Chapter 13: Viruses and Prions
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Viron
a virus particle
Naked virus
capsid and nucleic acid
Enveloped virus
capsid, nucleic acid, and lipid bilayer
capsid
Outer protein coat of a virus
neucleocapsid
nucleic acid + capsid
helical
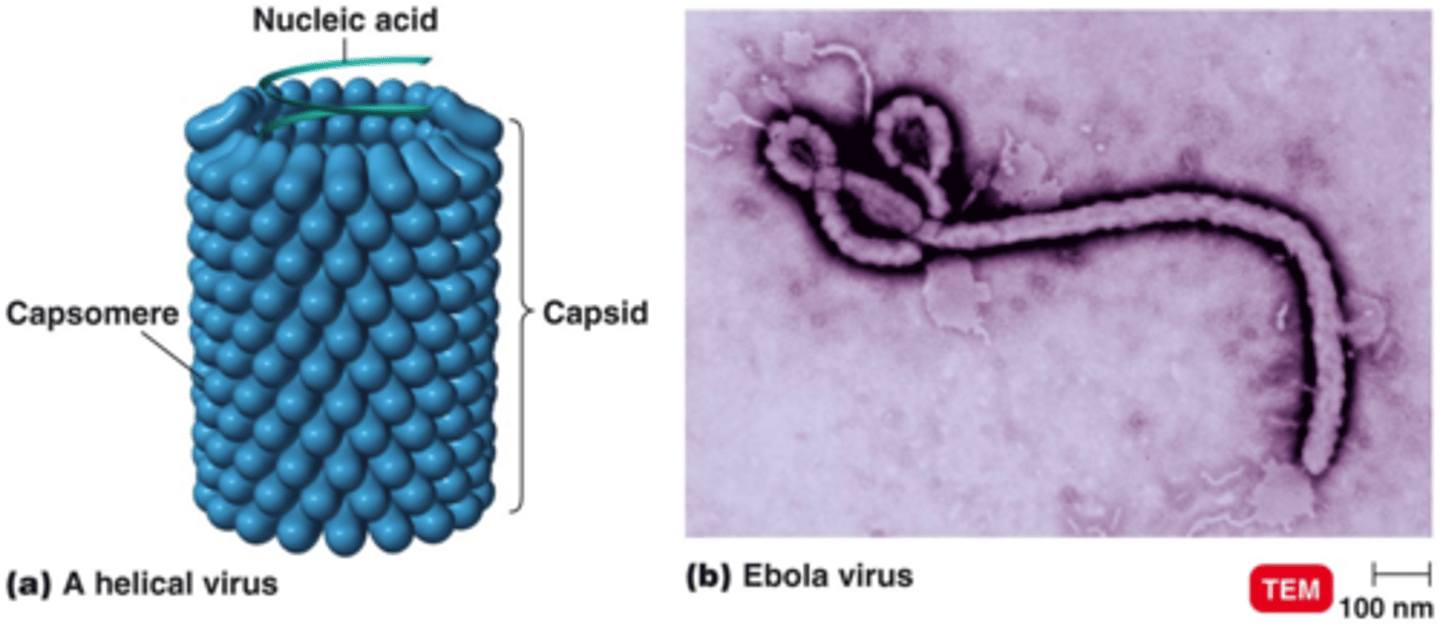
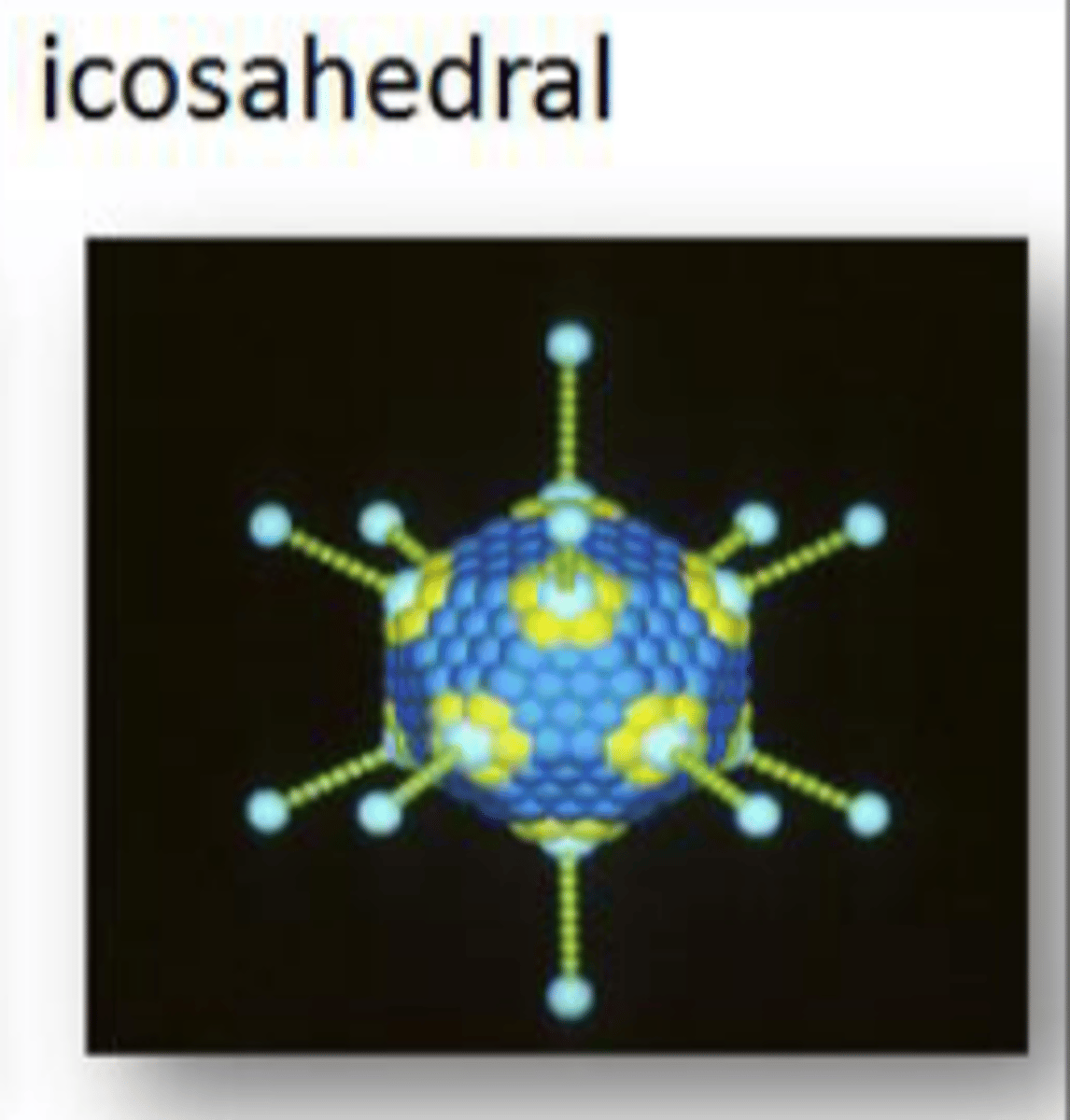
isometric

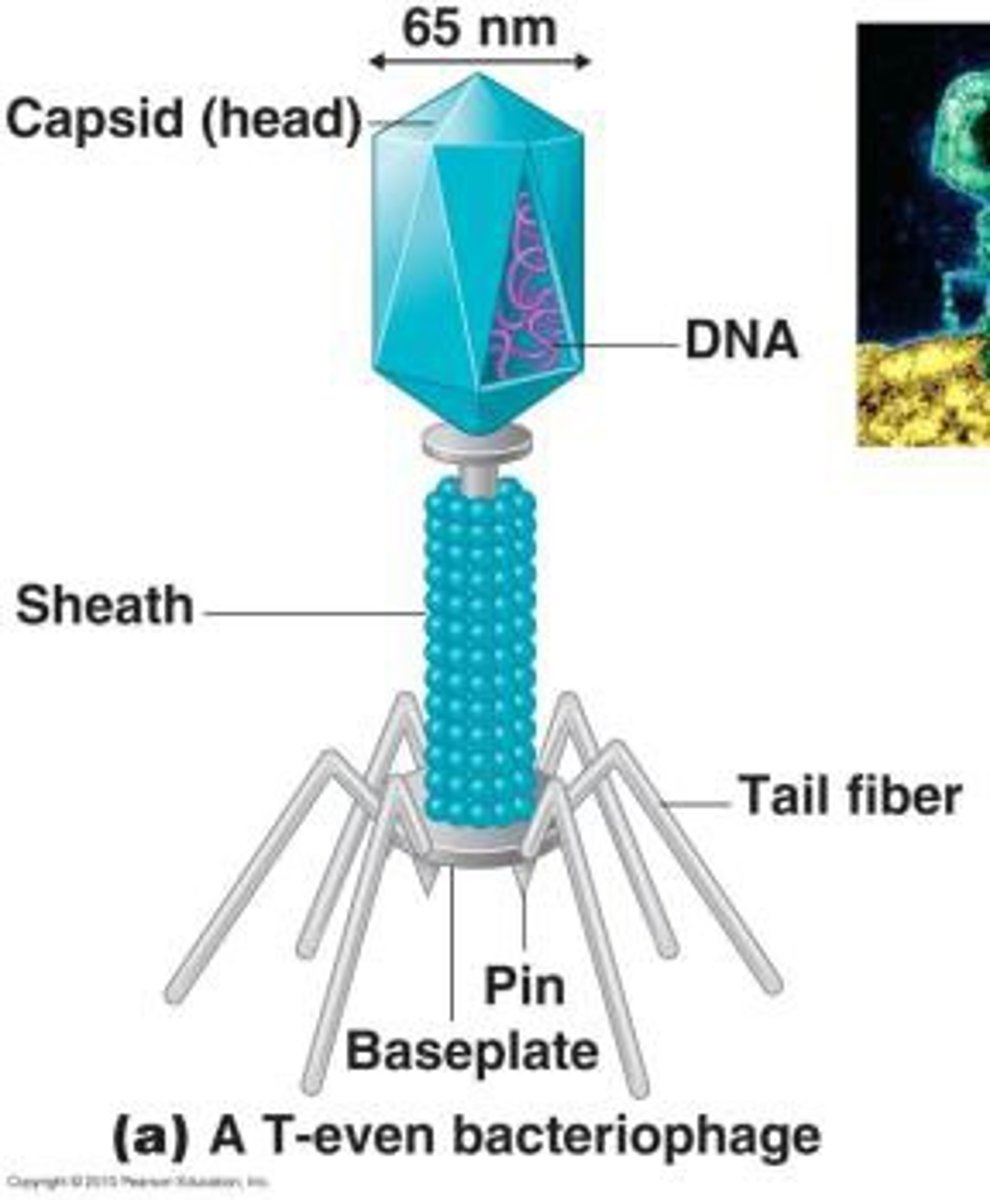
Complex virus
False (enveloped and naked viruses can have spikes)
True or Flase
Only enveloped viruses can have spikes
Matrix proteins
fill the region between capsid and envelope
Nucleic acid of virus
-can have DNA OR RNA (not both)
-single or double stranded
-circular or linear DNA
-linear RNA
10nm
viruses can be as small as ___
and as large as 500nm
Virus replication
Host/tissue specific
Due to host receptors for the virus
True
True or False
Viruses cannot replicate outside of host
Nucleic acids
Viruses uses host proteins, enzymes, ribosomes, and ____
feline leukemia
viral disease that impairs the cat's immune system and can cause cancer
Virus-Host Interactions
Disease or genetic alteration
Productive infection
viral infection in which more viral particles are produced
-Host will either lyse and die
-Or will replicate and produce more viruses
Latent state
Virus integrates into plasmid or genome
No symptoms or clinical signs evident
-Host cell will multiply and phenotype will change
Bacteriophage Lytic replication
1. Attachment: Phage binds to bacterial cell
2. Penetration: Phage injects DNA into the cell
3. Replication (synthesis): Phage commandeers host cell factors to transcribe and translate viral genes
4. Assembly (maturation): formation of active phage
5. Release: Bacterial cell lyses and new phages are released
Bacteriophage
Can be used as a possible treatment to bacterial infections
Lysogeny
1. Attachement: attaches to host
2. Injection: injects linear DNA
3. Integration: Prophage integrates in DNA chromosome
4. Division: cell divides
5. Excision: of phage DNA
6. Replication: of phage
7. Release: Host cell lyses
Temperate bacteriophage
bacteriophages which can choose between a lytic and lysogenic pathway of development
lysogenic conversion
when a bacterium acquires a new trait from its temperate phage (typically toxins)
Streptococcus pyrogens
Produces Scarlet fever
Clostridium botulinum
Produced Botulism
Corynebacterium diphtheria
Produces diphtheria
Transduction
Transfer of bacterial gene info using bacteriophage
Generalized transduction
random bacterial DNA is packaged inside a phage and transferred to a recipient cell
Specialized transduction
a highly specific part of the host genome is regularly incorporated into the virus (only during lysogenic infections)
transducing particle
bacteriophage progeny that contains part of a bacterial genome instead of phage DNA due to an error during packaging
Hybrid DNA molecule
Virus and bacteria DNA
Animal viruses
characterizes by genome structure, virus particle structure, presence of envelope
- viridae
family names
(based on genome, structure, and envelope)
- virus
Genus
Species
derived from disease cause
Animal Virus Replication
1. Attachment
2. Penetration
3. Uncoating
4. Biosynthesis/Genome Replication
5. Assembly (maturation)
6. Release
7. Shedding
Shedding
Leaving host (typically the same as entry)
Transmission
Entry into a new host
Release
Leaving a cell (typically by budding, exocytosis, and lysis)
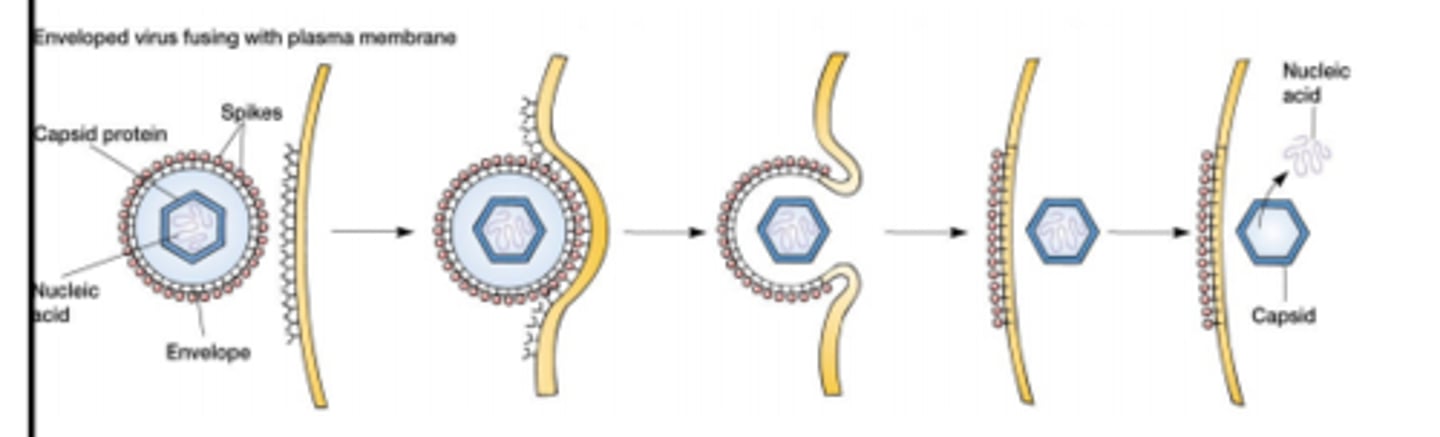
Fusion
Virus fuses to cell membrane for penetration
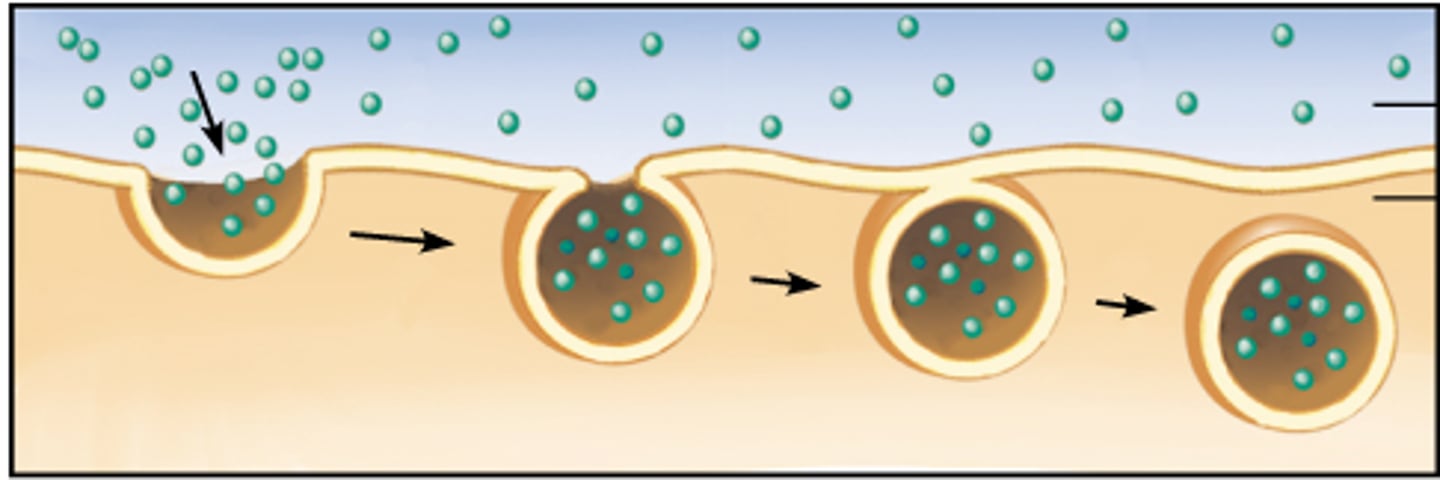
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Acute infections
-short (days-months)
-Infected cells may die (may or may not lyse)
-Virus shed during infection
Immunity
Host will develop this when they beat the virus
Persistent infection
an infection that stays in the system for a long time and you may or may not have symptoms
Chronic infection
Virus continually produced
latent infection
infection in which the infectious agent is present but not causing symptoms
prodomal stage
vague feelings of discomfort; nonspecific complaints
Disease stage
Symptoms manifest and spread is possible.
Covalescent stage
recovery phase
tumor
A mass of abnormal cells that develops when cancerous cells divide and grow uncontrollably.
Benign tumor
A tumor that remains at its original site in the body.
malignant tumor
a tumor that spreads throughout body