A&P Unit 2 (Epithelial)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
what are the 4 major tissue types?
epithelial
connective
muscle
nervous
what are the functions of epithelial tissue?
protects, covers, and lines
filters biochemical substances
absorbs nutrients
provides sensory input
manufacture secretions/excretions
secretion
substance that remains in the body
excretion
substance that leaves the body
what are 4 defining characteristics of epithelial cells?
they are polar
have lateral surfaces connected to neighboring cells by junctional complexes
they are avascular
most are innervated
how is an epithelial cell polar?
the cell has 2 different sides; apical and basal
what is an example of a junctional complex?
BBB- blood brain barrier
how is an epithelial cell avascular?
they lack blood vessels and capillaries, and rely on on underlying tissues for nutrients
what are the 3 major cellular junctions in epithelial cells?
tight junction
desmosome
gap junction
what does a tight junction do?
fusion of outermost layers of plasma, connecting adjoining cells; allows an organ no leakage
ex. of tight junctions
urinary bladder or digestive tract
what does a desmosome do?
strong, welded plaque, connecting adjacent cells; allows expansion
ex. of desmosomes
skin, heart, or uterus
what does a gap junction do?
linked by connexons, extend from cytoplasm of one cell to another; quick transport of ions & nutrients
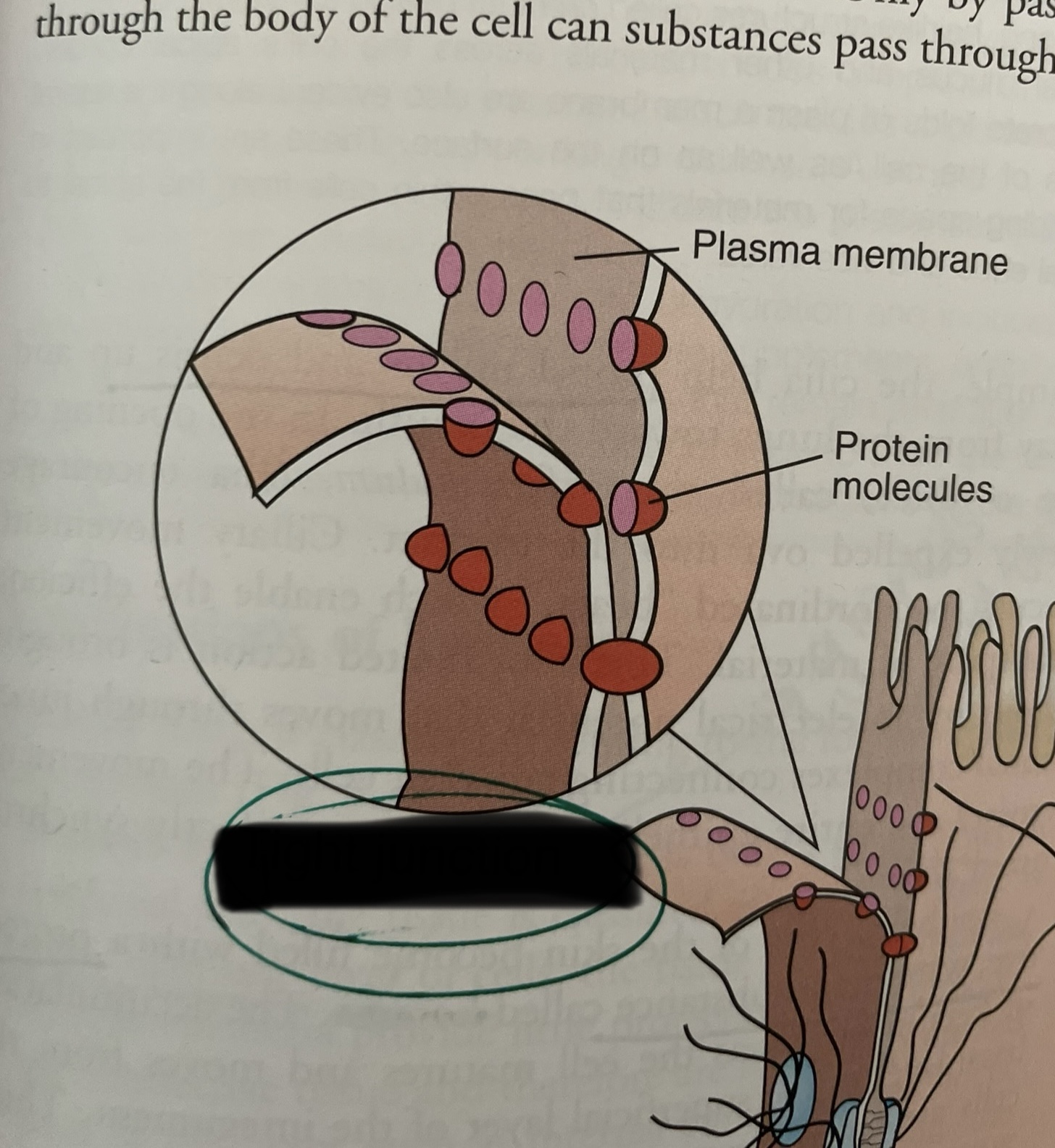
what type of junction is this?
tight junction
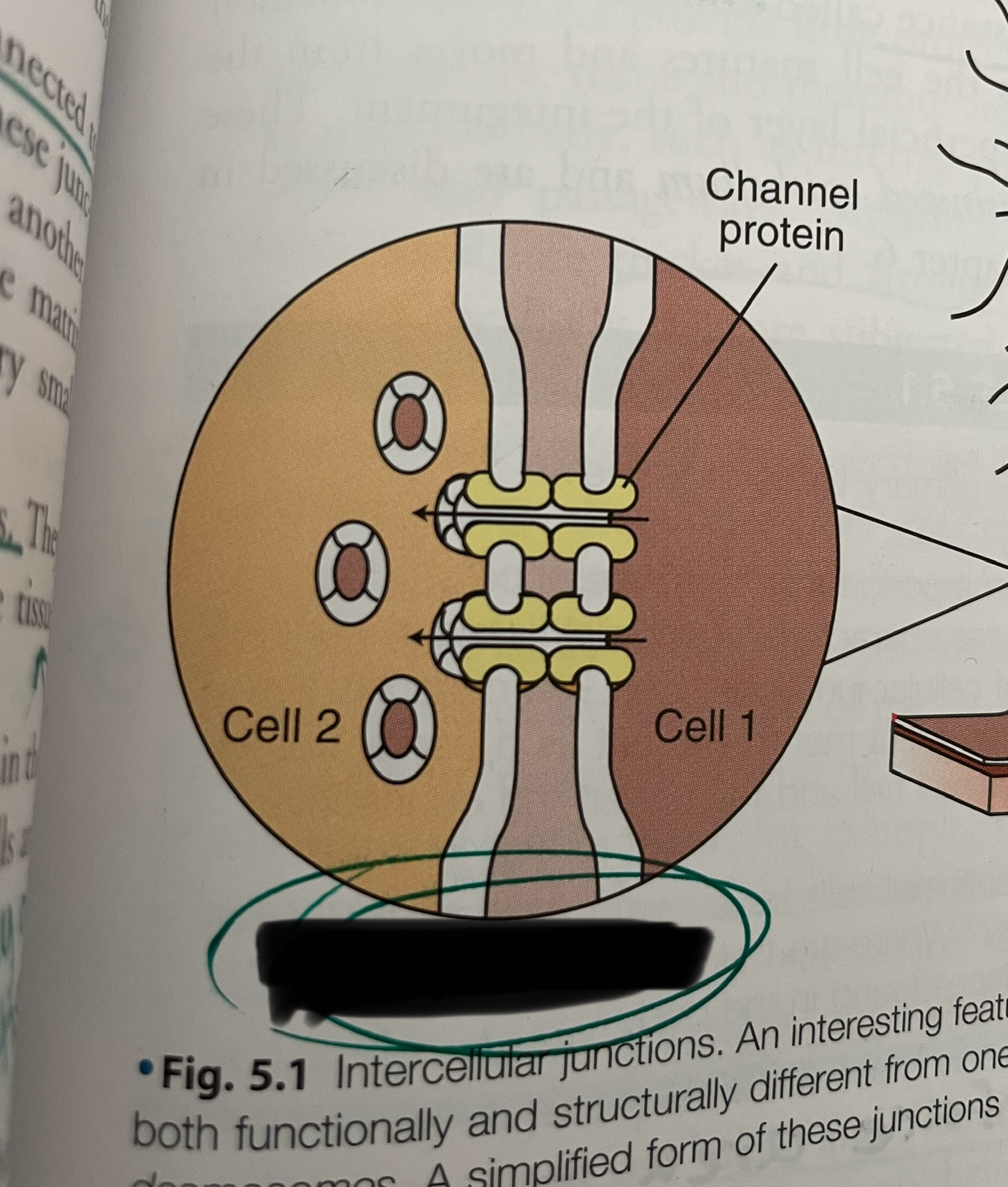
what type of junction is this?
gap junction
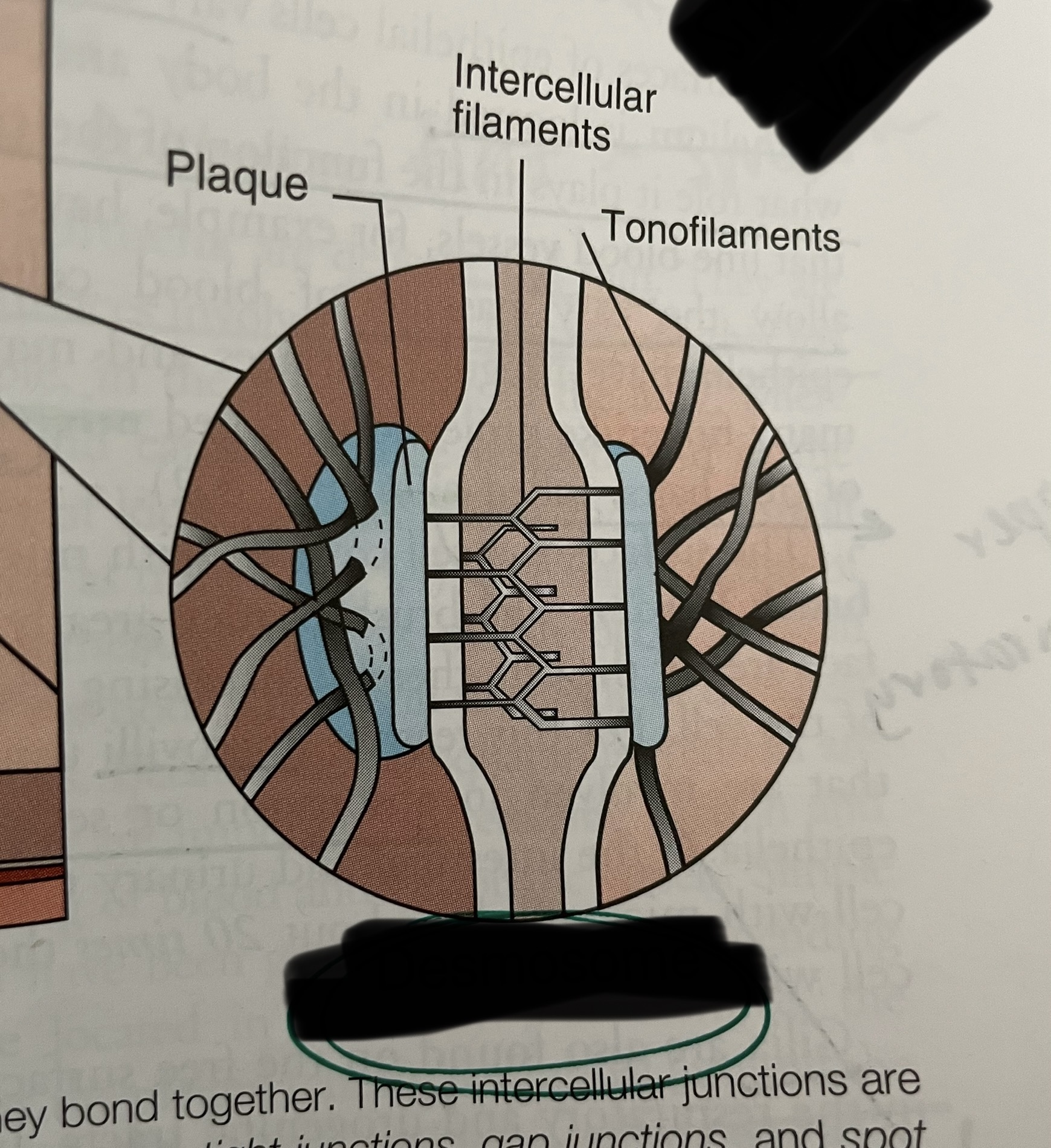
what type of junction is this?
desmosome
ex. of gap junctions
GI tract, heart, or smooth muscle tissue
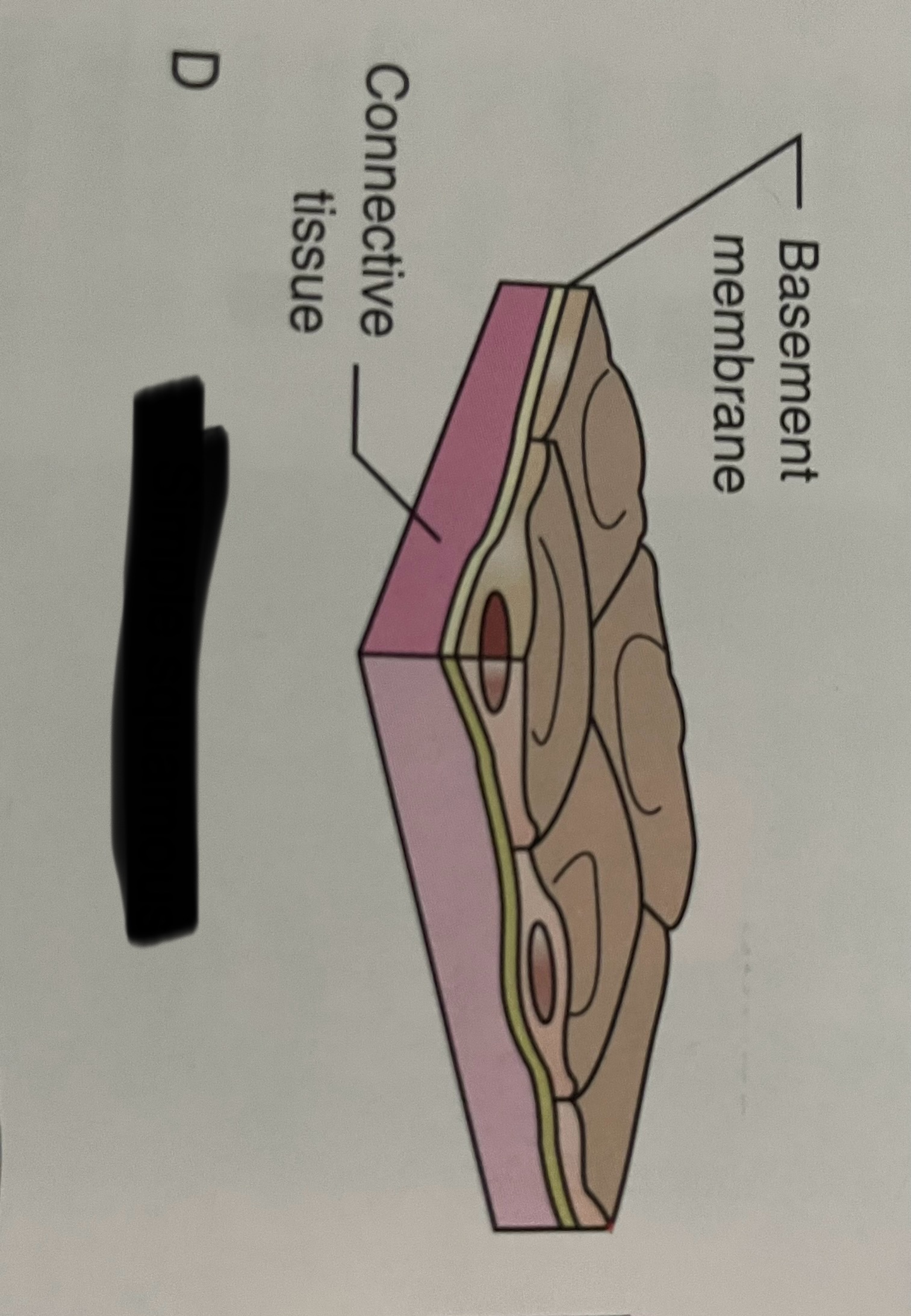
what is the basement membrane?
nonliving of fibers making up the foundation of the epithelial cell
what does the basement membrane do?
helps prevent the cell from being torn off by pressures like stretching or erosion
where can microvilli be found?
on epithelial tissue of the intestine; usually cells that secrete/excrete
where can cilia be found?
on epithelial tissue of the upper respiratory; move something along
what is keratin?
a protective, waterproof substance that fills epithelial cells of the skin
how do we classify epithelial cells?
number of layers of cells
shape of the cells
presence of surface specializations
number of layers of cells
simple= single layer
stratified= more than one layer
shape of the cells
squamous= flat and smooth
cuboidal= cube shaped
columnar= column shaped
presence of specializations
cilia, microvilli, keratin, etc
where would you find simple squamous?
lining surfaces involved in the passage of either gas or liquid
where would you find simple cuboidal?
sheltered regions of the body where secretion and absorption take place, like ovaries or glands
where would you find simple columnar?
GI tract from the stomach to the rectum
what 2 cells make up the lining of the gut?
absorptive and goblet cells
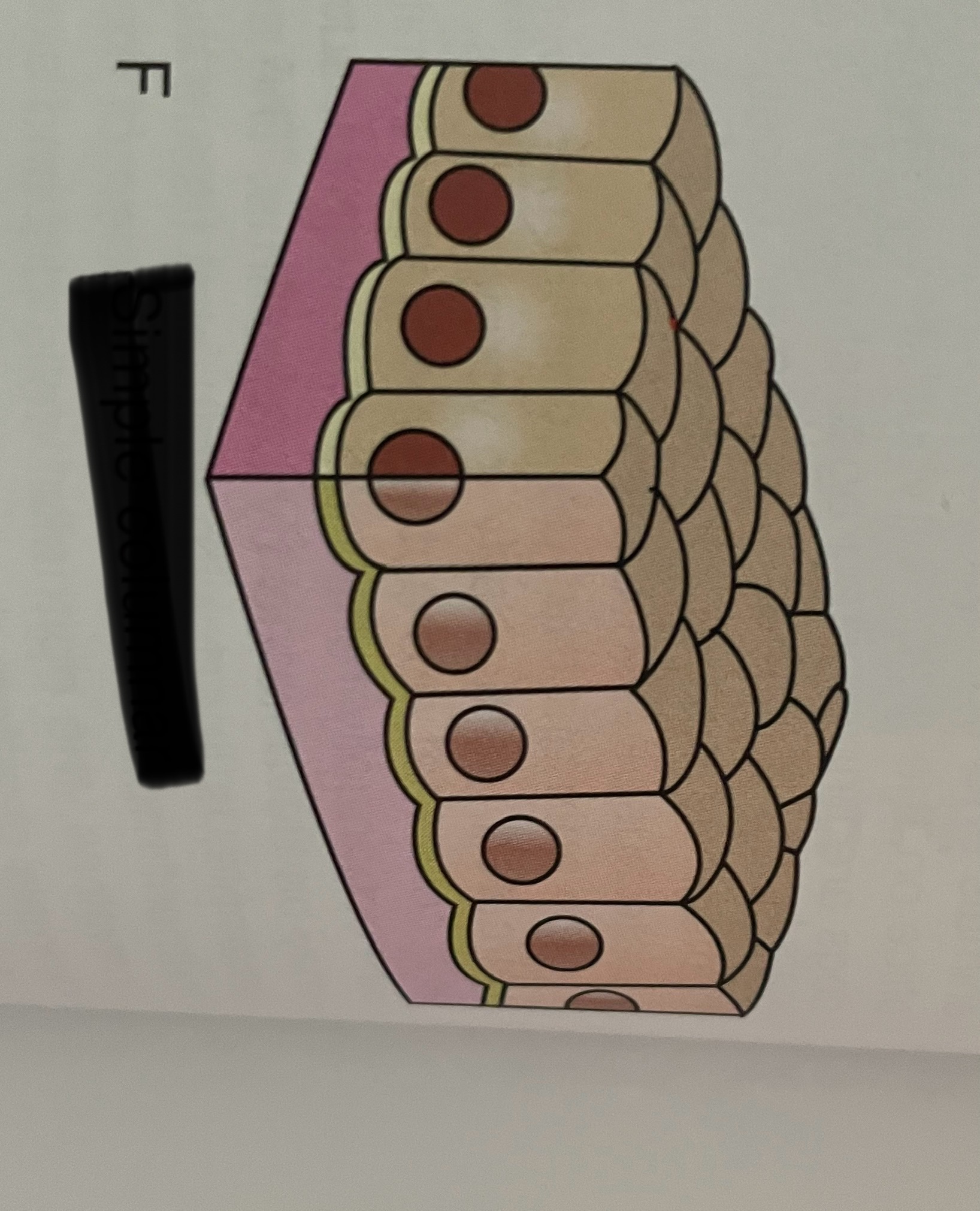
where would you find stratified squamous?
regions of the body subject to mechanical and chemical stress, like the mouth, esophagus, vagina, and rectum
where would you find stratified cuboidal?
excretory ducts, such as sweat, mammary, or salivary glands
where would you find stratified columnar?
rare, only in parts of the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems
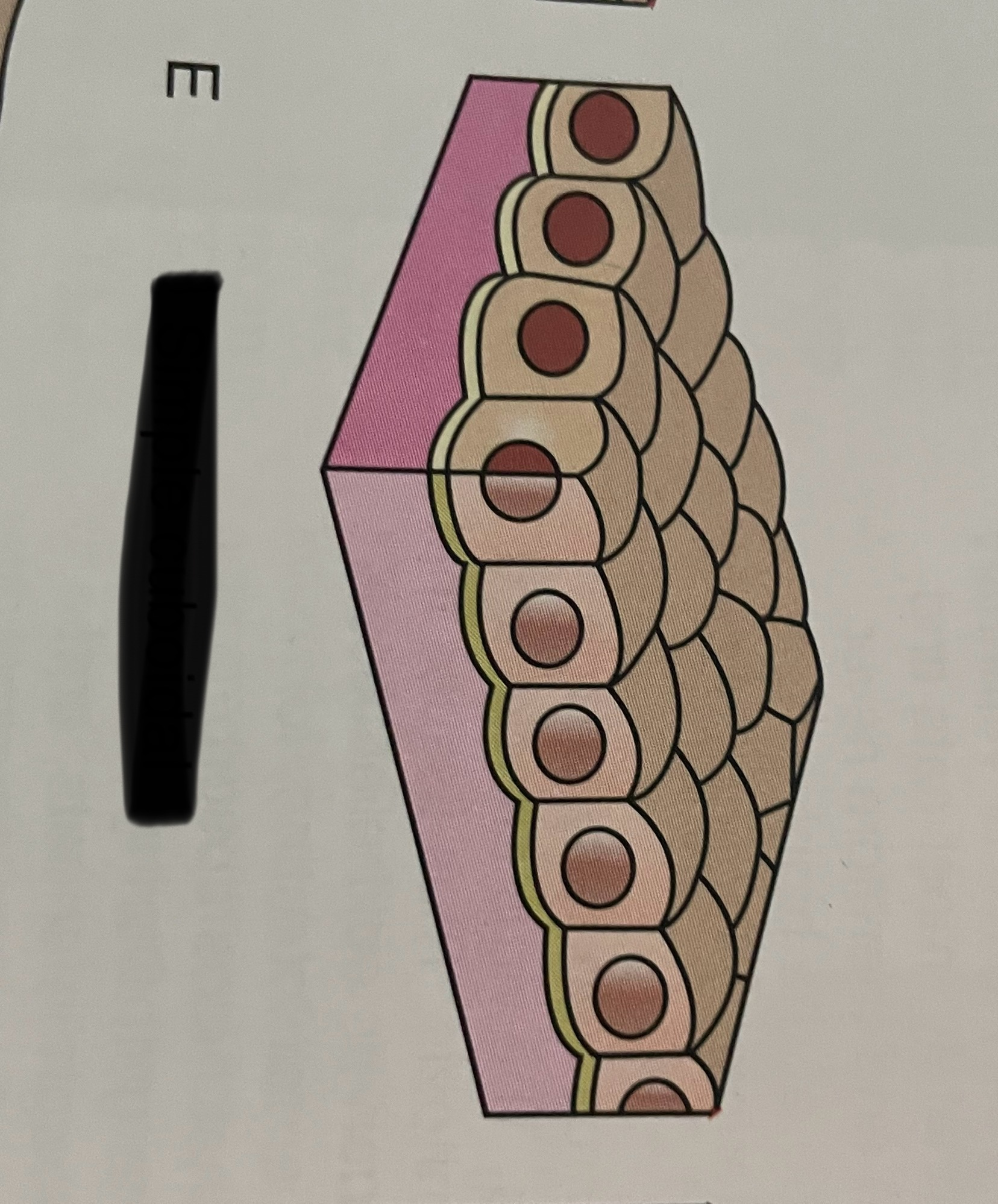
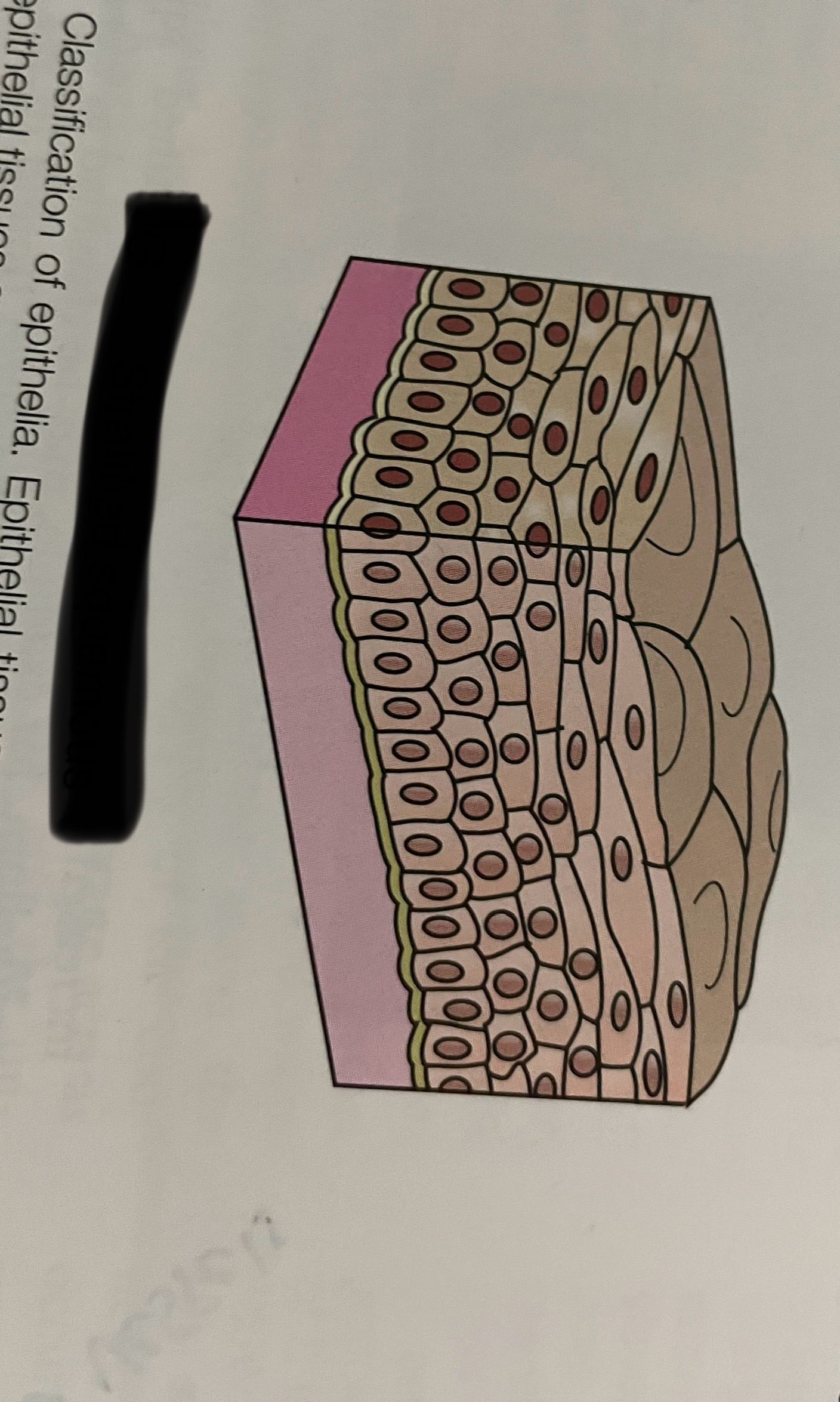
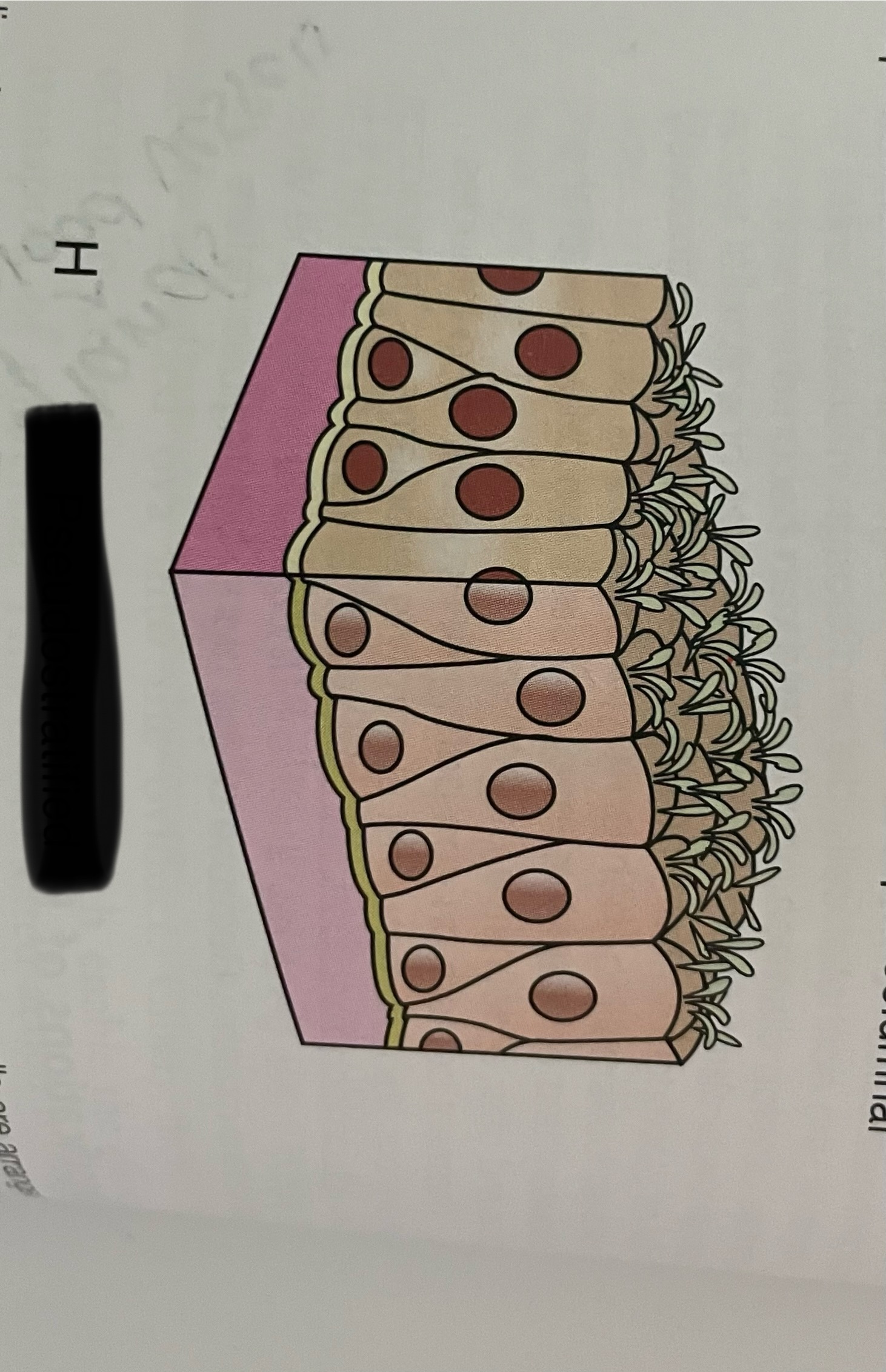
what is psuedostratified columnar?
epithelial that is not truly stratified
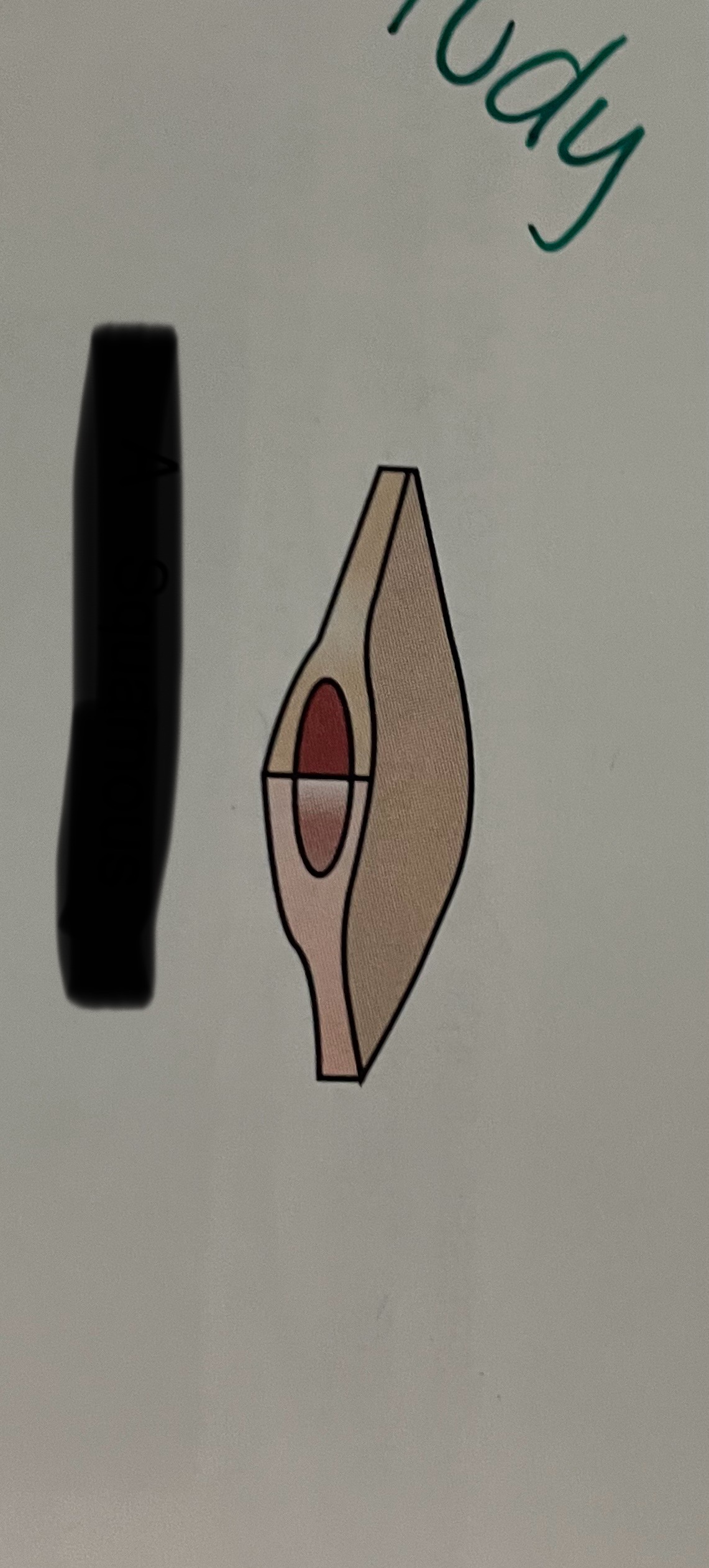
which cell shape is this?
squamous
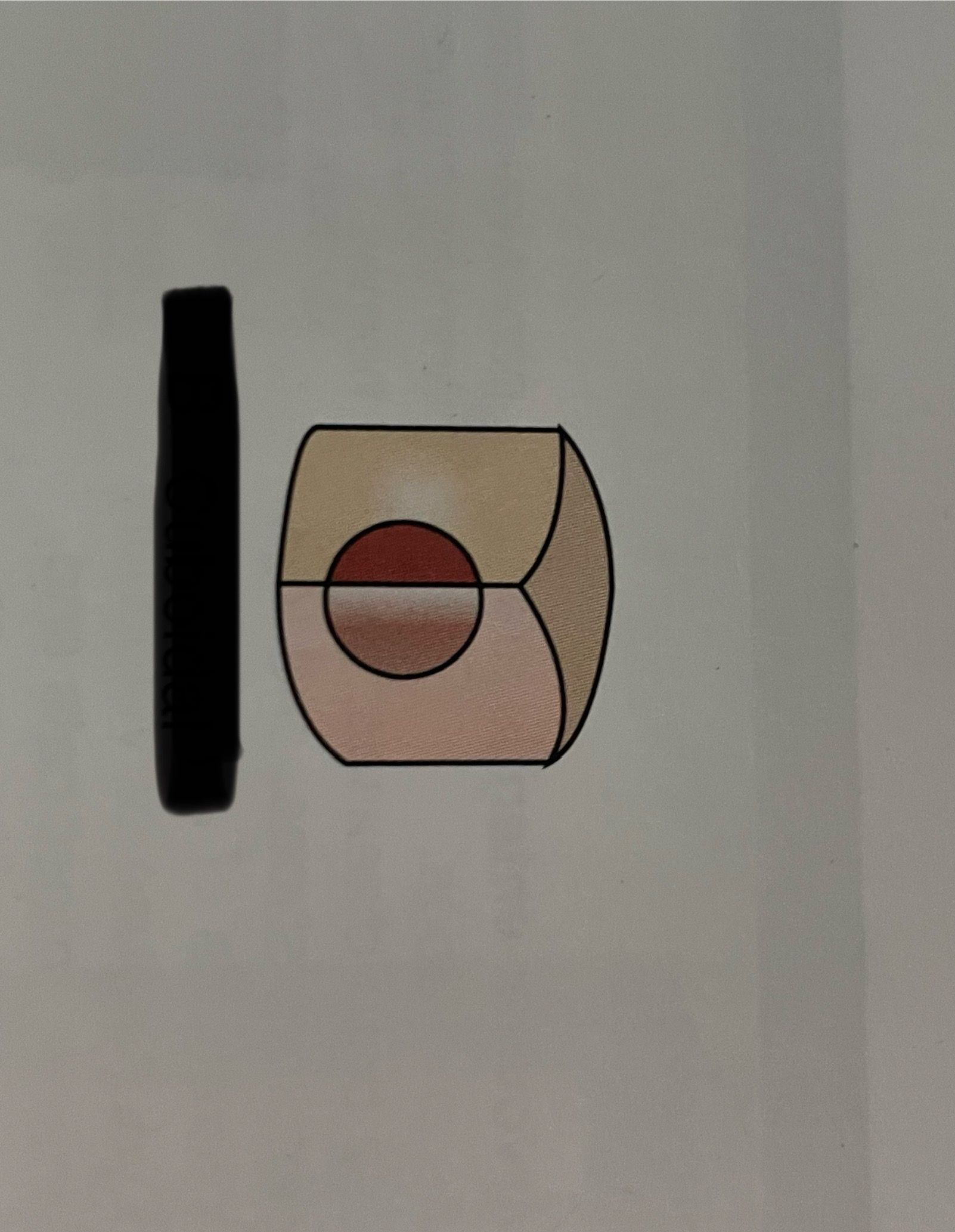
which cell shape is this?
cuboidal
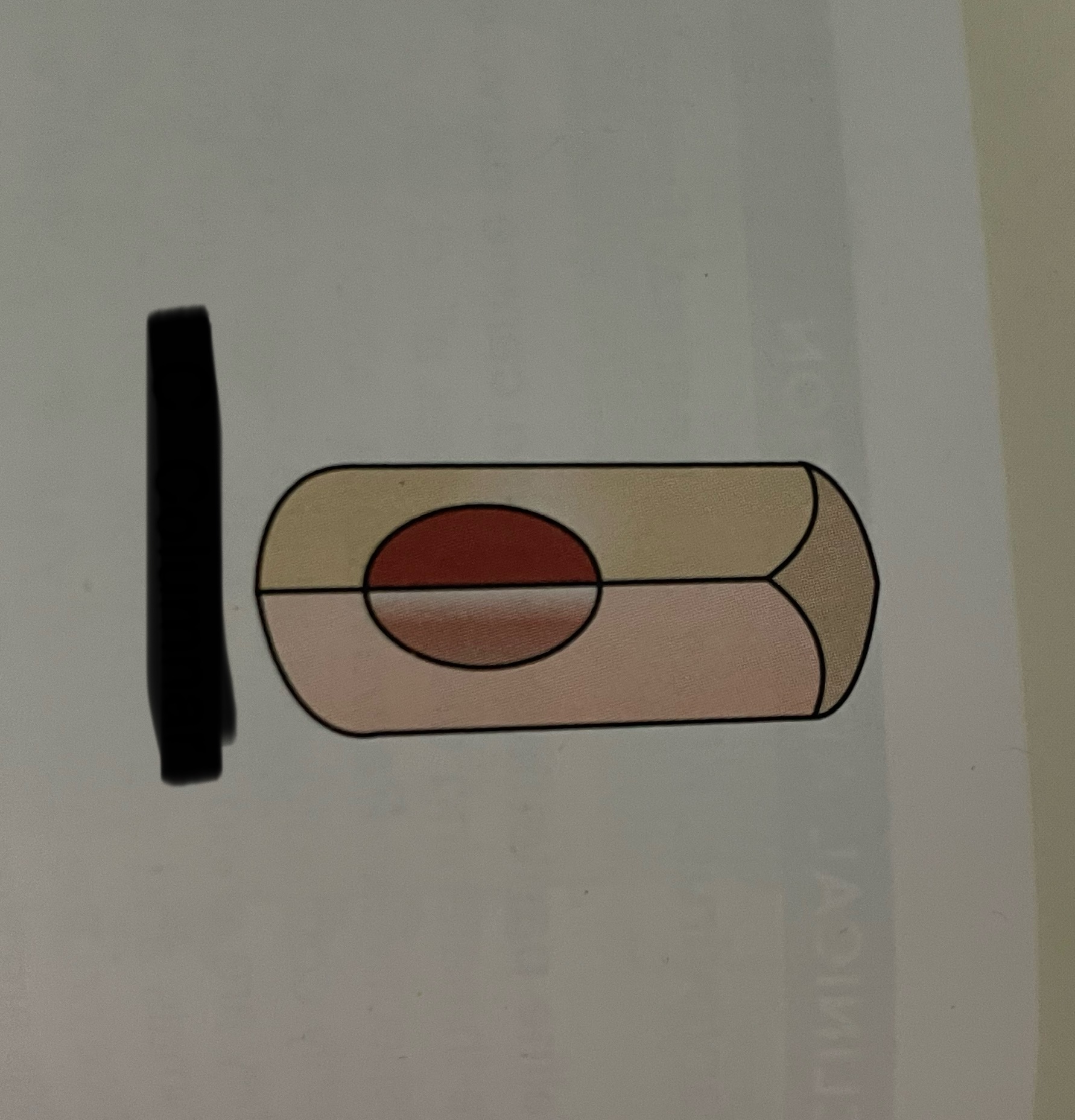
which cell shapes is this?
columnar
what type of layering is this?
simple squamous
what type of layering is this?
simple cuboidal
what type of layering is this?
simple columnar
what type of layering is this?
stratified squamous
what type of layering is this?
pseudostratified
what is a gland?
a cell or group of cells with the ability to manufacture and discharge a secretion
how can we classify glands?
presence or absence of ducts
number of cells that compose them
complexity of the structure
type of secretion produced
how the secretion is stored or discharged
endocrine glands
do NOT have ducts
exocrine glands
DO have ducts
what is the ONLY unicellular exocrine gland that is ductless?
the goblet cell
what do goblet cells secrete?
mucin, found in the upper respiratory, GI tract, and conjunctiva
multiceullular exocrine glands
made of a secretory unit and duct
simple exocrine glands are __________, while compound exocrine glands are __________
unbranched, branched
merocrine glands
remain intact through secretion
apocrine glands
lose the apex of the cell through secretion
holocrine glands
are completely destroyed through secretion
serous secretions
are watery and contain a high concentration of enzymes
mucous secretions
are thick and composed of glycoproteins (mucus)
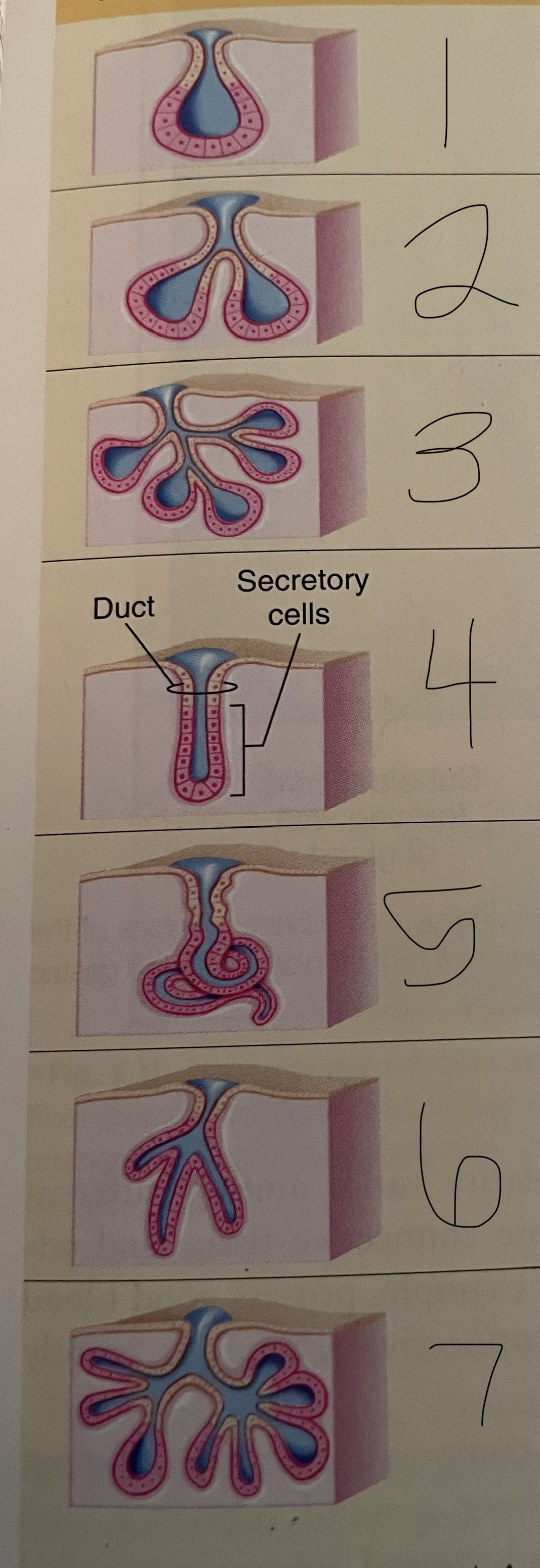
what are numbers 1-7?
simple alveolar
simple branched alveolar
compound alveolar
simple straight tubular
simple coiled tubular
simple branched tubularcompound tub