Carbohydrate Engorgement of Ruminants
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to carbohydrate engorgement of ruminants, focusing on etiology, pathogenesis, clinical findings, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is carbohydrate engorgement of ruminants commonly known as?
Grain overload or lactic acidosis.
What are the primary causes of carbohydrate engorgement in ruminants?
Access to highly fermentable feedstuffs and sudden ingestion of toxic amounts.
Which grains are considered the most toxic for carbohydrate engorgement?
Wheat, barley, and corn
Less toxic → oats and sorghum
Pathogenesis of grain overload
Inc VFFA → dec rumen pH → dec rumen motility → inc lactic acid (D and L isomers) → acid resistant lactobacillus spp proliferate producing pactic acid → inc rumen osmolality 280 mOsm/L - 400mOsm/L
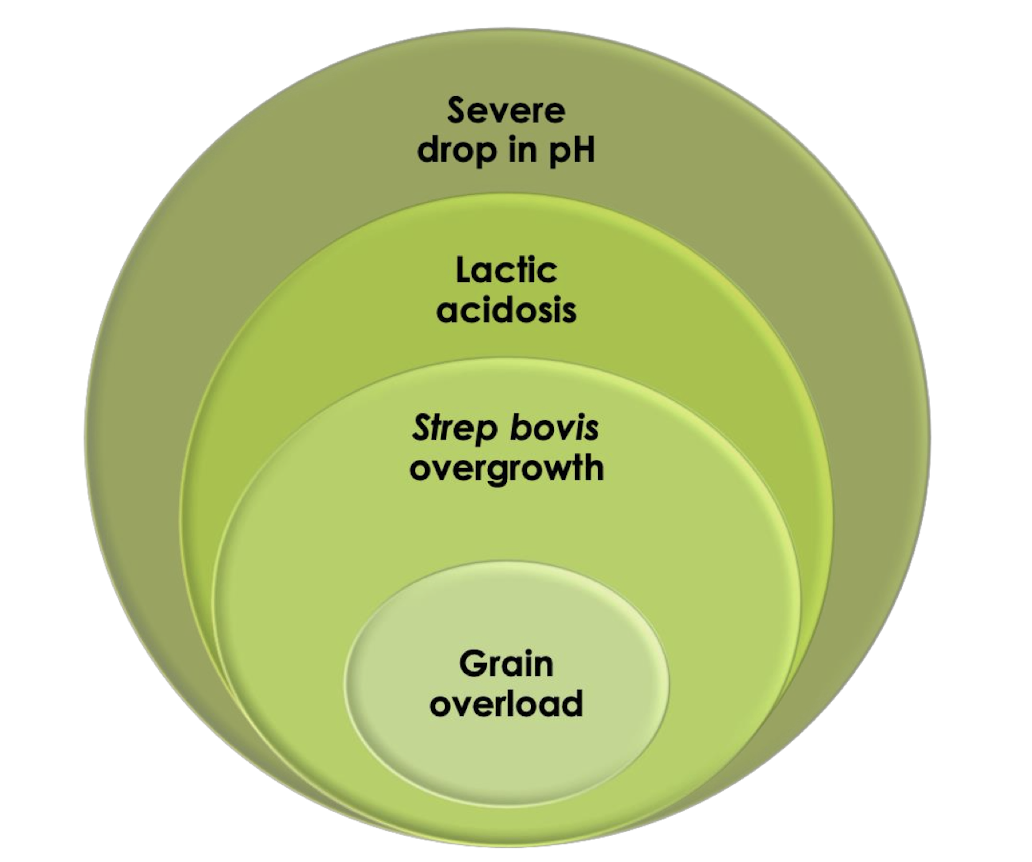
What pH level indicates severe lactic acidosis in ruminants?
A rumen pH of less than 5.
What clinical sign indicates dehydration in ruminants due to carbohydrate engorgement?
Dehydration of 6-12%.
What is the mortality rate for untreated animals with carbohydrate engorgement?
Up to 90%
Treated → 30-40%
cattle and sheep more affected
Clinical findings for grain overload
abdominal pain
dehydration
diarrhea
splashy rumen
depression
lameness
scleral inj
tachycardic → 80-140bpm
rumen fluid → pH <5, sour odor, dead protozoa, predom gram +
metabolic acidosis
inc PCV and TP inc BUN and creatinine (azotemia)
inc AG
dec calcium
What identifies the clinical finding 'splashy rumen'?
Increased rumen fluid osmolarity and the presence of lactic acid.
What is lactic acidosis?
A metabolic disorder caused by the accumulation of lactic acid in the blood, often resulting from grain overload in ruminants. Causes accumulation in the rumen → inc rumen fluid osmolarity drawing more water into the rumen
What should be included in the treatment to correct lactic acidosis in ruminants?
Sodium bicarbonate IV and alkalinizing agents(magnesium hydroxide)
Restore fluids and electrolytes → hypertonic NaCl, LRS
restore forestomach and intestinal motility
rumenotomy
rumen lavage with large kingsman tube
antibiotics
antihistamines
What is a rumenotomy used for?
To treat severe cases of ruminal acidosis.
What happens in the pathogenesis of lactic acidosis?
Increased volatile fatty acids and decreased rumen pH.
How can ruminal acidosis be diagnosed?
Biochem → hemoconcentration, hyperlactetamia, hypocalcemia, low bicarb
Blood gas → lactic acid
Urine → pH <5
What are common clinical signs of carbohydrate engorgement?
Abdominal pain, dehydration, diarrhea, and lameness.
What type of bacteria proliferates during carbohydrate engorgement?
Acid-resistant Lactobacillus species.
How does primary rumen tympany (bloat) occur?
Excessive retention of gases due to prevented eructation.
What specific feedstuff can cause frothy bloat(primary)?
Leguminous pastures and finely ground grain in feedlot
What are the consequences of chronic bloat in ruminants?
Potential permanent shifts in microbiota due to high grain diets.
What type of management can help prevent carbohydrate engorgement?
Slow adaptation to grain and maintaining sufficient fiber.
What is the cause and treatment method for relieving free gas bloat(secondary)?
Diet that leads to extra gas and failure to eructate → Passing a stomach tube.
What are the effects of lactic acid absorption in ruminants?
It leads to profound lactic acidosis.
What is the common morbidity rate observed in ruminants with carbohydrate engorgement?
10-50%.
Name a non-ionic detergent used as an anti-foaming cagent for bloat.
Poloxalene (Alfasure)
What dietary change can contribute to the risk of subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA)?
Excess concentrates and lack of coarse fiber → Acidosis is a dec in the alkali in the body fluids relative to the acid content
What is the recommended pH level for normal rumen fluid?
Above 5.
What clinical finding might be seen in cows with bloat?
Distended left paralumbar fossa
Discomfort (grunting, colic)
Open-mouth breathing
Anorexia
Salivation
Anxious
Depressed terminally
Sudden death
What are the components of a treatment regimen for metabolic acidosis?
IV fluids, sodium bicarbonate, and electrolytes.
What is a significant diagnostic indicator seen in rumen fluid analysis?
Absence of protozoa and predominance of gram-positive bacteria.
What should be monitored in treated animals to gauge recovery?
PCV and total protein levels.
What leads to the development of hepatic abscesses in ruminants?
Bacterial invasion via portal circulation after lactic acidosis → Fusobacterium necrophorum & Archanobacter pyogenes → diffuse coagulation and hyperplasia of bile duct epithelium and poss renal tubular degeneration
What is the prognosis for treated animals with carbohydrate engorgement?
30-40% mortality.
Why does bloat occur primarily in lush pastures?
High water content and protein levels in legumes.
Name a potential neurotransmitter affected by toxins from carbohydrates.
Histamine.
ethanol, methanol, tyramine → CNS depression
thiaminase → development of polio
death of gram - can cause endotoxin release
What effect does the absence of protozoa have on rumen health?
It indicates a shift in microbial flora towards lactic acid-producing bacteria.
What role do antioxidants play in rumen health post-engorgement?
They help in mitigating oxidative stress caused by toxins.
How do synthetic agents like Poloxalene work against ruminal bloat?
They lower surface tension and promote bubble coalescence.
In cases of foamy bloat, what dietary aspect should be limited to reduce risk?
Legume grazing.
What symptom might indicate a severe case of ruminal acidosis?
Sudden death.
What general strategy can assist in preventing carbohydrate engorgement?
Dietary changes should be made gradually.
What type of feed magnifies the risk of rumen bloat due to gas retention?
Finely ground grain.
What percentage of bloat cases can spontaneously regress?
Mild cases.
What causes hypoxia in ruminants suffering from bloat?
Increased thoracic pressure due to gaseous distention.
What immediate action should be taken in case of frothy bloat?
Administer anti-foaming agents.
What is the effect of ruminal fluid pH on lactate production?
Lower rumen pH increases lactate production.
Why is gradual adaptation to grain important for ruminants?
To prevent engorgement and subsequent acidosis.
What dietary component supports good rumen motility?
Sufficient long stem hay.
What tool is used during a rumenotomy to access the rumen?
A Kingman tube.
How is elevated blood pressure caused by bloat?
Due to pressure on the posterior vena cava.
What should be monitored during treatment for lactic acidosis?
Blood gas analysis and renal parameters.
Pathogenesis of bloat
Production of stable, proteinaceous FOAM
Formed from leaf cytoplasmic 18-S soluble protein and saponins
FOAM traps normal amount of gases
CO2, methane
FOAM prevents the coalescence of small gas bubbles
Gas remains trapped in the rumen fluid
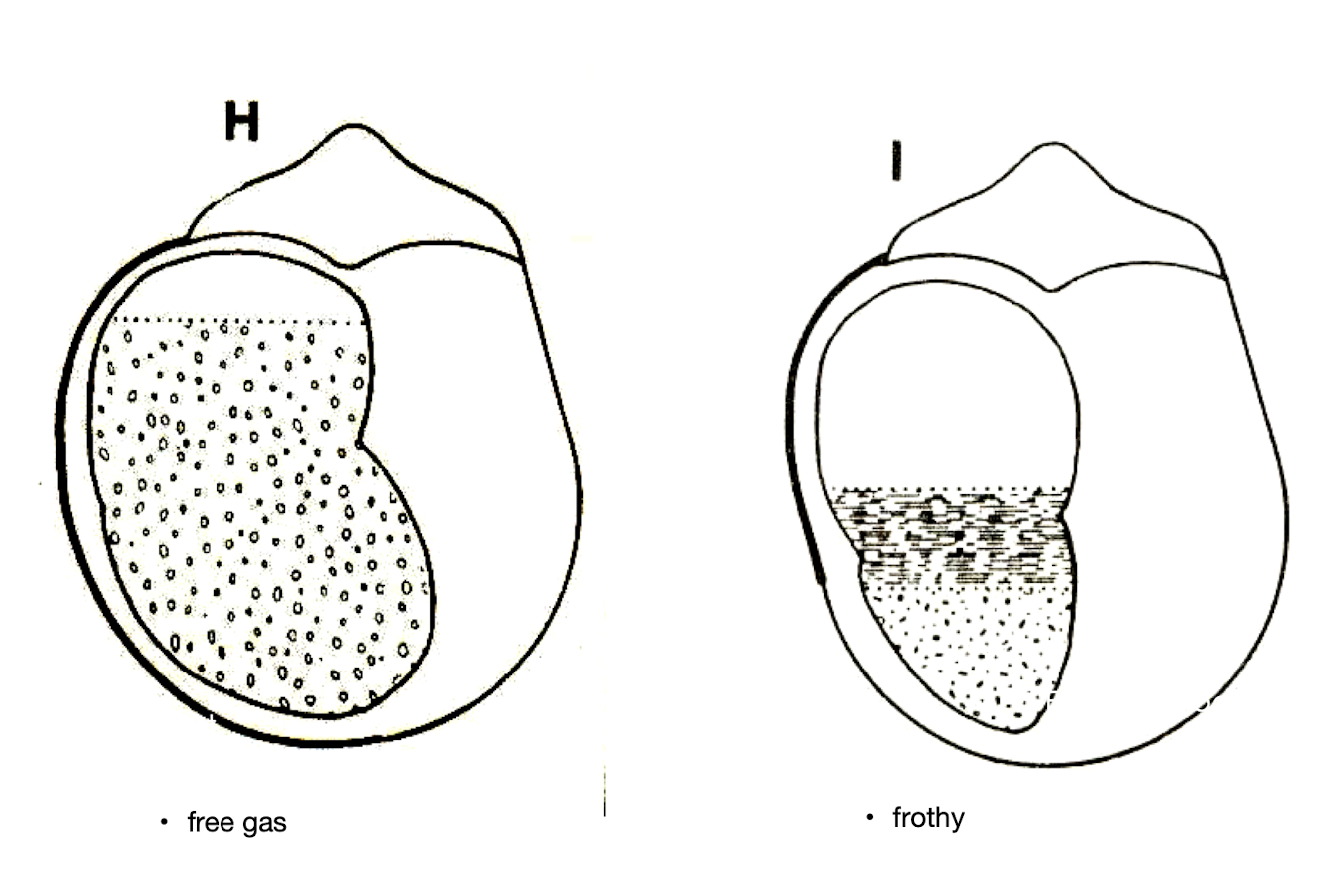
Boat therapy
Fluid and electrolyte replacement IV
Anti-inflammatory agents –flunixin meglumine (Banamine)
Antibiotics
Antimycotic therapy
Rumen transfaunation
Thiamine
B-complex vitamins