Anatomy and Physiology 2-Chamberlain-Exam 1-Study Guide
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Properties of muscles
Excitability: Ability of muscle to respond to stimuli.
Contractility: Ability of muscle to contract or shorten its size.
Extensibility: Ability of muscle to stretch.
Elasticity: Ability of muscles to return to original length after stretching.
Fusiform Muscles
A muscle that has the shape of a spindle, which is wider in the middle and narrowing towards both ends. An example is biceps brachii.

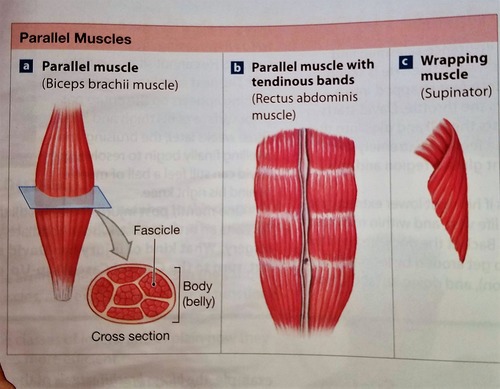
Parallel muscle
A muscle with a common point of attachment, with fascicles running parallel to each other. Ex. Rectus abdominis
Circular Muscle
These muscles appear circular in shape and are normally sphincter muscles that surround an opening such as the mouth Ex. Orbicularis Oculi

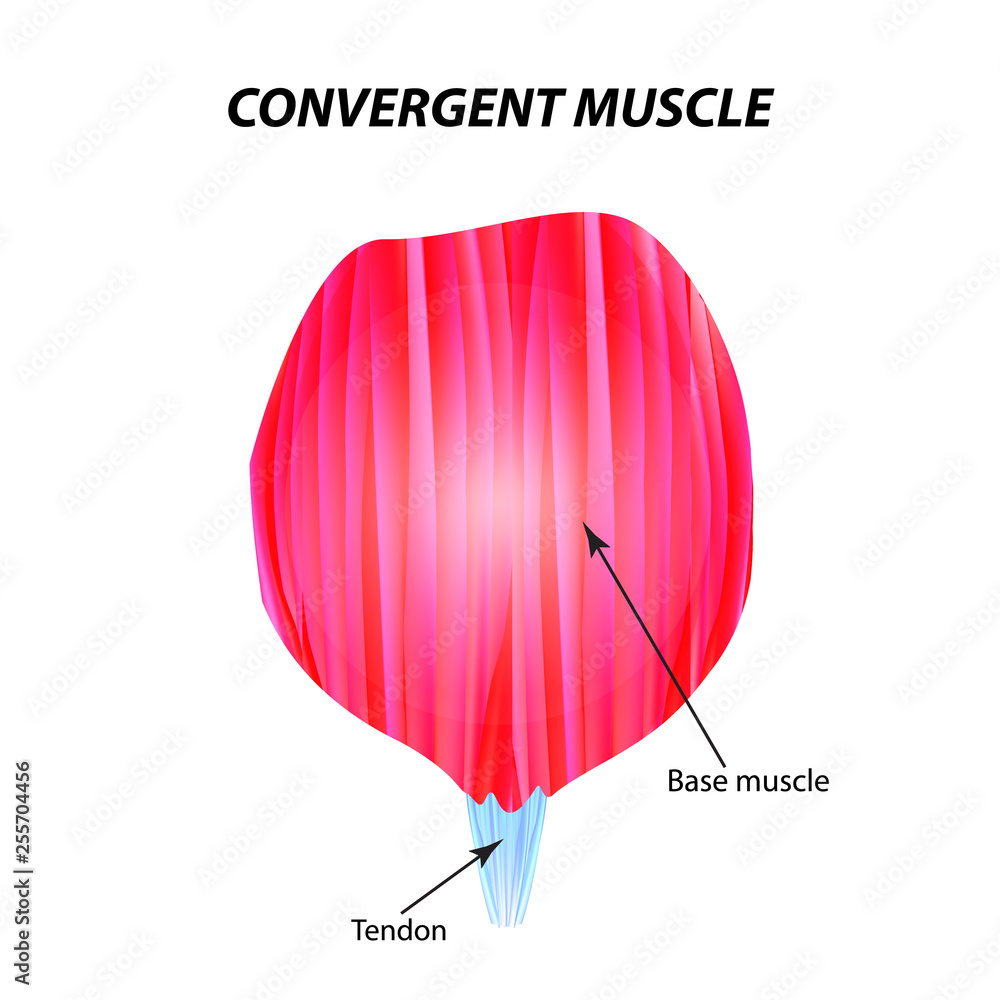
Convergent Muscle
fan-shaped-broad at one end and narrower at the other. Example: Deltoid (shoulder)
Cross bridge Formation
formed from the binding of actin with myosin. The formation shows muscle shortening caused by the movement of the contractile protein. The cross-bridge muscular contraction cycle is identified in all muscle types, including cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles. Cross-bridge cycling is caused by the cyclic attachment and detachment of contractile proteins.
Power stroke
The attachment of a myosin head from the thick filament to an active site on actin on the thin filament is a cross bridge.
Energy
-Mitochondria
-Glycolysis,
-Krebs Cycle (most efficient)
-Creatine (least efficient)
Insertion
further away, attachment Ex. Biceps brachii
Actions
Concentric-muscle shortens
Eccentric-lengthens
Isometric-remains the same
Function of muscle
Innovation
The nerve that operates
Afferent neurons
Carry information from sensory receptors found all over the body towards the central nervous system
Efferent neurons
Carry motor information away from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands of the body in order to initiate an action
Voltage gated channels
Respond to direct changes in membrane potential
Ligand-gated channels
Respond to chemical stimuli
Mechanical gate
Respond to mechanical vibration or pressure stimuli
Postsynaptic potential
when you add spatial summation (presynaptic neurons)
Muscle Identification
Pectoralis major
Latissimus dorsi
Deltoid
Rotator cuff: (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, teres major)
Biceps brachii
Triceps brachii
Brachioradialis
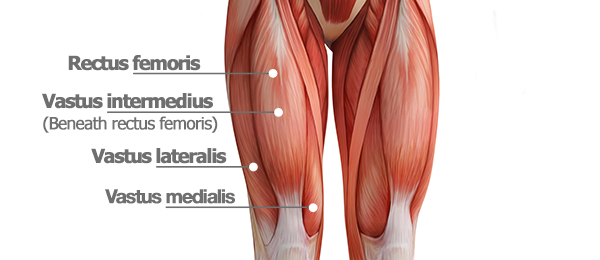
Quadriceps on Thigh
Rectus femoris.
Vastus lateralis.
Vastus medialis.
Vastus intermedius
L F E
balance
first-class lever is a spine
seesaw
E L F
power,
crowbar
leverage
ankles
F E L
rowing
chopsticks
Advantage: range of motion
Disadvantage: decrease in power
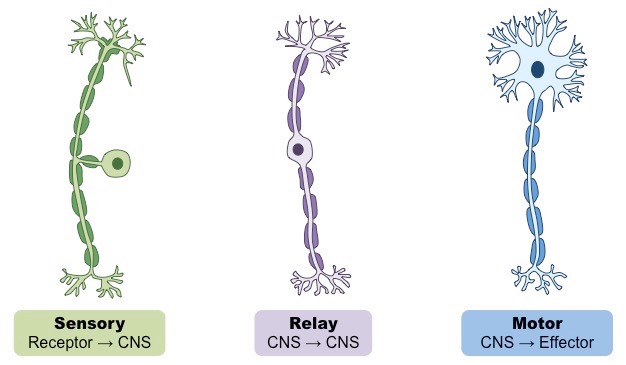
Functional Classification of Neurons
Sensory
Motor/efferent
Inter/association
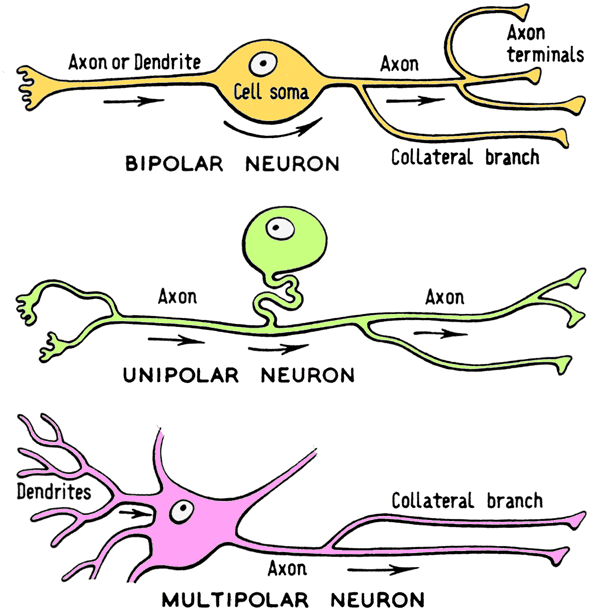
Types of Neurons
Multipolar-Most Common
Unipolar-Sensory Receptors
Bipolar-Retina of the Eye