Feline infectious Disease & Vaccines part 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
FIV & FELV overview
Caused by Retroviruses
• Slow to develop
• Clinical signs occur at varying times
• Found in cats that are seemingly healthy
retrovirus overview
Enveloped viruses
• Sensitive to heat & disinfectants
• Often create oncogenic infections
Feline Leukemia virus
More pathogenic
Major cause of death
Prevalence has decreased

FeLV transmission
Disease of social cats
shed in saliva
Grooming and licking
Transplacently
fomites
What cats are at a great risk for FeLV
Those exposed via prolonged
close contact
Cats living with infected cats or
with cats of unknown status
Cats allowed outdoors
unsupervised
Kittens born to infected mothers
FELV pathogenesis
Oronasal exposure
Replication in regional lymphoid
tissue
Spread to lymphoid tissues &
bone marrow*
Latent bone marrow infection
established
Further spread & shedding
FeLV possible outcomes for regressor cats
Regressor cats
Viral replication stopped by CMI response then
Virus eliminated from body
Cats have high levels of FeLV neutralizing
antibody
Never have (+) antigen test
Possible outcomes for transient viremia cats (virus in blood)
Transient viremia (3-6 weeks)
• Virus spreads within lymph tissue
• Cats are infectious to others
• Have (+) antigen test
• Many will clear viremia/terminate the virus
& develop antibodies
• Those that don’t —>persistently infected
Possible outcomes for persistent viremia FeLV
Persistent viremia
• Bone marrow infected
• Precursor cells produce infected
granulocytes and platelets
• High level viremia
• Have (+) antigen test
Possible outcomes for latent (dormant) bone marrow infection FeLV
Those that don’t eliminate the virus
• Have (-) antigen test
• Can be re-activated (+) test
• Latent cats don’t shed virus until re-
activated
FeLV clinical signs
The incubation period is months to years
Most persistently infected cats die
Related to non-neoplastic disease
FeLV early signs
Lethargy, fever, lymphadenopathy
or no signs at all
Later stages of chronic infection

FeLV diagnosis
ELISA test (IDEXX Snap Test) detects FeLV antigen
Positive cats should be retested in 4-6 months
IFA test used to confirm ELISA
FeLV vaccines do not interfere with results on
ELISA, IFA, or any other available FeLV tests!
FeLV treatment
symptomatic and supportive care
FeLV prevention
Decrease exposure
Keep infected and infection
free separated
Don’t allow sharing of
house items
Test all new cats prior to
entering the home
Vaccination
FeLV vaccination
Start at 8 weeks booster once in 3-4 weeks then 1 year booster
Not a core vaccine
Recommended that all kittens be vaccinated
FeLV immunodeficiency Virus
An acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Comparable to HIV in humans
Increased risk for opportunistic infections, neurologic diseases, and tumors
Does not cause a severe clinical syndrome
With proper care, infected cats can live many years and die from unrelated causes

FIV transmission
shed through saliva
Saliva and blood most make contact
disease of fighting cats
Bite wounds necessary
Infection rates highest in free-roaming adult male cats
FIV pathogenesis
• Primarily replicates in T lymphocytes
• Infected cats are persistently viremic (peaks @ 8-12 weeks)
• Antibodies formed 2 weeks after infection
• Viremia declines as cat enters asymptomatic carrier phase
• Viremia causes progressive destruction of cell-mediated immunity
• Viremia peaks again as terminal phase begins
FIV clinical signs
• Acute phase
• Fever, lethargy, lymphadenopathy,
neutropenia
• Asymptomatic carrier phase
• Clinically normal
• Terminal phase
• Anemia, recurrent fever, weight loss
• Chronic infections
FIV diagnosis
ELISA test - detects circulating antibodies
May not produce antibodies for 2 weeks - several months
Terminally ill may not have detectable antibodies
Kittens of infected moms may test positive up to 5 months because of colostral antibodies
FIV treatment
If no clinical signs are present
• No treatment is indicated
• Cat should be kept strictly indoors and
should not be vaccinated (may consider
vaccinating with only KILLED vaccines)
• If clinical signs are present
• Always look for underlying disease
• FIV alone is typically not responsible for
clinical signs
• Treat underlying disease as indicated
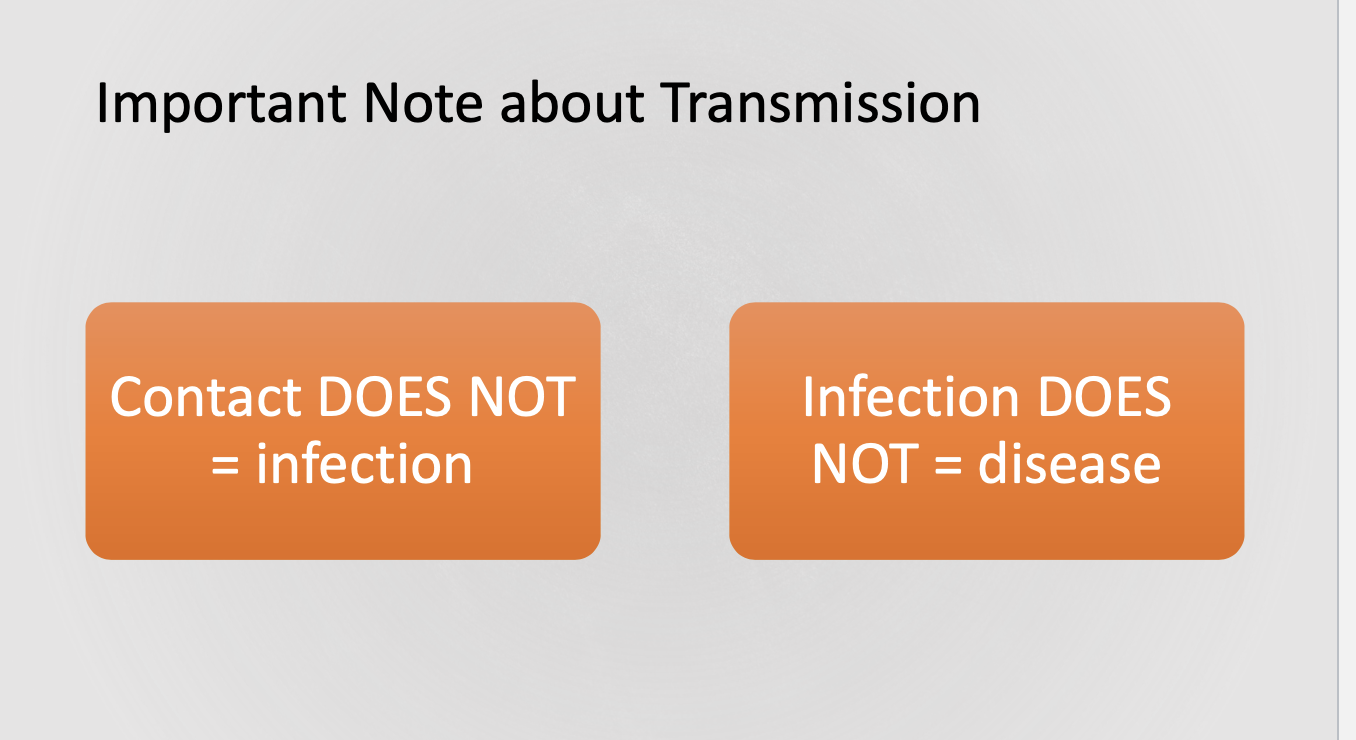
FIV control
Vaccination not available but is also NOT recommended
What to do with positive FIV animals
Keep indoors to reduce exposure/ spread
spayed/ neutered
Feed a nutrion/ balanced diet
wellness visits every 6 months
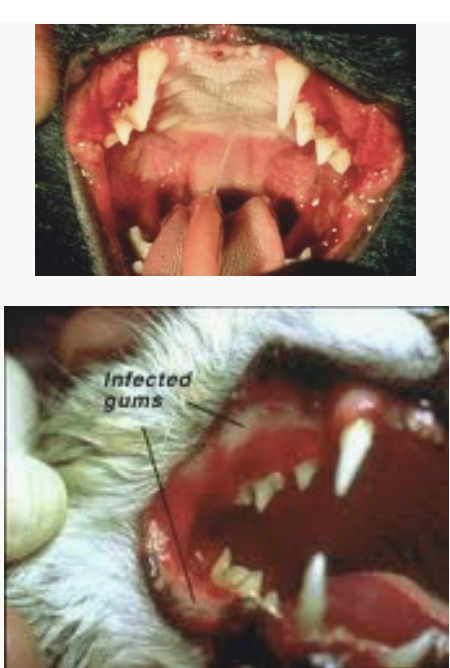
IDEXX FeLV & FIV Testing
FeLV- detects the presence of circulating
ANTIGEN
• FIV- detects presence of ANTIBODY
• False Negative FIV test results
• Binding of Ab to Ag in terminal
phase
• Can take 2 weeks to several
months to develop Ab
• Evaluate all test results in conjunction
with clinical signs
What do we do with a positive test FELV
FeLV Positive Test
• If suspicious disease present- likely
true
• If kitten- retest in 1-2 months
• If healthy adult- can wait/retest or
perform additional test
what do we do with a FIV positive test
• If suspicious disease present, likely
true
• If kitten <12 weeks, likely has
maternal antibodies
• If healthy adult- may be true positive
or vaccinated
Feline infectious peritonitis
Caused by certain strains of feline coronavirus
• Large, enveloped RNA viruses
• Susceptible to disinfectants and heat
• Most strains of feline coronavirus are avirulent
• Cats that are infected generally do not show any
symptoms during the initial viral infection
• Small percent of infected cats (5 to 10 %), either by a
mutation of the virus or by an aberration of the immune
response, the infection progresses into clinical FIP
FIP transmission
Shed in feces and oronasal secretions
Litterboxes most common source of infection
FIP pathogenesis
Not all cats infected with FIP virus develop
disease
Roughly 1/9 cats infected with FCoV (corona virus) develop FIP
• Effective cell mediated immunity (CMI)
important to restrict viral replication and
elimination of virus
• Defective CMI leads to formation of non-
protective antibodies
• When these antibodies contact FIP virus,
immune complexes form leading to immune-
mediated vasculitis
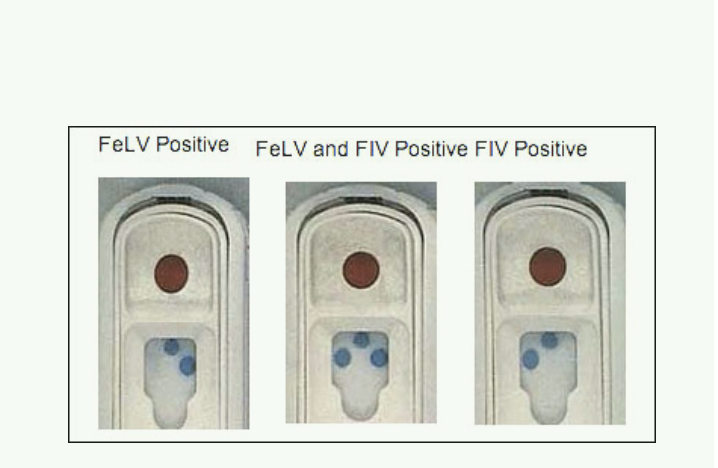
FIP clinical signs
Incubation weeks to months
Onset of clinical signs varies from slow to acute
Early signs nonspecific
FIP Clinical signs 2 forms
Effusive (wet) form-more common
Non-effusive (dry) form
FIP diagnosis
Biopsy results are needed for definitive diagnosis, so FIP is seldom confirmed until necropsy
Lab findings
History & clinical signs
FIP treatment

Symptomatic treatment FIP
Antibiotics
• Corticosteroids
• Fluid therapy
• Abdominocentesis
• Nutritional support
FIP control
ID and removal
Breeding bloodlines free of FIP
Proper cattery management
Vaccine isn’t reliable or recommended