HAHAHAHA4
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
The choice of the kind of pipe to be installed depends upon the following considerations: 1. Quality and durability 2. Resistance to external and internal contact with foreign matters 3. Resistance to acid waste and other chemical elements that will pass into it 4. Cost of materials and labor
PIPING MATERIALS

This is known technically as Gray Cast Iron Pipe, it is fabricated from an alloy containing carbon and silicon. It is commonly used for drainage systems due to its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
CAST IRON SOIL PIPE
that portion of the pipe which, for a short distance, is sufficiently enlarged to receive the end of another pipe of the same diameter for the purpose of making a joint. It is also know as a bell.
Hub
the end of the pipe that fits into a bell or spigot
Spigot

generally used for building installation
SV (Service/Standard Weight) Type

extra-duty pipe used for underground installation
XV (Extra Heavy Weight) Type

a type of pipe commonly used in plumbing and construction, characterized by its nominal diameter and wall thickness.
Standard Pipe

a type of pipe fitting designed to connect two pipes with a single hub, allowing for efficient flow direction.
Single Hub Pipe

Double Hub Pipe

Hubless Pipe

A type of pipe made from cast iron that is specially treated to resist corrosion and damage from acidic substances, making it suitable for chemical applications.
ACID-RESISTANT CAST IRON PIPE

It is made of asbestos fibers and Portland cement. • Used as soil, waste, ventilation pipe, and downspouts • Suited for concrete embedment because of similar properties
ASBESTOS PIPE

Commonly used for storm as well as sanitary sewer installations • Made of clay to which water has been added and cast into lengths of 2 feet 6 inches. • Resistant to most acids and is well-fitted for underground work
VITRIFIED CLAY PIPE

• It is made from 99.7% pig lead; various alloys are available for special applications • Used for connections to floor-mounted water closets, radioactive waste, and special laboratory corrosive wastes • Rarely used in modern plumbing system since medical findings showed that the use of this material has harmful effects to human.
LEAD PIPE

It is made of mild steel that is drawn through a die and welded • Easily corroded by alkaline and acid water
GALVANIZED STEEL PIPE
– made by drawing a flat strip of steel through a die to form the round shape and then electric butt welded down the seam
Welded Pipe
made by piercing red hot solid, cylindrical billet of steel with series of mandells while passing the metal through rollers
Seamless Pipe

Manufactured from an alloy containing 85% and 15% zinc. • Most expensive • Joints can be either screwed or soldered • Resistant to acids and has a smooth interior surface
BRASS PIPE

Used in water supply systems for hot and cold, sanitary (drainage, waste, and vent) systems • A seamless tube made from almost pure copper and are manufactured in rigid (hot temper) and area available in lengths by the foot in straight lengths and other type is flexible (soft temper) which is manufactured in lengths ranging from 30 to 60 feet in coil form
COPPER TUBES
heaviest, used in municipal residential applications. Available in both rigid and flexible forms with diameters ¼”, 3/8”, ½”, ¾”, and 1”
Type K (green)
– lighter than type K, used in residential water lines. K and L are manufactured in hard (20” lengths) and soft (60’, 100’, and 200’). Diameters ¼” to 1”
Type L (blue)
hard (20’ lengths). Recommend for light domestic water lines and is not permitted in some city codes.
Type M (red)
rigid only (20’ lengths) in drawn, soft form, with plain ends. Available in diameters from 2” – 6”. Lightweight and easy to assemble but is prone to corrosive attack by ordinary sewage, has poor fire resistance, and needs a dielectric union to eliminate galvanic corrosion.
Type DMV (yellow)
350’ coils and rigid in 20’ lengths. Most refrigeration copper has moisture removed and ends sealed for better performance of refrigerants.
Type ACR (air conditioning and refrigeration)

Suitable for drainage and vents as well as for water supply systems – hot and cold applications.
PLATICS OR SYNTHETIC PIPE
epoxy and phenolic, not affected by heat, and will remain permanently rigid. More resistant to solvents than thermoplastic.
Thermostat (TS)
– softens when subjected to heat and rehardens upon the removal of heat.
Thermoplastic (TP)

Rigid, strong, and economical pipe • Has excellent chemical resistance, good crush resistance, and impact strength • Functional up to 123°F in pressure systems and pressure 180°F in nonpressure system
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)

Has excellent chemical, crush, and fire resistance, high impact, and tensile strength, and non-toxic • Can be used for hot and cold water applications • Functions at 180°F in pressure systems and at higher temperatures in low and non-pressure systems • Does not require special solvent cement used for other types of plastic welding
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC)

Has good chemical resistance, excellent impact strength, especially at lower temperatures, and maintains rigidity at high temperatures
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)

Has good crush resistance, fair impact strength, and moderate chemical resistance • It is lightweight but brittle at low temperatures
. Rubber modified Styrene (SR)

• Excellent chemical resistance, resistance to sulfur-bearing compounds, lightweight, good tensile strength, and saltwater resistant
Polypropylene (PP)

This is strong, tough, and abrasiveresistant fluorocarbon material • It has excellent resistance to most acids, bases, and organic solvents • Is ideally suited for handling wet or dry chloride, bromine, and other halogens
. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)

Excellent resistance to paraffins and solvents, high resistance to surge fatigue, non-toxic, and approved for potable water
Polyacetal (ACETAL)
1. Polyethylene (PE)
2. Polybutylene (PB)
Types of Plastic Synthetic Pipes (Flexible)
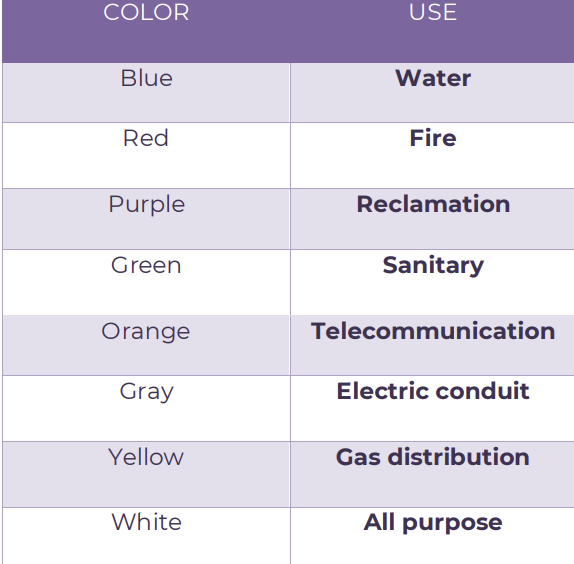
COLOR INDICATOR FOR PVC PIPES
used when installing pipes to go around corners, to join pipes, to reduce the diameter of the pipes, and to set traps.
Fittings
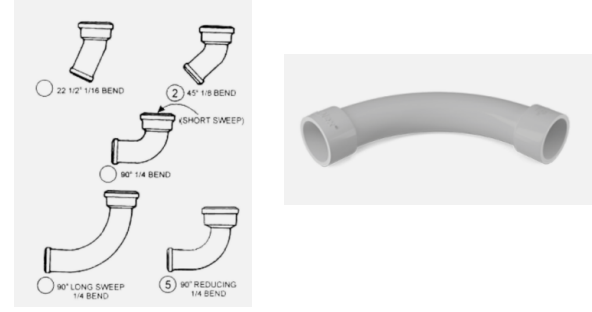
It is a pipe fitting used to change direction especially used on sanitary drainage systems • A ¼ bend is 90° angle fitting available either in short sweep (short curvature) or long sweep (long curvature)
BENDS (SWEEP)
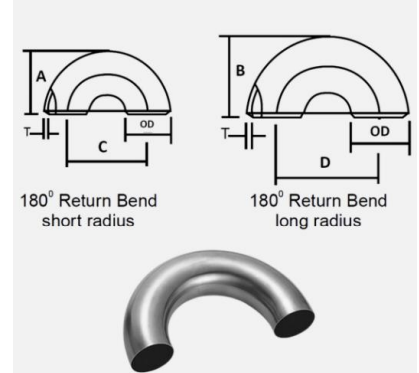
It is a pipe fitting that provides a 180° change in direction with a very short radius • Suitable for use in water supply and vent systems
RETURN BEND ELBOW

A malleable iron fitting for threaded pipe, having a 45° or 90° bend with an outside thread on one and an inside thread on the other
STREET/SERVICE ELBOW
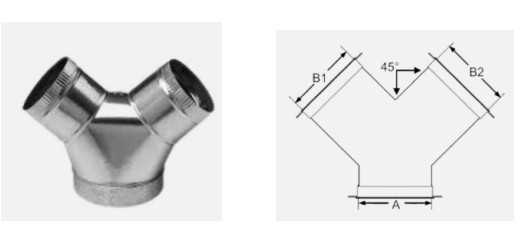
A fitting used to connect branch pipe into a straight run of piping at a 45° angle
WYE/WYE BRANCH
A single fitting which is a combination of a wye branch and a 1/8 bend • Used in the drainage system in changing direction such as horizontal branch to vertical (stack)
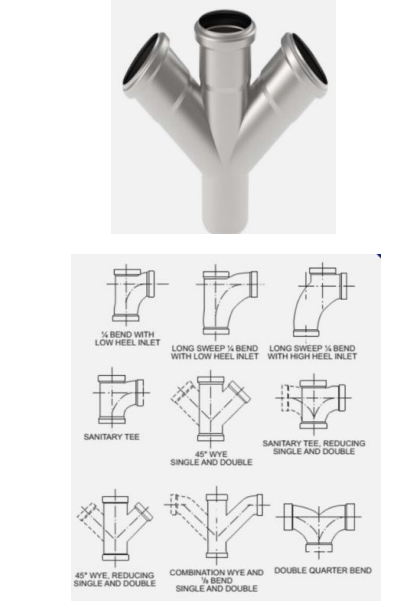
COMBINATION WYE BRANCH
A one-piece fitting composed of 1/8 bend and wye branch where the branch inlet is parallel to the drum • This is used when two stacks are provided where on stack is used as a vent and the other for soil or waste or both soil or waste stack
UPRIGHT WYE COMBINATION
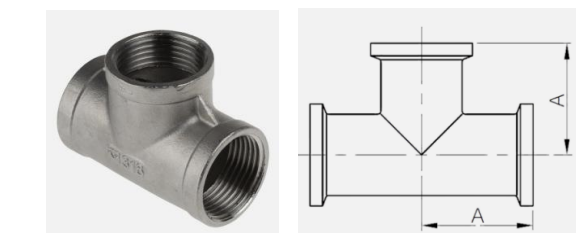
Is a fitting used to connect a branch pipe into a straight run of piping at right angles • Note: in drainage systems where flow characteristics are important, the code requires the use of sanitary tee. On the other hand, where flow is not a consideration, such as water supply and vent system, standard tees can be used
TEE
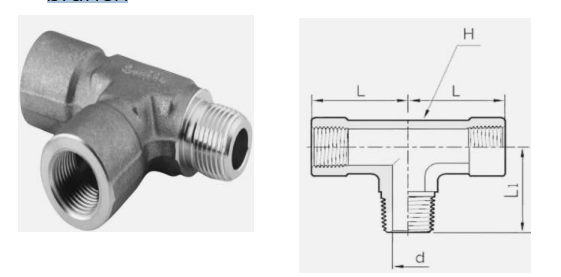
A malleable iron fitting for threaded pipe in the form of a tee leaving outside thread on one and inside thread on the other branch
STREET TEE/SERVICE TEE
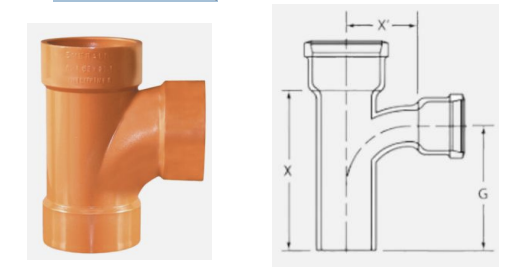
A tee used as fitting for a soil pipe which is designed with a slight curve in the 90° angle transition so as to channel flow from a branch line toward the direction of the main flow,
SANITARY TEE
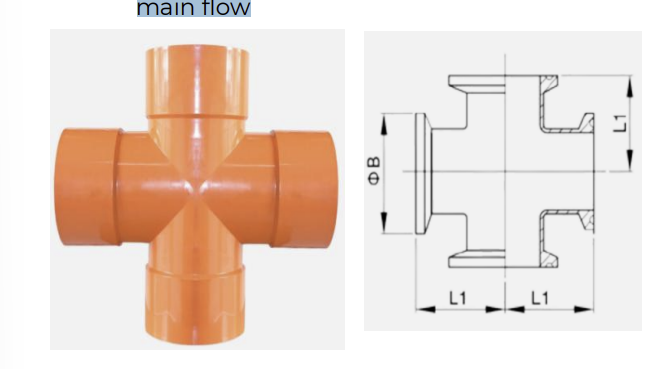
• A type of cross pipe used as fitting, designed with a slight curve in each 90° transitions so as to channel flow from branch lines toward the direction of the main flow
SANITARY CROSS TEE

A bell-end tee, which has a branch that is tapped to receive a threaded pipe or fitting
TAPPED TEE

Is a short internally threaded section of a pipe used to joint two pipes
COUPLING
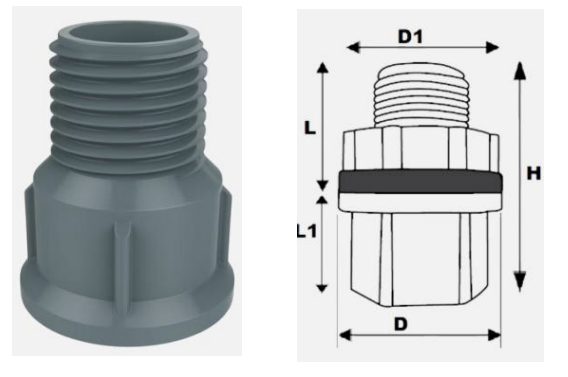
It has a similar application with a coupling but its ends are enlarged to provide additional mechanical strength
SOCKET
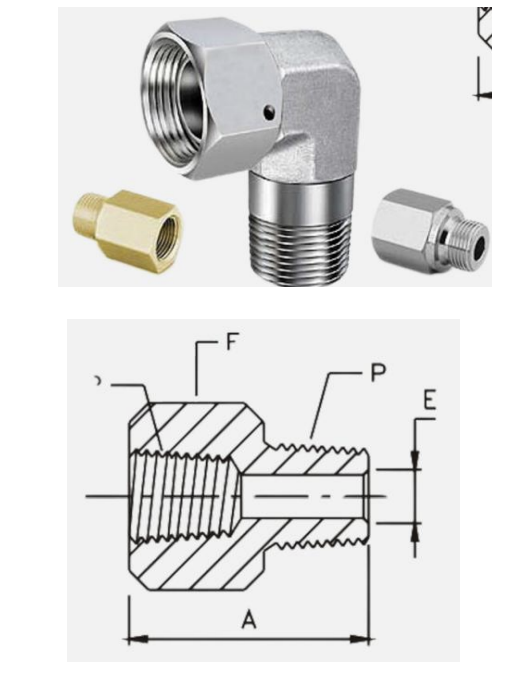
A type of fitting to connect different pipe materials such as galvanized steel pipe to plastic pipe in which galvanized pipe being threaded and the plastic having no threads • A type of transition fitting
ADAPTER
• A short length of pipe with external threads at each end • Used to join couplings or fittings
NIPPLE

a type of nipple with the entire length externally threaded
Close Nipple

– a type of nipple having both ends externally threaded and the mid-section unthreaded
Open/Shoulder Nipple
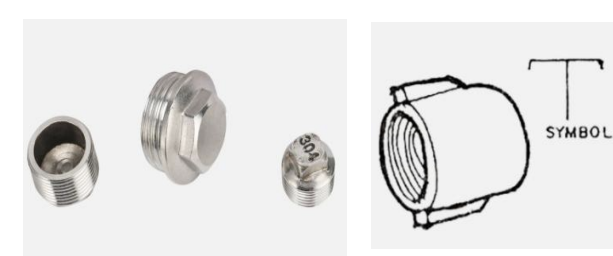
An internally threaded fitting used to close the end of a pipe
CAP
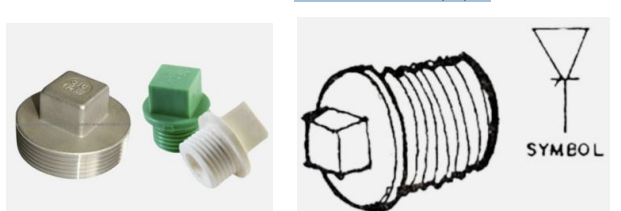
• An externally threaded fitting usually with square head • Used to close the end of a pipe
PLUG
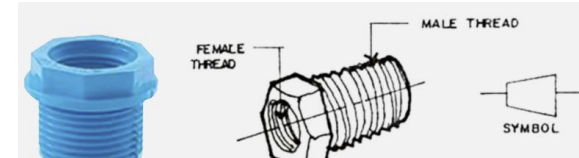
• A pipe fitting which is threaded on both the inside and the outside so that it can be used to connect two pipe of different sizes (diameters)
BUSHING
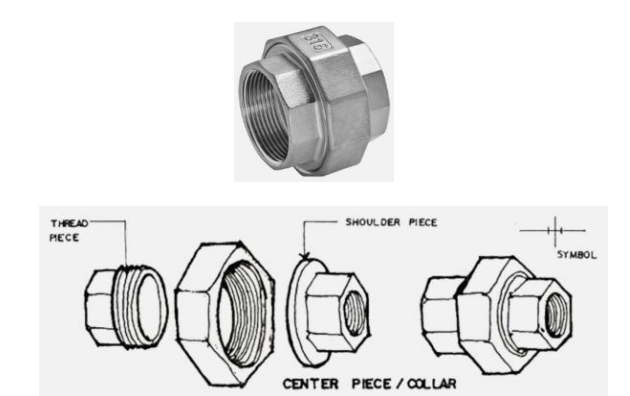
• A pipe fitting, used to connect the ends of two pipes neither of which can be turned • Consists of three pieces, the two end pieces
UNION PATENTE
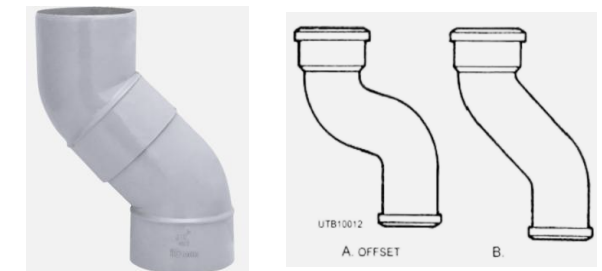
A change in the direction of a pipeline (other than 90°) e.g. by a combination of elbows or bends, which brings one section of the pipe out of line with but into a line parallel to another section
BEND OFFSET

A pipe fitting with inside threads, larger at one end than at the other
REDUCER

• A tapered coupling used for jointing a pipe to another of larger size (diameter)
INCREASER
1.Risers
2. Branches
3. Pipes to individual fixtures or equipment
Valve

These are valves that control the flow of liquid moving through the valve by means of a gate-like wedge disc that fits against a smooth machined surface (called seat) within the valve body • Most used valve in plumbing • Designed to be fully open or fully closed
Gate valve

It is a compression-type valve in which the flow of water is controlled by means of a circular disc that is forced (compressed) onto or withdrawn from an annular ring (known as valve seat), which surrounds the opening through which water flows
Globe valve
Types of globe valve:
o Plug Type
o Conventional
o Composition

• A valve that permits the flow of water within the pipe in only one direction and closes automatically to prevent backflow
CHECK VALVE

• A globe valve in which the inlet and outlet opening are at a 90° angle to one another • Used for individual plumbing fixture control such as lavatory, water closet, etc.
ANGLE VALVE

VALVE • A valve in which the flow of fluid is controlled by a rotating drilled ball that fits tightly against a resilient (flexible) seat in the valve body
BALL VALVE
Also called as “spanner”, is a tool operated by hand, and is made for tightening or loosening bolts, anything that needs to turn
Wrenches

Have a sturdy, cast-iron housing and I-beam handle with full floating forged hook jaw, featuring self-cleaning threads with replaceable hook and heel jaws
Straight Pipe Wrench

Is a pipe wrench having an adjustable L-shaped jaw sliding in a sleeve that is pivoted to and loosely encircles the handle so that pressure on the handle increases the grip
Stillson Wrench

• A wrench with one fixed and one adjustable jaw at right angles to a straight handle
Monkey Wrench

An ideal wrench for pip work close to a wall, in tight quarters, or in closely parallel lines
End Pipe Wrench

The design gives multi-sided, secure grip on all hex nuts, square nuts, unions, and valve packing nuts
Hex Wrench
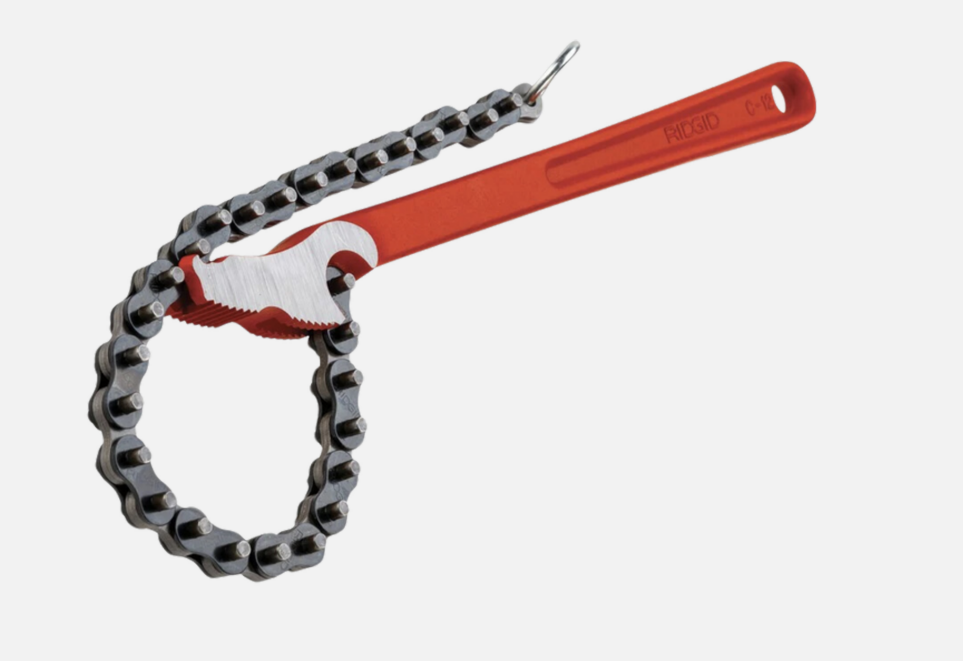

A double jaw gives fast, rachet-like action in either direction
The heavy-duty model has replaceable alloy steel jaws while the light-duty model has a one-piece forged alloy steel handle and jaw ideal for use in close quarters
Chain Wrench
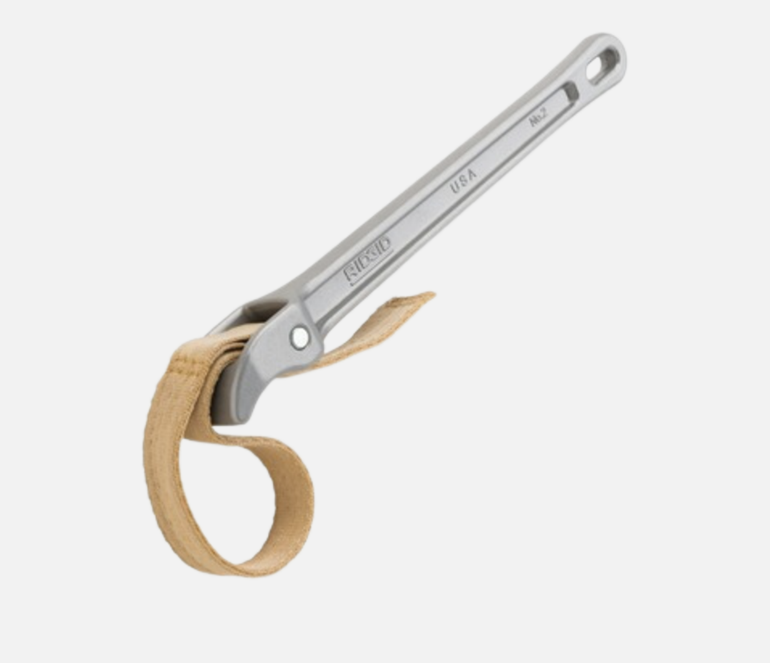

Best type of wrench for any polished pipe
• It has strong, woven nylon strap that gives tight grip and also has polyurethane-coated strap
Strap Wrench
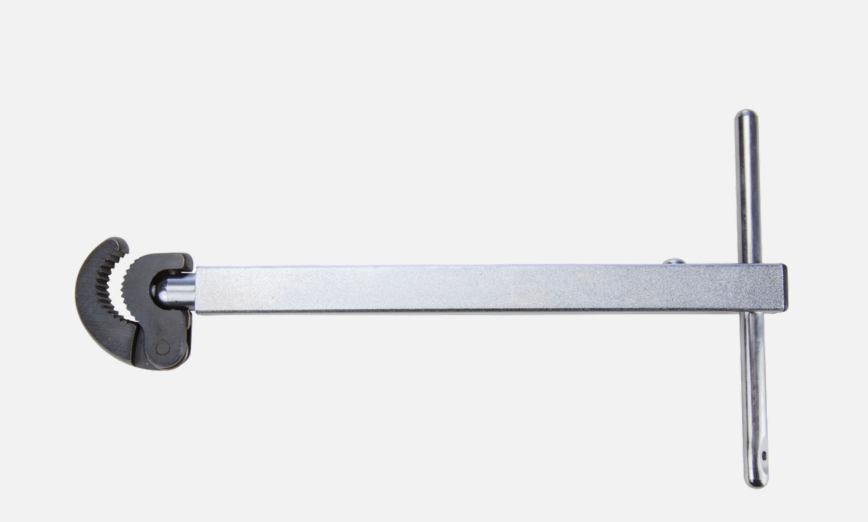
• An ideal tool for use in tight spaces and under-sink applications • It has spring-loaded jaws of forged alloy steel that provide fast, one-hand ratcheting
Basin Wrench
A tool used for cutting pipes • The main body of the tool revolves the pipe which consists of one or more sharp wheels and rollers • The pipe is then forced by a screw on the other end of the tool
Pipe Cutters

• Fast and clean pipe cutting
• Has an extra long shank that protects adjustment threads with an extra large handle for quick and easy adjustment
• Suitable for steel/stainless with diameters 1/8” to 6”
Heavy Duty Pipe Cutters

• Designed for rapid cutting of 2” to 12” steel pipe, heavy wall steel pipe, and cast iron pipe
Hinge Pipe Cutters

• Provides the fastest way to cut cast iron soil pipe, clay pipe, and small diameter concrete pipe with a chain soil pipe cutter
Soil Pipe Cutters

• A tapered bit having sharp, spiral-fluted edges along the burrs from the inside of a pipe, especially after cutting
Pipe Reamers

• Is a tool used to remove broken threaded ends of pipe or fittings
Pipe Extractor

• Used to create internal threads or to rethread metal piping and fittings, or other metal fabricated objects
Pipe Taps

Any of several types of adjustable tools for cutting external threads on pipe ends
Pipe Die/Threader
are receptacles intended to receive water, liquid, or water-carried wastes and discharge them into the drainage system..
plumbing fixtures
• Is a fixture used to carry organic body wastes to the sewer system • Can be installed on a floor or suspended from a wall
Water Closet
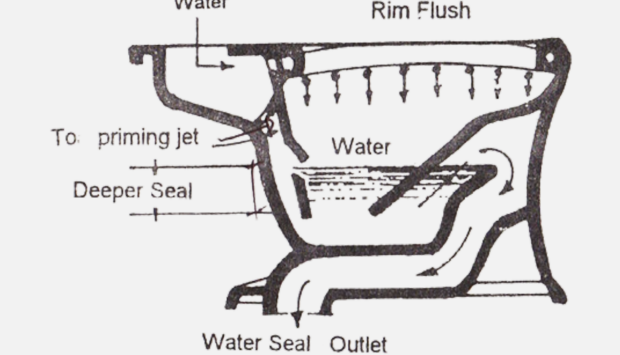
The least efficient, noisiest, less expensive, with a bulging front
The trap is at the front of the bowl is flushed by small streams of water running down from the rim
Siphon Washdown
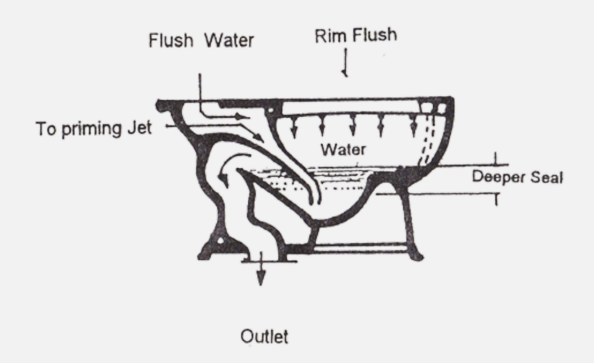
Expensive and more efficient
Larger amount of standing water, larger trap way causing less clog and flushing action is greater
Siphon Jet
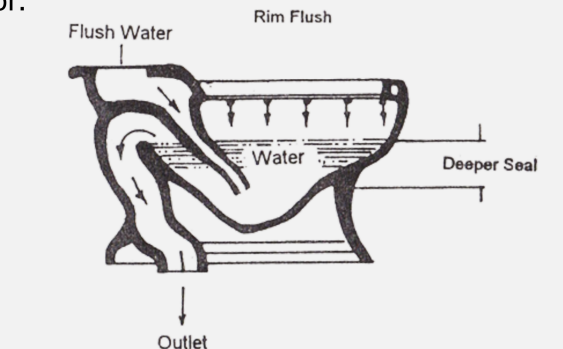
o Very efficient, less noisy, and the most expensive flushing by whirlpool action
o It has large amount of standing water almost covering the whole bowl’s interior
Siphon Vortex
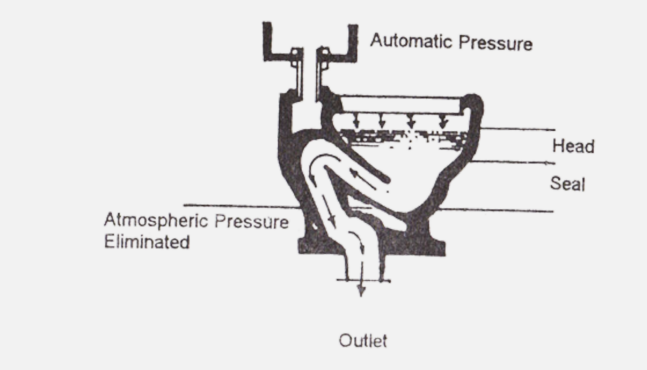
More expensive than washdown
o Flushes through a siphon action created in the trapway, moderately noisy
Reverse Trap
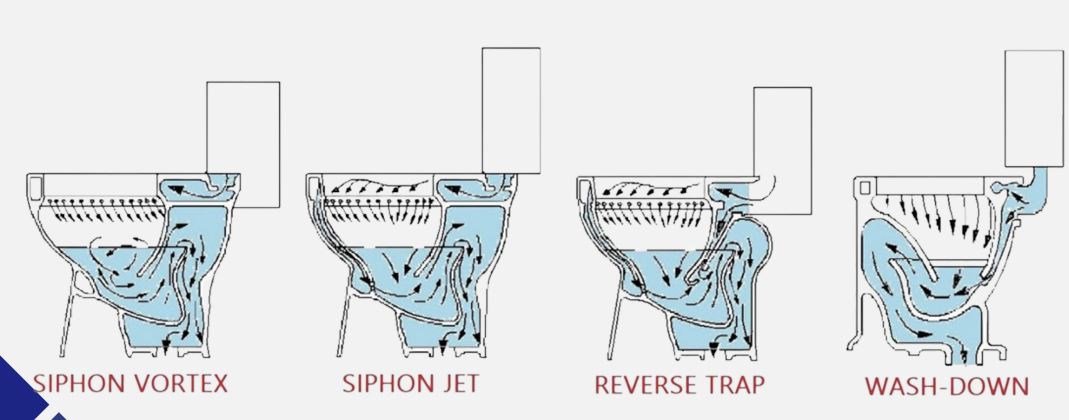
Comparison of Different Water Closets
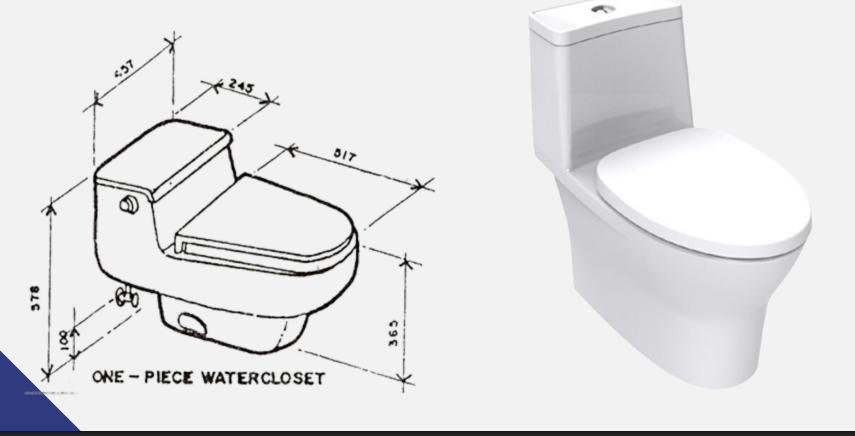
The water closet fixture is manufactured with the bowl and the flush tank molded into a single unit
One-piece Water Closet
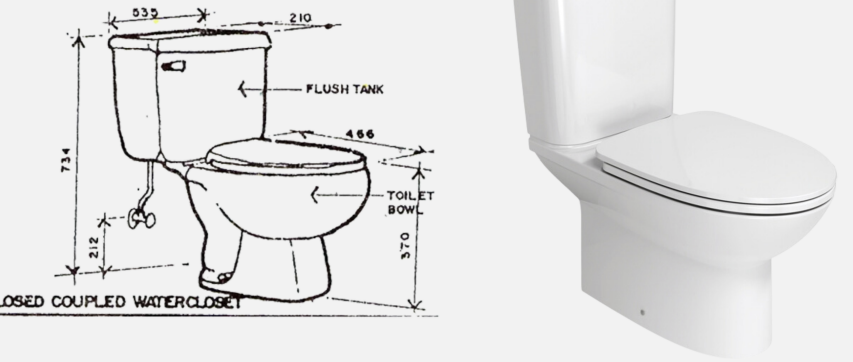
A water closet wherein the flush tank is separate but is attached to the toilet bowl o It is a two-piece model
Closed-Coupled Water Closet
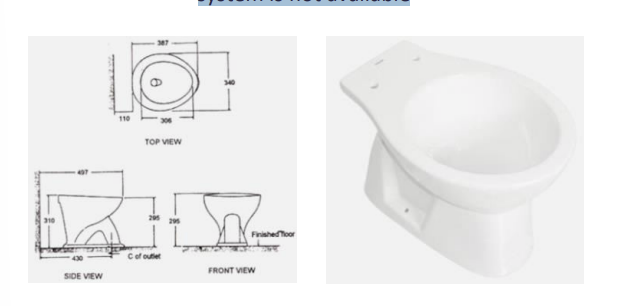
A water closet compromising only a bowl without a flush tank
Flushing action is obtained only through water poured from a pail or bucket
This is used in areas where running water system is not available
Pail Fluish Water Closet
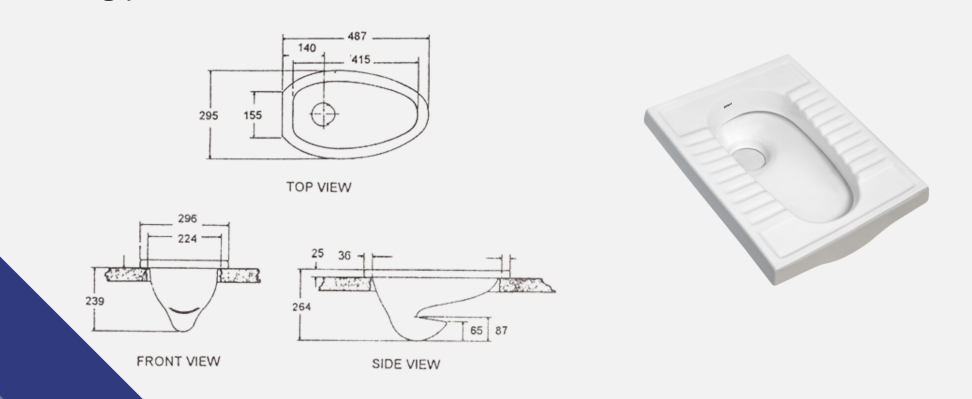
A water closet that is otherwise known as “eastern type” water closet since the user assumes a squatting position rather than a sitting position
Squat Bowl Water Closet
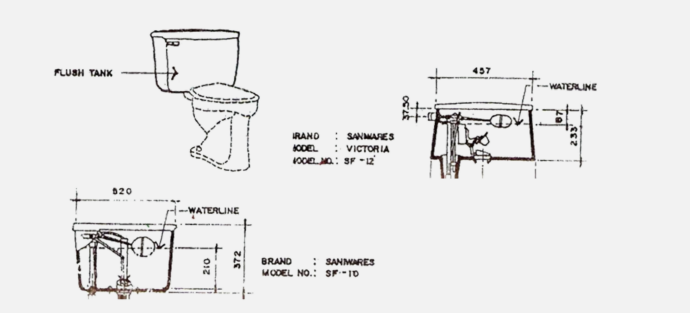
o A tank’s flushing mechanism is mechanically operated to flush the water closet
o It holds a supply of water for flushing the water closet which flushed 3 to 6 liters
Flush Tank
delivers a preset amount of water into a water closet for flushing
o It is a valve designed to supply a fixed quantity of water for flushing purposes
o It is activated by direct water pressure without the use of a flush tank
Flushometers