17 SQ: Primary Shaping
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the main task for primary shaping processes?
Creating cohesions from shapeless materials
How can primary shaping be categorized?
According to nature of shapeless material (DIN 8580)
Nature:
Liquid
Plastic
Pulpy
Granular/Powdered
Splintered/Fibrous
Gaseous/Vaporous
Ionized
Primary Shaping by Welding
Primary Shaping by AM
Name advantages of casting processes
Complex geometries realizable
Near net-shape production (less post-processing and machining afterwards)
Wide range of materials
Wide range of parts (mass)
Economic
Circular economy
Name disadvantages of casting processes
Sometimes expensive systems
Sometimes bad surface qualities
Tradeoff between mass production and surface quality/precission/complexity of geometry
How can casting processes be categorized?
In permanent form and lost form
Lost form:
Sand Casting
Investment Casting
Lost Foam Casting
Permanent Form:
Die Casting
Mold Casting
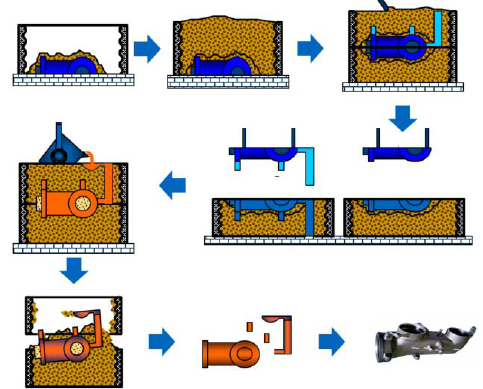
Sketch the sand casting process
Covering of one half of the mold with casting sand
Filling the box with coarse casting sand
Repeat for the other half
Join the two halves and add feeders and degassing pipes
Open boxes and take out the mold
Pour molten material and wait to solidifaction
Take part out, remove feeders, bur and degassing pipes
Why is sand casting or lost foam casting more suited for iron-based materials than mold casting or die casting?
Because mold and die casting require the material to be melted to a fully liquid phase, which is more energy expensive for ferrous alloys
Why are cooling rates for sand casting typically slower than for mold or die casting?
Due the higher heat capacity of sand when compared to metal
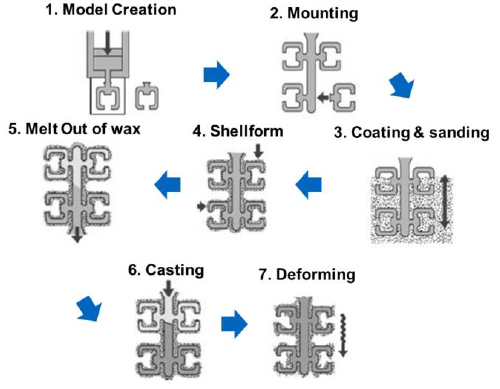
Give a process description of investment casting
Wax mold is created (and mounted together if the case)
Coating and sanding
Shellform completed with the sound around the wax positive mold
Wax is molten out
Casting
Deforming
What are the main advantages for investment casting?
High surface quality and precission
Small components realizable
Near net-shape production
What is the main difference between common sand casting and lost foam casting?
Sand casting leaves the mold used to do the form in sand untouched, while in lost foam casting the mold is burnt by the melts
What casting processes are suited for what types of materials?
All metals: sand casting, lost foam casting, investment casting
Low melting temp. alloys: die casting and mold casting
Name typical casting deffects
Undersize
Cavities
Warpage
Cold shut
Stress cracks
Inclusions
Gas porosity
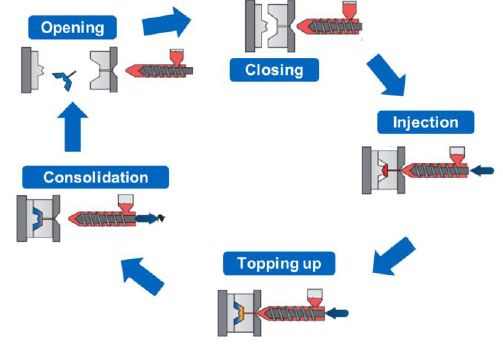
Name the process steps for injection molding
Closing
Injection
Topping up
Consolidation
Opening
What are the main differences between injection molding and extrusion?
Injection Molding: with a mold and higher pressures
Extrusion: without mold for linear components
Both of them use the same screw + temp principle
True or false? Extrusion is suited for manufacturing parts with complex geometries in all three spatial directions. Why?
False. Extrusion can only create complex geometries in 2 dimensions, since the third dimension is the extrusion direction an is therefore basically linear
What are the advantages and drawbacks for Additive Manufacturing?
Advantages:
Lightweight design
Funtional Integration
Mass customization and personalization
High complexity in geometry
Disadvantages:
Small series
Not yet standarized
Pre- and post-processing needed
Expensive systems
When does it make sense to used addtivie manufacturing as porduction process?
For small series with high mass customization and personalization needed
For lightweight design
For functional integration as extremely complex geometries
Name additive manufacturing processes used for aerospace industry
Selective Laser Melting
Electronic Beam Melting
(Fused Depositon Modelling and Stereolithography)
What are the main differences between EBM and SLM? How does this affect the production process?
SLM (Selective Laser Melting): layered melting of powdered material with laser and with no vacuum
EBM (Electronic Beam Melting): layered melting of powdered material with electron beam and with vacuum → more complex and expensive process due to vacuum but with better results