CFB 26: Signal Transduction 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Organs like the pancreas sense changes in the environment and send signals (________) to responding organs (_____).
Hormones, liver
How do hormones generate specific effects?
Binding to membrane receptors
List 4 types of hormone signaling.
Endocrine
Paracrine
Autocrine
Plasma membrane-attached proteins
When is paracrine signaling often used?
Neurobiology
When is autocrine signaling often used?
Immune cells
When is signaling by plasma membrane-attached proteins used?
Development
What are the 2 major classes of receptors that recognize hormones?
Cytoplasmic
Cell surface
What is the difference between cytoplasmic and cell surface receptors?
Cytoplasmic receptors interact with ligands that can cross the cell membrane; cell surface receptors interact with ligands outside the cell
Examples of hormones that can interact with cell-surface receptors
Amino acid derivatives, derivatives of arachidonic acid, peptide hormones
Examples of amino acid derivative hormones
Epinephrine, histamine
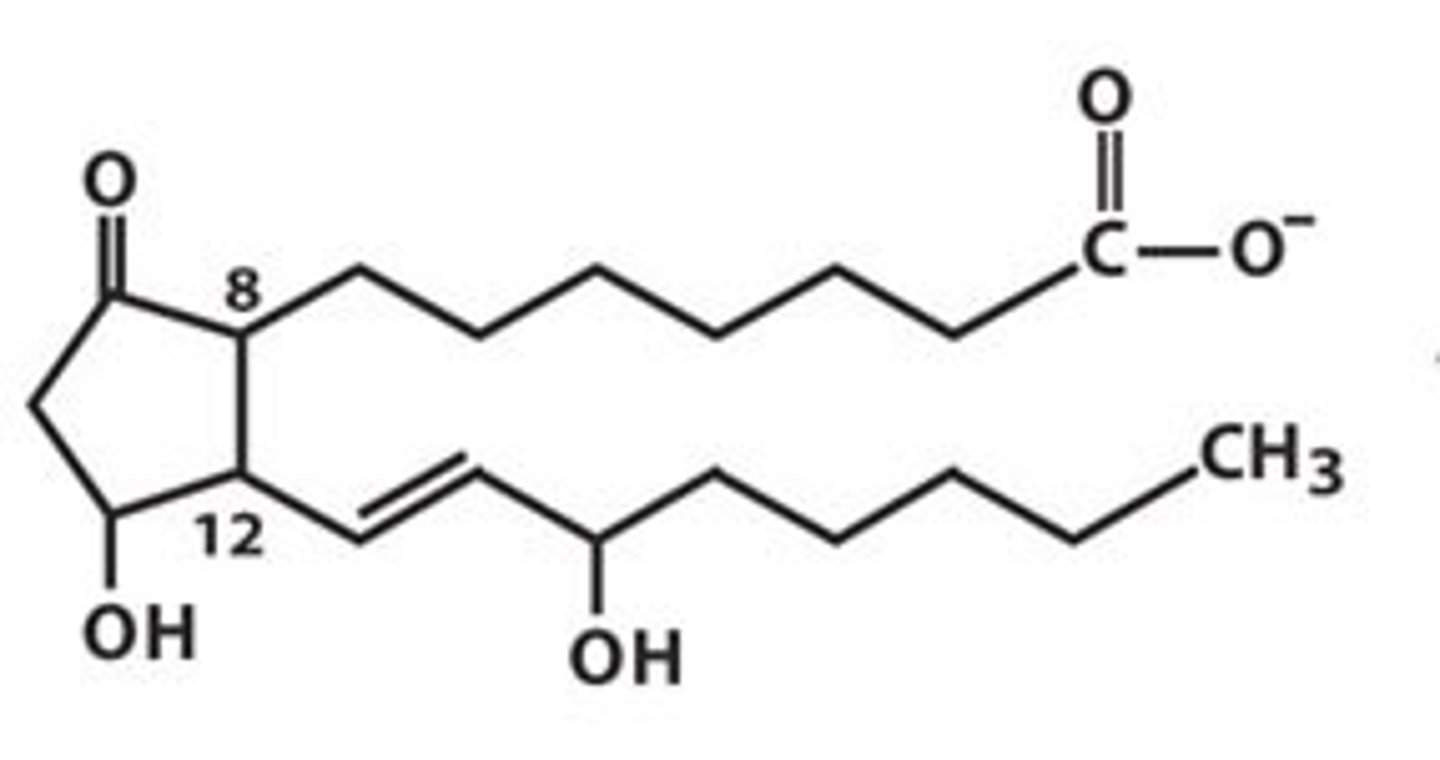
Examples of arachidonic acid derivative hormones
Prostaglandins (PGE2)
Examples of peptide hormones
FSH, glucagon, insulin
Which hormones work through cytoplasmic receptors?
Steroid hormones
Thyroxin (thyroid hormone)
What are the 3 most important features of hormones?
Time course of action
Receptors
Mechanism of action
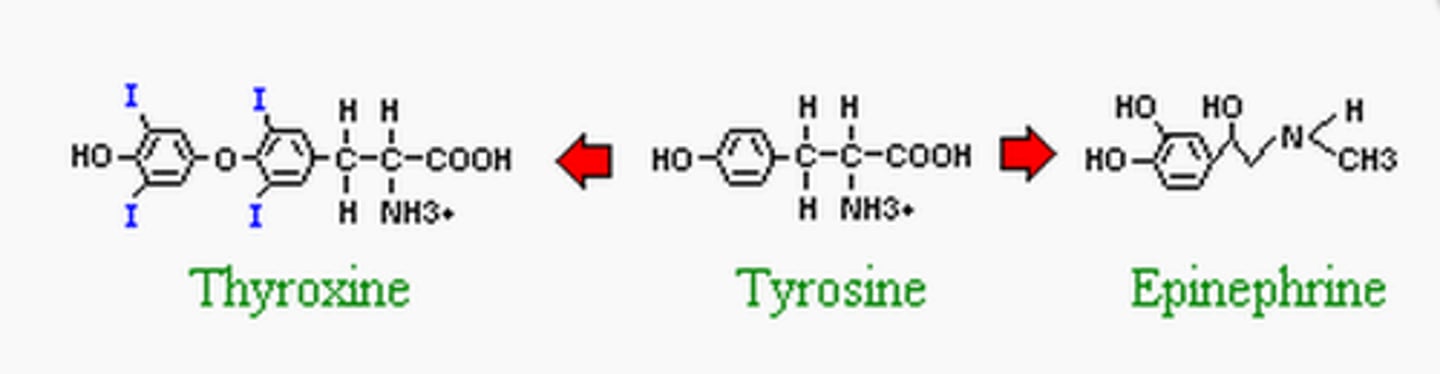
How are epinephrine and thyroxine similar?
Both derived from tyrosine
How are epinephrine and thyroxine different?
Thyroxine more hydrophobic so uses cytoplasmic receptors
Is insulin a steroid or peptide hormone?
Peptide
Insulin is made as precursor _________ and then what happens to it?
Proinsulin, cleaved
What is the function of signal sequence and connecting peptide?
Connecting peptide needed to fold protein correctly to allow disulfide bond formation
What is the precursor of prostaglandins?
Fatty acid (arachidonic acid)
What is prostaglandins' key enzyme?
Cyclooxygenase
What inhibits cyclooxygenase?
Aspirin
What is the target of aspirin?
Prostaglandins (cyclooxygenase)
Aspirin attaches an ______ group to cyclooxygenase to inactivate it.
Acetyl
What hormones use cytoplasmic receptors?
Steroid hormones (e.g. progesterone, estradiol, testosterone, thyroxine)
cAMP always has the same effects in cells.
False
What is the second messenger hypothesis?
Something generated in the cytosol in response to signal is what allows message to get transmitted from outside of cell to inside
Describe the discovery of cAMP by Sutherland.
Compared membrane-free extracts from unstimulated and stimulated cells for ability to activate phosphorylaes in a test tube
Purified substance from cytoplasm that appears after cell stimulation and activated phosphorylase when added to extract of unstimulated cells
Reconstruction of adenylate cyclase activation - realized that ___ was needed.
GTP
What is the adenylate cyclase (cAMP) cascade?
Receptor → G protein → adenylate cyclase → cAMP → Protein Kinase A
How does cAMP produce different effects in different cells?
Different cells have different substrates for PKA
T/F: All receptors that activate cAMP have similar overall structure.
True
All receptors that activate cAMP span the membrane how many times?
7
Receptors that use G proteins to signal have highly ____________ transmembrane regions.
Hydrophobic
Where does hormone bind to a GPCR?
Cell membrane
How do receptors for various hormones differ?
All have different extracellular domains
Where do G proteins bind?
Inner surface of cell membrane
Do G proteins differ among receptors that activate adenylate cyclase?
No -- same G protein, Gα
All have similar intracellular domains
What is the heterotrimer of the G protein cycle?
Inhibitory βγ subunits
GTP/GDP binding α subunits
What causes dissociation of subunits and GDP release allowing GTP to take its place?
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF)
What happens after GTP replaces GDP?
GTP then activates adenylate cyclase
What happens after GTP activates adenylate cyclase?
Gsα hydrolyzes bound GTP to GDP with the help of GAPs (GTPase activating proteins) to shut off the process
What happens to Gα upon GTP binding?
Structure change to have high affinity for adenylate cyclase
Cholera is a disease of excess __ secretion.
Cl-
Cholera toxin induces elevated ____ which causes excessive __ export by activating what?
cAMP, Cl-, cystic fibrosis chloride transporter (and then water transport follows into intestinal lumen)
What type of toxin is Cholera toxin?
ADP ribosyl-transferase
What does Cholera toxin do?
Splits NAD and attaches ADP ribose to Gsα
What does Cholera toxin block?
Gsα GTPase activity
What enzyme does caffeine inhibit?
cAMP phosphodiesterase
Caffeine blocks breakdown of ____.
cAMP
How is protein kinase A activated by cAMP?
cAMP promotes dissociation of regulatory (R) subunit and liberation of Catalytic (Cat) subunit
Other G protein G_ can couple to what different enzyme?
Gq; phospholipase C