Lecture 13: Nucleosides and Nucleotides
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
What does ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Transcribes and translates information into proteins
2
New cards
Nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids are derivatives of what?
Pyrimidines and purines
3
New cards
Draw adenine
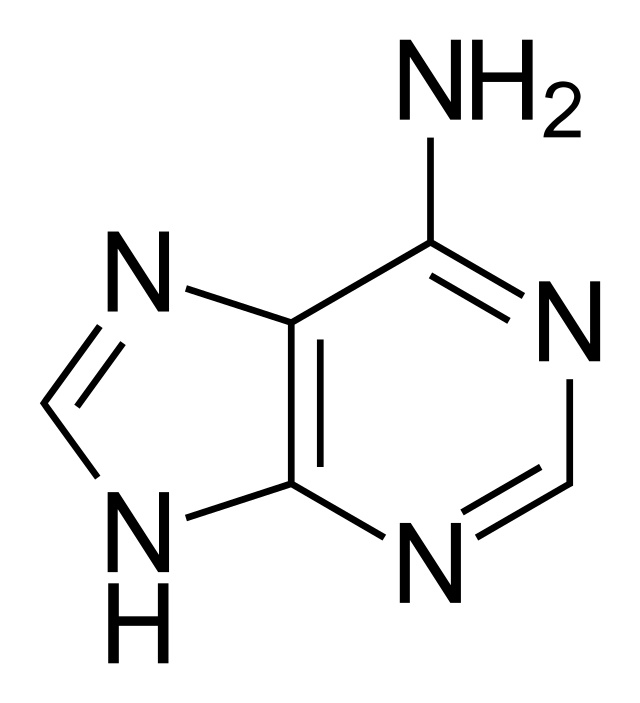
4
New cards
Draw guanine
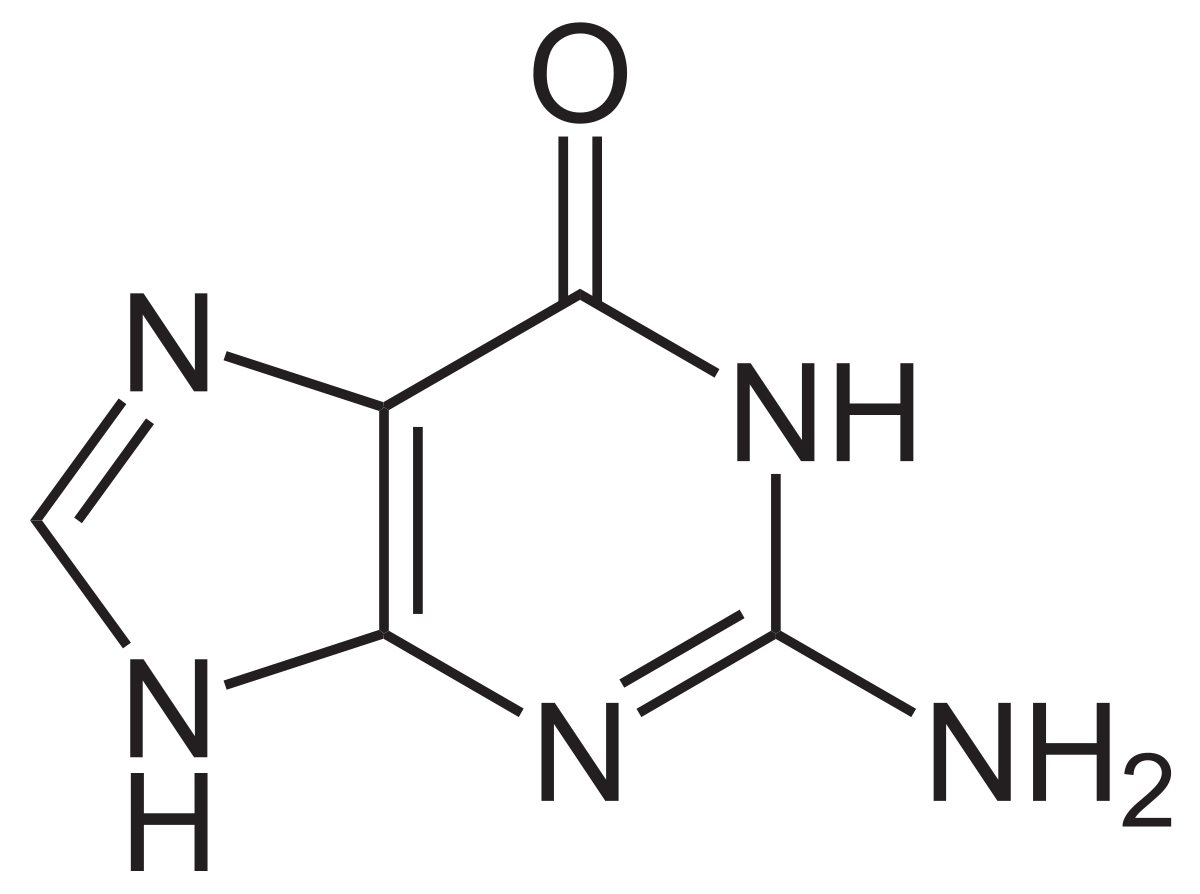
5
New cards
Draw cytosine
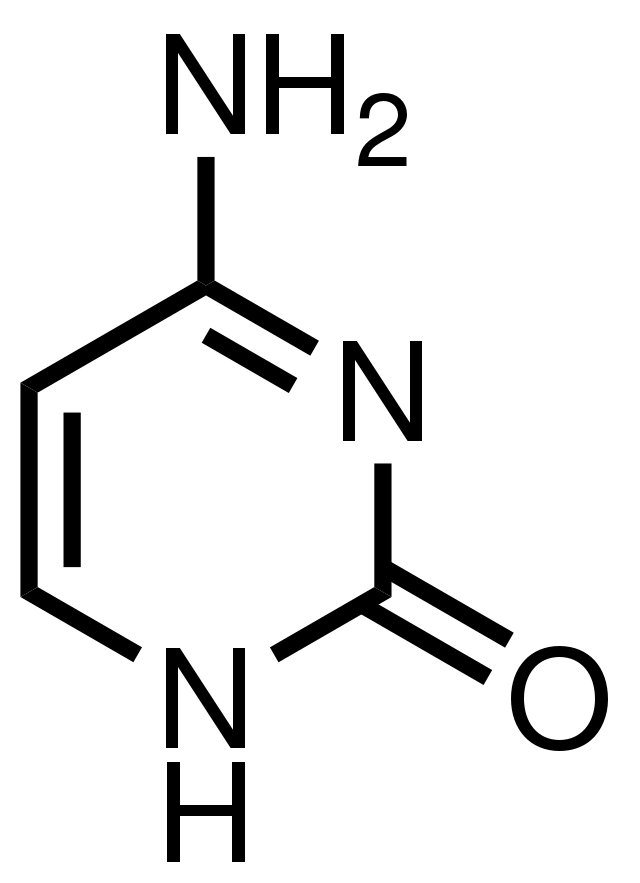
6
New cards
Draw uracil
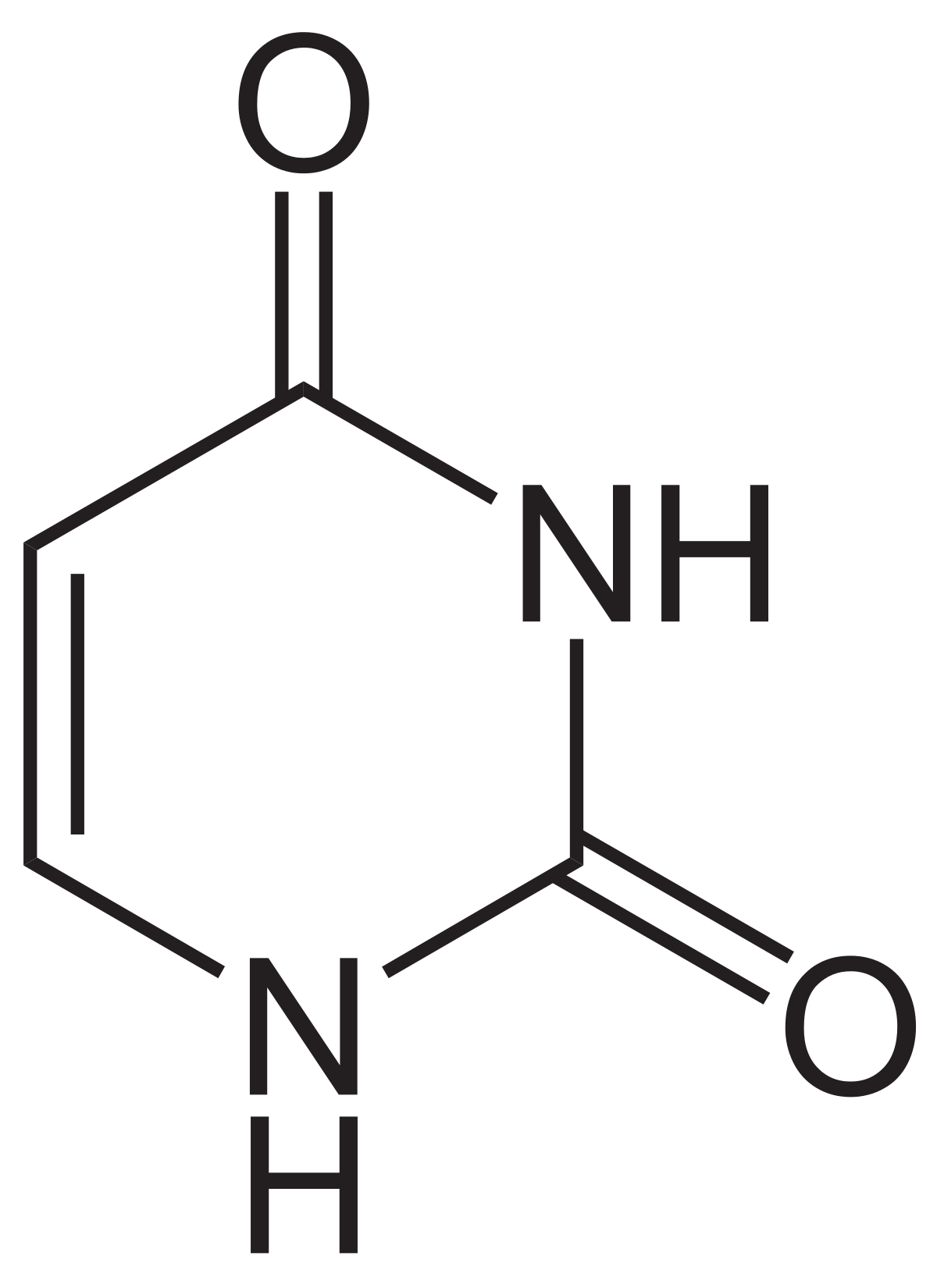
7
New cards
Draw thymine
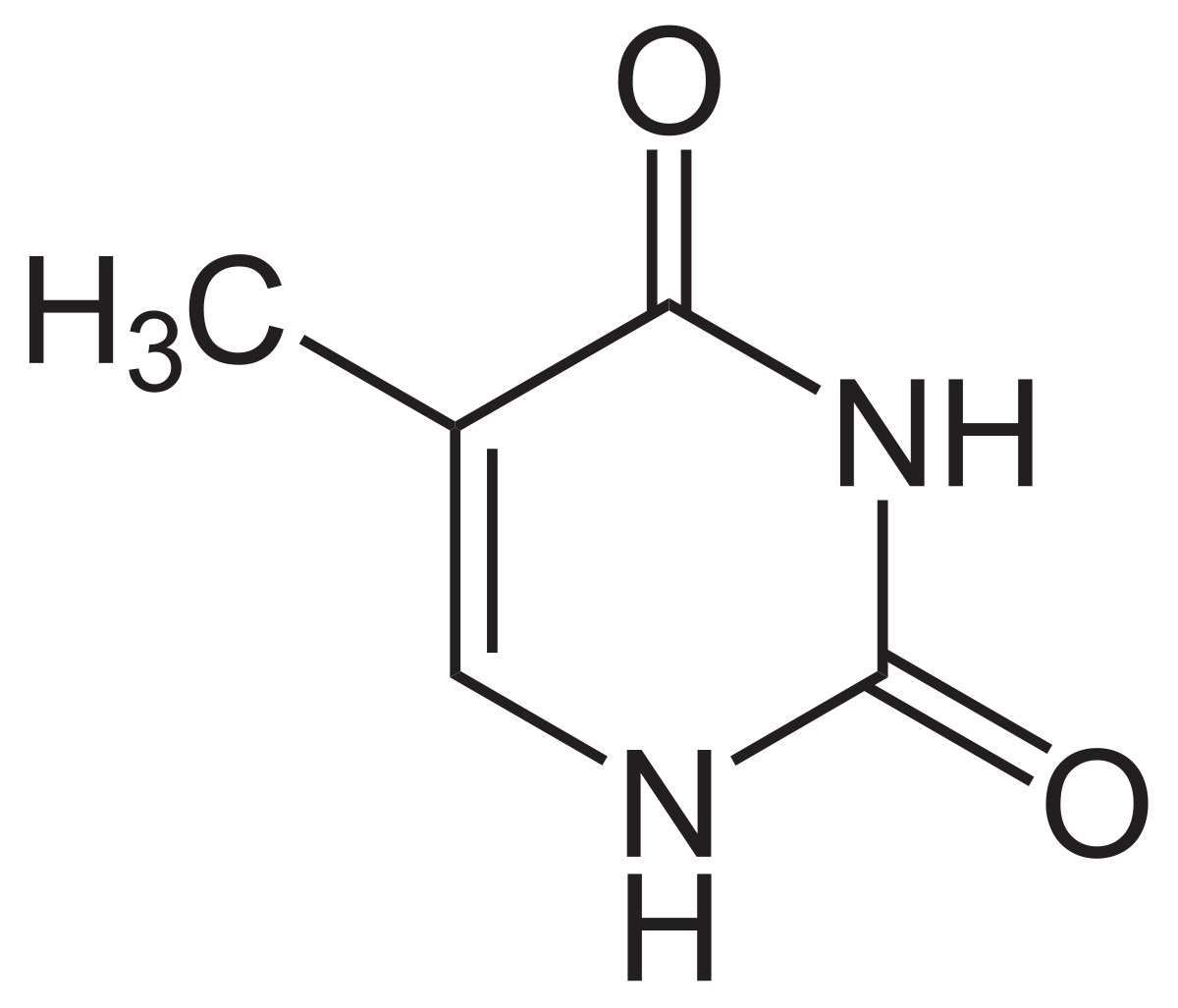
8
New cards
What are the two purines?
Adenine and guanine
9
New cards
What are the two pyrimidines?
Cytosine, uracil and thymine
10
New cards
All pyrimidine and purine bases absorb what?
UV light
11
New cards
RNA contains what type of molecule?
Ribose
12
New cards
DNA contains what type of molecule?
Deoxy-ribose
13
New cards
Nucleosides are a combination of?
Sugar and base
14
New cards
Nucelotides are a combination of
phosphate sugar and base
15
New cards
Nucleic acids are a combination of what?
Phosphate, sugar and base. With sugar connected to phosphate
16
New cards
Nucleosides bases is linked via?
Glycosidic bond
17
New cards
Carbon of glycosidic bond is
Anomeric
18
New cards
Most nucleotides are
Ribonucleotides
19
New cards
ATP is central to what?
Energy metabolism
20
New cards
GTP is drives what
Protein synthesis
21
New cards
CTP drives what?
Lipid synthesis
22
New cards
UTP drives what?
Carbohydrates metabolism
23
New cards
Transfer RNA does what?
Transport amino acids
24
New cards
Ribosomal RNA does what?
Combines with proteins to form ribosomes, site of protein synthesis
25
New cards
Messenger RNA does what?
Processes initial mRNA to its mature form in eukayrotes
26
New cards
Small interfering RNA
Affects gene expression
27
New cards
Micro RNA
Affects gene expression
28
New cards
Sequence is always read
5 to 3
29
New cards
Guanine is always connected to
Cytosine
30
New cards
Thymine connects to
Adenosine
31
New cards
G-C pairs are stabilized by
3 hydrogen bonds
32
New cards
A-T base pairs are stabilized by
2 hydrogen bonds
33
New cards
Strands run in
opposite direction
34
New cards
Modification of nucleic requires ability to
Hydrolyze phosphodiester bond that hold them together
35
New cards
Hydrolysis can be performed by
Acid/Base hydrolyssi and Enzymatic hydrolysis
36
New cards
Exonucleases
Start at end of polynucleotides
37
New cards
Endonucleases
Cleave at internal site within polynucleotide
38
New cards
Does type require ATP for hydrolysis or does not require ATP for hydrolysis?
Requires ATP
39
New cards
Does Type 1 able to methylate DNA at specific locations or does it not methylate DNA?
Able to methylate DNA at specific locations
40
New cards
Does Type 1 cut at random sites, cut at specific nucleotide sequences, and cuts at specific sites?
Cut at random sites
41
New cards
Does type 3 require ATP for hydrolysis or does not require ATP for hydrolysis?
Requires ATP
42
New cards
Does Type 3 able to methylate DNA at specific locations or does not methylate DNA
Able to methylate DNA at specific locations
43
New cards
Does type 3 cut at random sites, cuts at specific nucleotide sequences and cuts at specific sites?
Cuts at specific nucleotide sequences
44
New cards
Does type 2 require ATP for hydrolysis or not?
Does not require ATP for hydrolysis
45
New cards
Does type 2 able to methylate DNA at specific location or does not methylate DNA?
Does not methylate
46
New cards
Does Type 2 cut at random sites, cut at specific nucleotide sequences, and cuts at specific sites?
Cuts at specific sites