T11 Histology of Cartilage & Bone
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
osteoarthritic knee characteristic
cartilage tear
joint soft tissue components
cartilage, ligament, synovium
synovium function
secrete fluid that lubricate joint
cartilage types
fibrocartilage, hyaline, elastic
cartilage characteristic
firm and resilient connective tissue
cartilage composition
chondroblast, chondrocyte, extracellular matrix, type 2 collagen, ground substance
cartilage vascular/avascular
avascular
cartilage function
support soft tissue, formation and growth of long bone, durability of articular joints
chondroblast - what, location, function
progenitor of chondrocyte; border between perichondrium and matrix; produce type 2 collagen and ECM
perichondrium
CT lining cartilage mass
chondrocyte - what, location, function
mature cartilage cell; inside lacuna; produce type 2 collagen and ECM
what surrounds chondrocytes
territorial matrix
chondrogenesis types
appositional (from perichondrium), interstitial (from within cartilage)
appositional growth
chondroblast divide into chondrocyte and secrete new matrix to add cartilage beneath surface of perichondrium
perichondrium layer is site of what
chondrogenesis
what gene controls perichondrium differentiation
Sox9
interstitial growth - when, where
early hyaline cartilage formation, endochondral ossification, when still have mesenchyme; inside cartilage mass or articular cartilage or epiphyseal plate of long bone
articular cartilage lacks
perichondrium
interstitial growth process
mesenchyme differentiate into chondroblast > secrete ECM to form lacunae and become chondrocytes > divide to form isogenic groups > form own lacunae and spread apart
hyaline cartilage - components, location
type 2 collagen, GAGs, proteoglycan; articular surface, epiphyseal plate, respiratory
elastic cartilage - components, location
type 2 collagen, elastic fiber; ear pinna, epiglottis, eustachian tube
fibrocartilage - components, location
type 1 and 2 collagen, dense regular CT; IV disc, TMJ joint, pubic symphysis, insertion of tendon and ligament
hyaline cartilage characteristic
hydrated, allow matrix to respond to pressure loads (resilient)
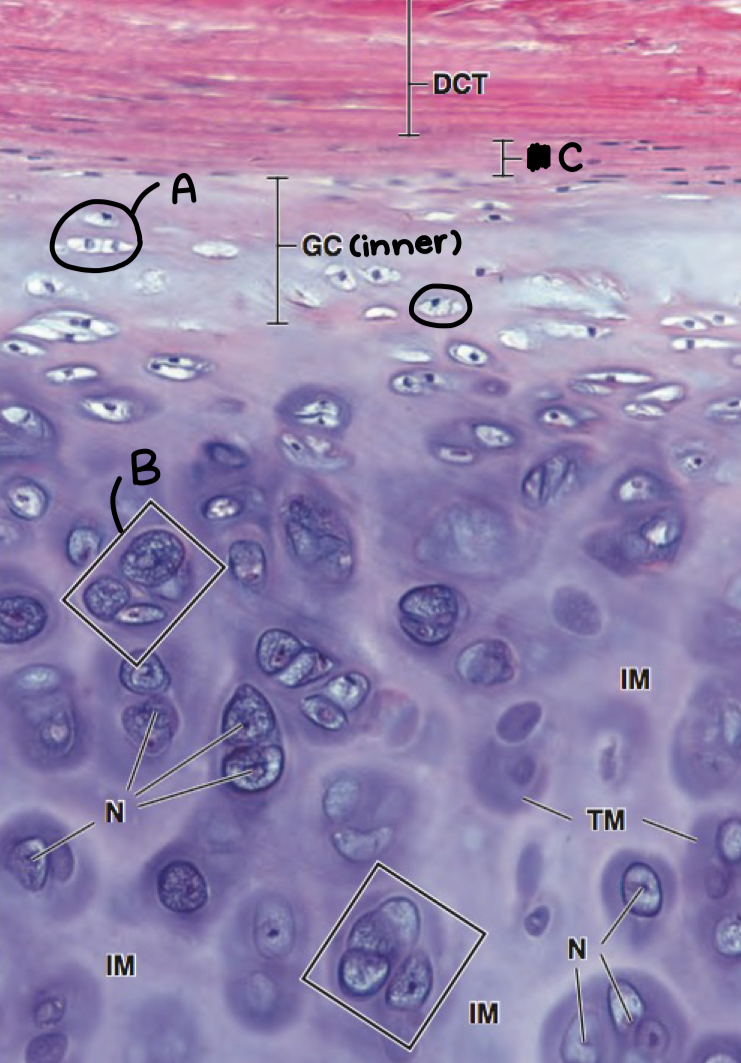
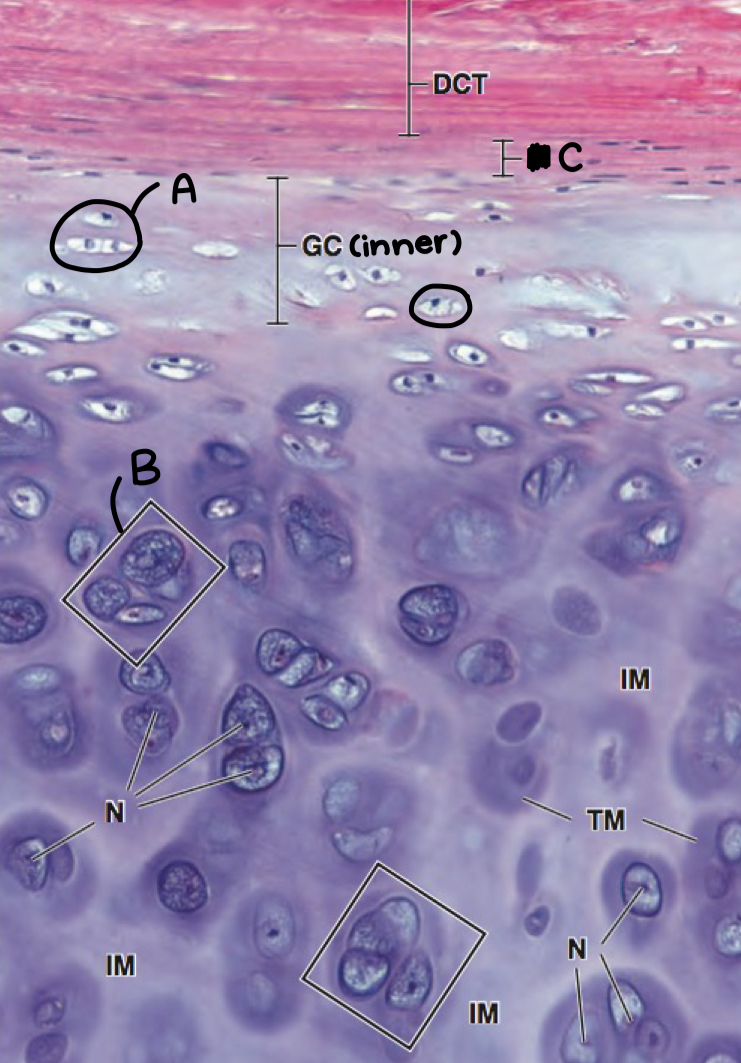
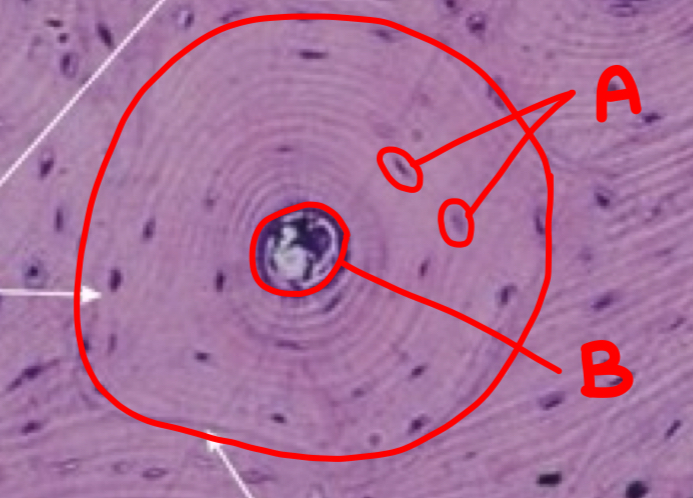
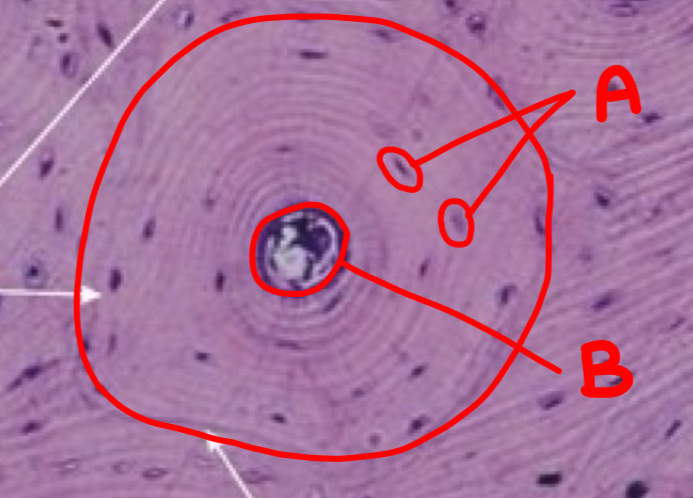
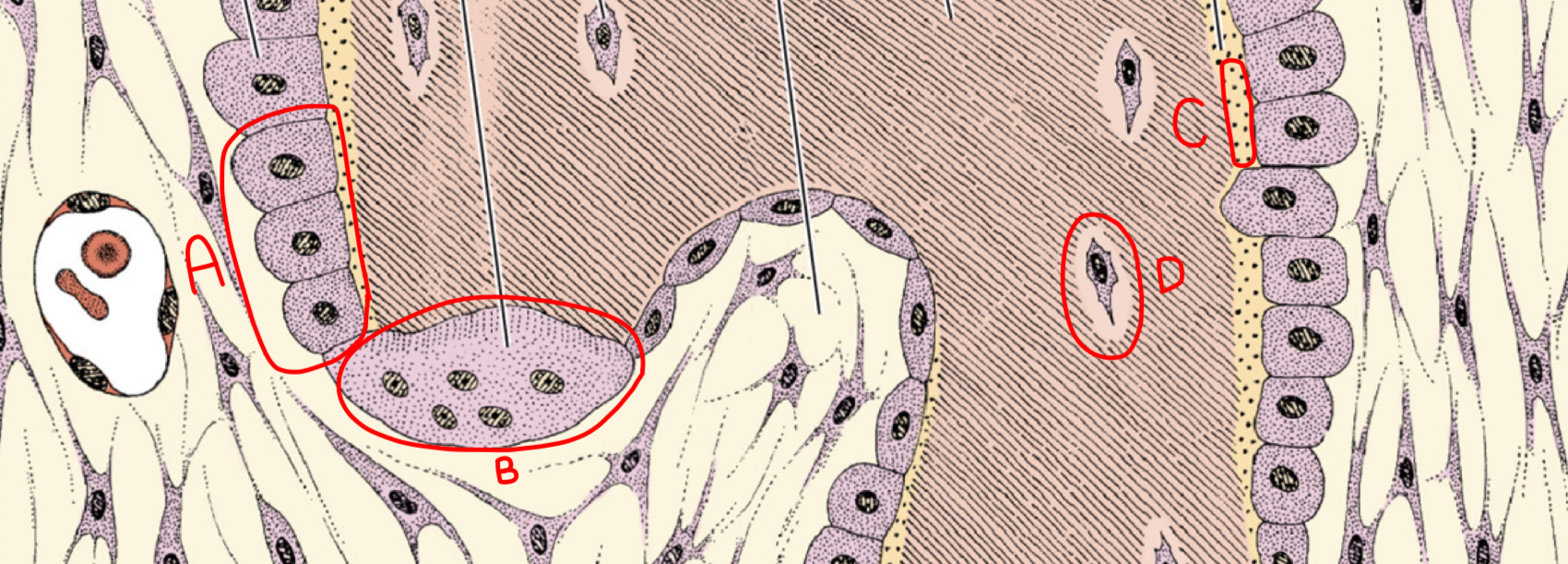
what is a and what morphologic characteristic says so
chondroblast; no lacuna
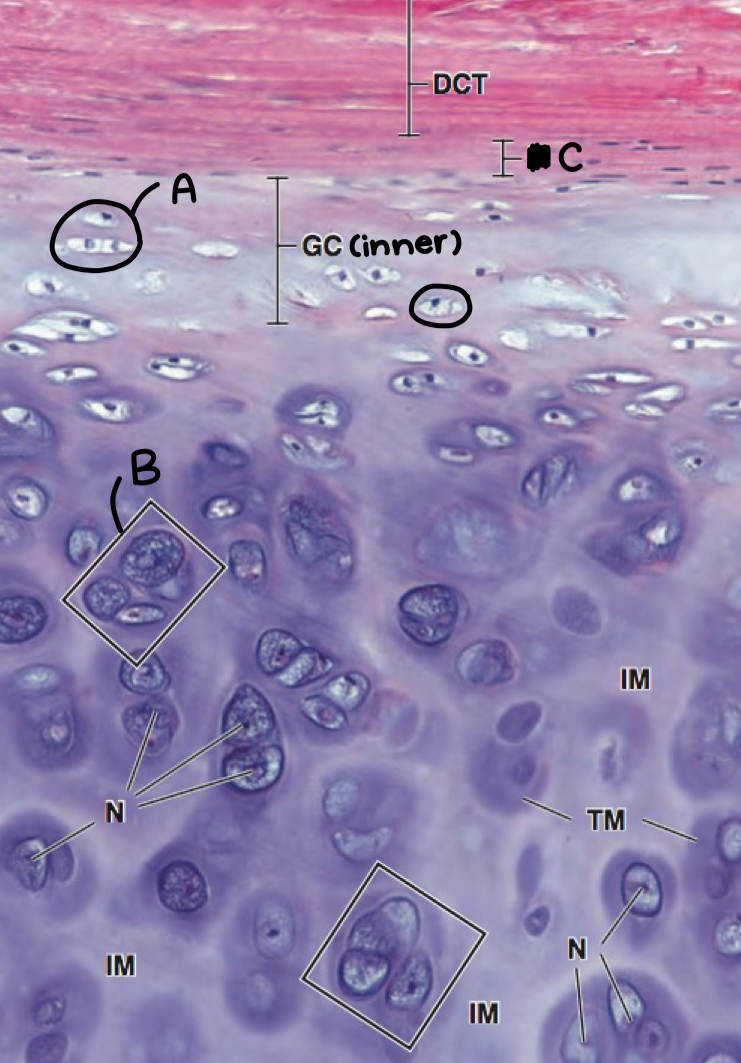
what is b
isogenous chondrocyte
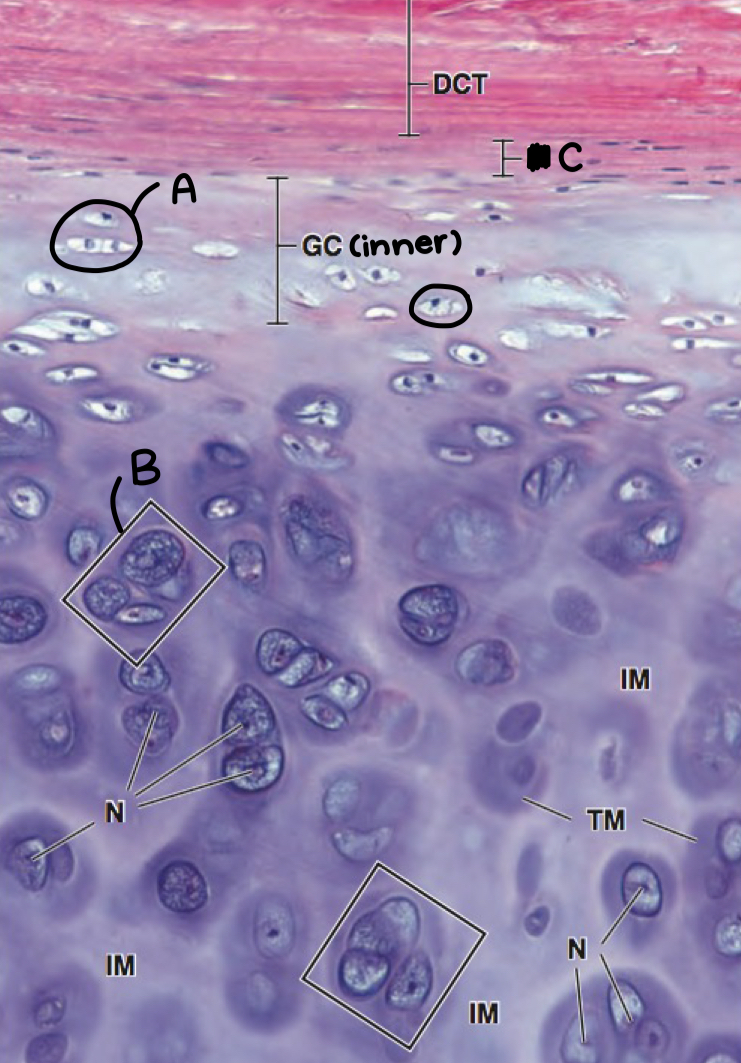
what is c
perichondrium
hyaline cartilage calcification or no
calcification
elastic cartilage calcification or no
no
what cartilage
hyaline cartilage
what cartilage
hyaline cartilage
what cartilage
elastic cartilage
what type of cartilage doesn’t have perichondrium
fibrocartilage
morphology of fibrocartilage
row-like chondrocyte
what cartilage
fibrocartilage
cartilage repair after injury
limited capability due to avascularity (stops but can’t reverse injury)
hyaline cartilage calcification occurs when
endochondral ossification, aging
bone components
cell + matrix + periosteum, endosteum
bone functions
support; protect; reservoir of calcium, phosphate; lever system
bone types
lamellar, woven
lamellar bone
osteon, haversian system, most common, compact and cancellous
osteon/haversian system
concentric lamellae around canal containing blood vessels, nerves, loose CT
cement line
collagen-rich outer border of osteon
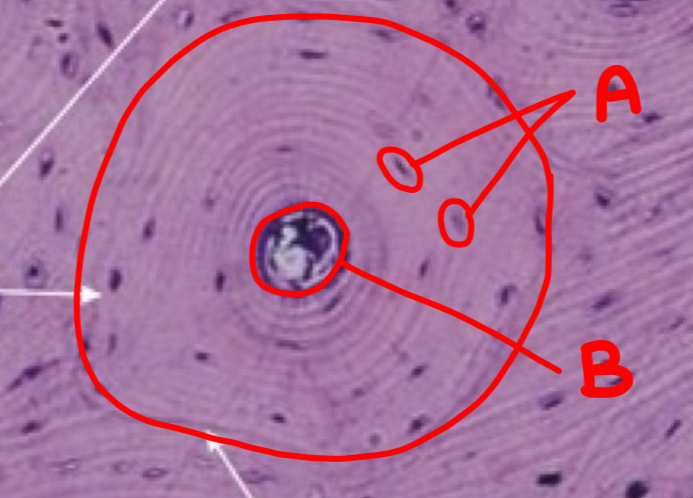
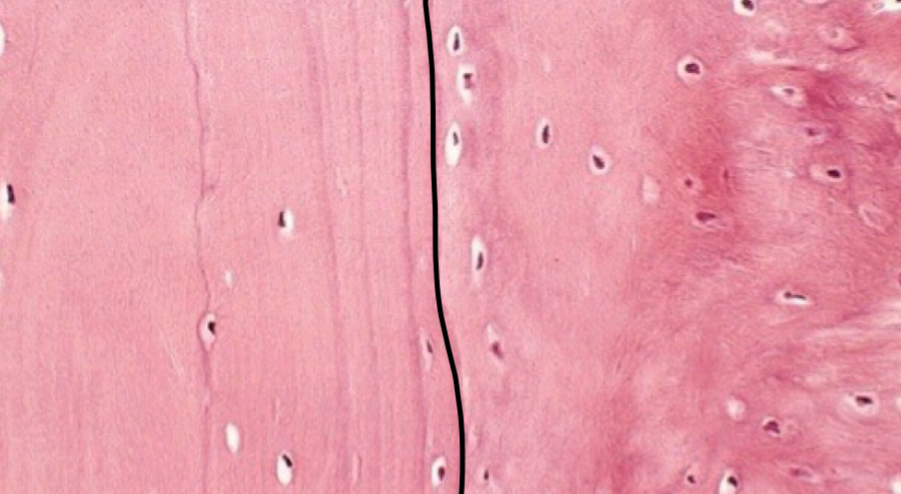
what type of bone is depicted and what is inside the circle
lamellar bone; osteon
what is a
osteocyte
what is b
haversian canal
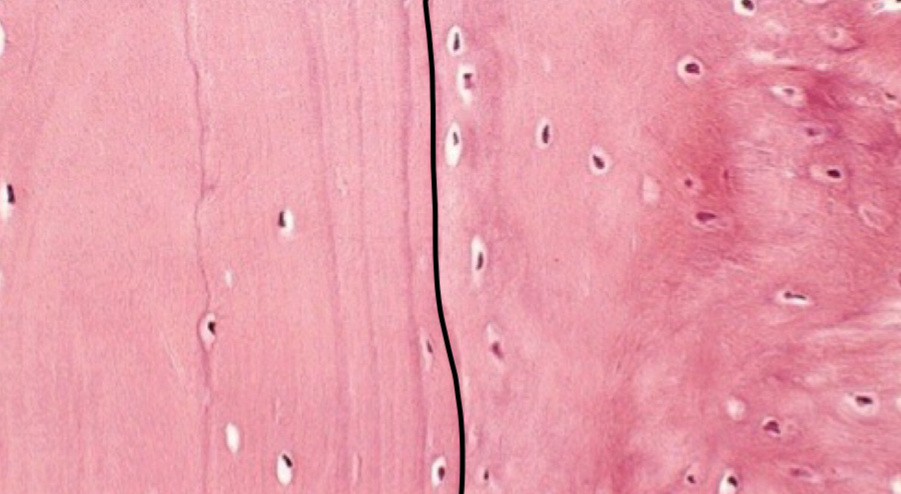
what cell has extended cytoplasmic processes and what are the processes called
osteocyte; canaliculi
what is the function of the central canal in lamellar bones
communicate with marrow cavity through transverse perforating or volkmann canals
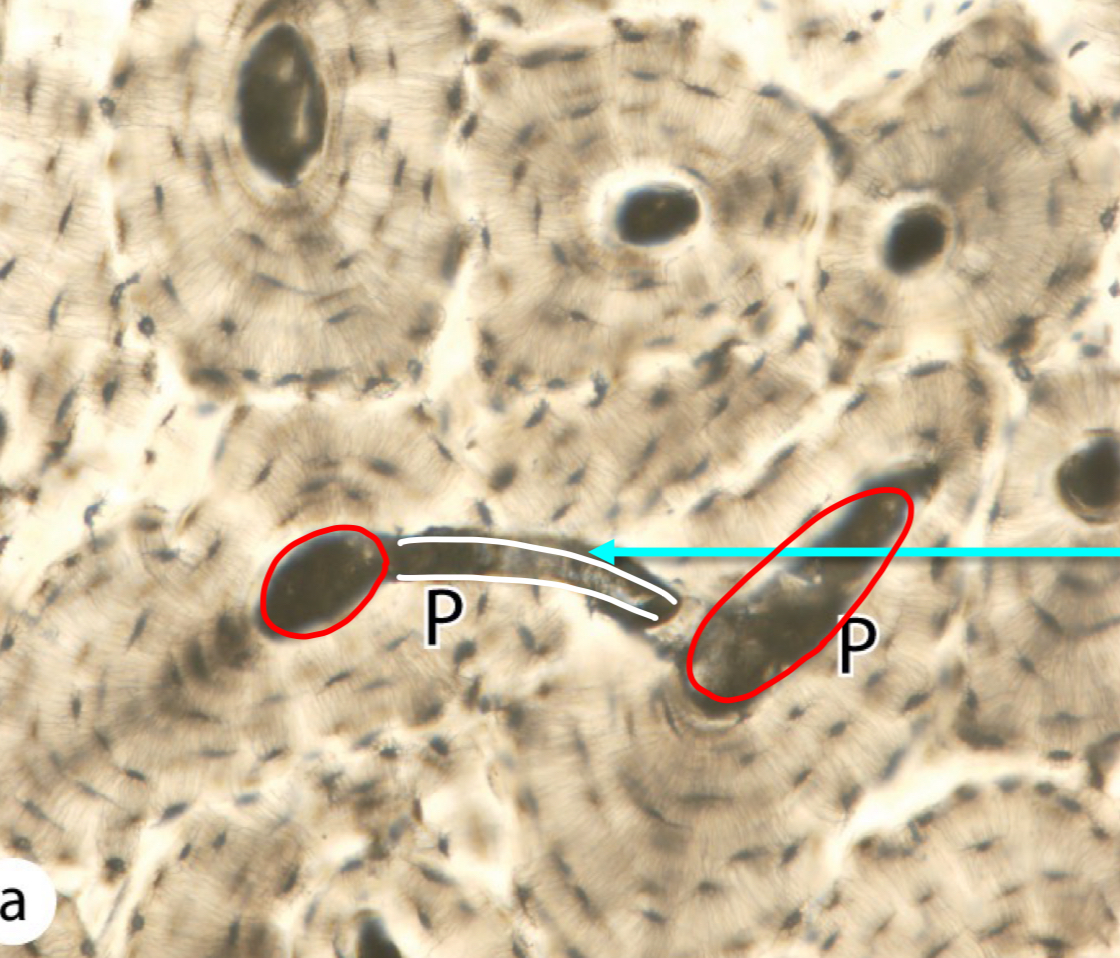
what is circled in red
haversian canal
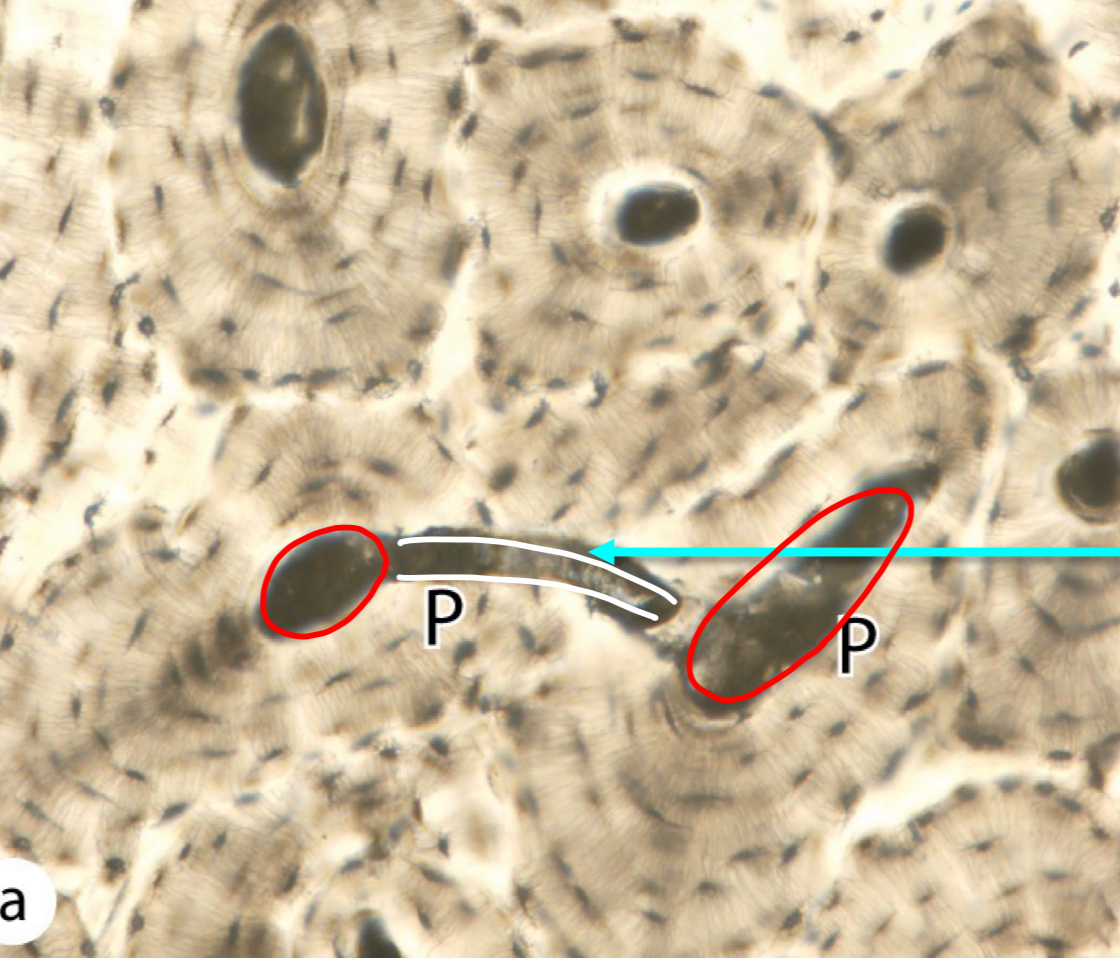
what is outlined in white
volkmann canal
woven bone characteristic
newly formed, non-lamellar, random type 1 collagens, temporary
woven bone present when
embryonic development, fracture repair
what bone is depicted on the left
lamellar bone
what bone is depicted on the right
woven bone
compact (cortical) bone - percentage, characteristics
majority; haversian system, concentric lamella, osteocyte in lacuna
cancellous (trabecular, spongy) bone - percentage, characteristics
minority, concentric lamella but not osteon
what type of bone
cancellous
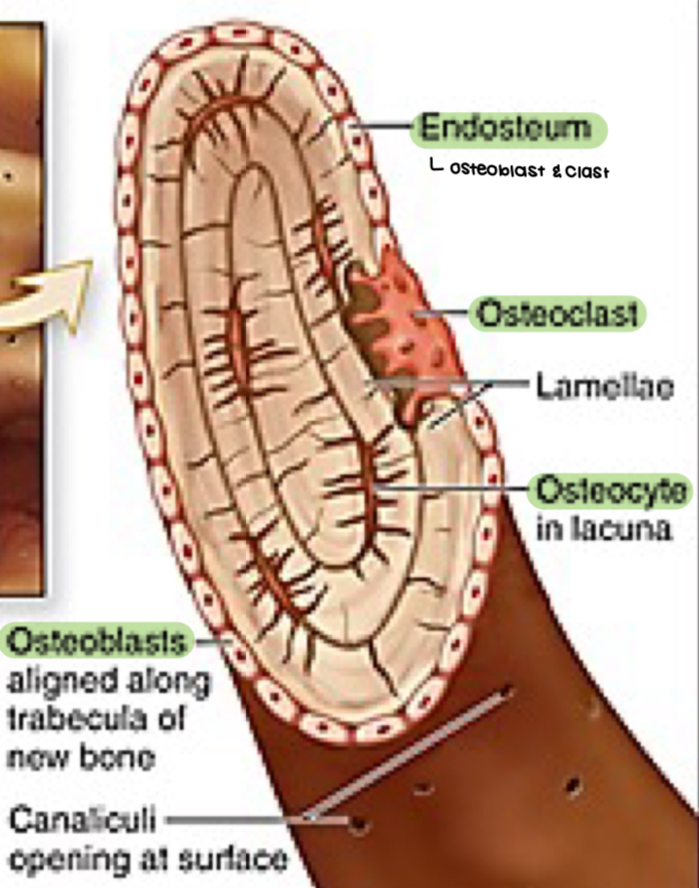
endosteum of cancellous bone contains
osteoblast and osteoclast
parts of long bone
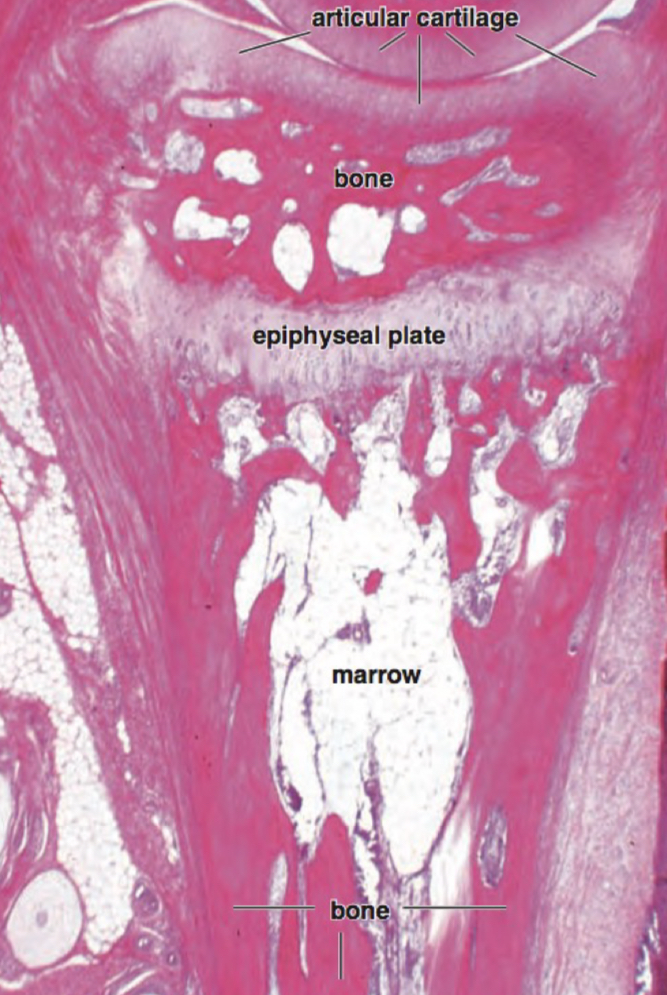
epiphysis, diaphysis, epiphyseal plate
epiphysis
expanding end, spongy bone with thin layer of compact
diaphysis
main shaft, compact bone with central marrow
epiphyseal plate
hyaline cartilage part, not fused when young
red bone marrow
children, red blood cells, hemopoietic
yellow bone marrow
older, adipocyte cells, found in diaphyseal of long bones
osteoblast - function; location
synthesize and secrete organic components (type 1 collagen, proteoglycan, glycoprotein); outermost surface of bone matrix
osteocyte - location, morphology
in lacuna; cytoplasmic processes (canaliculi)
osteoclast - derivation, morphology, function
monocyte; multinucleated; bone resorption and remodeling
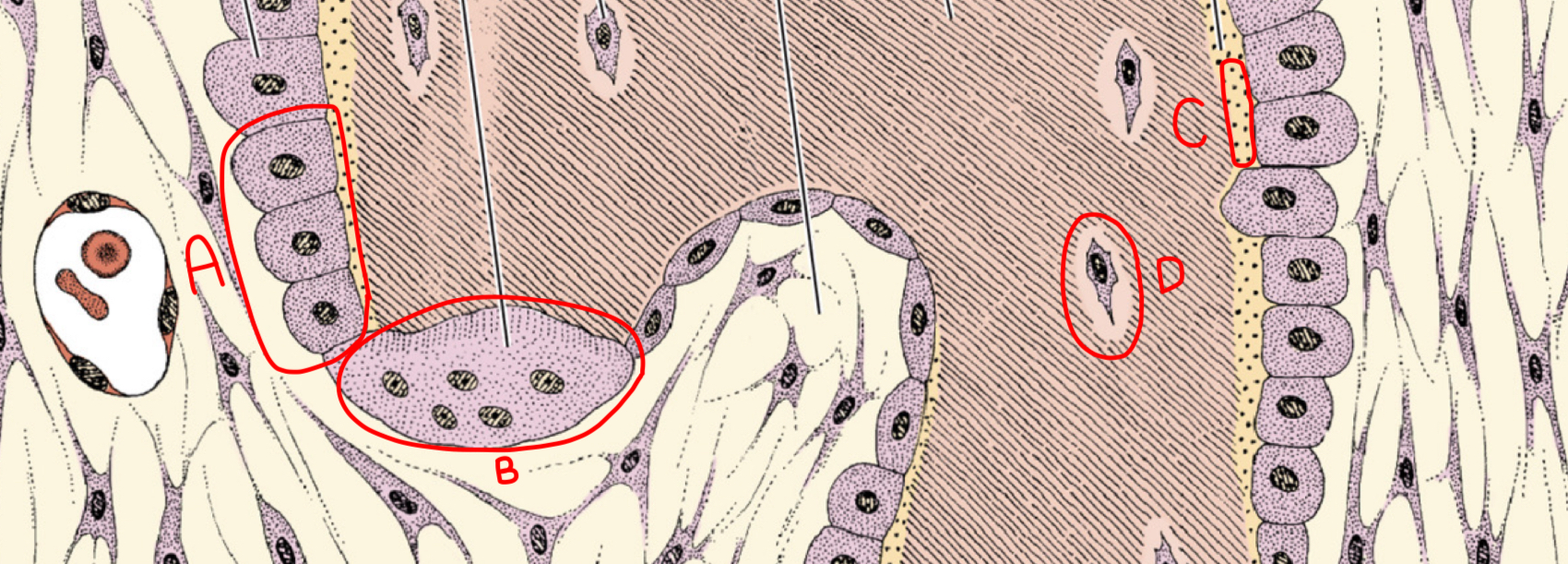
what is a
osteoblast
what is b
osteoclast
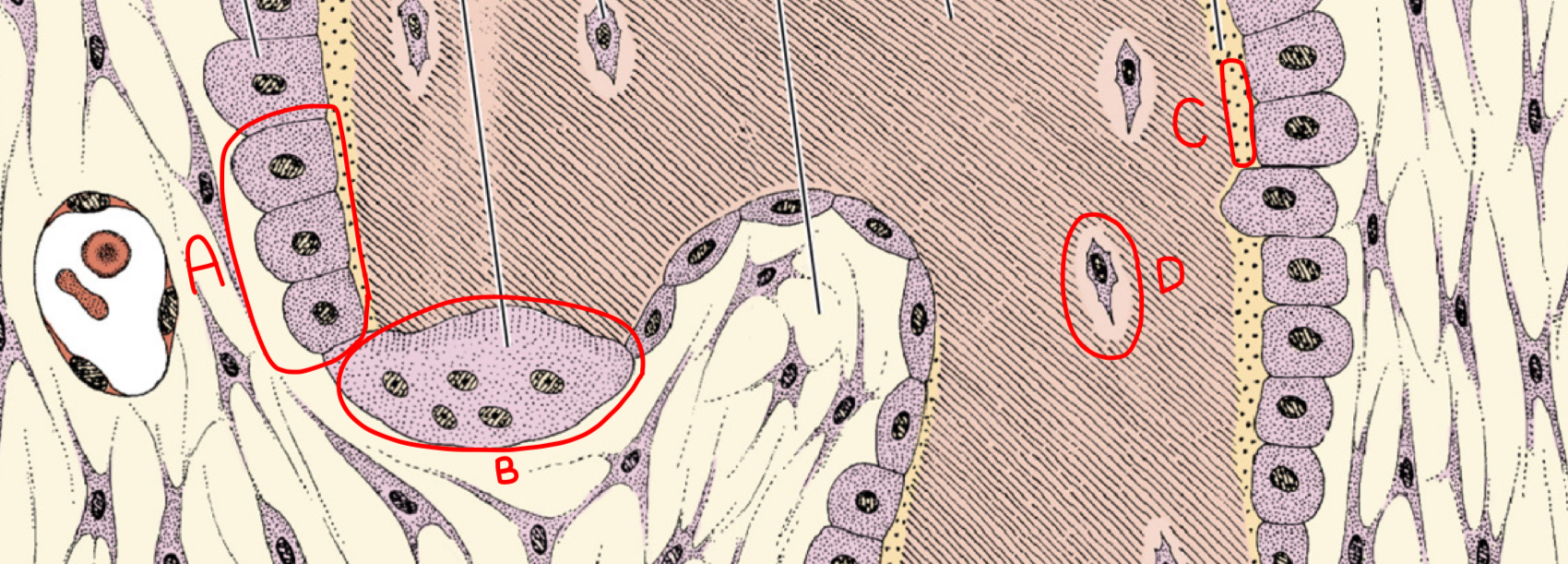
what is c
osteoid (new matrix)
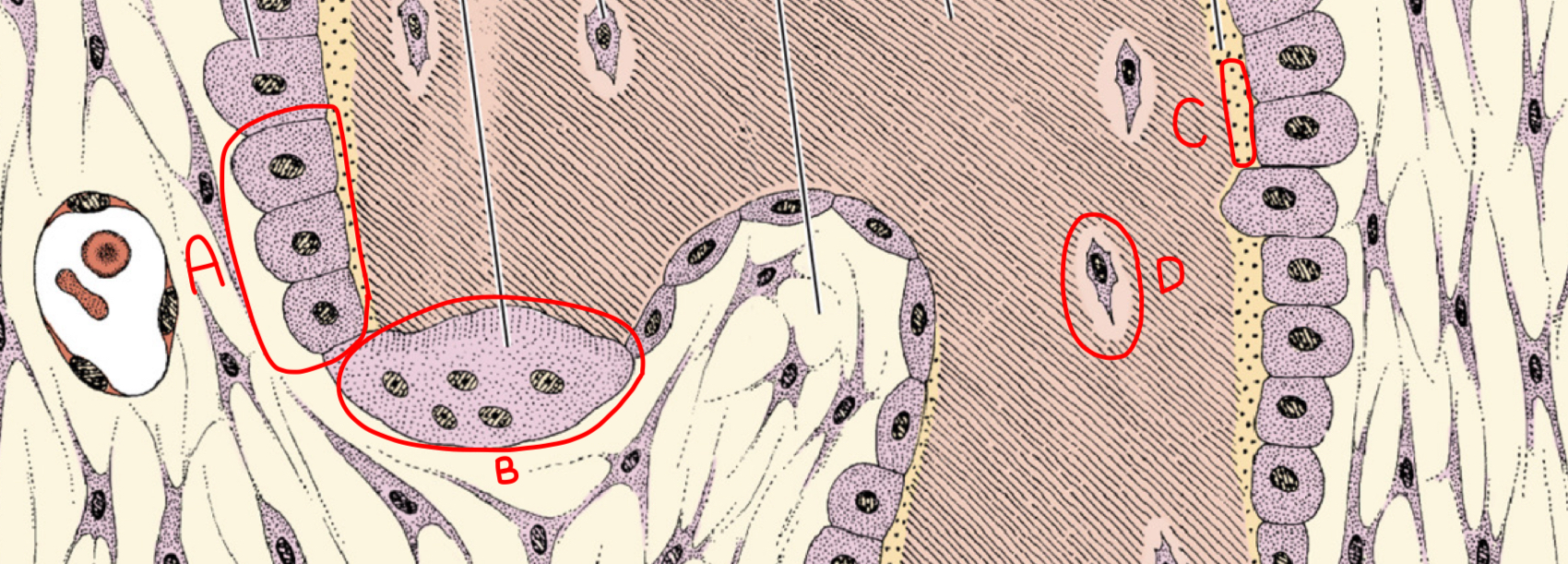
what is d
osteocyte
osteoblasts secrete
osteoid containing type 1 collagen, proteoglycan, glycoprotein (osteonectin)
formation of mineralized bone process
osteoblast release matrix vesicles and fiber > mineralization around vesicles > matrix compact to become mineralized bone
osteocyte
mature bone cell enclosed by matrix with dendritic processes for communication
osteocyte function
calcium homeostasis, detect stress for bone remodeling
what connections are formed between dendritic processes of osteocytes
gap junctions
hawship’s lacuna (resorption bay)
bone resorption area
regions of osteoclast during bone resorption
ruffled border, clear/sealing zone (adhesion molecules), basolateral (exocytosis or digested material)
acidified vesicles role in bone resorption
make area near ruffled border acidic to destroy bone
bone matrix composition
calcium hydroxyapatite, type 1 collagen, osteonectin, osteocalcin
perforating or sharpey fiber
bind periosteum to bone
inner periosteum contains
osteoblasts, osteoprogenitor
periosteum function
nourish osseous tissue, provide supply of osteoblast
endosteum
cover small trabeculae of bony matrix
osteogenesis types
intramembranous ossification, endochondrol ossification (intracartilaginous)
intramembranous ossification process
ossification center forms in condensed membrane > osteoid is secreted > woven bone and periosteum form > compact bone forms
endochondral ossification
within hyaline cartilage, for long bone development
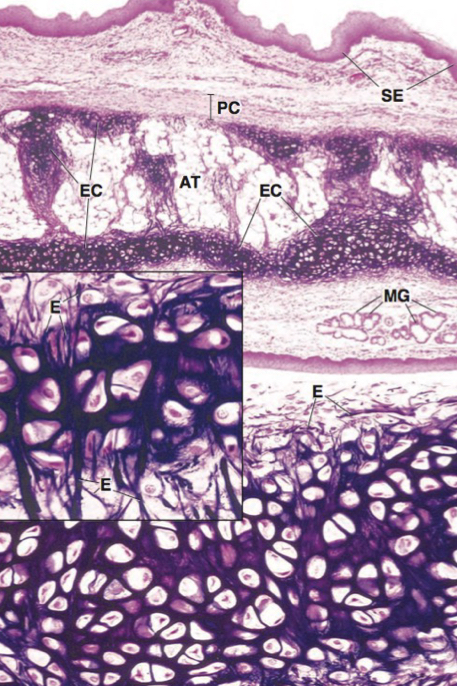
endochondral ossification process
hyaline cartilage model > blood vessel penetrate for primary ossification in diaphysis > secondary ossification in epiphyses > bone replace cartilage
what regions of cartilage remain after bone development
articular cartilage, epiphyseal plate
ossification: resting zone
normal chondrocytes
ossification: proliferating zone
cell division (stacked cells)
ossification: maturation and hypertrophic cartilage zone
enlargement
ossification: calcified cartilage zone
chondrocyte replaced by calcium, apoptosis, no nuclei
ossification: ossification zone
cartilage removal and bone deposit
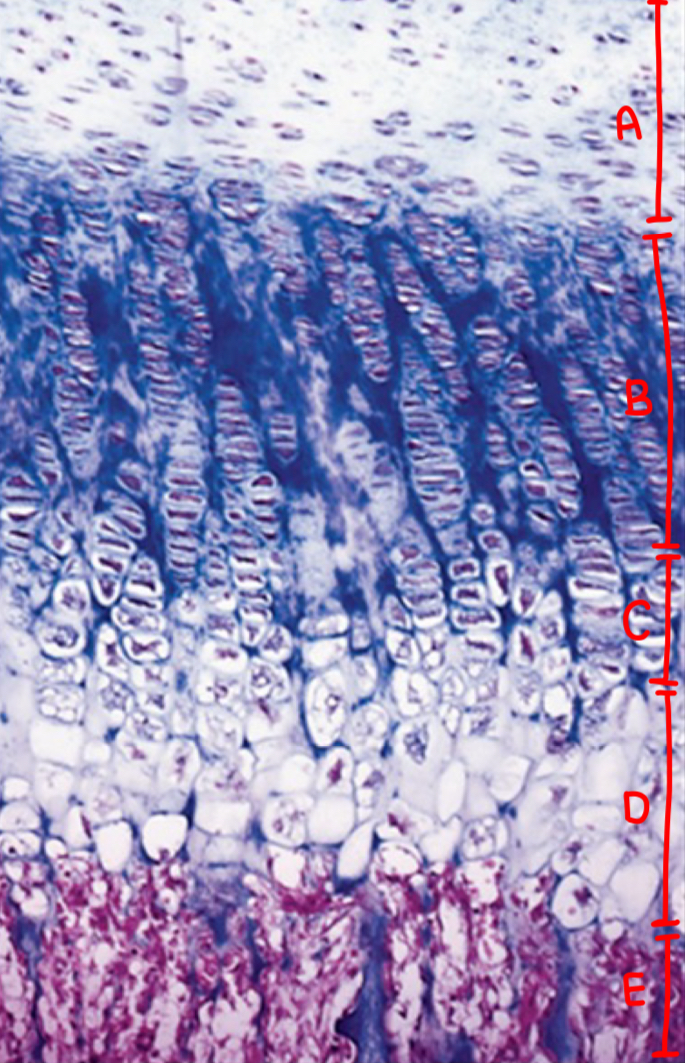
what is a
resting zone
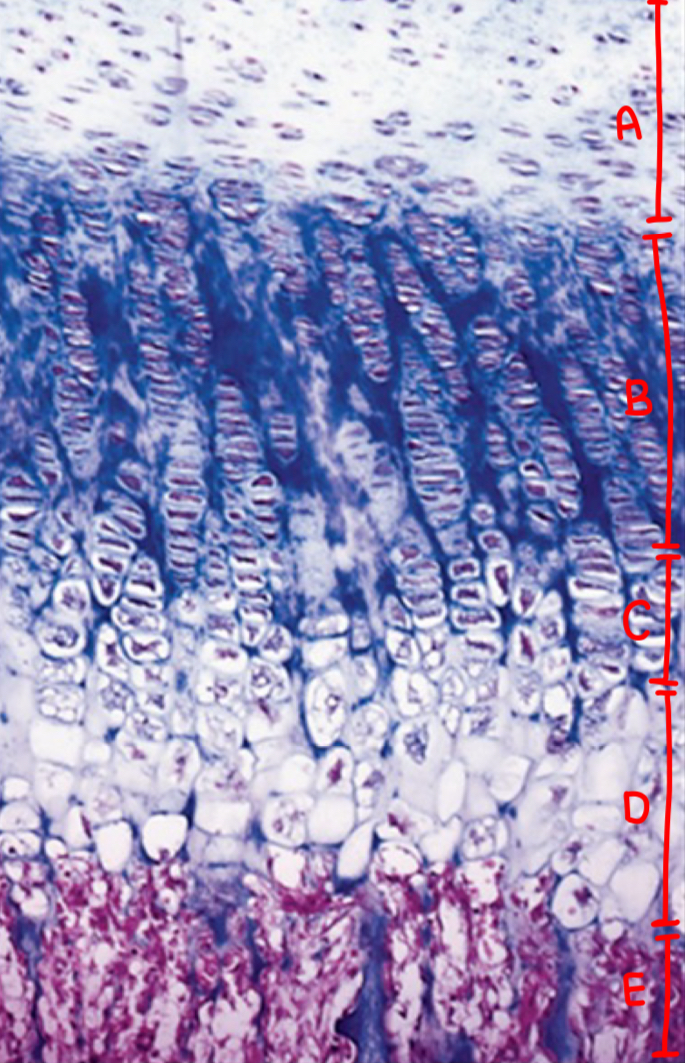
what is b
proliferating zone
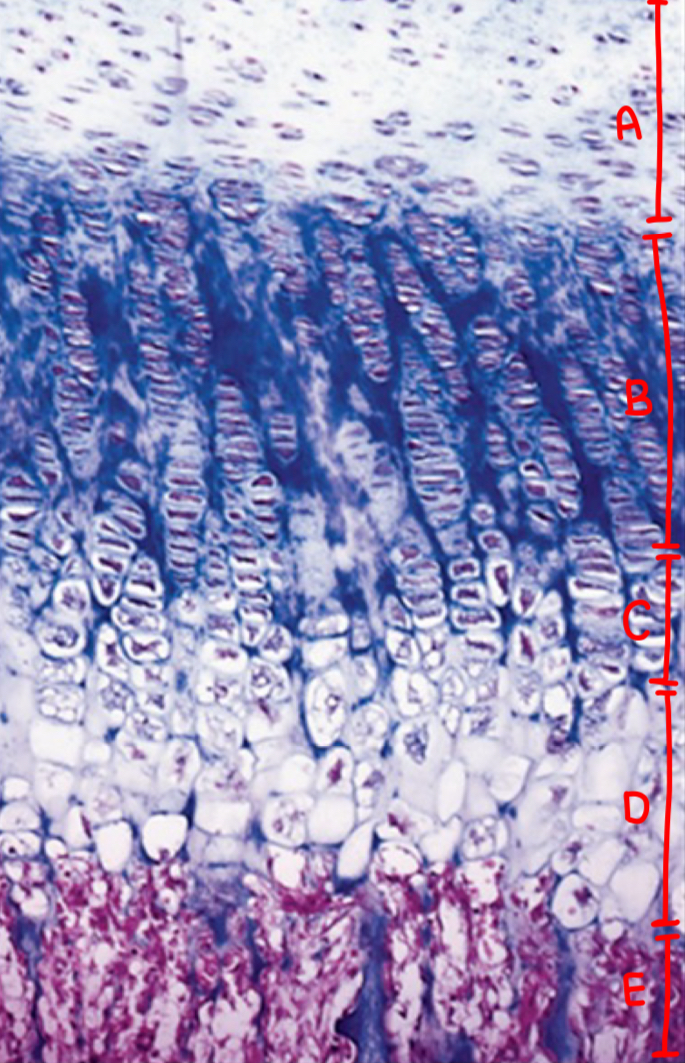
what is c
maturation and hypertrophic cartilage zone
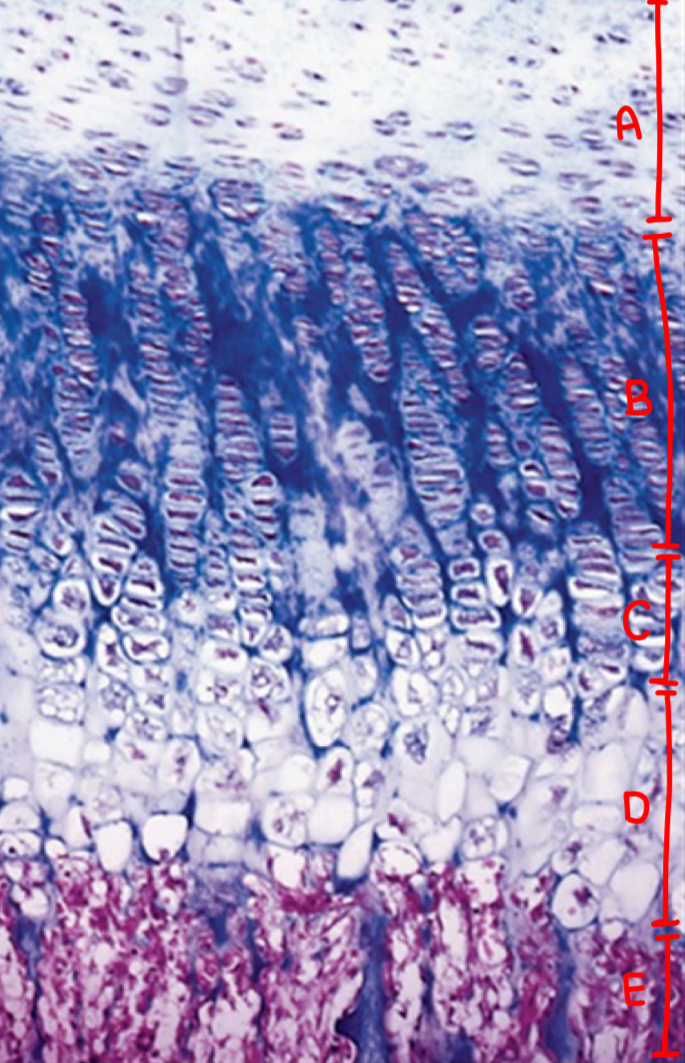
what is d
calcification zone
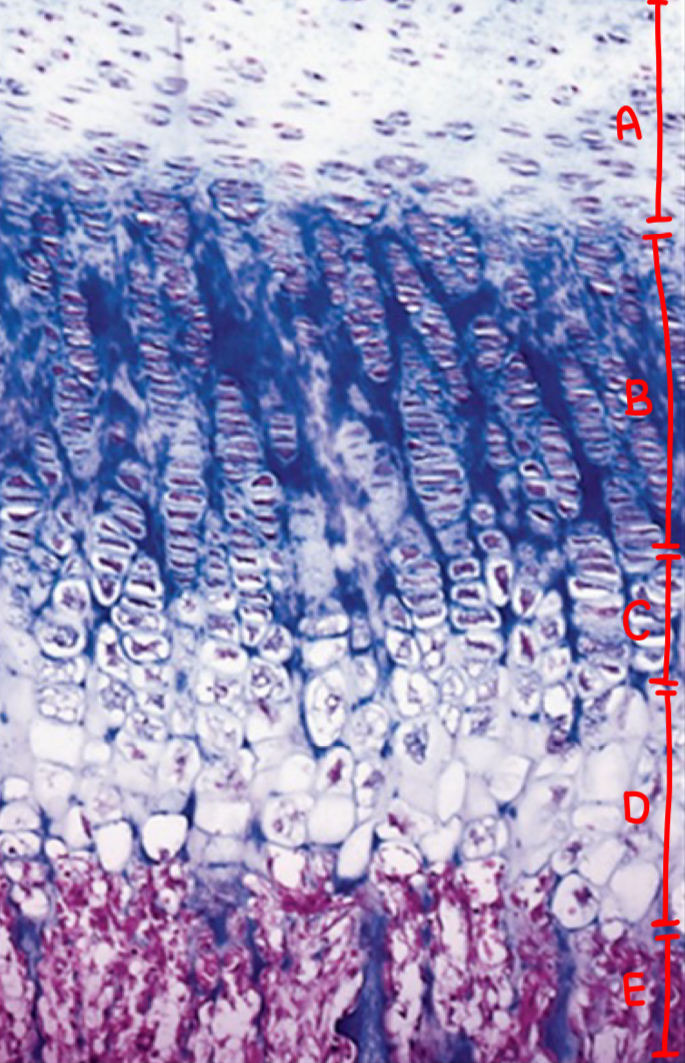
what is e
ossification zone
what is the direction of bone growth
towards the center of the diaphyses
bone remodeling purposes
bone plasticity, cranial bone growth, stress adaptation