CH 39 Respiratory System & 40 The Circulatory System
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
gills
Increase surface area for diffusion
Move water into the mouth, through the gills, and out of the fish through the open operculum or gill cover
Lungs
minimizes evaporation by moving air through a branched tubular passage & is covered in mucus to prevent direct contact of tissue with air. Inhaled air passes through the larynx, glottis, and trachea. Bifurcates into the right and left bronchi, which enter each lung and further subdivide into bronchioles. Produces negative pressure which draws air into the lungs.
air pressure
Air exerts a pressure downward, due to gravity. A pressure of 760 mm Hg is defined as one atmosphere (1.0 atm) of pressure
partial pressure
is the pressure contributed by a gas to the total atmospheric pressure
alveoli which are (sites of gas exchange) are surrounded by an extensive capillary network
Lungs of mammals are packed with millions of___
the rib cage
Contraction of the external intercostal muscles expands?
thorax & lungs
Contraction of the diaphragm expands the volume of?
Tidal volume
Volume of air moving in and out of lungs in a person at rest
Vital capacity
Maximum amount of air that can be expired after a forceful inspiration
hemoglobin
loads up with oxygen in the lungs, forming oxyhemoglobin
Consists of four polypeptide chains: two α and two β. Each chain is associated with a heme group that has a central iron atom that can bind a molecule of O2
Bohr shift
Hemoglobin’s affinity for O2 is affected by pH and temperature. Facilitates oxygen unloading in the tissue. If there is high levels of CO2, that means that oxygen is needed so the hemoglobin lets go of the oxygen. This pH effect is known as
plasma
About 8% of the CO2 in blood is dissolved in?
hemoglobin
20% of the CO2 in blood is bound to?
bicarbonate
Remaining 72% diffuses into red blood cells and becomes?
Hypoventilation
Insufficient breathing Blood has abnormally high PCO2
Hyperventilation
Excessive breathing Blood has abnormally low PCO2
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Refers to any disorder that obstructs airflow on a long-term basis
Asthma
Allergen triggers the release of histamine, causing intense constriction of the bronchi and sometimes suffocation
Emphysema
Alveolar walls break down and the lung exhibits larger but fewer alveoli
Lungs become less elastic
Eighty to 90% of deaths are caused by cigarette smoking
invertebrate circulatory system
Sponges, cnidarians, and nematodes lack a separate circulatory system
Sponges circulate water using many incurrent pores and one excurrent pore
Hydra circulate water through a gastrovascular cavity (also for digestion)
Nematodes are thin enough that the digestive tract canalso be used as a circulatory system
Larger animals require a separate circulatory system for nutrient and waste transport
Open circulatory system
No distinction between circulating and extracellular fluid
Fluid called hemolymph
Closed circulatory system
Distinct circulatory fluid enclosed in blood vessels and transported away
Fishes
Evolved a true chamber-pump heart
Have a 2 chambered heart
Blood is pumped through the gills, and then to the rest of the body
Amphibians
Advent of lungs required a second pumping circuit, or double circulation
Pulmonary circulation moves blood between the heart and lungs
Systemic circulation moves blood between the heart and the rest of the body
3 chambered heart
Reptile heart
3-chambered heart
2 atria and 2 ventricles
But there is incomplete separation of the ventricles
Mammals, birds, and crocodilians
4-chambered heart
2 separate atria and 2 separate ventricles
Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and delivers it to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs
Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and delivers it to the left ventricle, which pumps it to rest of the body
Extracellular matrix – plasma
Cells – RBCs, WBCs, platelets
blood connective tissue contains?
Transportation, Regulation & Protection
Functions of circulating blood?
92% water, Nutrients, wastes, and hormones, ions, & proteins (albumin a-globulins, b-globulins)
Blood plasma is made up of?
hematocrit
___ is the fraction of the total blood volume occupied by red blood cells
RED BLOOD CELLS (ERYTHROCYTES)
About 5 million per microliter of blood
Mature mammalian erythrocytes lack nuclei
Live for 120 days
RBCs of vertebrates contain hemoglobin
Pigment that binds and transports oxygen
WHITE BLOOD CELLS (LEUKOCYTES)
Less than 1% of blood cells
Larger than erythrocytes and have nuclei
Can migrate out of capillaries into tissue fluid
Granular leukocytes
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are all types of ___
Agranular leukocytes
Monocytes and lymphocytes are all types of ___
platelets
Cell fragments that pinch off from larger cells in the bone marrow
Function in the formation of blood clots
arteries
Blood leaves the heart through the ___
heart
Veins carry blood back to the ___
Endothelium, elastic fibers, connective tissue and smooth muscle
Arteries and veins have walls too thick for exchange of materials & are composed of which four tissue layers?
rapid exchange of gases and metabolites between blood and body cells
Capillaries are composed of only a single layer of endothelial cells which allow?
Lymphatic system
Significant amount of water and solutes in the blood plasma filter through the walls of the capillaries to form the interstitial (tissue) fluid. Fluid that does not return to capillaries is returned to circulation in the subclavian vein. What body system is this?
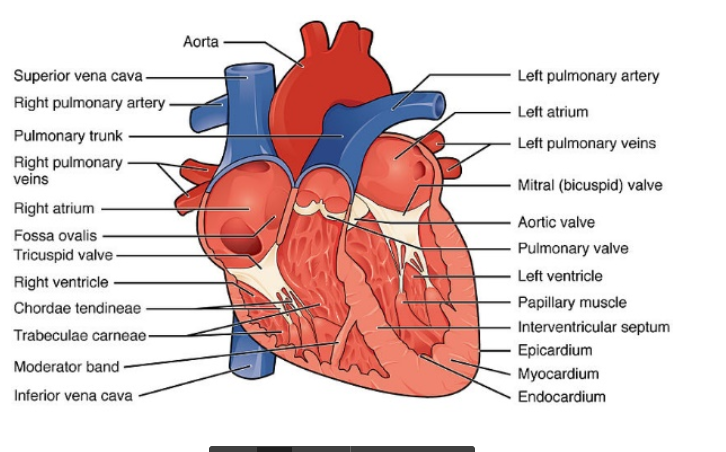
Just in case
Ms. Equigua asks a question about the heart
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
Maintain unidirectional blood flow between atria and ventricles
= On the right
Tricuspid valve
= On the left
Bicuspid, or mitral, valve
Semilunar valves
Ensure one-way flow out of the ventricles to the vessels
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
right ventricle
Pulmonary valve located at the exit of the?
Left ventricle
Aortic valve located at the exit of the?
(diastole)
Ventricles relaxed and filling
(systole)
Ventricles contracted and pumping
AV valves closing
Lub
closing of semilunar valves
Dub
sinoatrial (SA) node
Located in wall of right atrium
Acts as pacemaker
Autonomic nervous system can modulate rate
Atherosclerosis
Accumulation of fatty material within arteries
Impedes blood flow
Arteriosclerosis
Arterial hardening due to calcium deposition
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Aldosterone – encourages kidney to excrete postassium and retain sodium
Atrial natriuretic hormone – increases sodium excretion and decreases blood pressure
Nitric oxide (NO) – vasodialator
Blood volume is regulated by which four hormones?