Earth's Internal Structure and Plate Tectonics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Core
Innermost layer of Earth, consisting of iron.
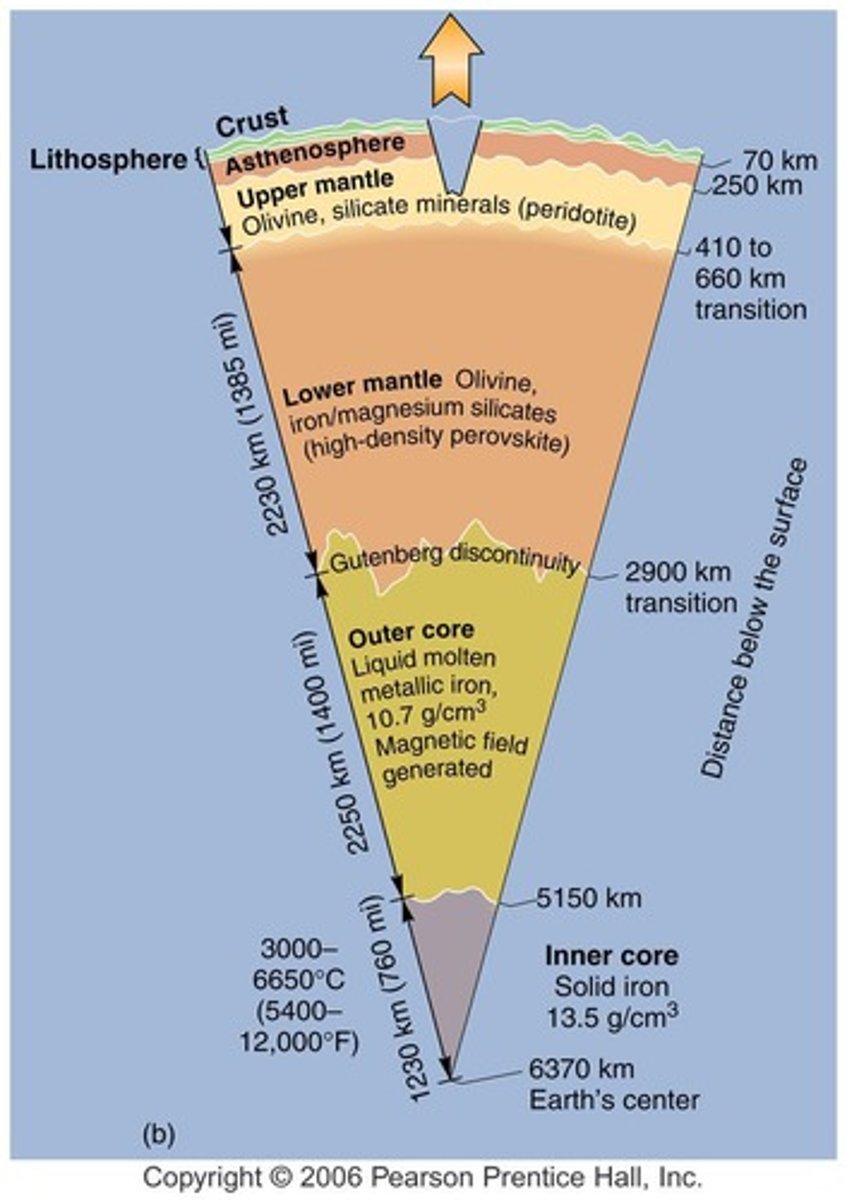
Mantle
Middle layer, composed of semi-solid rock.
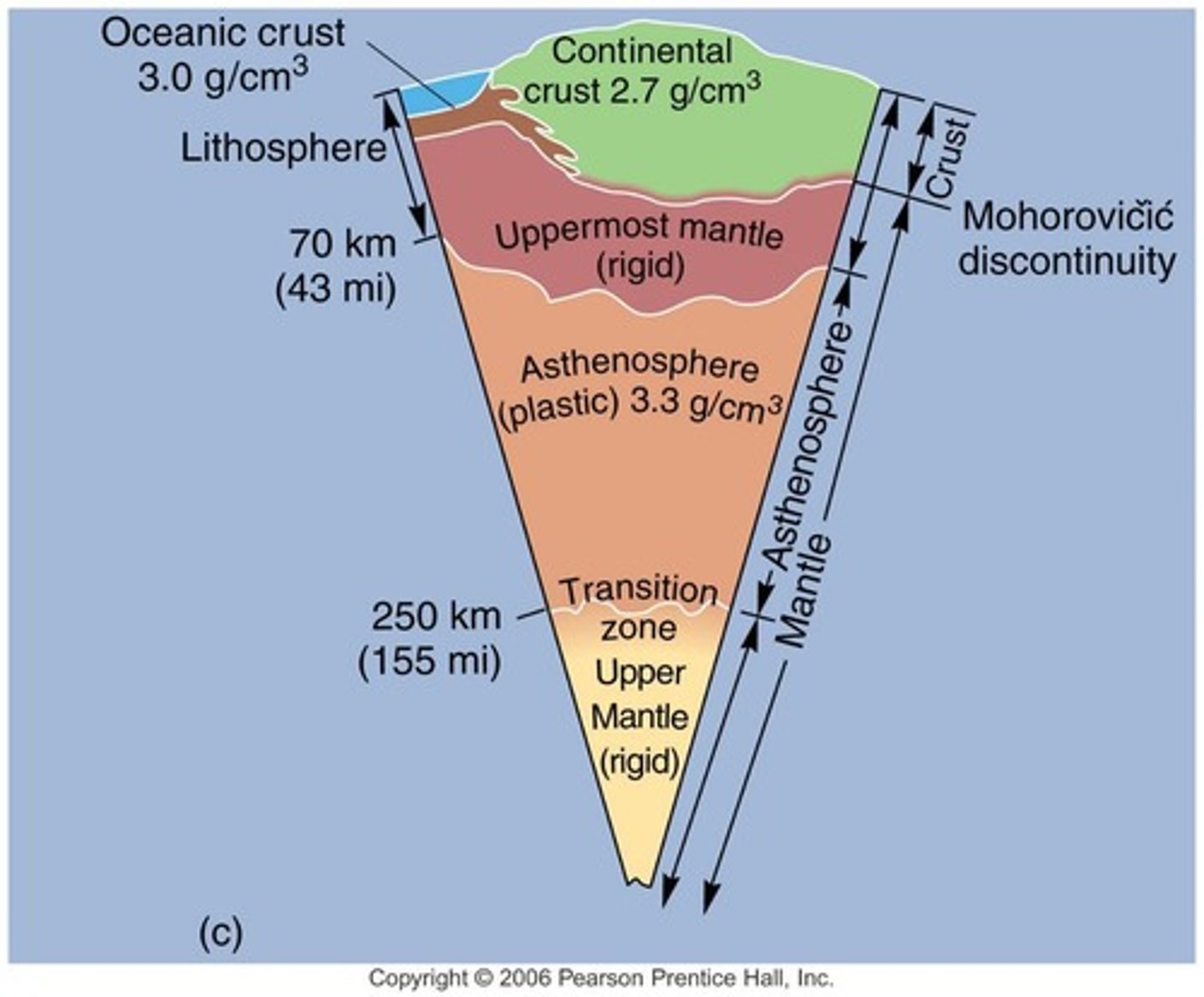
Crust
Thin outer layer of Earth's surface.
Asthenosphere
A soft, hot layer of the Earth’s mantle below the crust that slowly flows and allows tectonic plates to move on top of it.
Lithosphere
Rigid outer layer, includes crust and upper mantle.
Inner Core
Solid iron center, high pressure and heat.
Outer Core
Liquid layer generating Earth's magnetic field.
Gutenberg Discontinuity
Boundary between core and mantle.
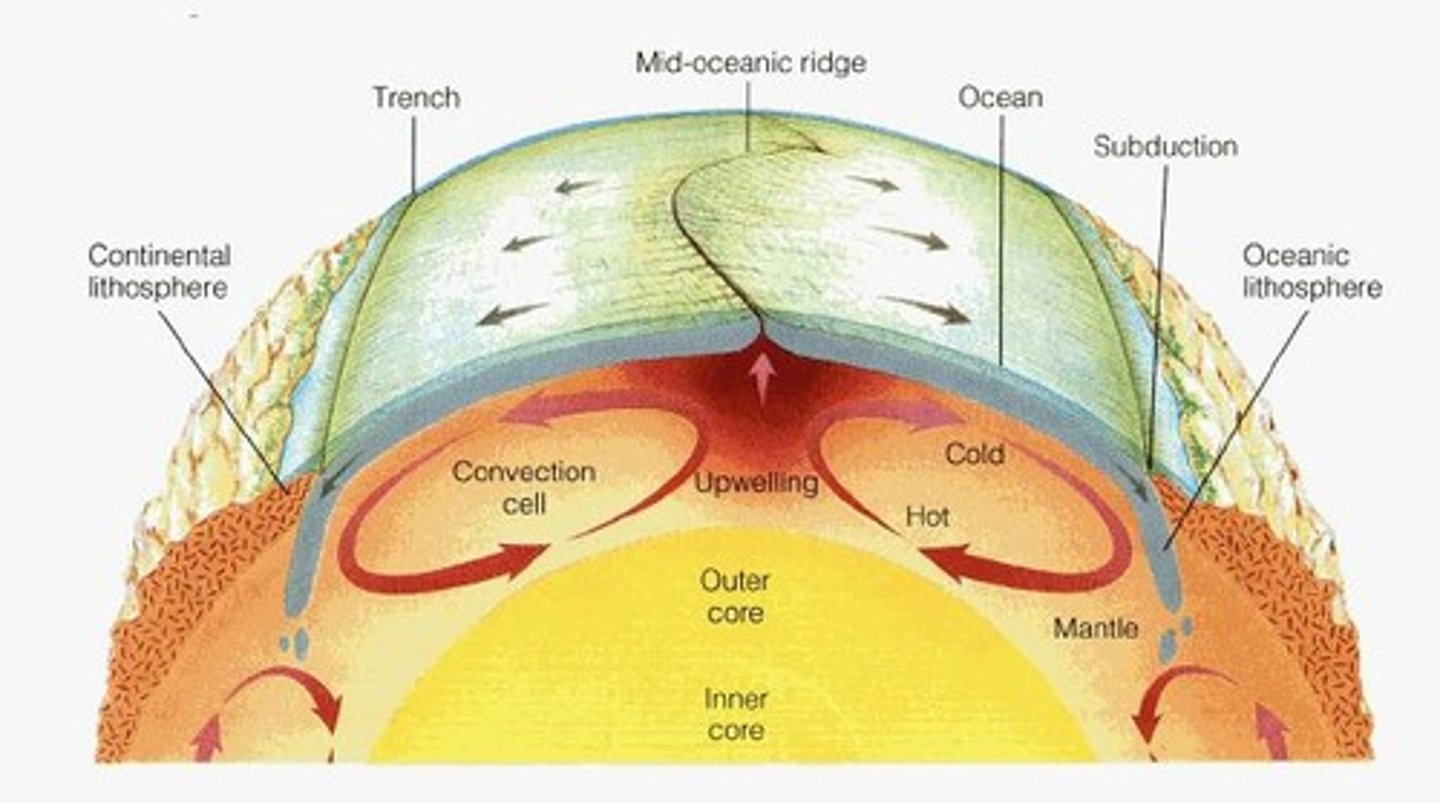
Mohorovicic Discontinuity
Boundary separating crust from mantle.
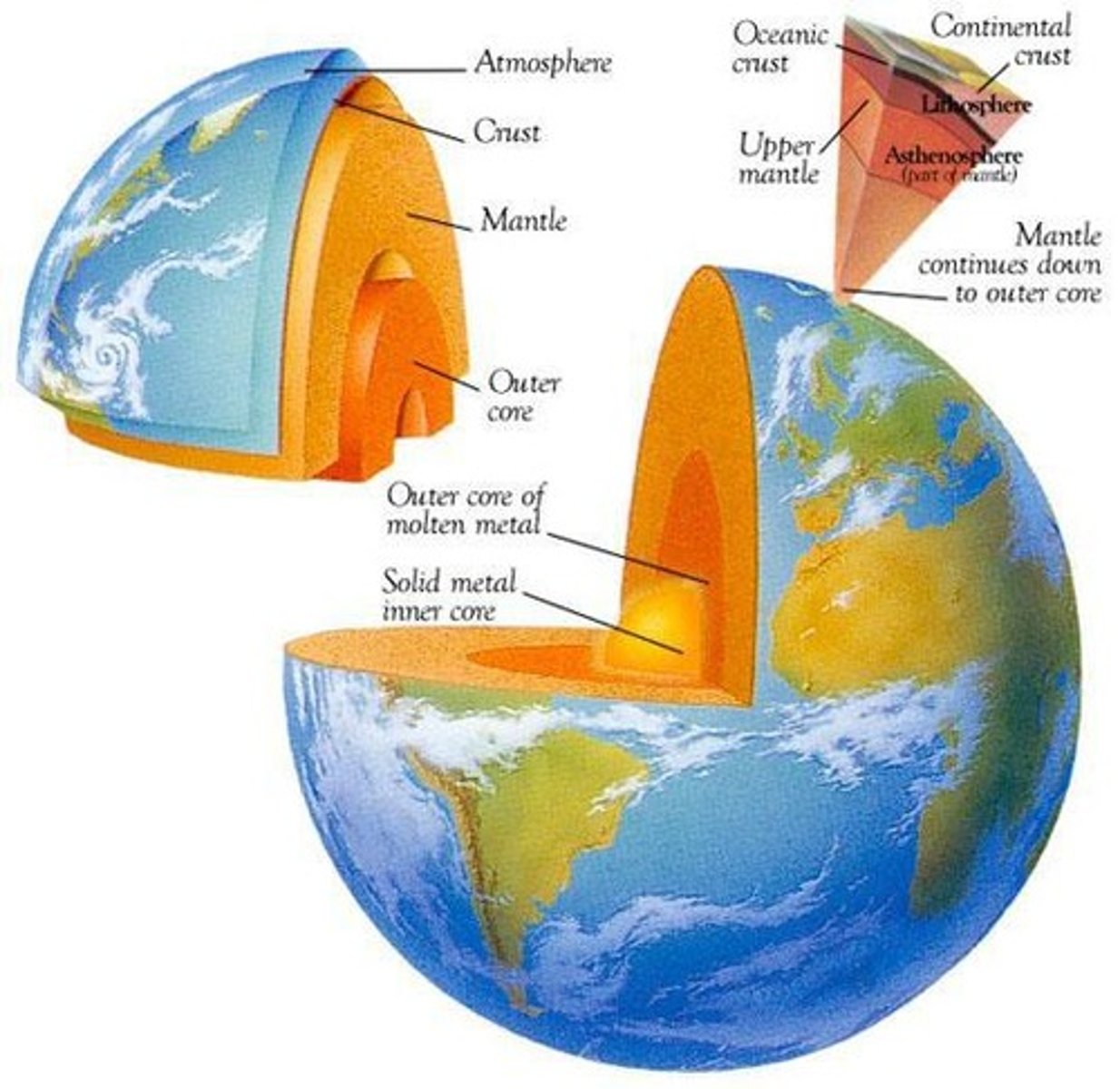
Continental Crust
Thicker crust, primarily granite composition.
Oceanic Crust
Thinner crust, primarily basalt composition.
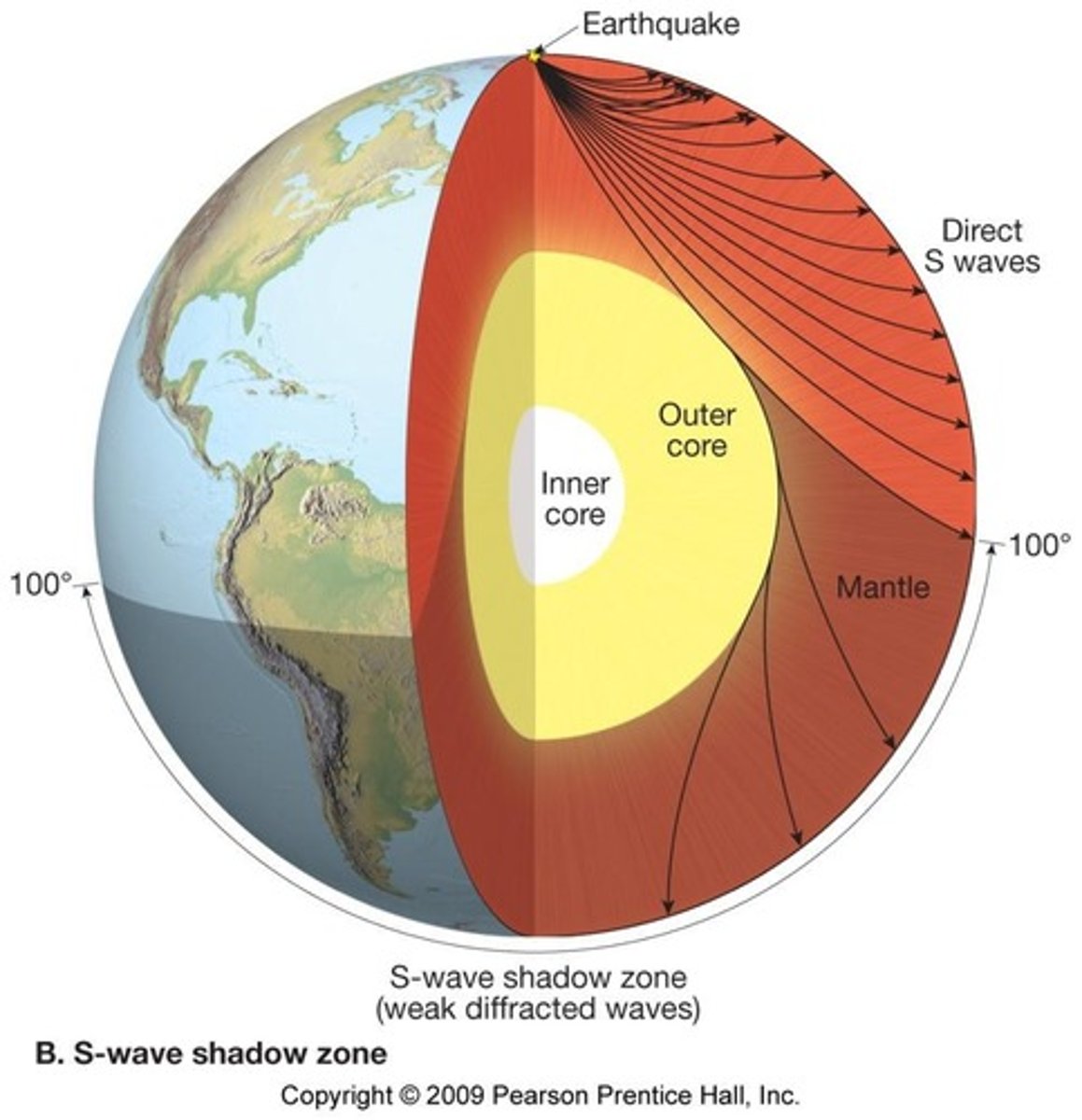
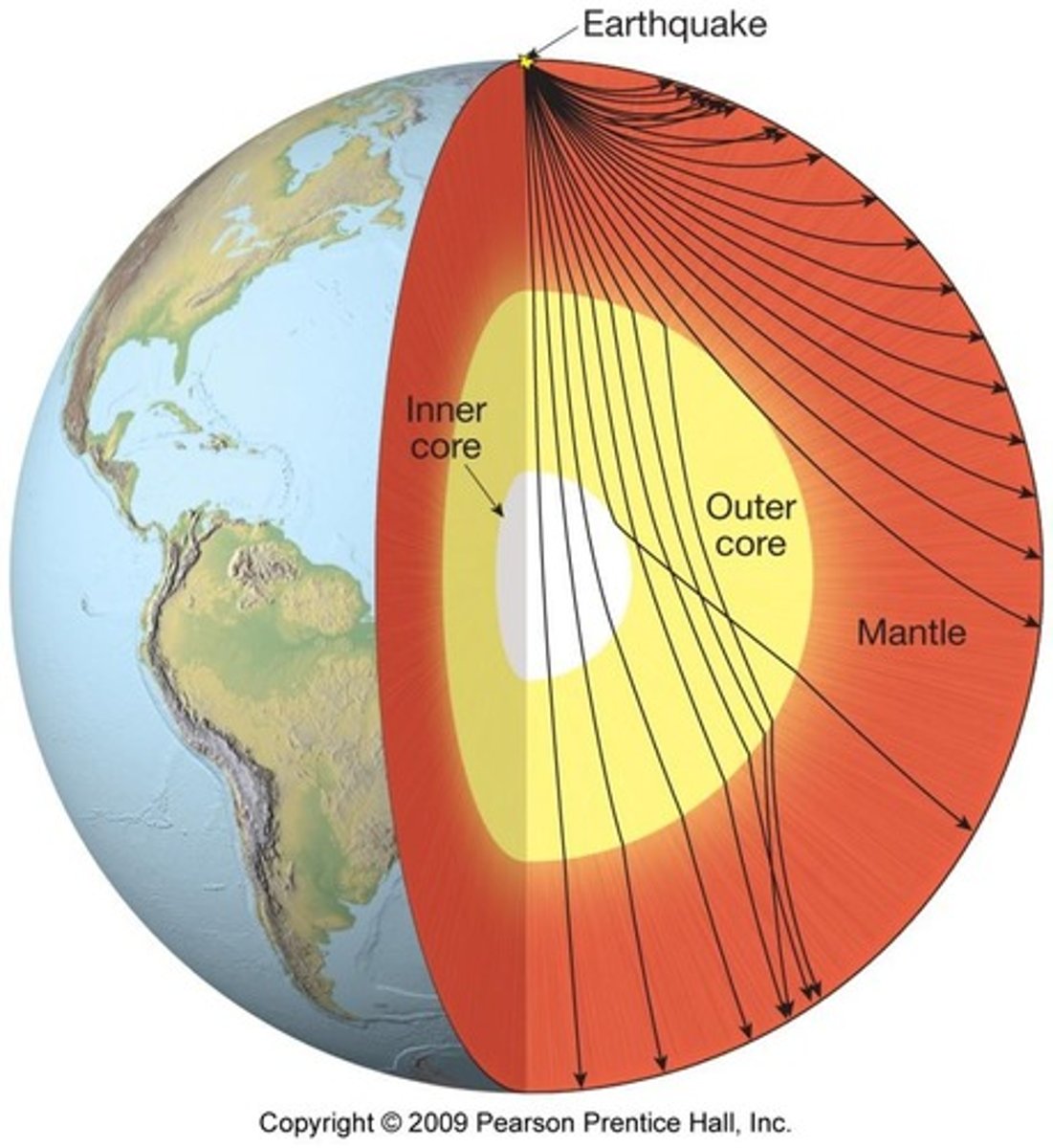
Seismic Waves
Waves used to study Earth's interior.
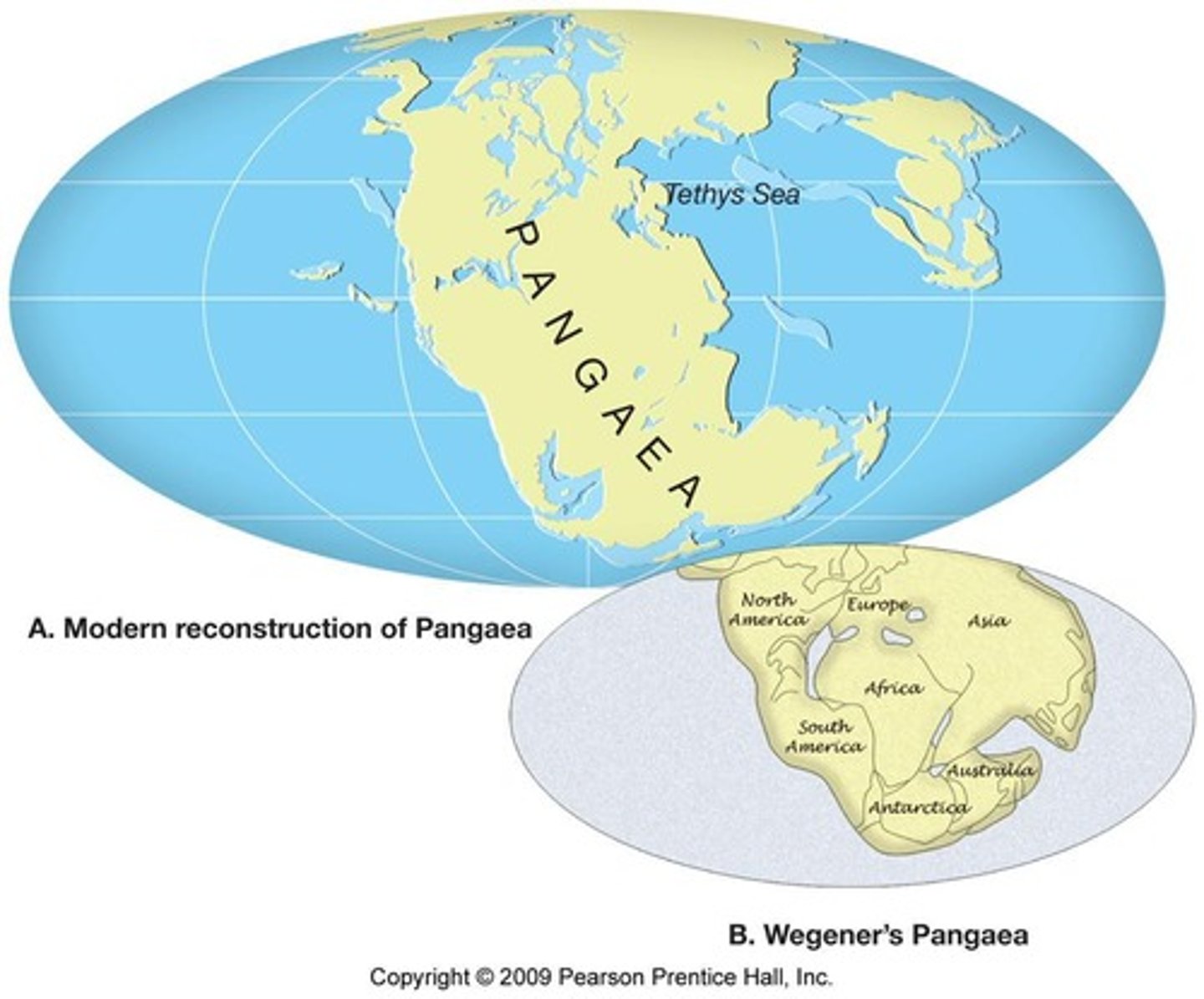
Pangaea
Supercontinent that existed 200 million years ago.
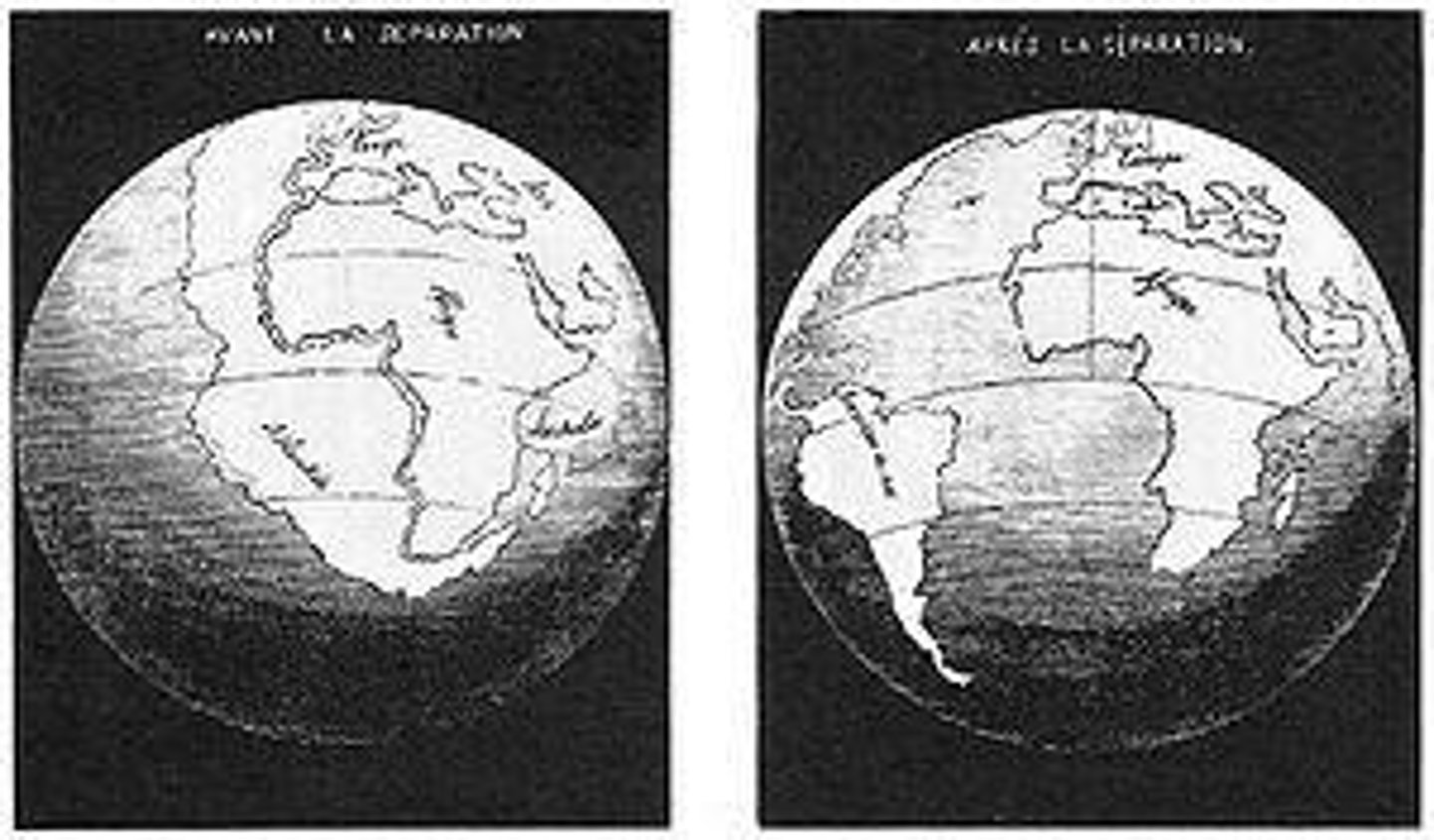
Continental Drift
Theory proposing continents move over time.
Convective Currents
Movement in asthenosphere causing plate motion.
Divergent Boundaries
Plates move apart, creating new crust.

Convergent Boundaries
Plates collide, leading to subduction zones.
Transform fault Boundaries
Plates slide past each other without creation. Help move segments of a mid-ocean ridges
Subduction
Process where one plate sinks beneath another.
Oceanic-Continental Convergence
Denser oceanic plate subducts under continental.
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence
Older oceanic plate subducts, forming islands.
Continental-Continental Convergence
Continents collide, forming mountain ranges.
Mid-Ocean Ridge
Underwater mountain range formed by divergent boundaries.
Earthquake Zone
Area where tectonic plate movement causes earthquakes.
Himalayas
Mountain range formed by continental-continental convergence.
Challenger Deep
Deepest point in Earth's oceans, 11,035 m below sea level.

Rates of Plate Movement
Tectonic plates move 2-15 cm/year.
Cratons
Stable portions of continental crust, tectonically inactive.
Where does plate activity occur
Plate activity mostly occurs at plate boundaries, where the edges of tectonic plates meet. Here's what happens at each type:
How do we know about Earth’s internal structure
Seismic waves
from earthquakes
• Deep wells
Three parts of the Solid Earth
Crust, mantle Core.