Comprehensive Tissue Types and Modifications in Human Anatomy
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Epithelial Tissue
Covers the body & organ surfaces, lines body cavities & organs
Connective Tissue
Binds, Supports, and protects tissues and organs
Muscle Tissue
Movement of skeleton/body structures
Nervous Tissue
Neurons transmit nerve signal & impulse to process information
Hypertrophy
Increase in size
Hyperplasia
Increase in number
Atrophy
Decrease in size - ex. broken leg, cast is off - both legs are different/ one leg was used more than the other
Metaplasia
Change in tissue
Dysplasia
Abnormal tissue growth
Neoplasia
Out of control growth
Necrosis
Cell death
Extracellular matrix
Ground substance + protein fibers
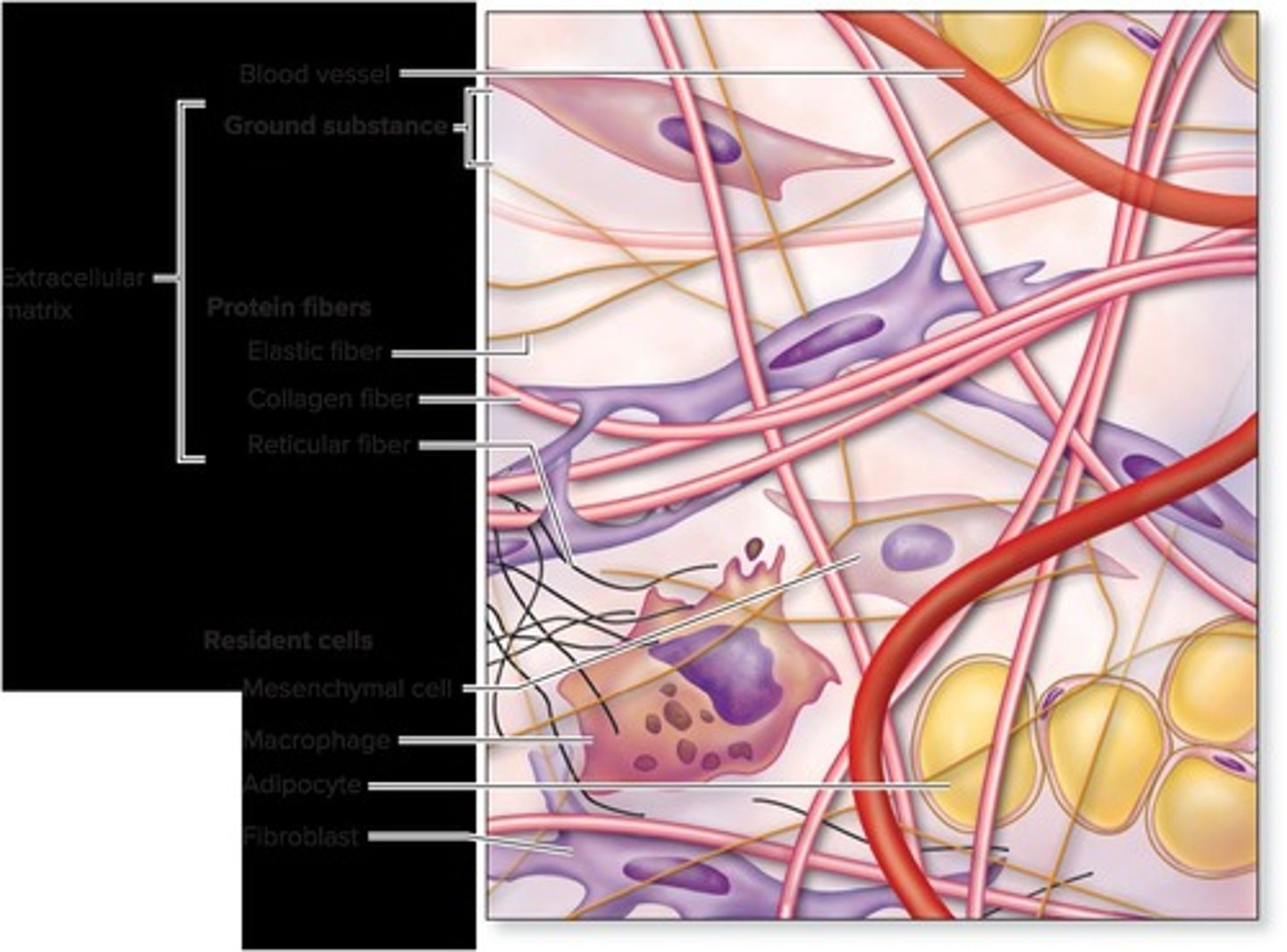
Resident Cells
Stationary → Housed in the connective tissue
Wandering Cells
Continuously moving through connective tissue
Dendrites
Receive incoming signals and transmit the information to the cell body
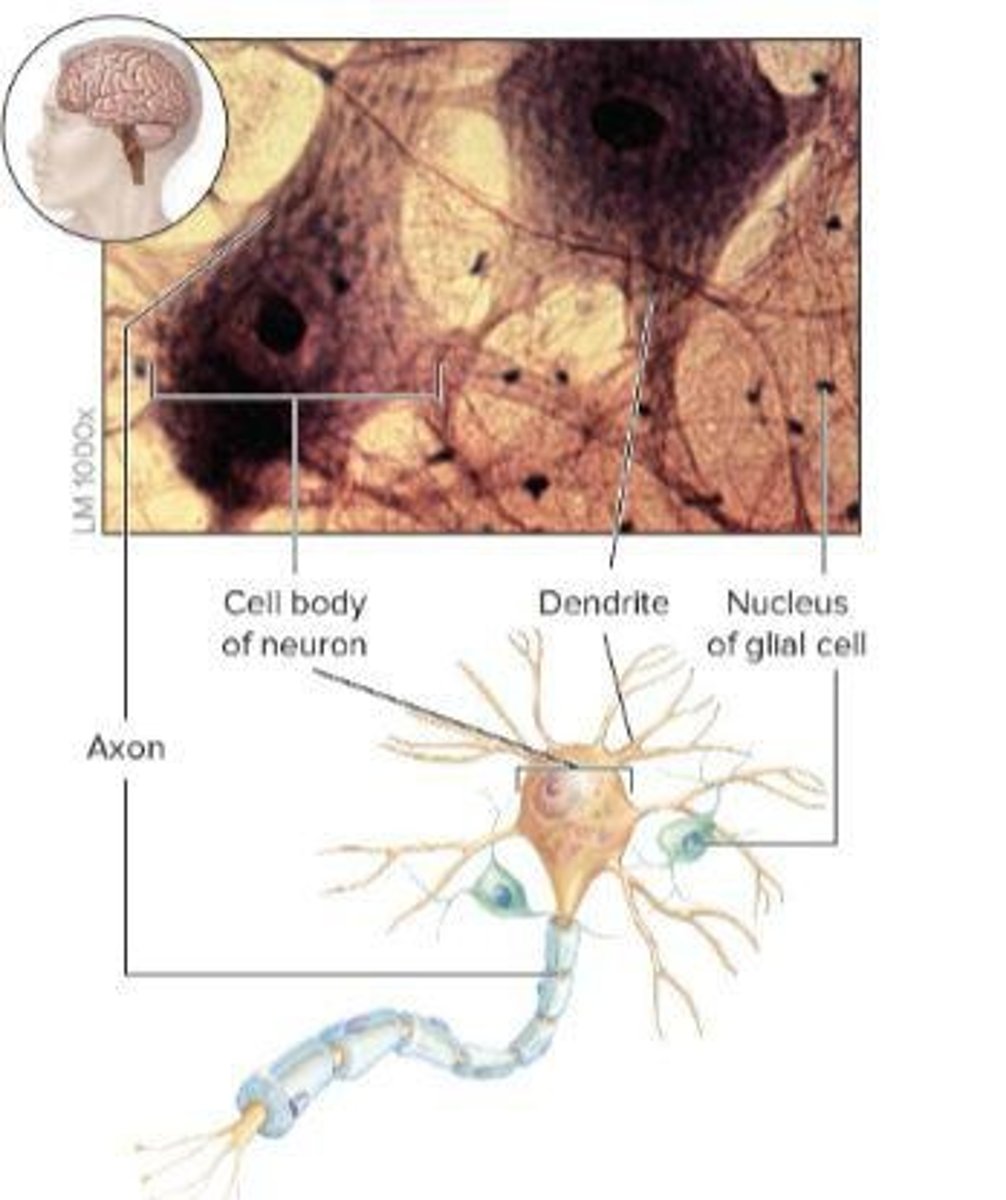
Cell Body
Houses both the nucleus and other organelles
Axon
The single long process extending from the cell body that carries outgoing signals to other cells
Simple
1 layer
Stratified
2 layers
Supporting Connective Tissue
Includes types like cartilage and bone
Fluid Connective Tissue
Includes blood and lymph
Connective Tissue Proper
Includes loose and dense connective tissues
Cardiac
Type of muscle tissue found in the heart