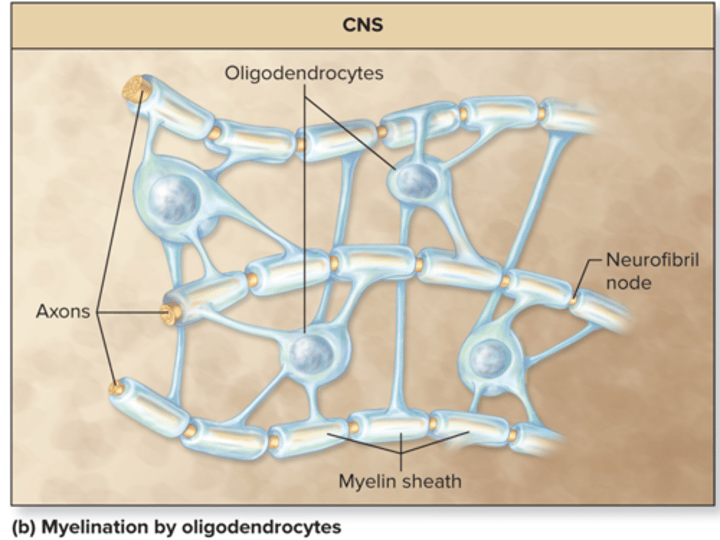
The main difference between PNS and CNS myelin sheath?
-oligodendrocyte can myelinate multiple axon to a multiple spot
-No neurilemma formed
what happens when to unmyelinated axon in PNS?
sits in depressed portion of neurolemmocyte
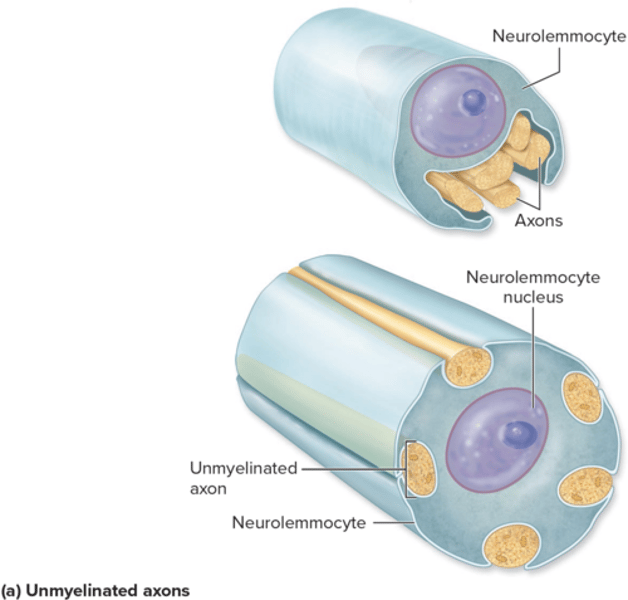
what happens when to unmyelinated axon in CNS?
does not associate with olifodendrocyte
mutiple sclerosis (MS)
-autoimmune disease
-progressive demyelination of neurons in CNS
What occurs to the neuron when a person have MS?
-oligodendrocytes are attacked by immune cells
- repeated inflammation events cause scarring and permanent loss of function
Guillain-Barre syndrome
-loss of myelin from peripheral nerves due to inflammation
effect of Guillain -Barre syndrome
muscle weakness begin sin distal limbs and advances to proximal muscles
Can axon regenerate?
PNS axon can regenerate but CNS is rare
PNS axon regeneration possibility
-neuron cell body needs to be intact
-enough neurolemma remains
PNS regeneration success is more likely when;
-amount of damage is less extensive
-distance between site of damage and structure that innervates is shorter
PNS axon regeneration: step 1
axon severed by trauma
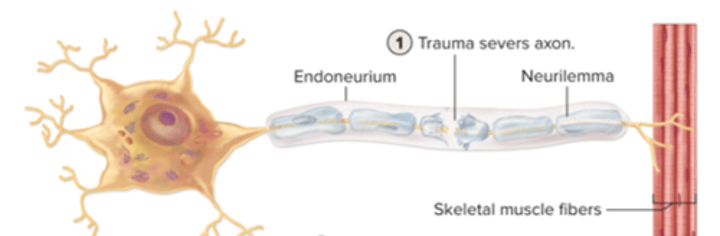
PNS axon regeneration: step 2
a. proximal portion of severed axon seals off and swells
b. distal portion of the axon degenerates and neurilemma survives
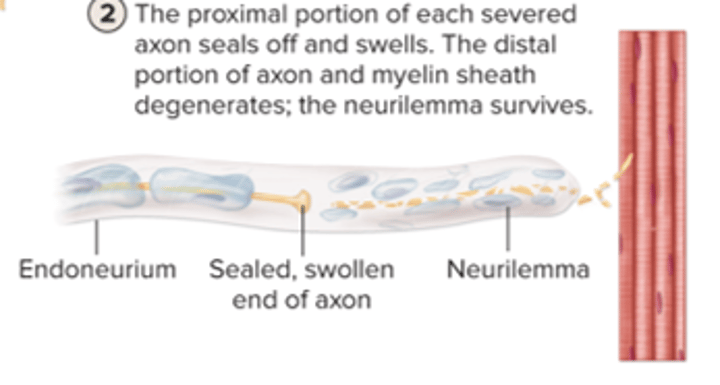
PNS axon regeneration: step 3
neurilemma and endoneurium form a regeneration tube
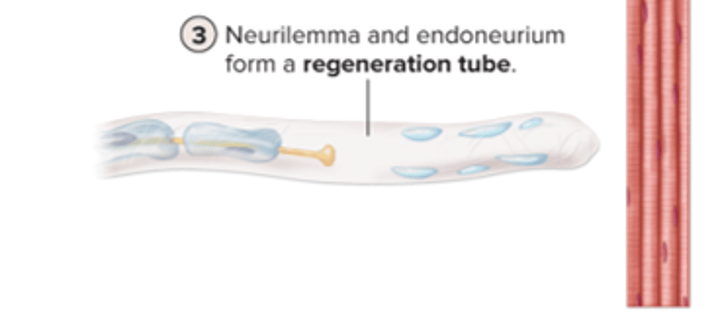
PNS axon regeneration: step 4
axon begins to regenerate and remyelination occurs
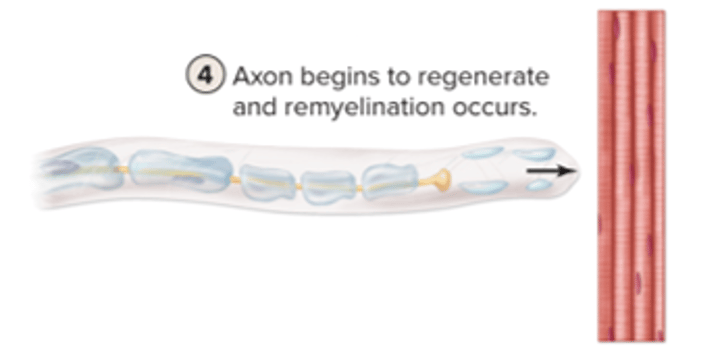
PNS axon regeneration: step 5
innervation to effector is restored
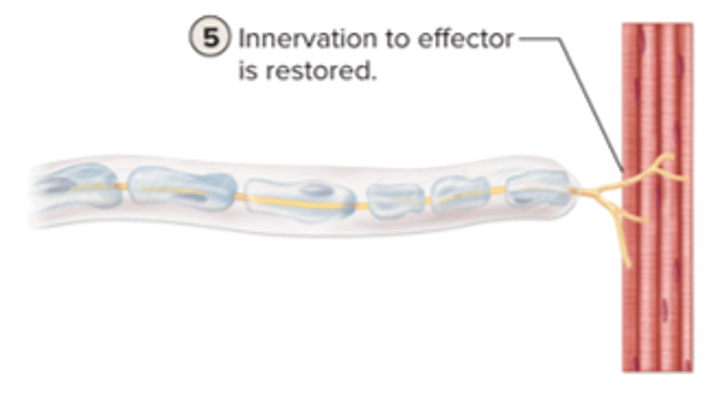
why CNS axon cannot regererate?
-oligodendrocytes secrete growth-inhibiting molecules, not growth factors
-regrowth is obstructed by scars from astrocytes and connective tissues