02.0D BIO Communities & Ecosystem Dynamics - Human Population Growth & Biodiversity (PART D)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Thomas Malthus
English Economist who believed that only war, famine, and disease could limit human population growth.
He also thought that human populations would be regulated by competition (war), limiting resources (famine), parasitism (disease), and other density-dependent factors.

Demography
The scientific study of human populations that examines characteristics of human populations and attempts to explain how those populations will change over time.

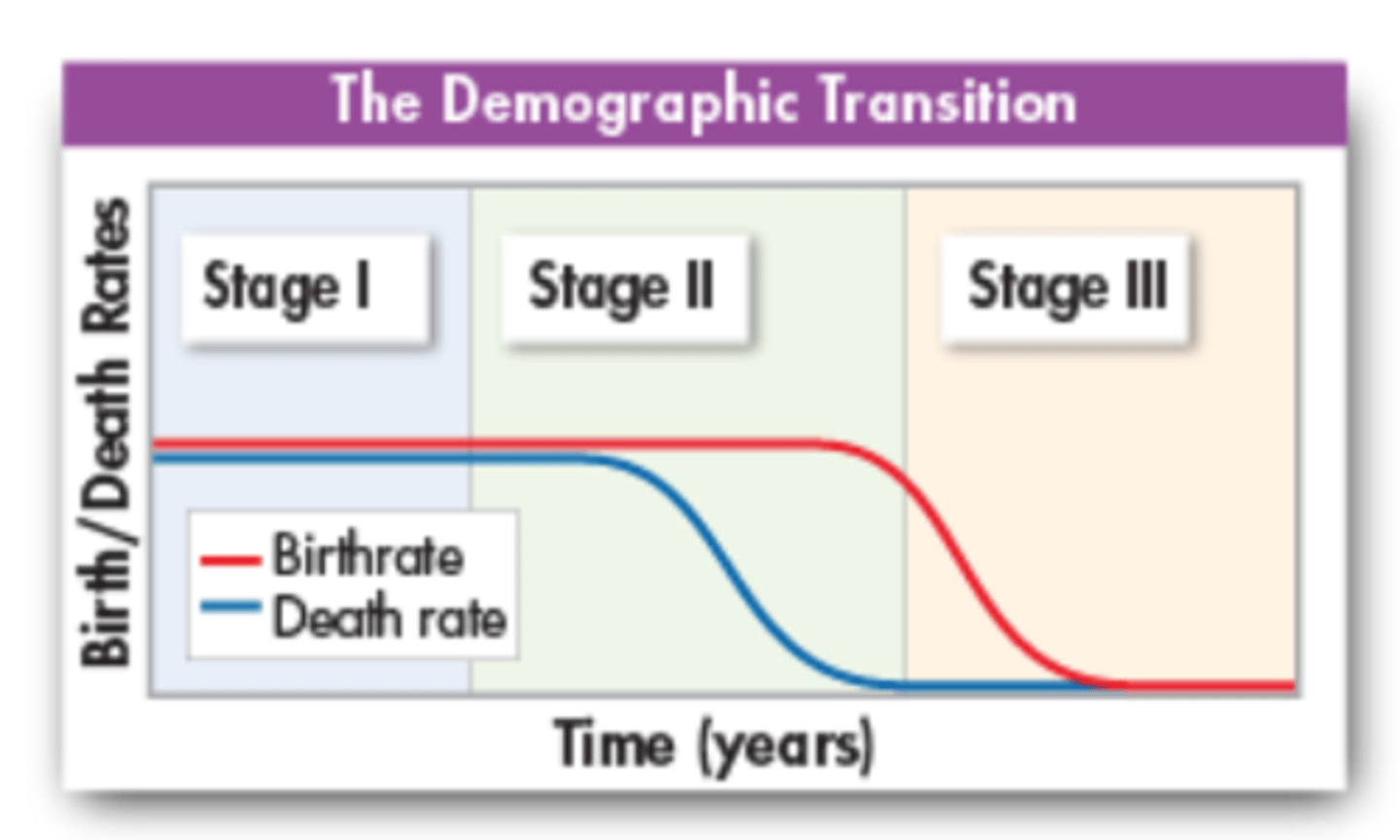
Demographic Transition
A dramatic change in a society's population from high birthrates and death rates to low birthrates and death rates.
Developed Countries
Countries that:
- Have low fertility rates
- Makeup 16% of world's population
- Use 80% of world's wealth
- Have 10-15% of the population in poverty
- Eat high on the food chain
- Fertility Rate < 2
- Negatively impact the environment due to affluence and technology
- Have a high % of older people

Developing Countries
Countries that:
- Have High fertility rates
- Makeup 84% of world's population
- Use 20% of world's wealth
- Have 45 % of population in poverty
- Have a large number of people that are malnourished
- Have a Fertility rate > 2
- Negatively impact the environment due to large population size
- Have a high % of younger people

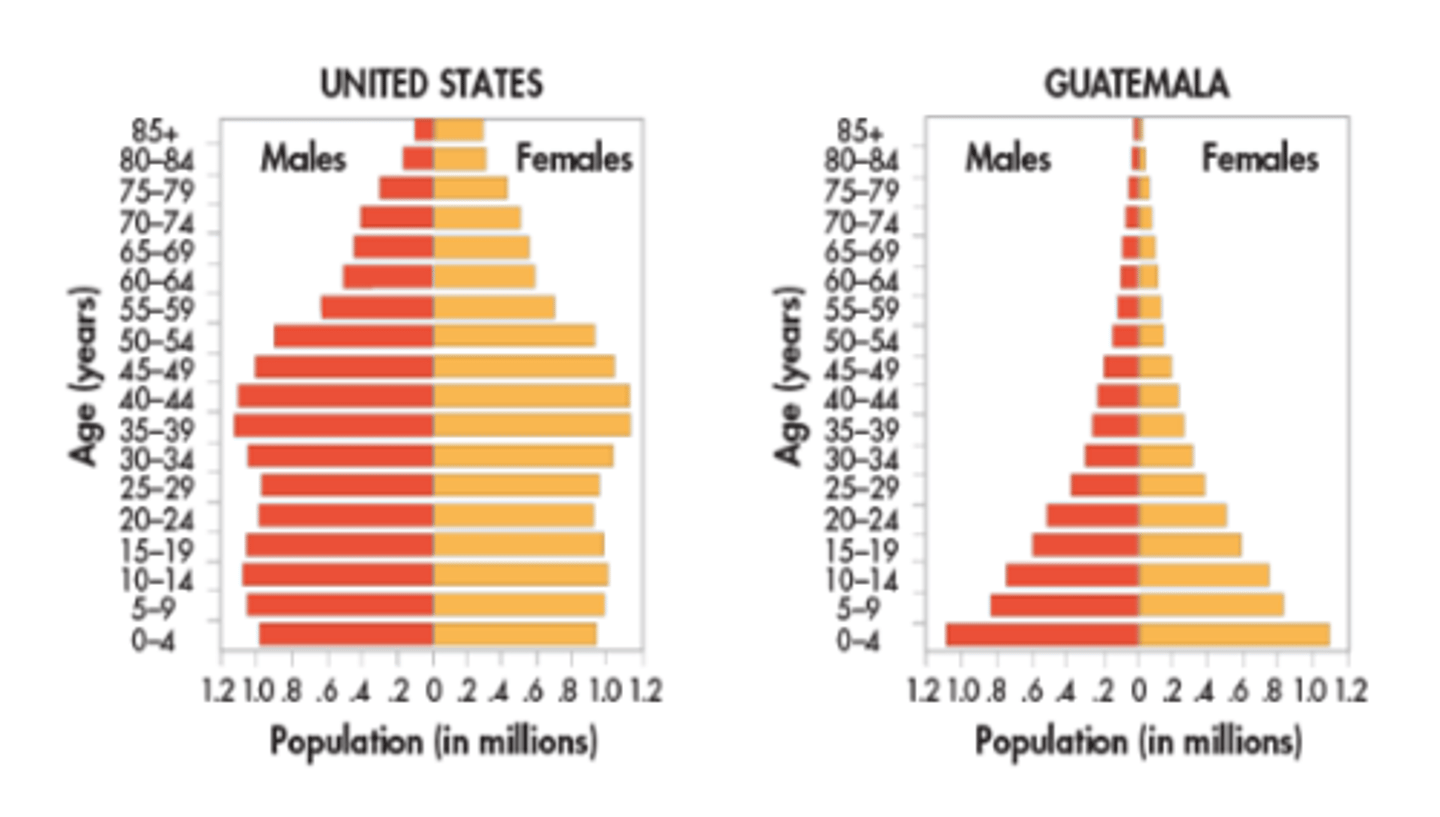
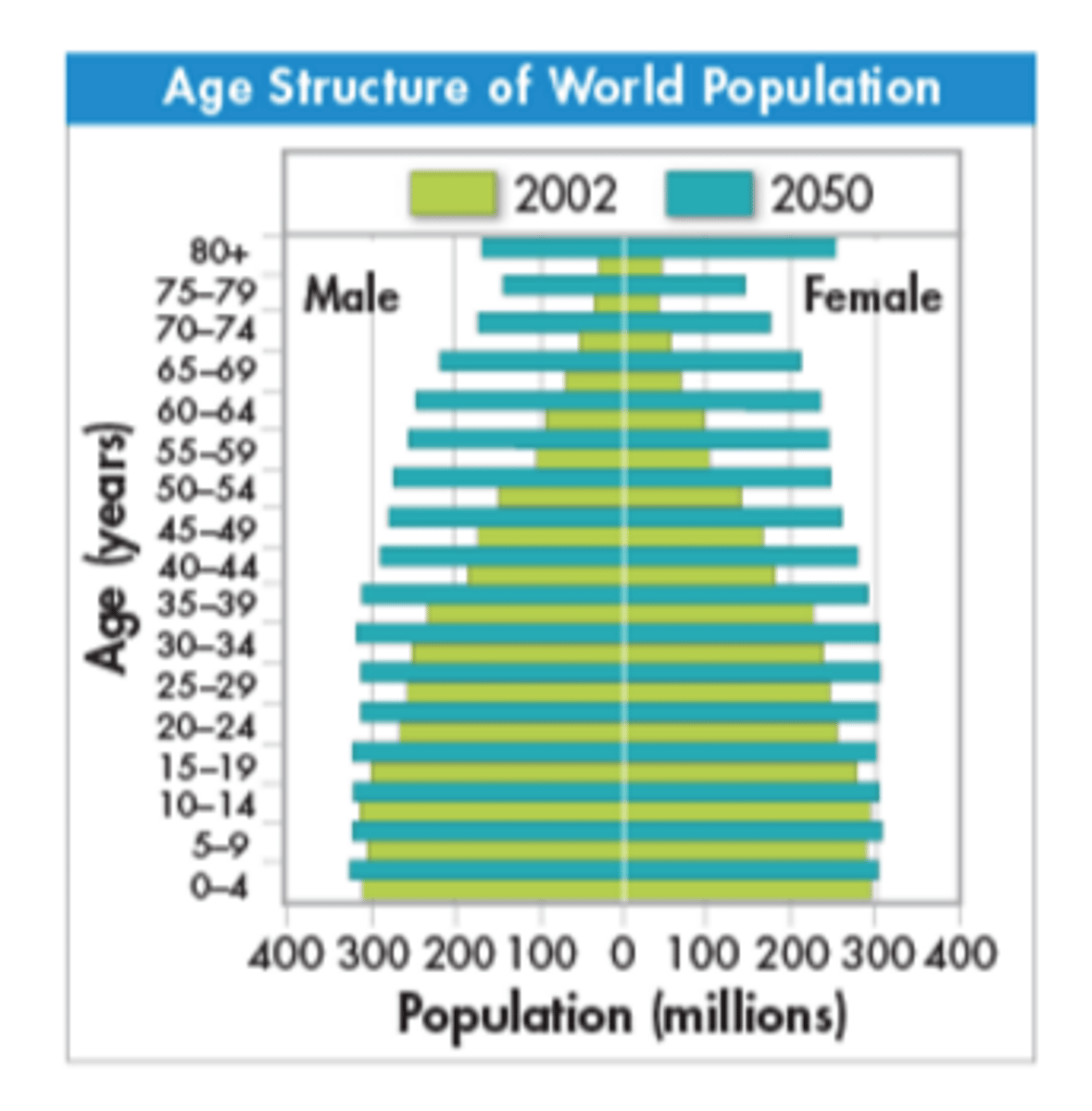
Age- Structure Diagrams
Diagrams that show the population of a country broken down by gender and age group. Used by demographers to predict needs.
Consequences of Large Population
Deforestation, loss of agriculture, resource depletion, less biodiversity, more pollution
Factors that controlled early human population growth
Food was hard to find. Predators and diseases were common and life-threatening.
Factors that contributed to decreased human death rates
Improved nutrition, sanitation, medicine, and healthcare.
Demographic Transition (Stage I)
Birth rates and death rates are both high. In the U.S. this stage occurred prior to the industrial revolution.
Demographic Transition (Stage II)
Advances in nutrition, sanitation, and medicine lead to lower death rates. Birthrates remain high for a time, so births greatly exceed deaths and the population increases exponentially.
Demographic Transition (Stage III)
As the level of education and living standards rise, families have fewer children and the birthrate falls; population growth slows.
Demographic Transition (Completed)
Birthrate meets the death rate, and population growth stops.
Population pyramid
Another name for an age-structure diagram.
Future Population Growth
Current data suggest that global human population will grow more slowly over the next 50 years than it grew over the last 50 years. Because the growth rate will still be higher than zero in 2050, our population will continue to grow.
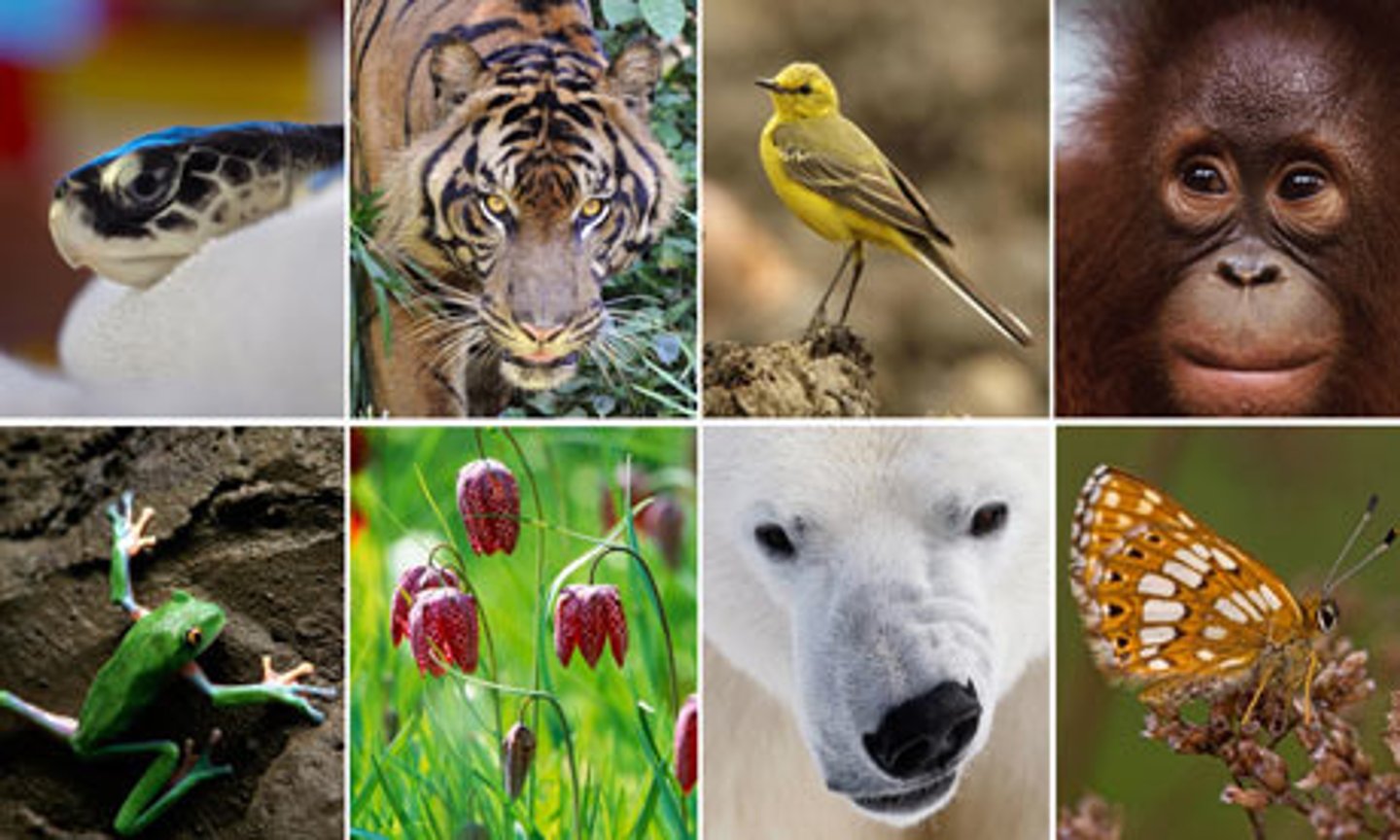
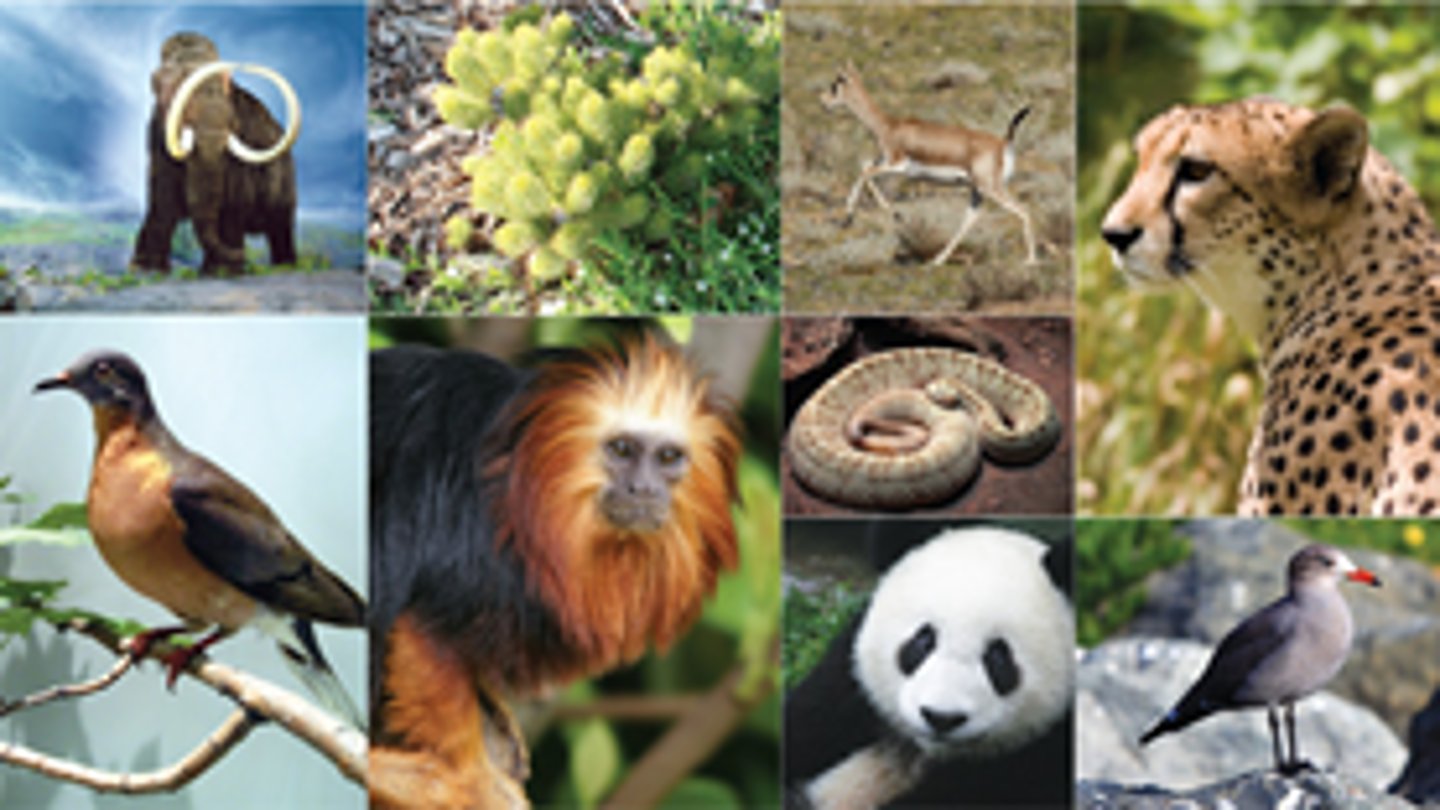
Biodiversity
The total of all the genetically based variation in all organisms in the biosphere. Three types include: ecosystem, species, and genetic diversity

Ecosystem Diversity
Refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere.
Species DIversity
The number of different species in the biosphere, or in a particular area.

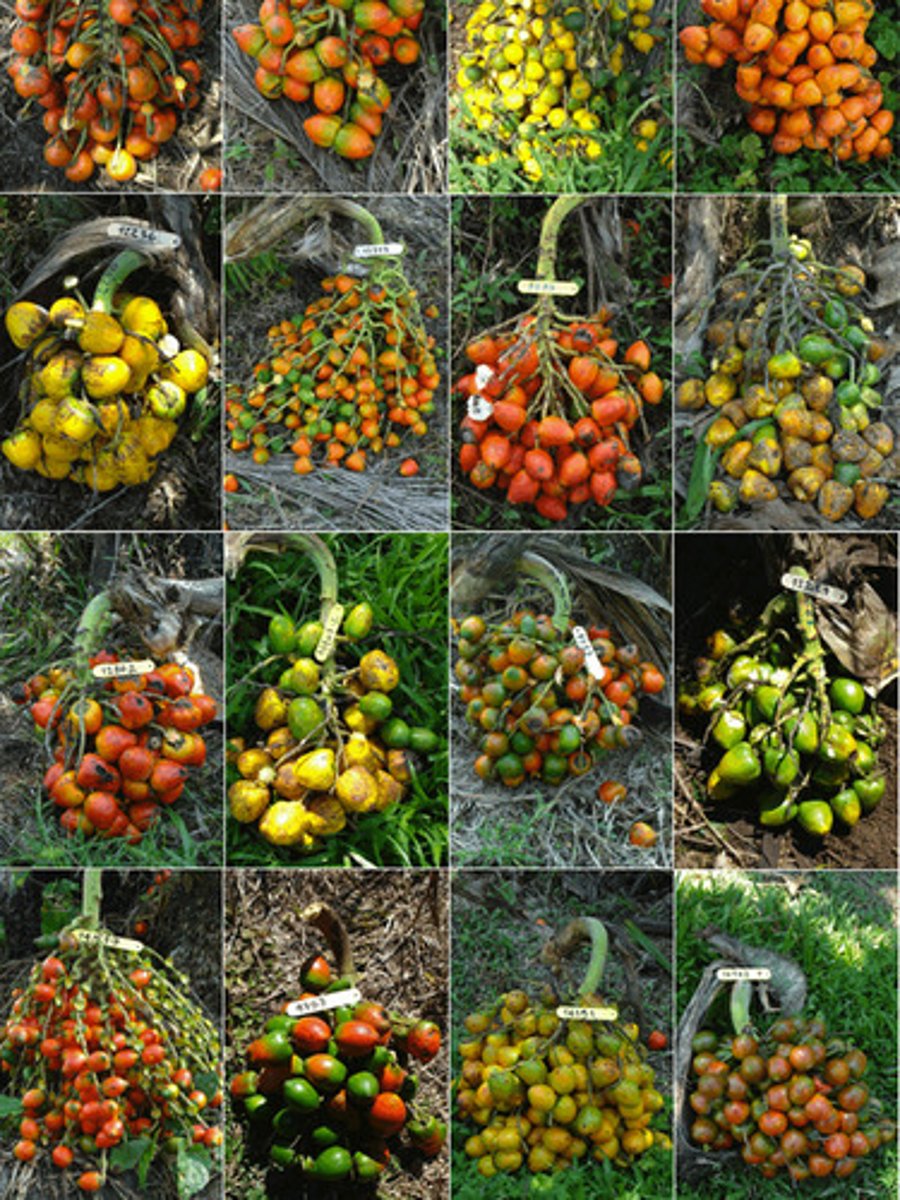
Genetic Diversity
Can refer to the sum total of all different forms of genetic information carried by a particular species, or by all organisms on Earth.

Threats to Biodiversity
Includes altering habitats, hunting, introducing invasive species, releasing pollution into food webs, and contributing to climate change.
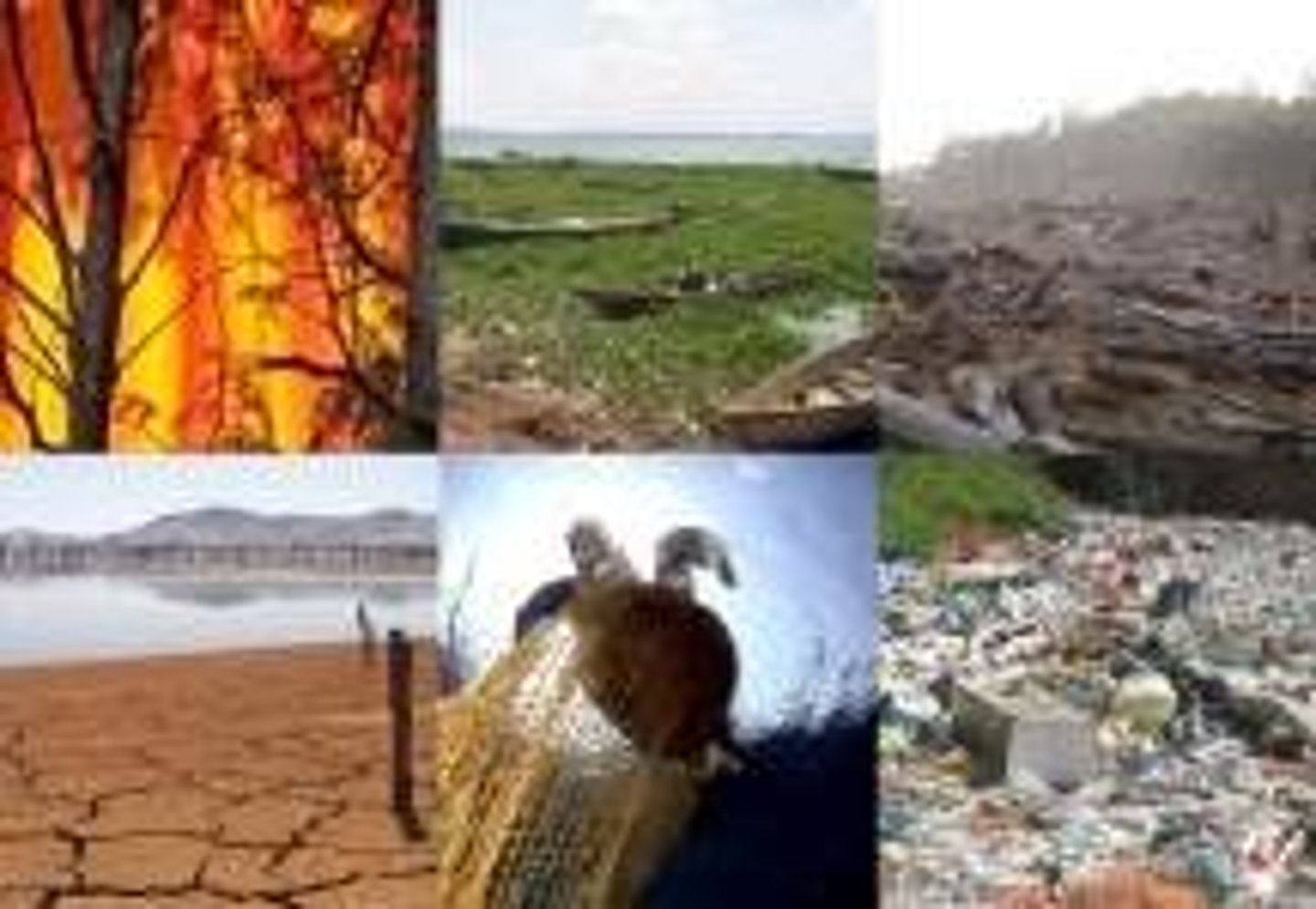

Altered Habitats
When natural habitats are eliminated for agriculture or for urban development, the number of species in those habitats drops, and some species may become extinct.
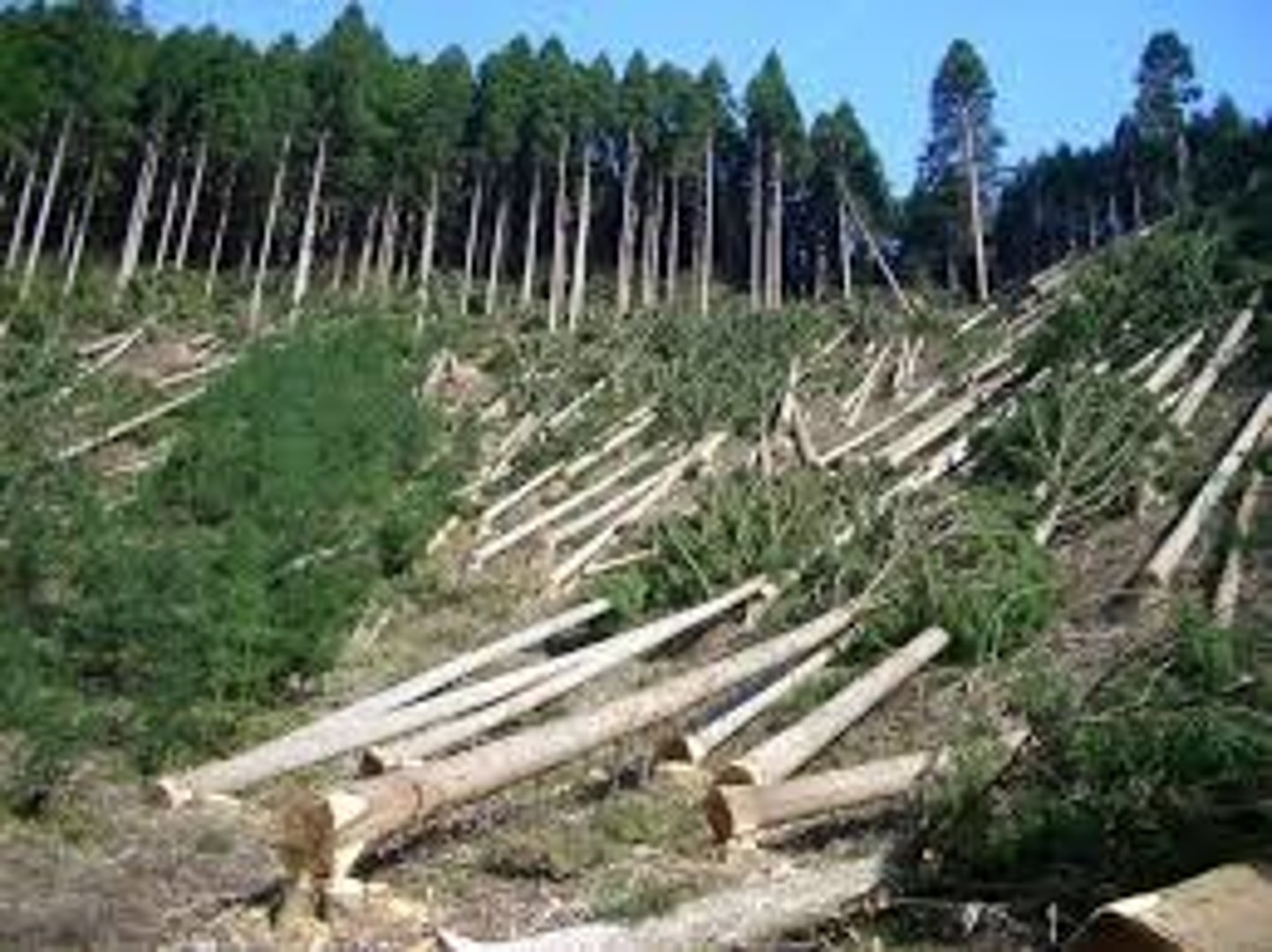

Habitat Fragmentation
A process that splits ecosystems into fragments. For example - deforestation in Florida leading to islands; putting a road through a forest.

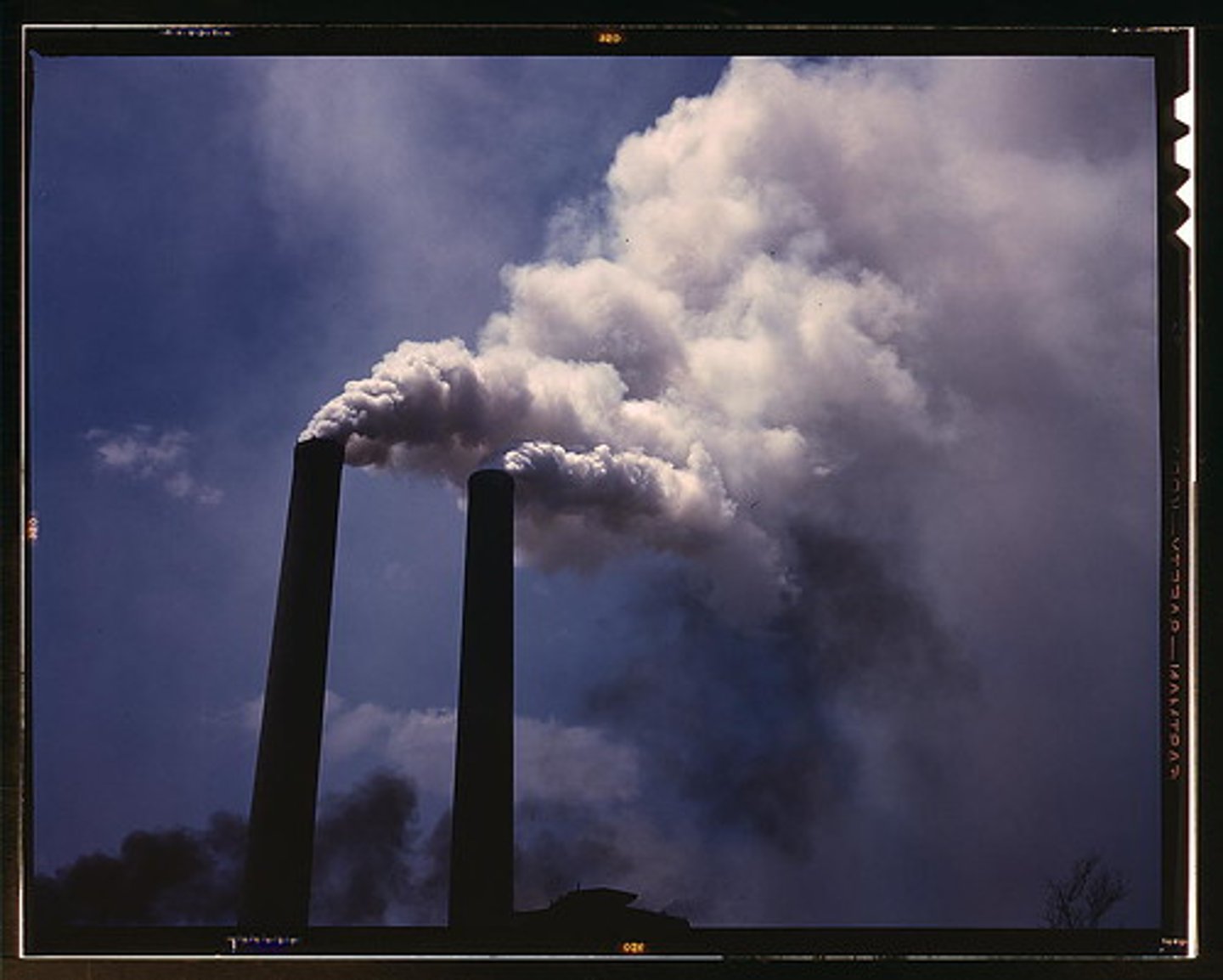
Pollution
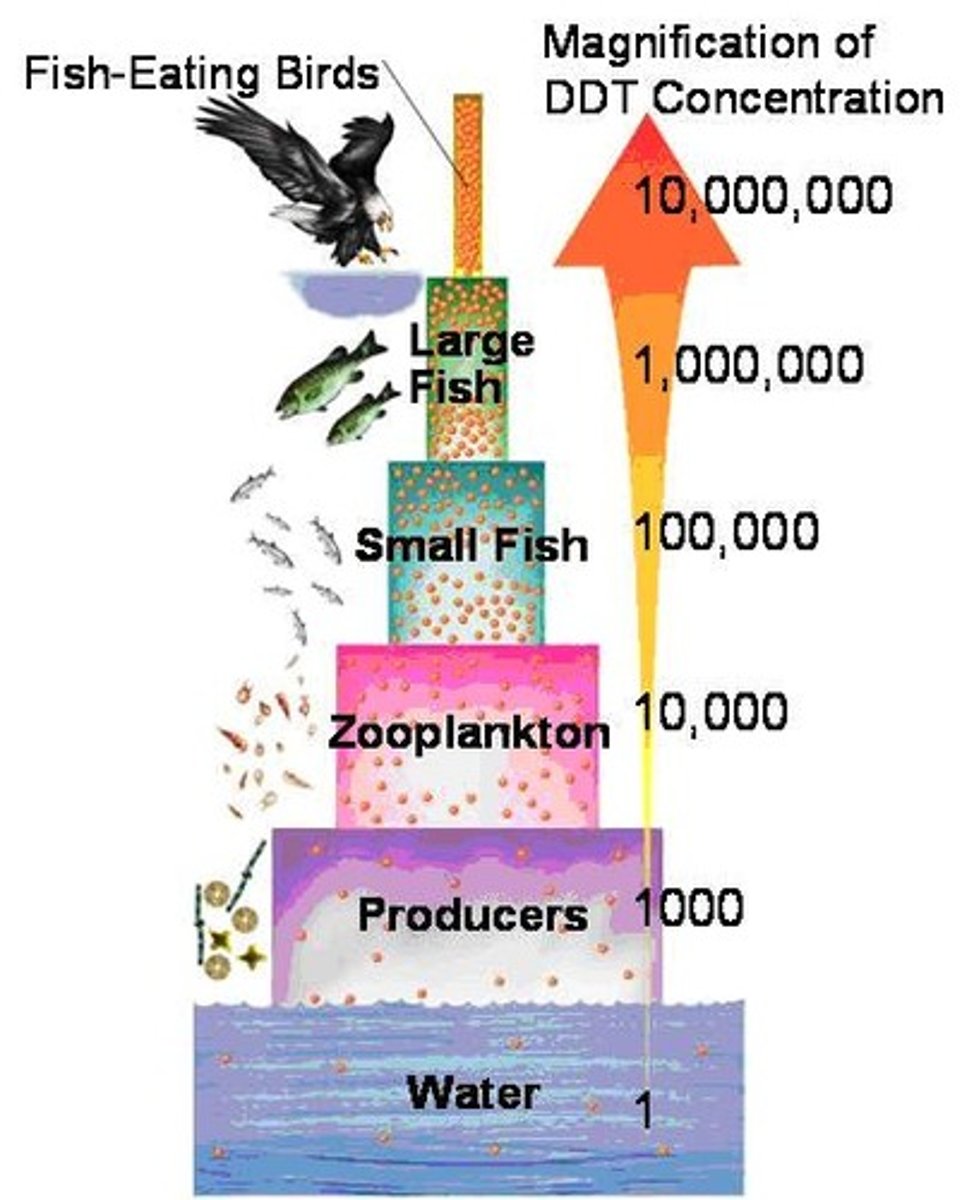
DDT, for example, prevents birds from laying healthy eggs.
Acid rain places stress on land and water organisms.
Increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is dissolving in oceans, making them more acidic, which threatens biodiversity in marine ecosystems.

Biological Accumilation
A process in which concentrations of harmful substances like DDT or other pollutants INCREASE in organisms over time.
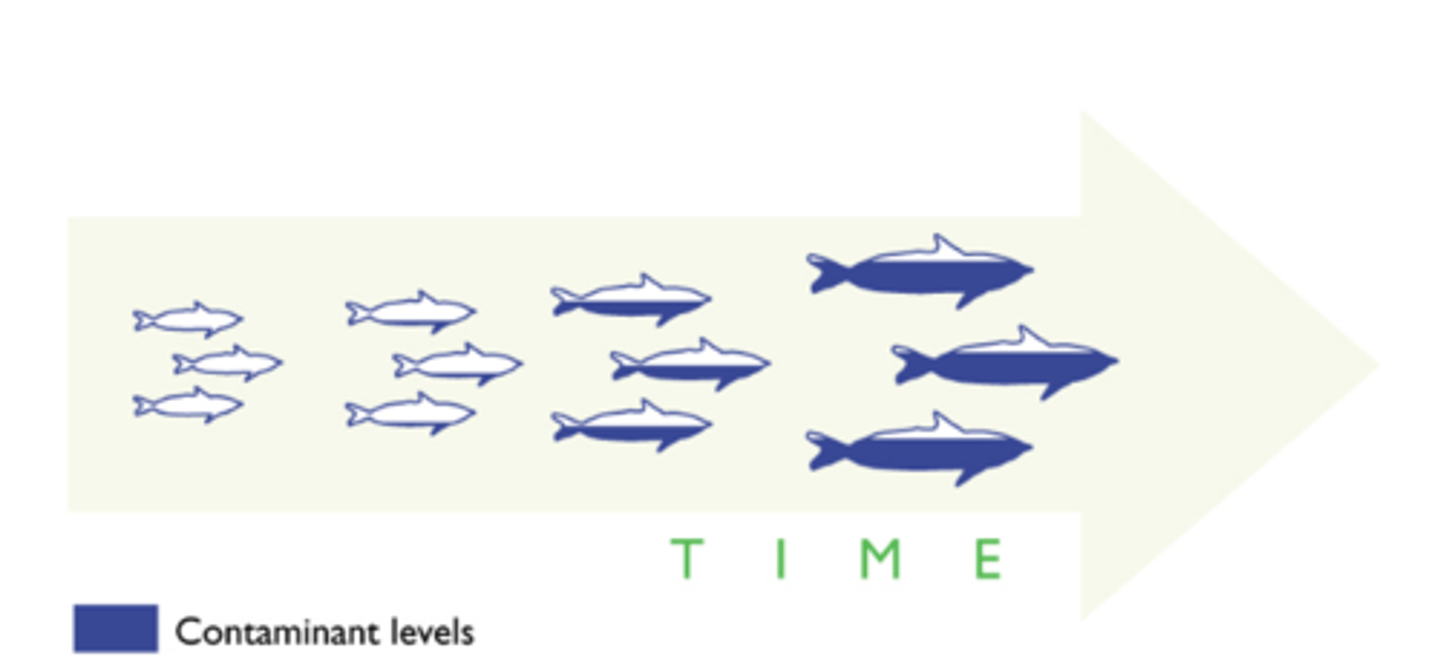
Biological Magnification
A process in which concentrations of harmful substances increase in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain or food web. Affects the entire food web, although the top-level carnivores are at the highest risk.
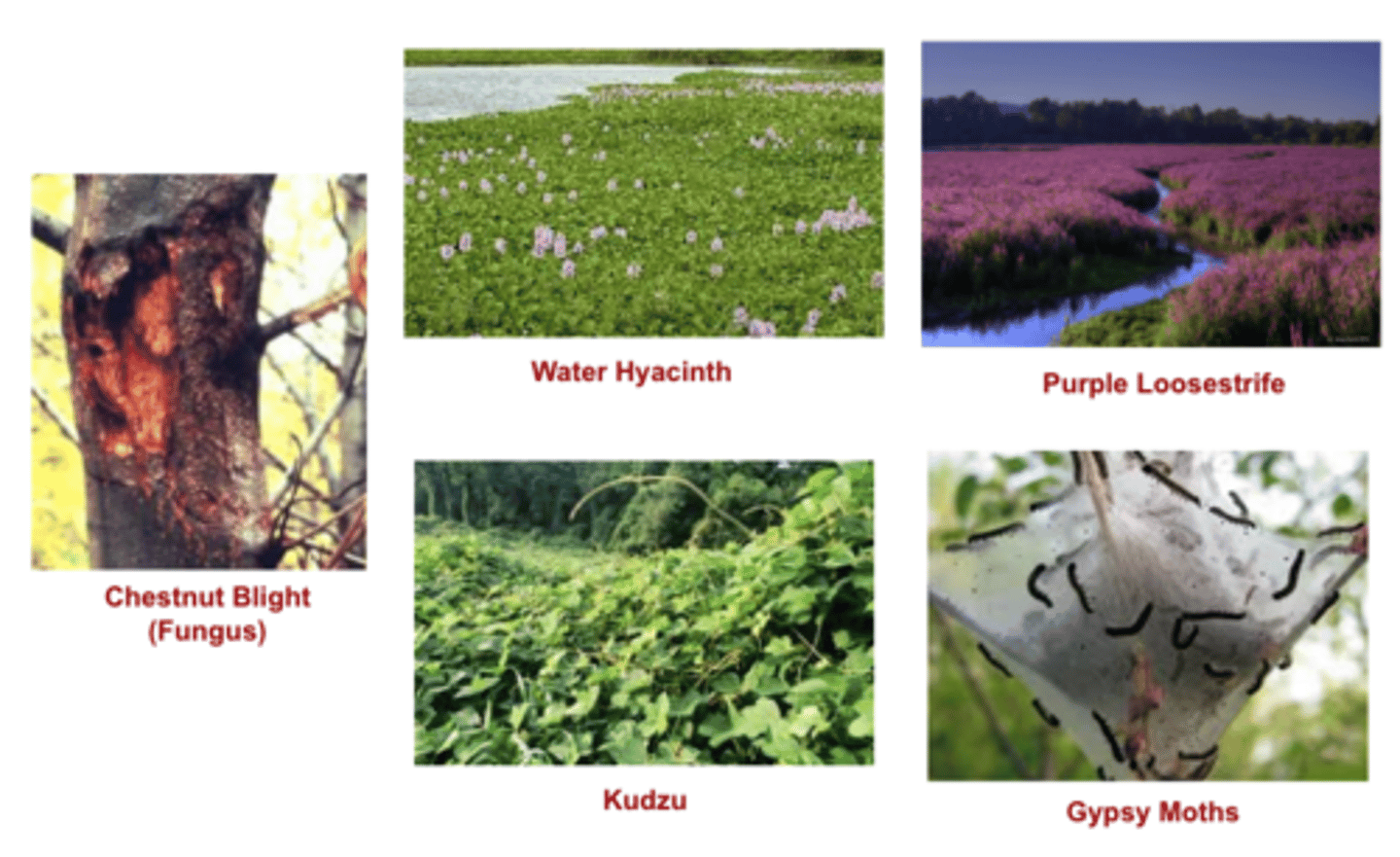
Introduced Species / Invasive Species
Species reproduce rapidly because their new habitat lacks the parasites and predators that control their population "back home". (Australian Rabbit, Hyrdrilla, Kudzu vine, etc)

Conservation
Efforts to protect individual species, preserve habitats and ecosystems, and make certain that human neighbors of protected areas benefit from participating in conservation efforts.