Genetic Diagrams
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Name all the Genetic Diagrams:
- Monogenic inheritance
- Dihybrid inheritance
- Multiple alleles
- Sex linkage
- Codominance
What is a monogenic cross?
A genetic cross that involves only 1 gene
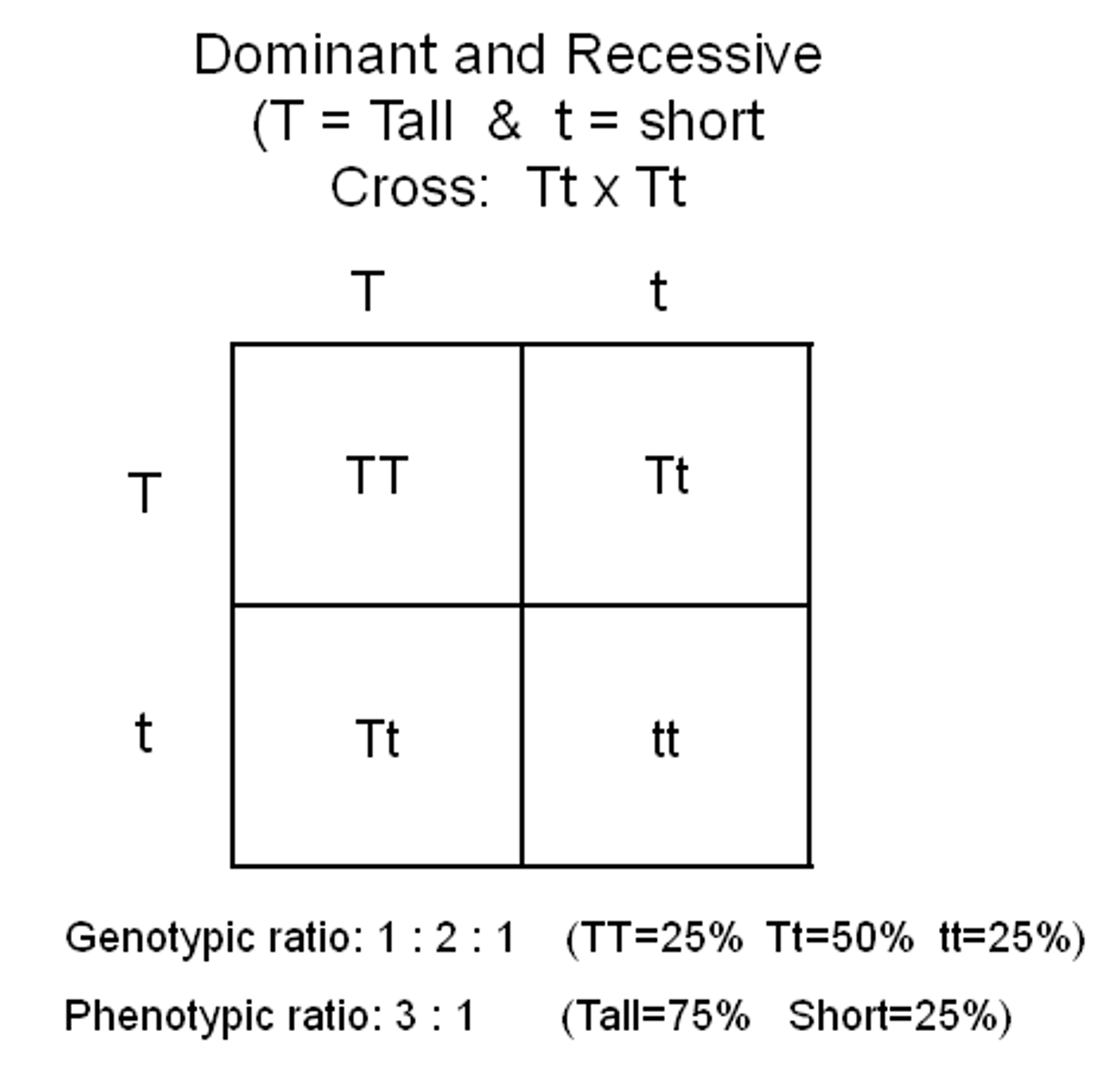
Monogenic inheritance: F1 Generation
Parental Genotypes: RR x rr
Parental Phenotypes: Round Wrinkled
Gametes produced: (circled) R R r r
F1 Genotype: (Draw a punnet square) Rr, Rr, Rr, Rr
F1 Phenotype: Round, round, round, round
Monogenic inheritance: F2 Generation
Parental Genotypes: Rr x Rr
Parental Phenotypes: Round Round
Gametes produced: (circled) R r R r
F1 Genotype: (Draw a punnet square) RR, Rr, Rr, rr
F1 Phenotype: Round, round, round, wrinkled
The F2 generation produces a 3:1 phenotypic ratio of the dominant trait (R - Round) to the recessive trait (r - wrinkled)
There is a genotypic ratio for 1:2:1 for RR:Rr:rr
What is a dihybrid cross?
A dihybrid cross is used to show the inheritance of 2 different genes, each with 2 alleles.
Dihybrid inheritance: What's the difference between a dihybrid cross to a monohybrid cross?
A cross is in a similar format to the monohybrid cross, but in a dihybrid cross it has 4 alleles, not 2
Dihybrid Inheritance Pea Example:
Y (dominant) = Yellow
y (recessive) = Green
R (dominant) = Round
r (recessive) = Wrinkled
Complete a cross between a double homozygous dominant pea (YYRR) and a double homozygous recessive pea (yyrr), commenting on the ratio of phenotypes achieved.
YYRR x yyrr
Gametes: (circled) YR yr
F1 Genotype: (Draw a punnet square 2 by 2) YyRr
F1 Phenotype: 100% Yellow Round seeds
Show a cross between 2 peas from the F1 generation, commenting on the ratio of phenotypes created.
YyRr x YyRr
Gametes: (circled) YR, Yr, yR, yr and YR, Yr, yR, yr
F2 Genotype: (Draw a punnet square 4 by 4)
F2 Phenotype:
9 Yellow Round = 1 YYRR, 2 YYRr, 2 YyRR, 4 YyRr
3 Yellow Wrinkled = 1 YYrr, 2 Yyrr
3 Green Round = 1 yyRR, yyRr
1 Green wrinkled = 1 yyrr
9:3:3:1
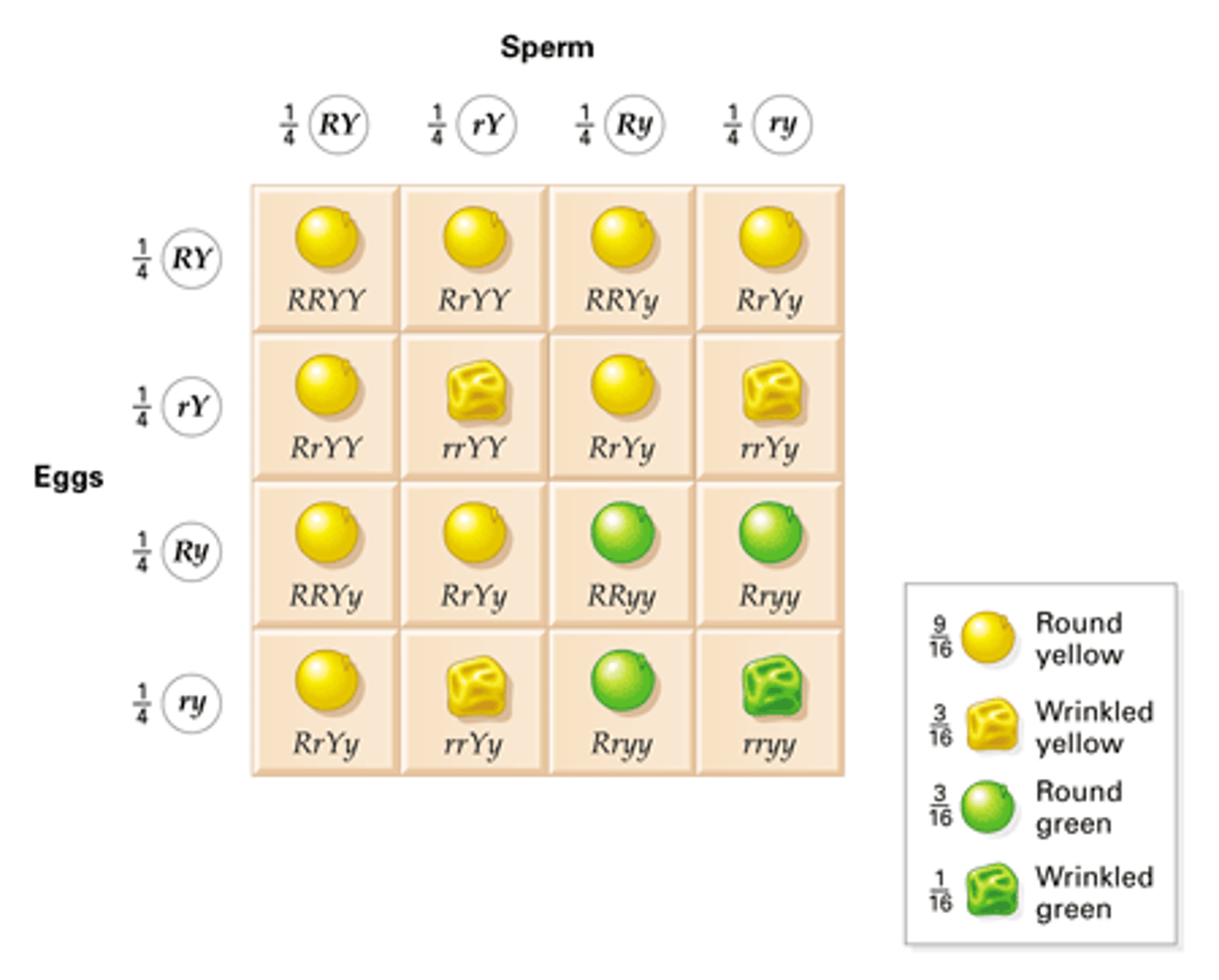
Under usual conditions, what ratio will you always get with dihybrid crosses?
9:3:3:1
Why wouldn't you get the 9:3:3:1 ratio in a dihybrid cross?
Something may have gone wrong, like epistasis, or if the double homozygous recessive (the 1 in 9:3:3:1) is disadvantages and inherits a disease and does not survive.
Multiple alleles
- A gene is a section of DNA that determines a specific characteristic
- Most genes have 2 alleles, one inherited from each parent
- However, some genes have multiple alleles. This means the genes have more than just 2 possible alleles.
- Even if a gene has more than 2 possible alleles overall, an individual can only carry 2 alleles at a time (one on each of their 2 homologous chromosomes)
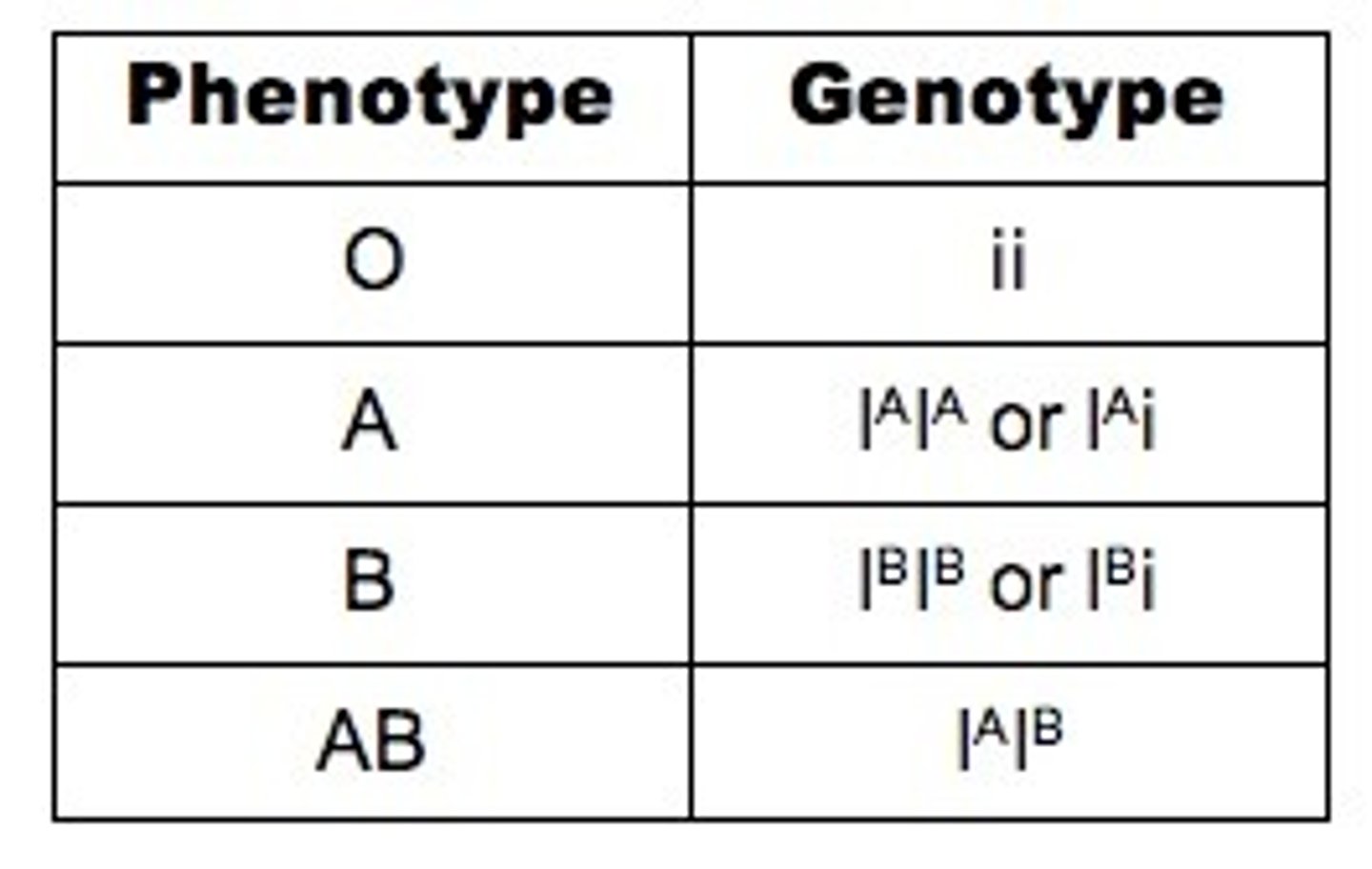
Multiple alleles: Blood
Sex Linkage
Sex linkage means the gene for a characteristic is found on a sex chromosome.
Boys
XY

Girls
XX

If a characteristic caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome (which is missing in the Y chromosome), will boys or girls more likely express it?
Boys, because they only have XY chromosomes. They cannot be carriers of a recessive disorder.
Girls have XX chromosomes, and the other X chromosome usually has the dominant allele.
Name a sex linked genetic disorder
Haemophilia
Why is haemophilia more prevalent in men?
A recessive allele codes for haemophilia, on the X chromosome. They cannot have a corresponding dominant allele on their Y chromosome, so they develop the condition.
Females whoa re heterozygous for the haemophilia coding gene are carriers. They don't suffer from the disorder, but they may pass on the allele.
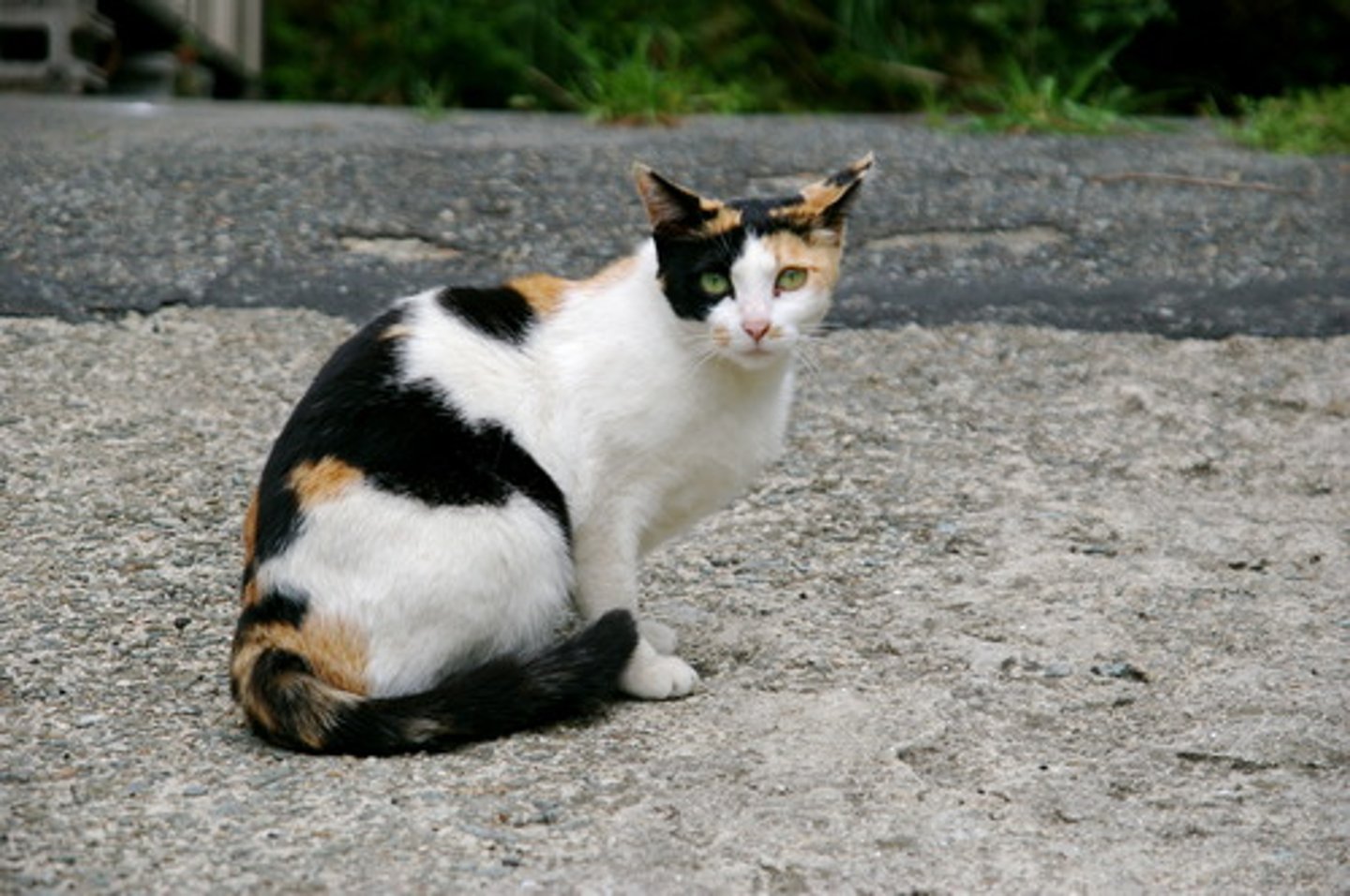
Another example of Sex Linkage
Calico cats

Codominance
Codominance occurs when 2 different alleles occur for a gene, both of which equally dominant.
As a result, both alleles of the gene are expressed in the phenotype of the organism if present.
What type of cell division occurs in sexual reproduction?
Meiosis
Genetic Variation in Meiosis
Crossing over in prophase I
Independent assortment at metaphase I and II
Random fertilisation of gametes