Respiratory SHAKER
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Respiration
-Process by which O2 is obtained from the environment and delivered to cells
-CO2 is transported from the cells to the environment
Pulmonary ventilation
Movement of air into and out of the lungs
External exchange of casses
-Takes place inside the lungs
-Diffusion of O2 into the blood stream from the air in the lungs
-Diffusion of CO2 out of the blood stream to the air in the lungs
Internal exchange of gasses
-Takes place in the tissues
-Diffusion of O2 into the cells from the blood stream
-Diffusion of CO2 out of the cells and into the blood stream
Upper respiratory tract
-Structures located outside the thoracic cavity
-Nose
-Pharynx
-Larynx
-Trachea
Lower respiratory tract
-Structures located inside the thoracic cavity
-Bronchi
-Lungs
Nasal cavities
-Separated into right and left by septum
-Lined with mucous membrane
-Nasal conchae ↑ surface area
Nasal cavity functions
-Warms air
-Humidifies air
-Traps foreign particles
-Olfactory receptors
Nasal conchae
The scroll like ridges on the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
Naso-pharynx
-Superior portion of the pharynx, located posterior to the nasal cavities
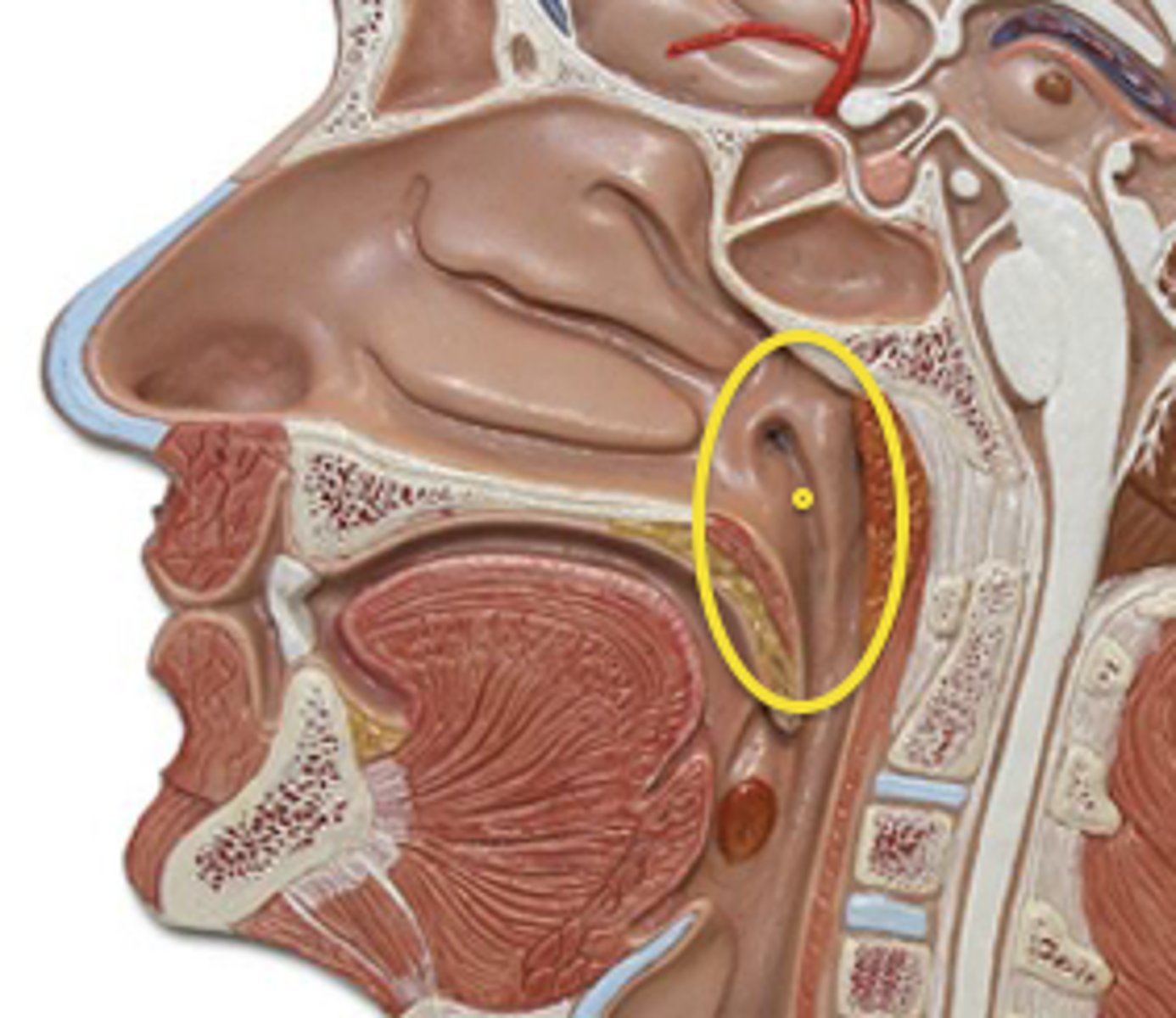
Eustachian tubes
Open into the naso-pharynx
Uvula
Extension of the palate that closes the naso-pharynx during swallowing
Oro-pharynx
-Middle portion of the pharynx, located posterior to the oral cavity
-Contains the palatine and lingual tonsils
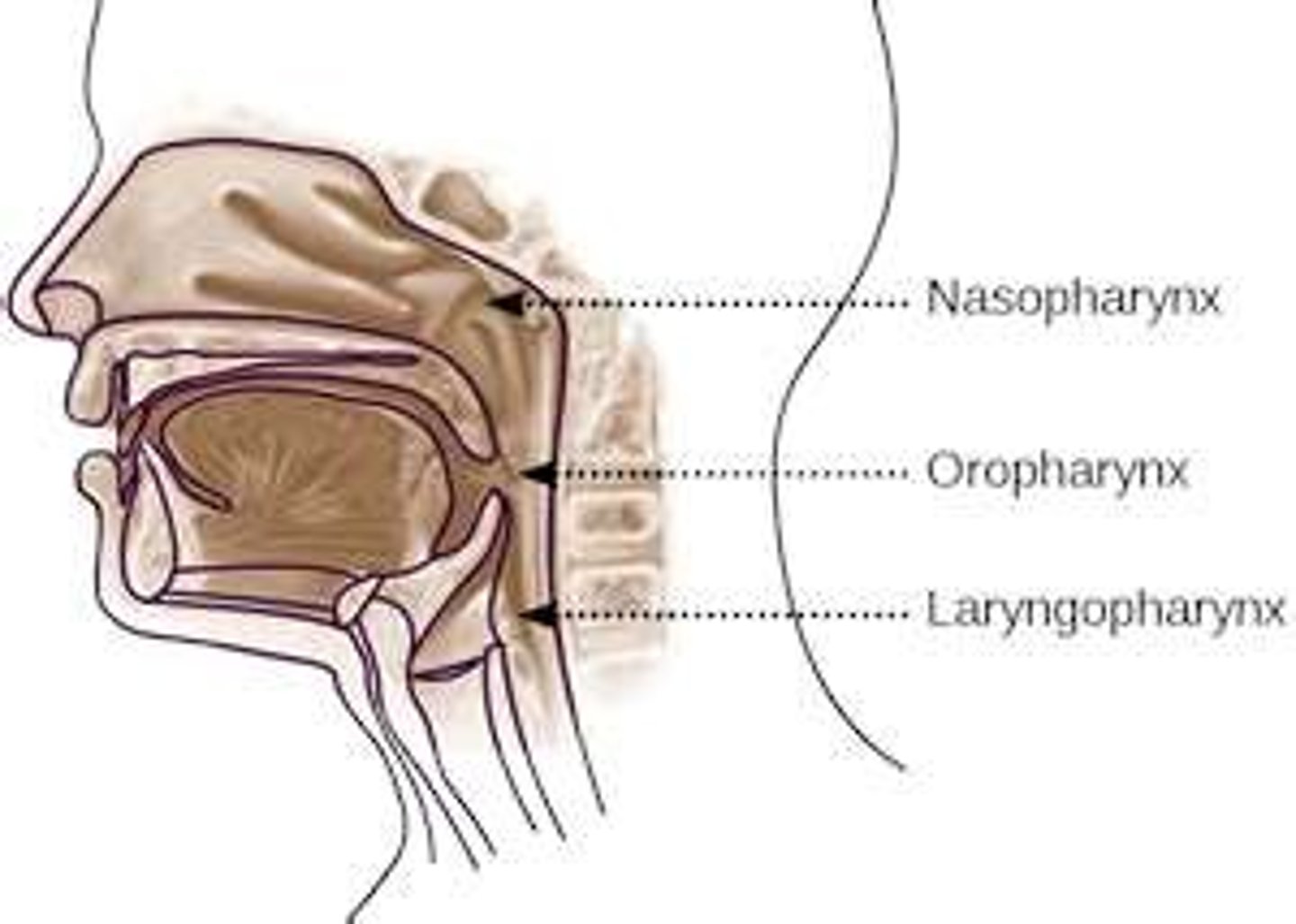
Laryngeal pharynx
-Inferior portion of the pharynx
-Posterior to the larynx and connects to the esophagus
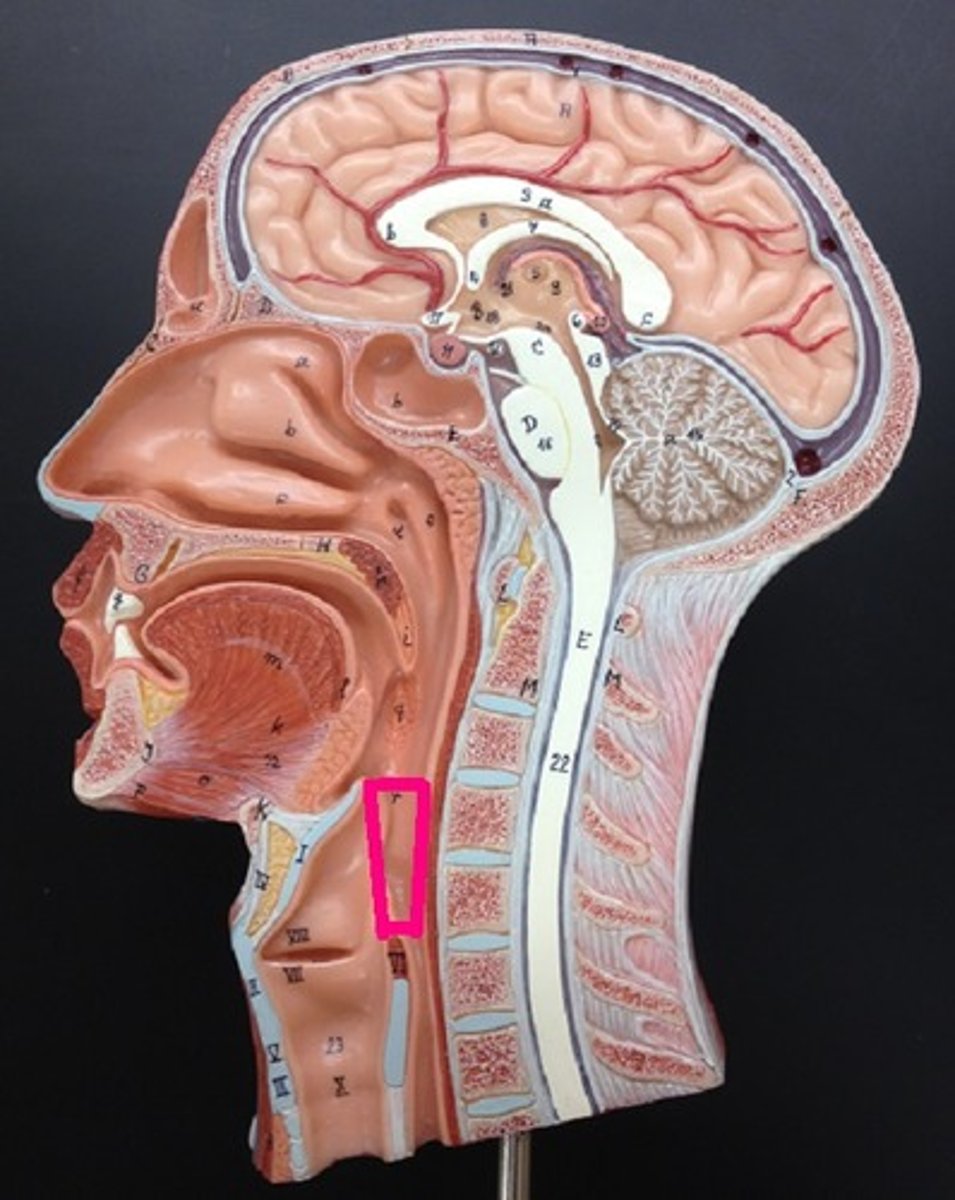
Larynx
-Made up of cartilages that are connected by ligaments
-Voicebox
Epiglottis
Cartilaginous structure that closes the larynx during swallowing
Glottis
Space between the vocal cords
Trachea
-Extends from larynx to upper part of thoracic cavity
-Anterior to esophagus
-Has C-shaped cartilages to keep it open
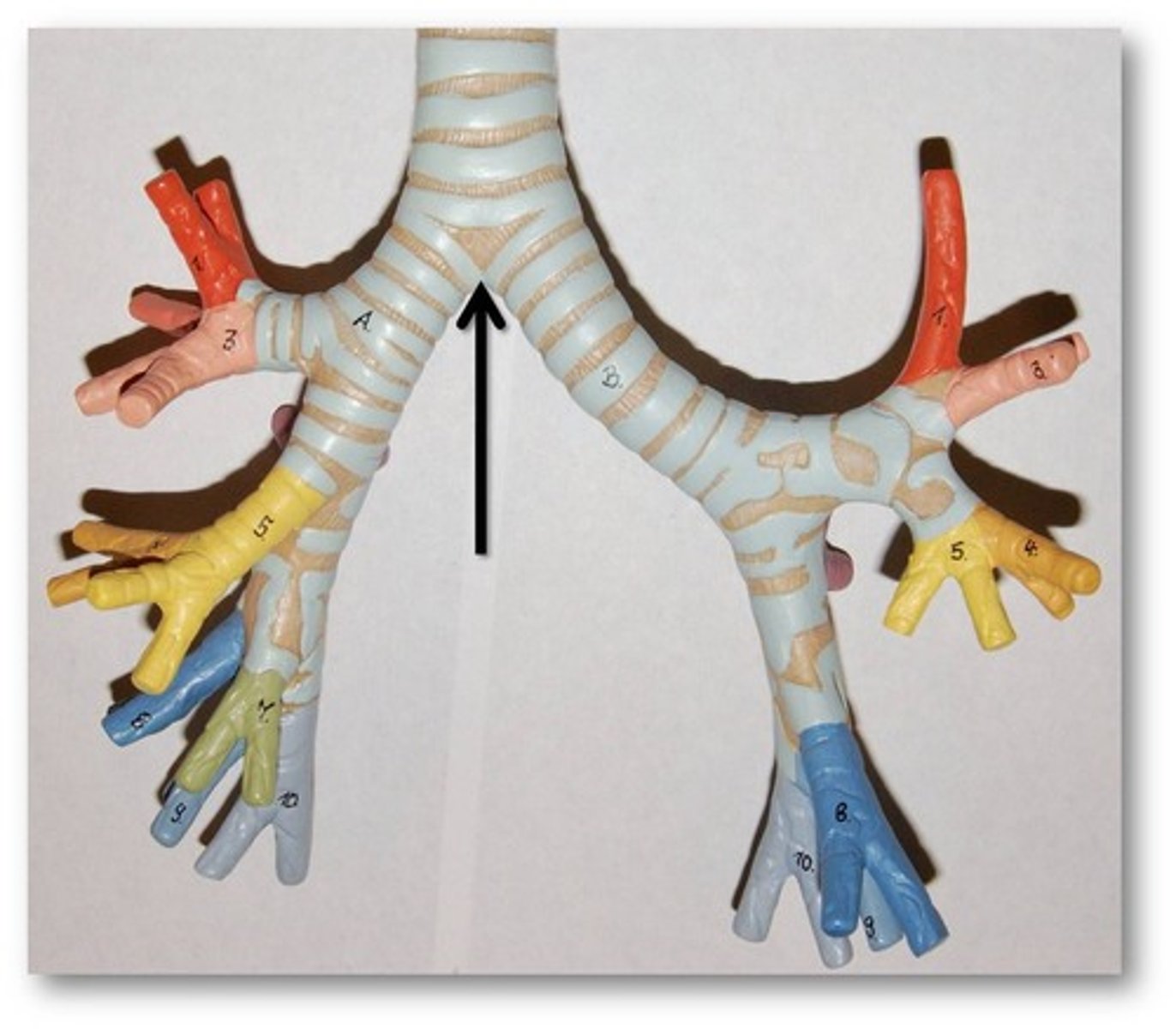
-Divides into two main stem bronchi at the Carina
Carina
Point at which the trachea bifurcates into the left and right mainstem bronchi.
Pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Lines the trachea, moves shit outta the respiratory tract
Bronchi
-Each enters the lung at the hilus
-Main stem bronchi-> secondary bronchi->
bronchioles-> alveolar duct
Hilus
Part of lung where vessels, nerves, and bronchi enter
Lungs
-Located in thoracic cavity
-Extend from the clavicles to the diaphragm
-Apex of lung is superior
-Base of lung is inferior
Pleura
Serous membrane surrounding the lungs
Right lung
Has 3 lobes
Left lung
Has 2 lobes
Alveoli
Sight of gas exchange
Ventilation
-Diaphragm
-External intercostals
-Internal intercostals
Surface tension
Water likes to stick to its self, which would cause alveoli to collapse
-Surfactant breaks surface tension in lungs
Elastic recoil
The tendency for the lungs to recoil or reduce in volume after being stretched or expanded
Negative pressure ventilation
The method by which we breathe (unlike frogs)
Room air
-21% O2
-0.04% CO2
Exhaled air
-16% O2
-4.5% CO2
Rule of 4
Every liter of O2 adds 4% O2 to room air
Ex. 2 liters would equal 29% O2
Diffusion limitations
-Pulmonary edema
-Mucous
-Structural damage
Oxygenated blood
97% saturated with O2
Deoxygenated blood
70% saturated with O2
CO2
-Acid component in blood gases
-Most is transported by blood as bicarbonate ion
Pa O2
-ABG
-Partial pressure of oxygen
80-100mm Hg
Pa CO2
-ABG
-Partial pressure of O2
-35-45mm Hg
SpO2
96-100%
Phrenic nerve
Stimulates the diaphragm to contract, stimulated by medulla oblongata
Respiratory pattern
Rate and depth of respiration
Medulla oblongata
Respiratory centers that control the rate and depth of breathinng
Hypercapnea
High levels of CO2, triggers ventilation
COPD
They can no longer breathe on the hypercapnic drive->Respiration chemically switches to HYPOXIC drive
Hypoxic drive
When the CO2 mechanism no longer works, low O2 levels trigger respiration
Pursed lip breathing
Done a few times an hour, can reduce CO2 in the lungs
Tidal volume
Volume of air the moves into and out of the lungs (500ml)
Residual volume
The volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum exhalation (1200mL)
Inspiratory reserve volume
The volume of air that can be forcefully inhaled after normal inhalation
Expiratory reserve volume
The volume of air that can be forcefully exhaled after normal exhalation
Vital capacity
The maximum volume of air that can be exhaled following maximal inhalation
Hyperventilatoin
Rapid, deep respirations
Hypoventilation
Slow, shallow breathing (COPD patients)
Effects of agina
-Diminished elastic recoil (compliance)
-Decreased respiratory muscle strength
-↓ wall compliance
-↓ in efficiency of protective mechanisms (mucus)
Pneumothorax
-Fluid in the intra-pleural space (pleural effusion)
-Can remove via thoracentesis