Chemistry 1.1 Particles in the atom and atomic radius
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are atoms?
Atoms are mostly empty space surrounding a very small dense nucleus that contains protons and neutrons.
What are electrons?
Electrons are found in shells in the empty space around the nucleus.
What is the definition of atomic number?
The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
What is the mass number?
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom or ion of an isotope
What is another name for mass number?
Nucleon number
What is an ion?
A charged species
What is the atomic mass unit?
1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
What is the relative charge of a proton?
+1
What is the relative charge of a neutron?
0
What is the relative charge of an electron?
-1
What is the relative mass of a proton?
1
What is the relative mass of a neutron?
1
What is the relative mass of an electron?
1/1836
What is the trend in atomic radius across a period? (e.g. Li to F)
Atomic radii decreases, Nuclear charge increases, and therefore there is a stronger force of attraction between the nucleus and the electron.
What is the trend in atomic radius down a group?
Atomic radii increases, as the number of shells of electrons increases, increasing shielding, which outweighs the increase in nuclear charge
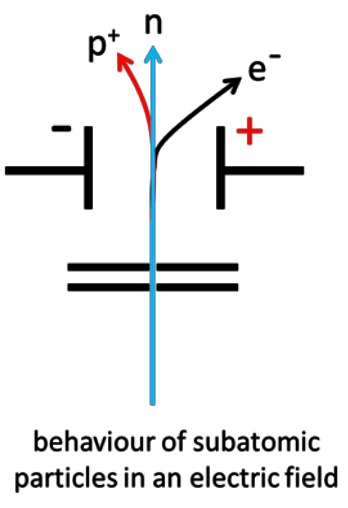
Describe the behaviour of beams of protons, neutrons and electrons moving at the same velocity in an electric field.
Protons are deflected on a curved path toward the negative plate. Electrons are deflected significantly more on a curved path toward the positive plate due to the low mass. Neutrons continue in a straight line.
What is the trend in ionic radii down a group? (2 points)
Ionic radii increases, due to the increase in the number of shells.
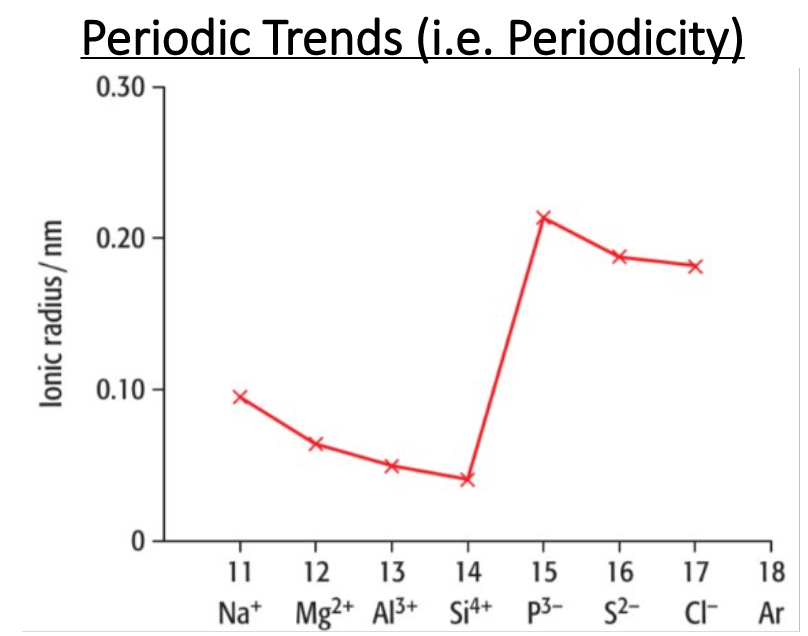
What is the trend in ionic radii for positive ions across a period?
Positive ions decrease in size as nuclear charge increases. There is a stronger force of attraction between the nucleus and outer shell electron.
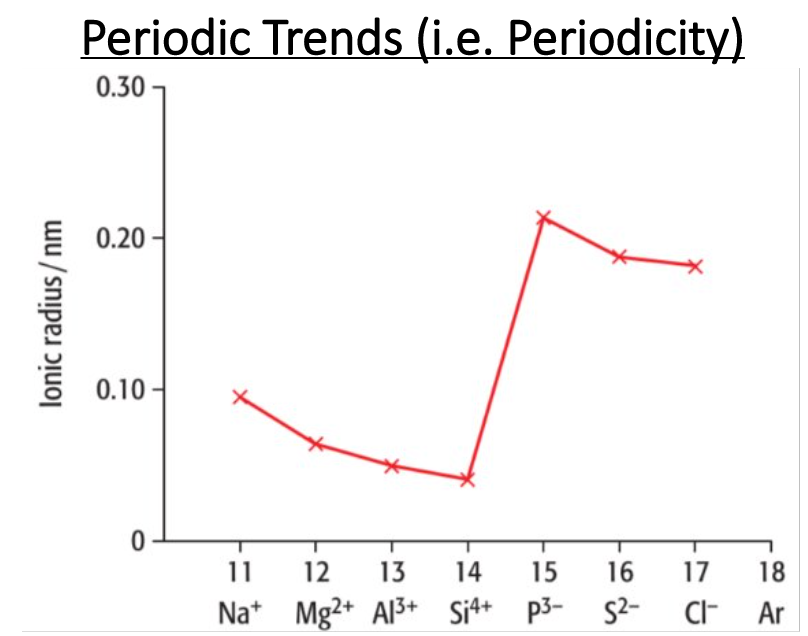
True or False: The higher the ion’s positive charge, the smaller the ion (as more electrons are lost)
True
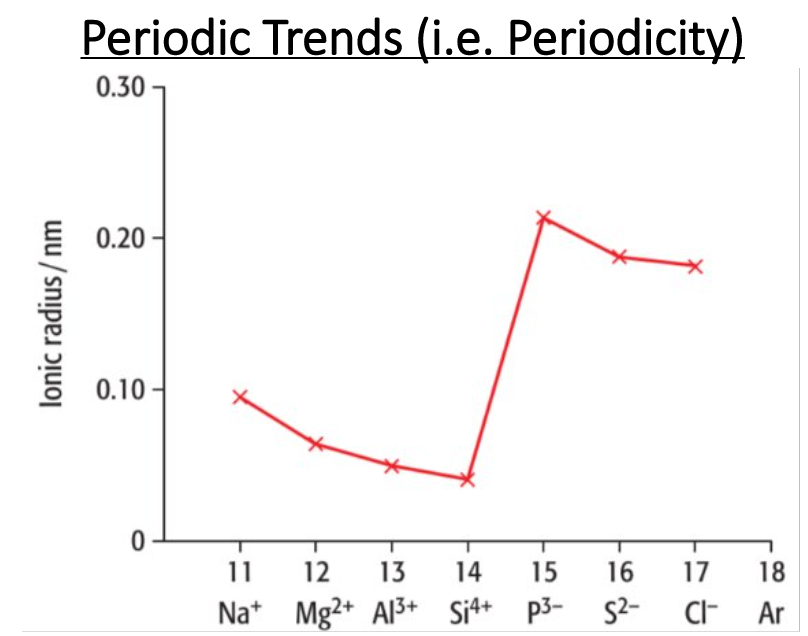
What is the trend in ionic radii for negative ions across a period?
Decrease in ionic radii as the atomic number increases, while the electrons remain the same, causing a greater nuclear charge, causing the ionic radii to decrease.
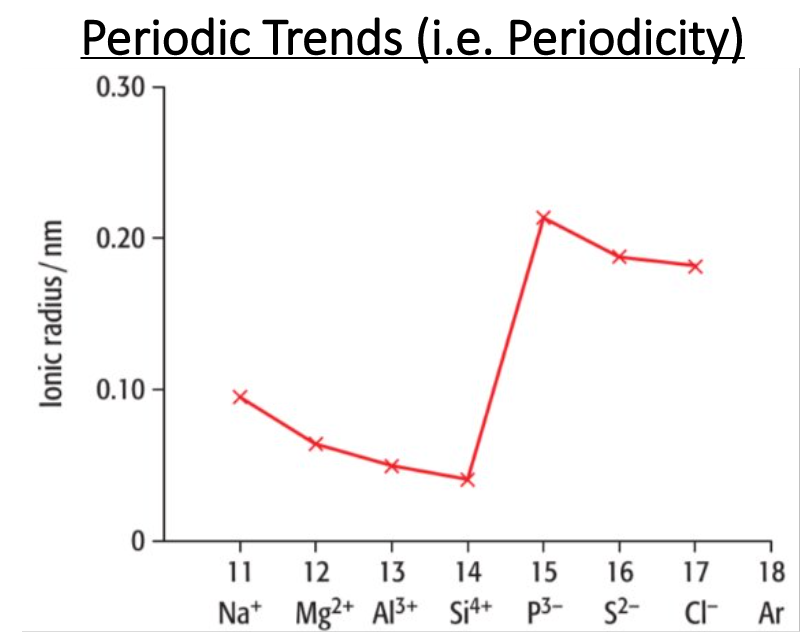
Explain the trend from Na+ to Si4+. Does the ionic radii increase or decrease? Why?
Decrease
Describe the trend from Si4+ to P3-. Does the ionic radii increase or decrease? Why?
Increase
Describe the trend from P3- to Cl-. Does the ionic radii increase or decrease? Why?
Decrease
What is an isoelectronic series?
A group of ions with the same number of electrons