IB Psychology: Biological Approach - Brain and Behaviour
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that transmit information from one neuron to another
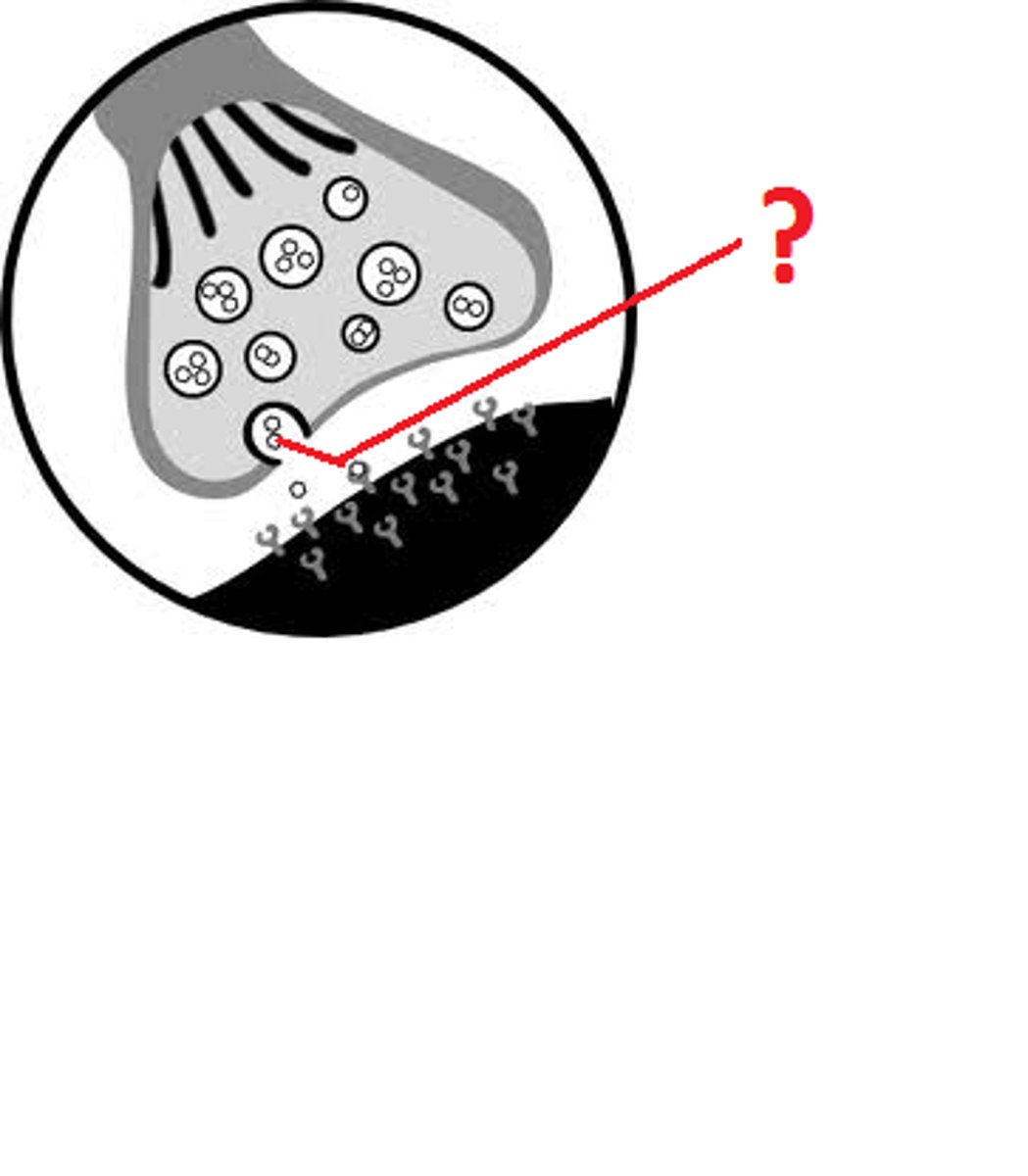
Neurotransmission
The process of transferring information from one neuron to another at a synapse
Synapse
the junction between two neurons (axon-to-dendrite) or between a neuron and a muscle
Excitatory
Causes next cell to fire
Inhibitory
Keeps next cell from firing
Agonists
drugs that increase the action of a neurotransmitter
Antagonists
drugs that block the function of a neurotransmitter
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter that regulates motor behavior, motivation, pleasure, and emotional arousal.
Dopaminergic pathway
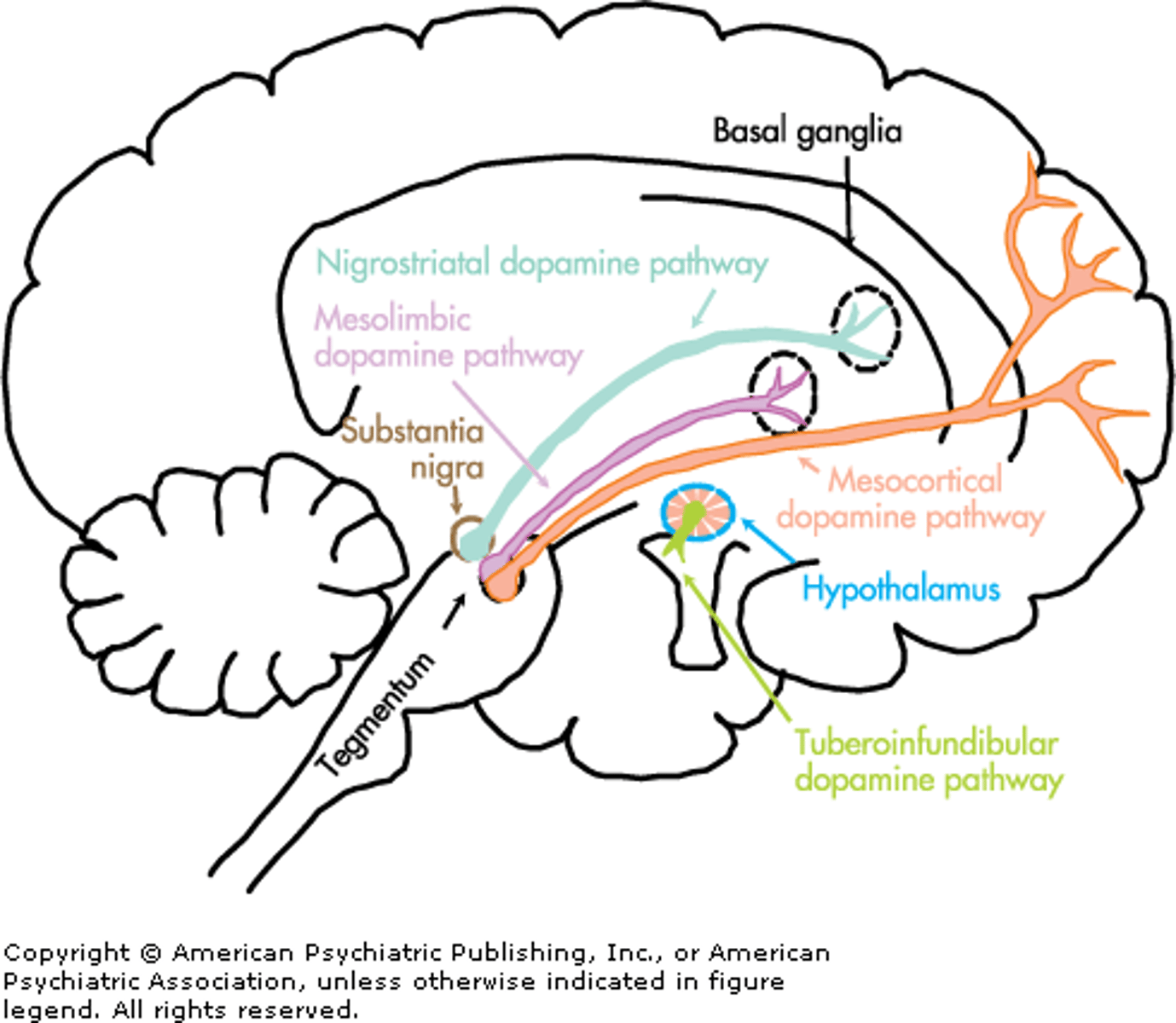
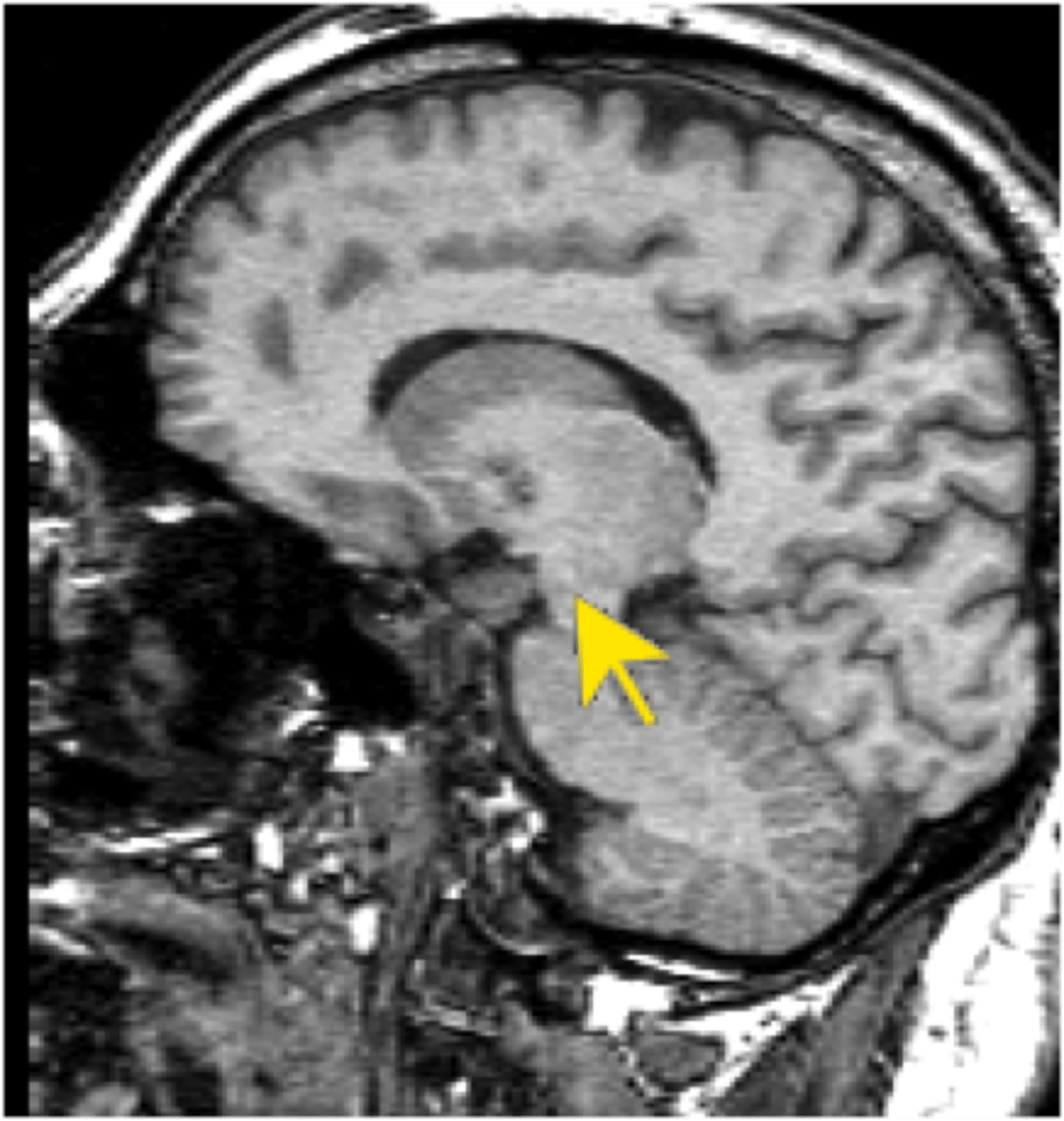
Ventral tegmental area (VTA)
Midbrain structure where dopamine is produced: associated with mood, reward, and addiction
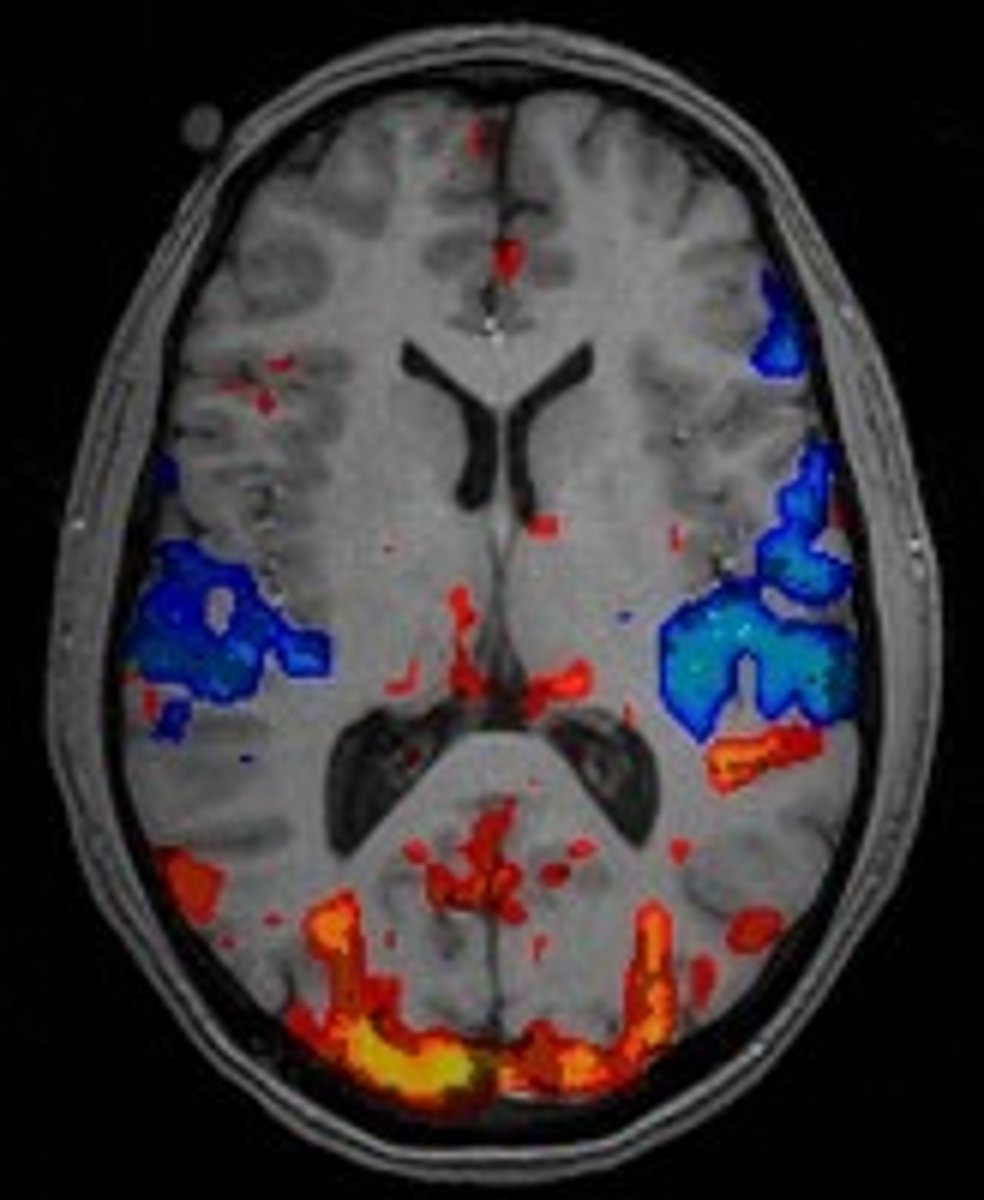
fMRI
Placebo
harmless medicine with no effect; dummy medicine
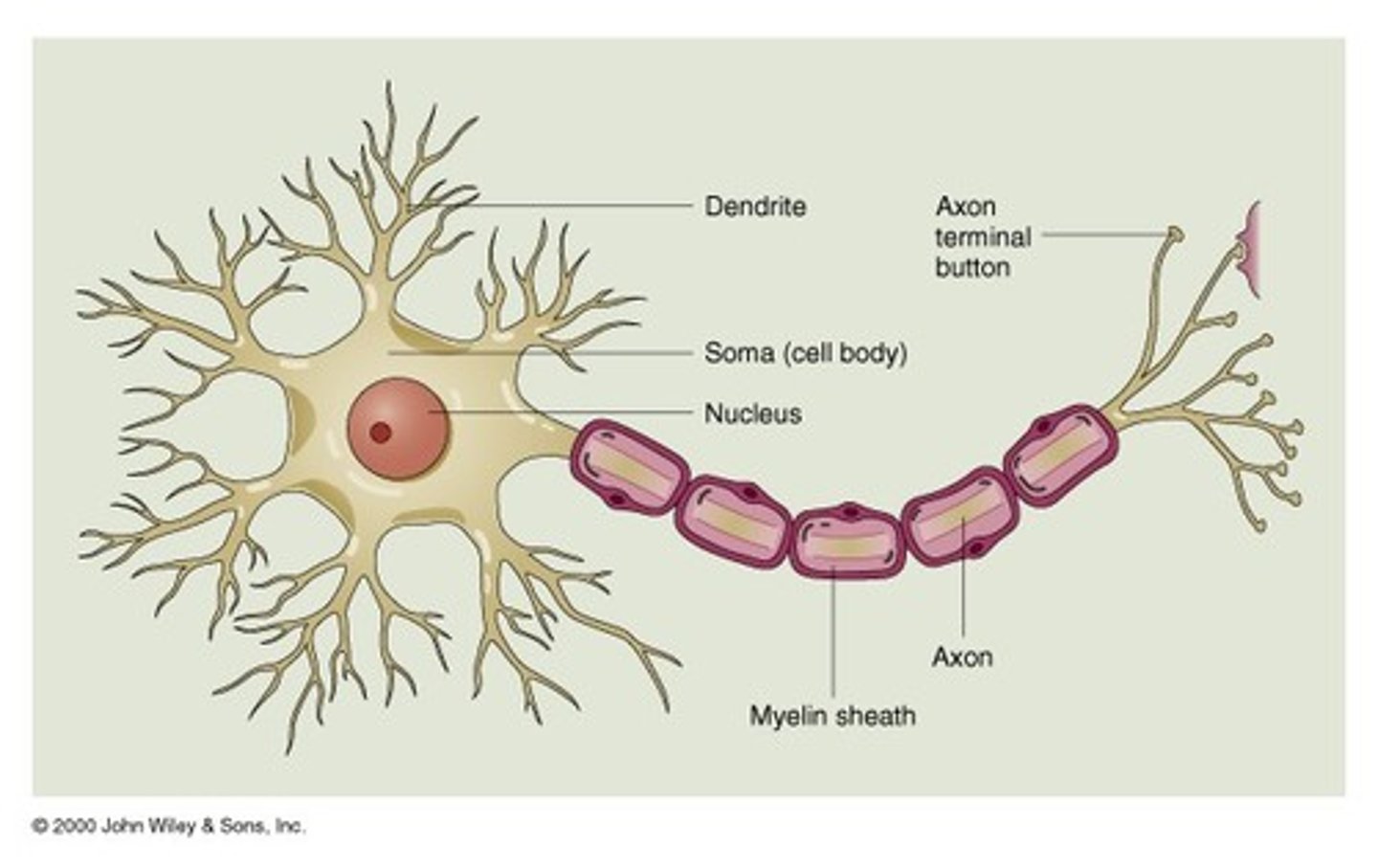
Dendrite
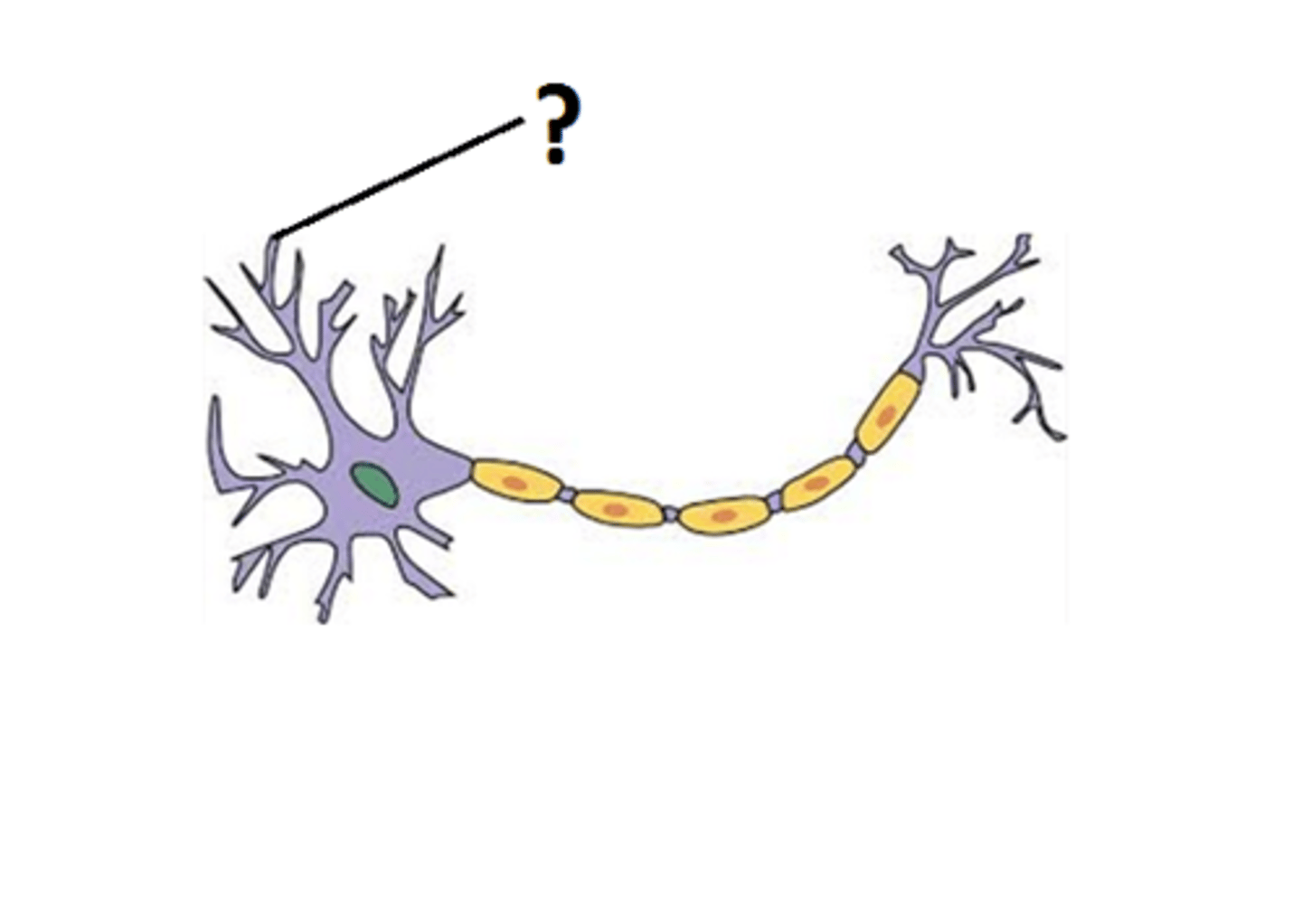
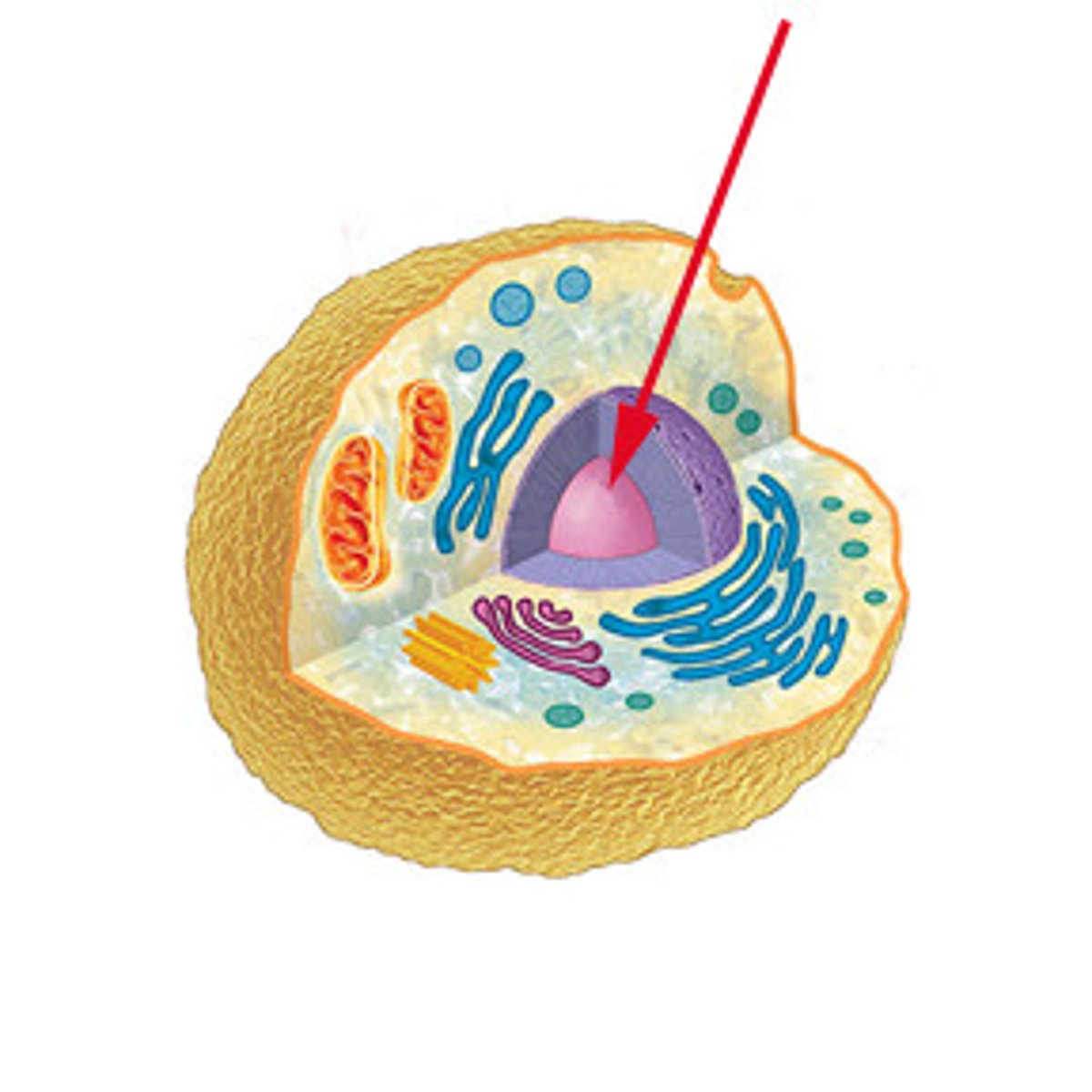
Nucleus
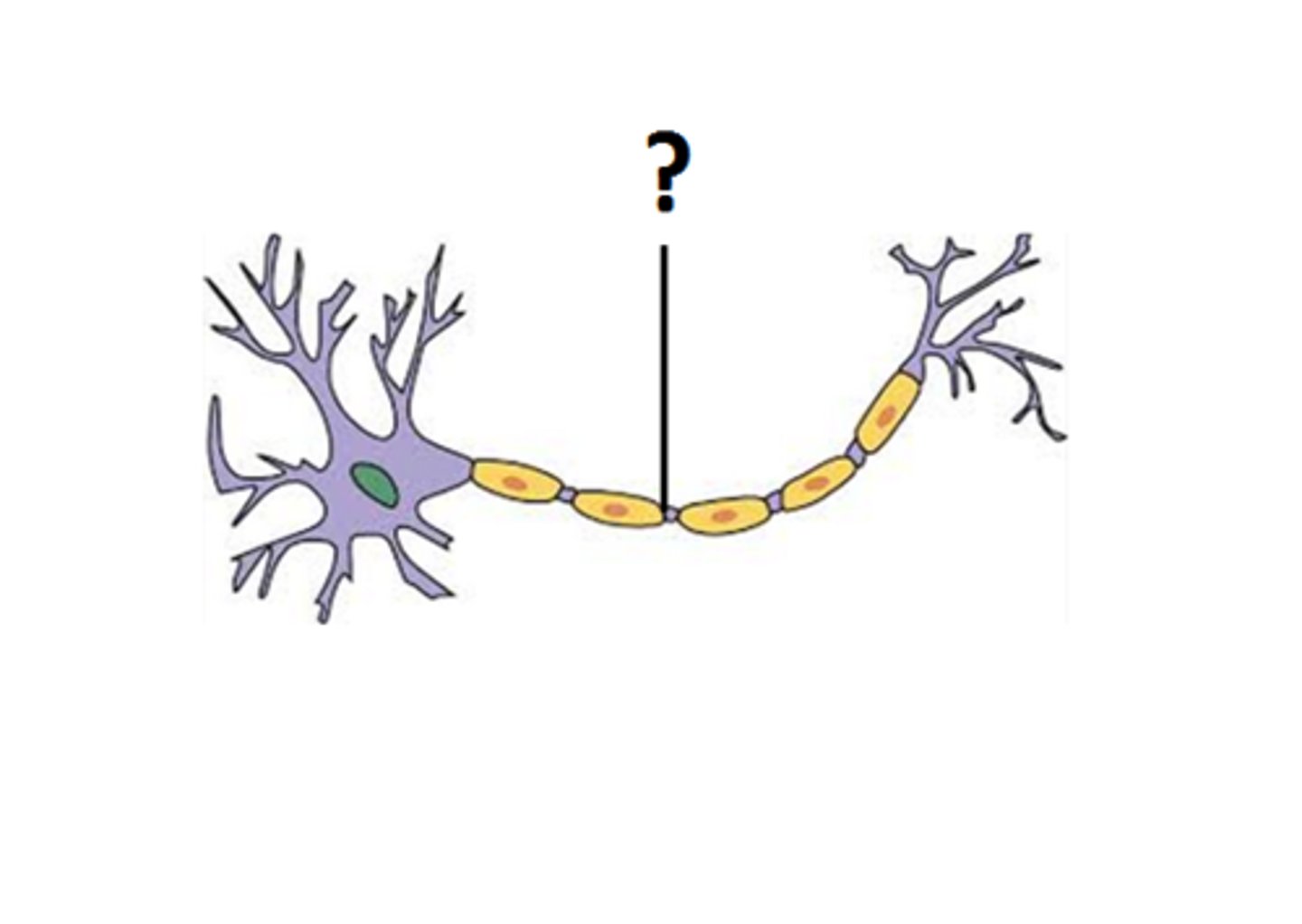
Axon
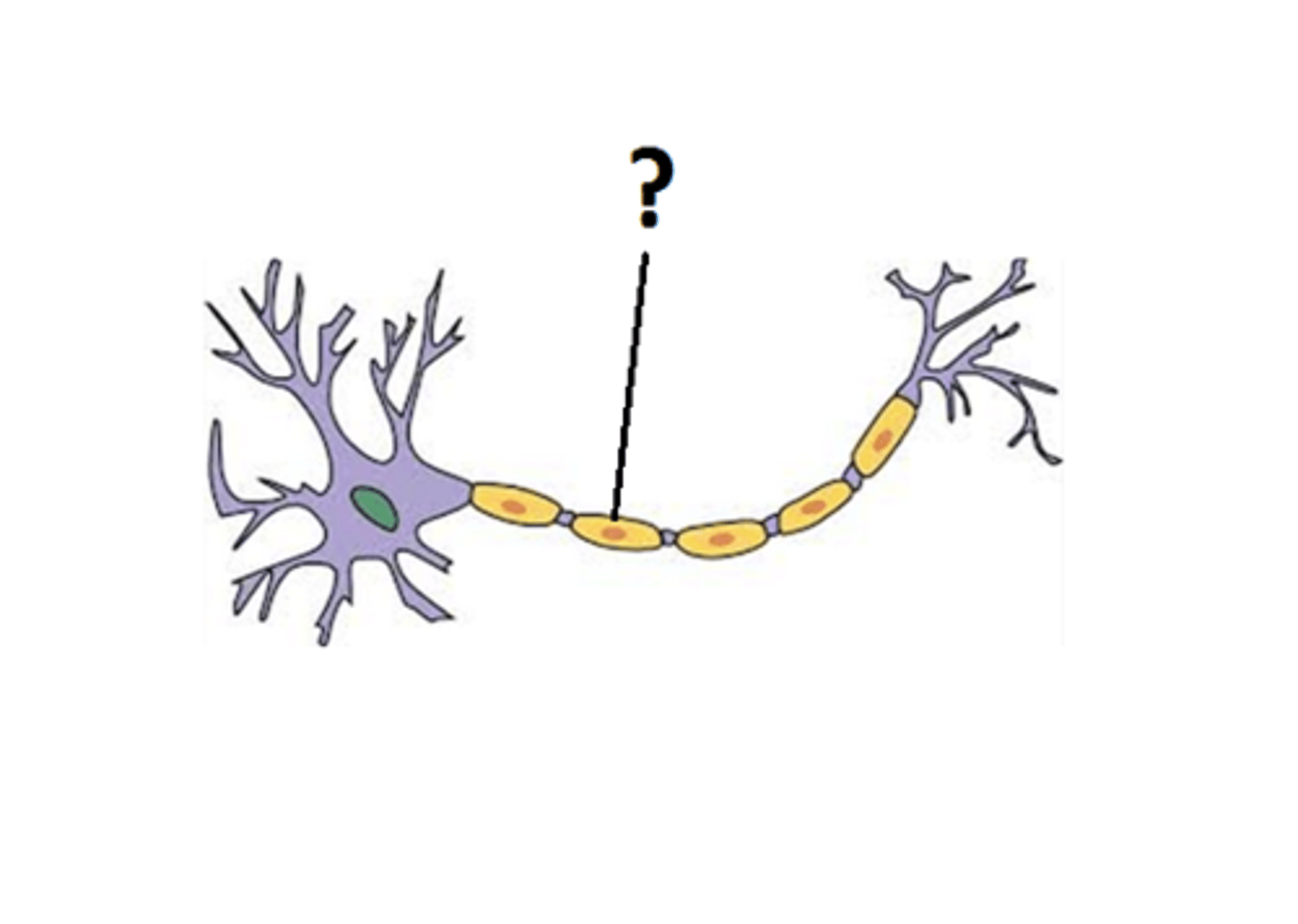
Myelin sheath
Vesicle
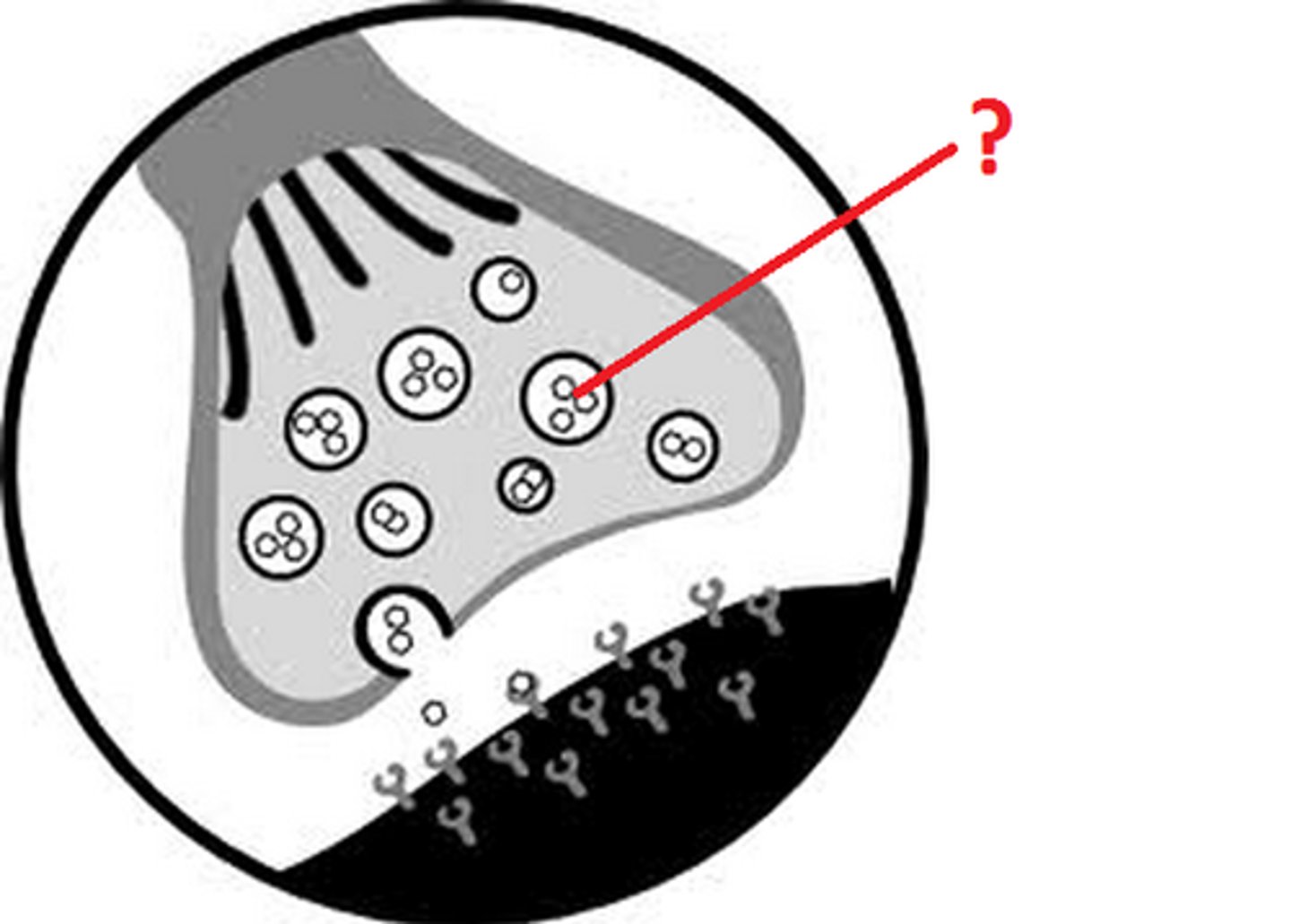
Pre-synaptic neuron
Delivers an impulse to another neuron
Post-synaptic neuron
Receives an impulse from another neuron
Receptors
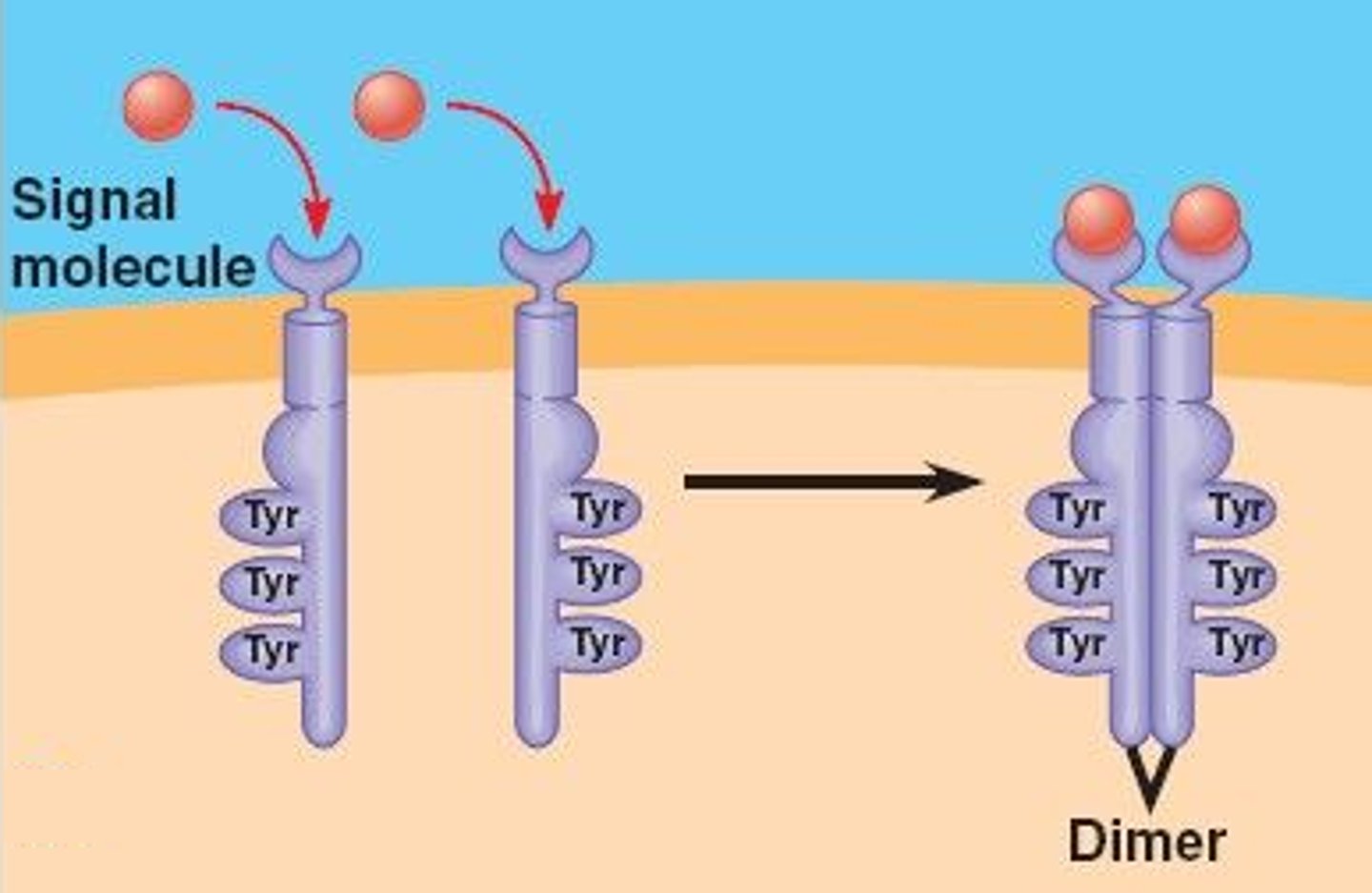
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Scopolamine
Blocks the acetylcholine receptor sites
Physostigmine
Breaks down the enzyme acetylcholinesterase which breaks down acetylcholine in the synapse.
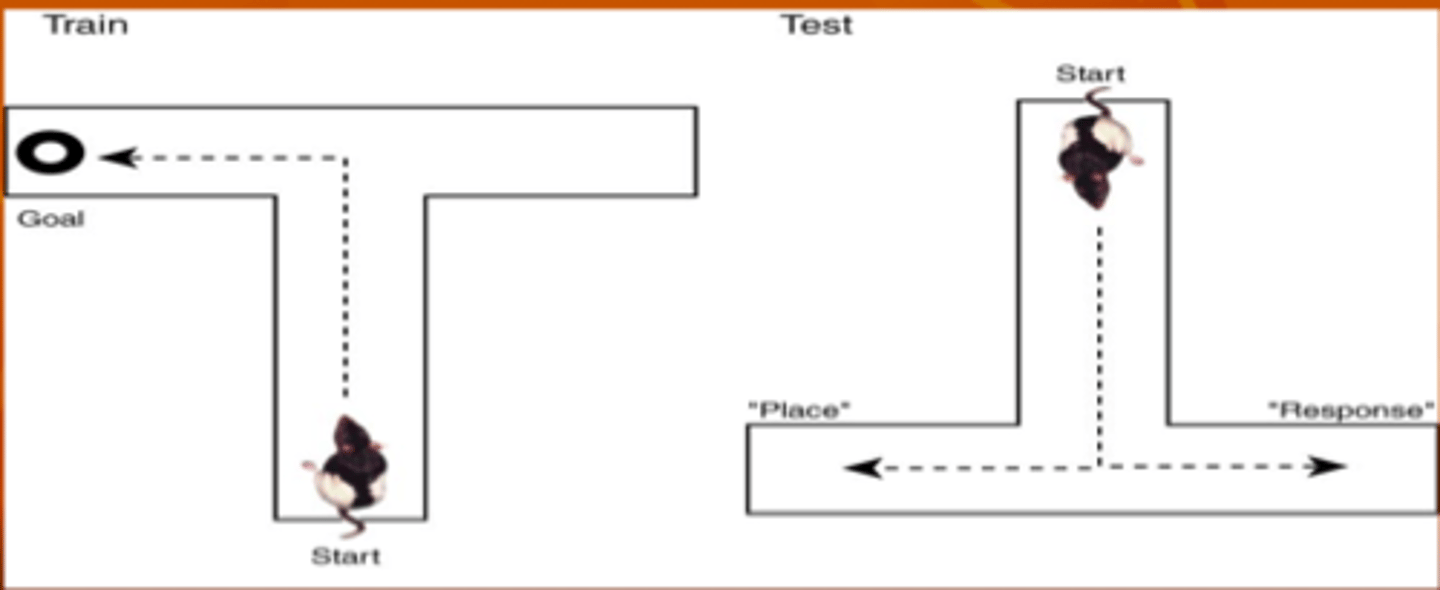
t-maze
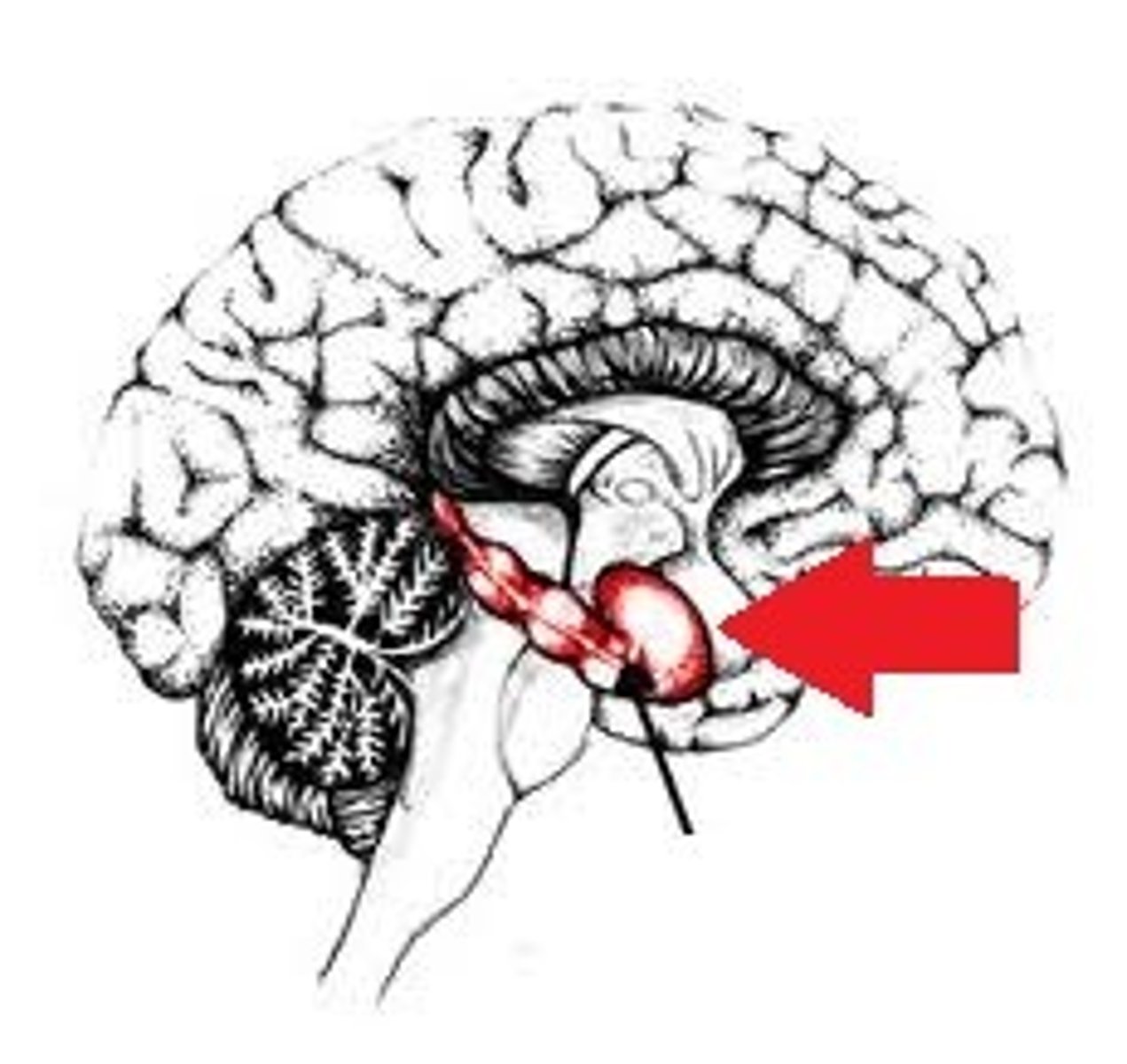
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process declarative memories for storage.
Broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
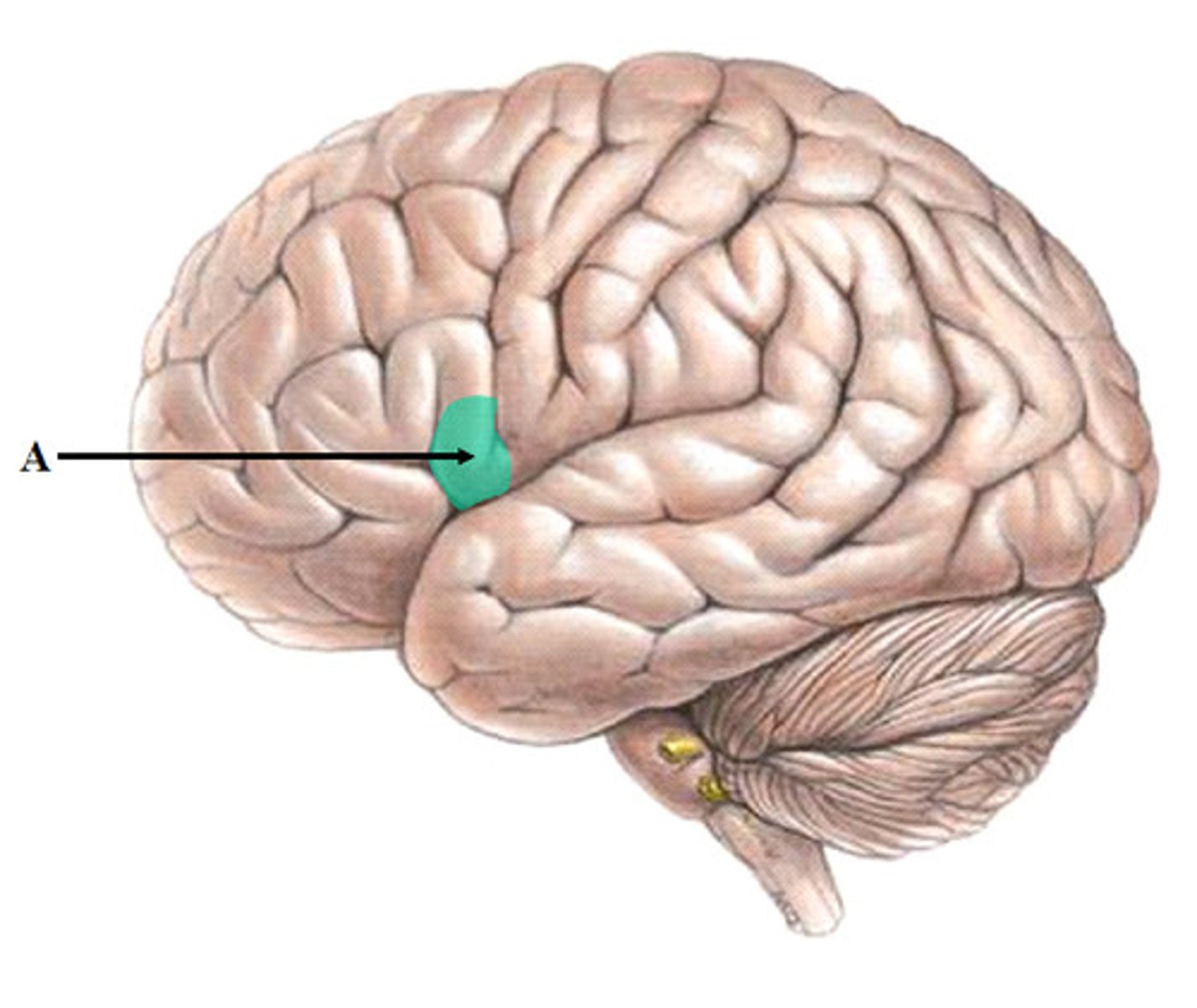
Wernicke's area
Controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
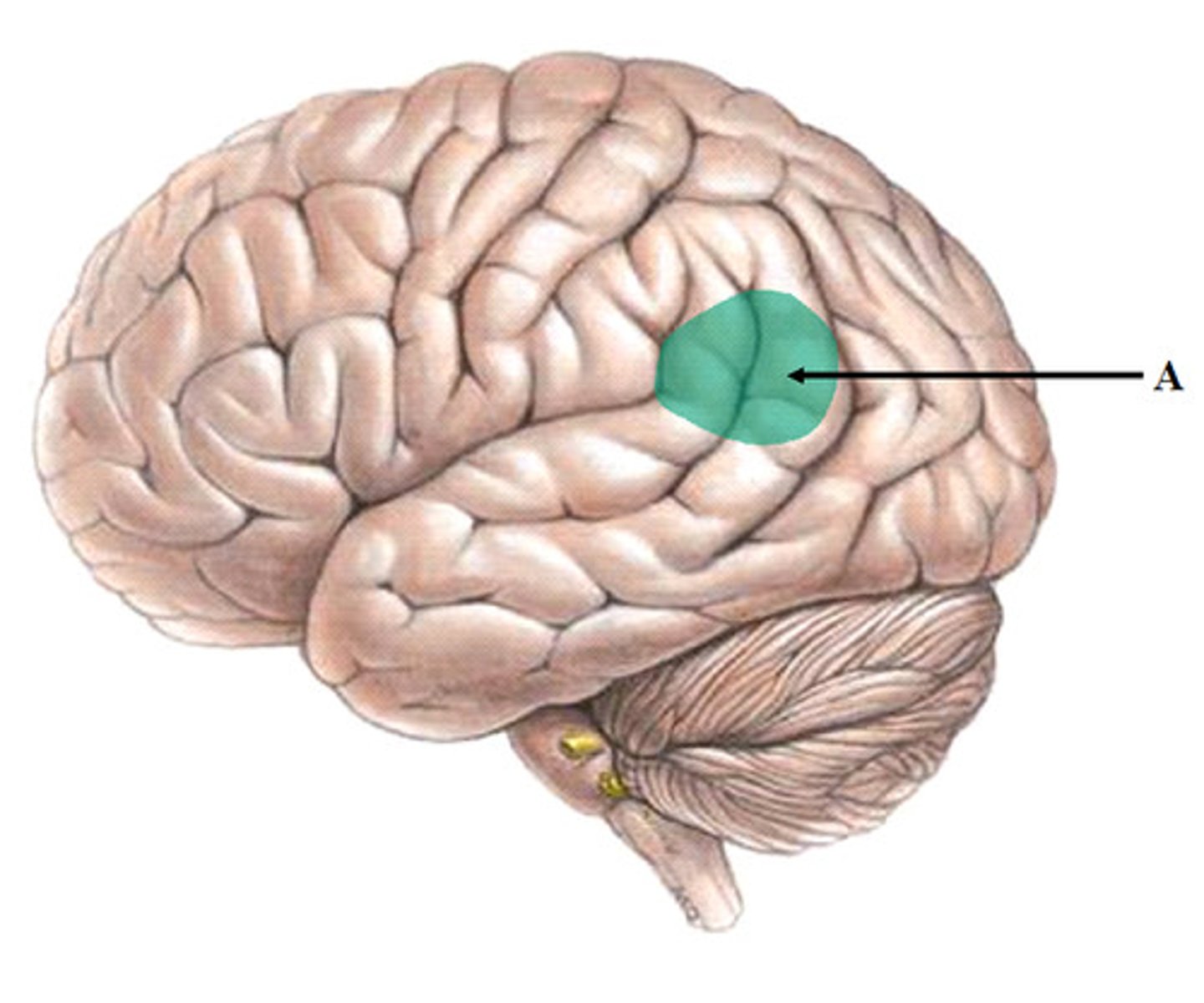
insula
Part of the brain that plays a role in compassion, empathy, taste, perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning and interpersonal relationships.
corpus callosum
A broad band of nerve fibers connecting the two hemispheres of the brain.
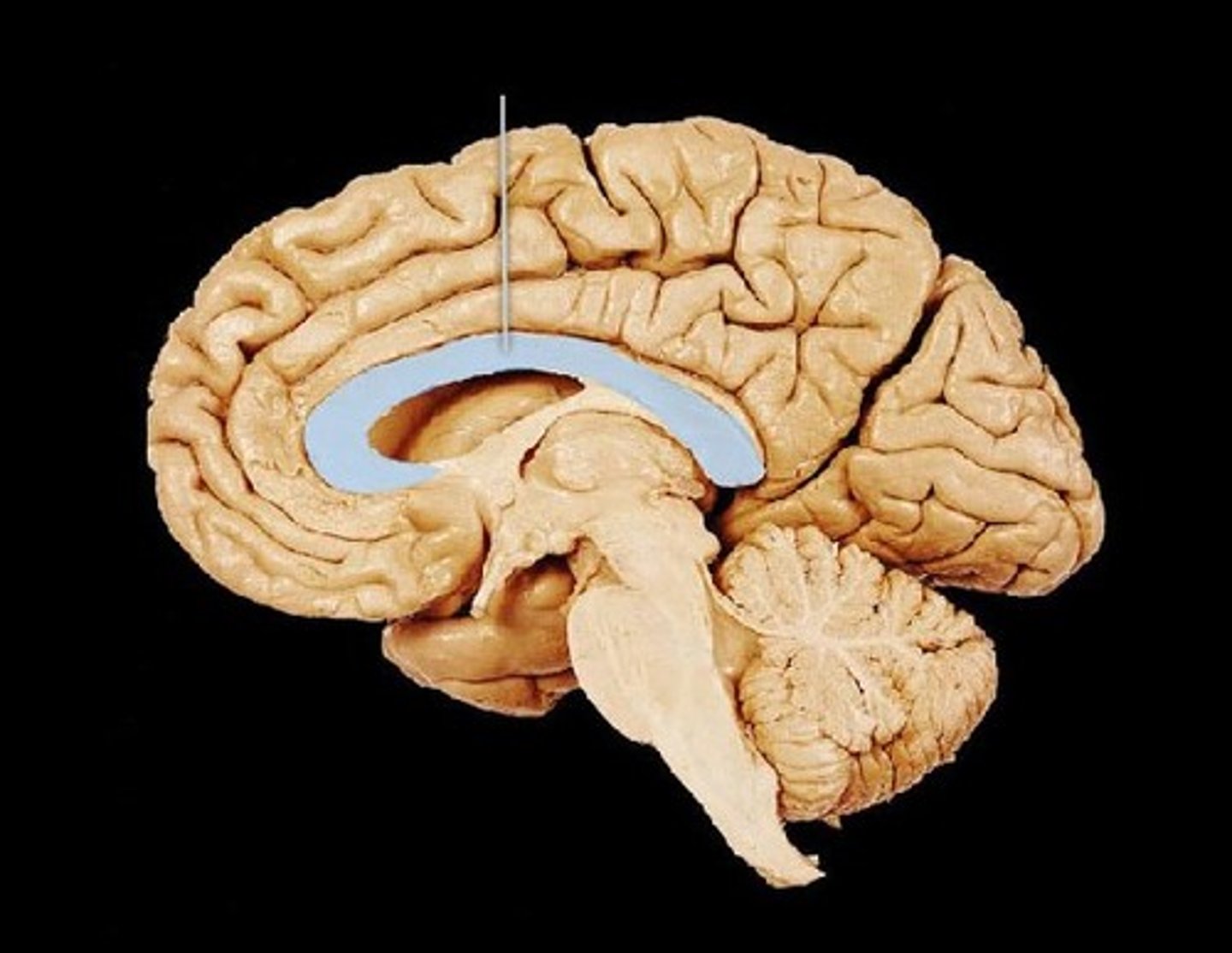
Split-brain patient
A patient who has had most or all of his or her corpus callosum severed.
equipotentiality
A theory proposed by Lashley that the effects of damage to the brain are determined by the extent rather than the location of the damage. For example, memory is distributed throughout the brain rather than confined to any specific location.
reductionist
Overly simplifies a complicated human process.
holistic
dealing with something as a whole rather than by its individual parts
Neuron
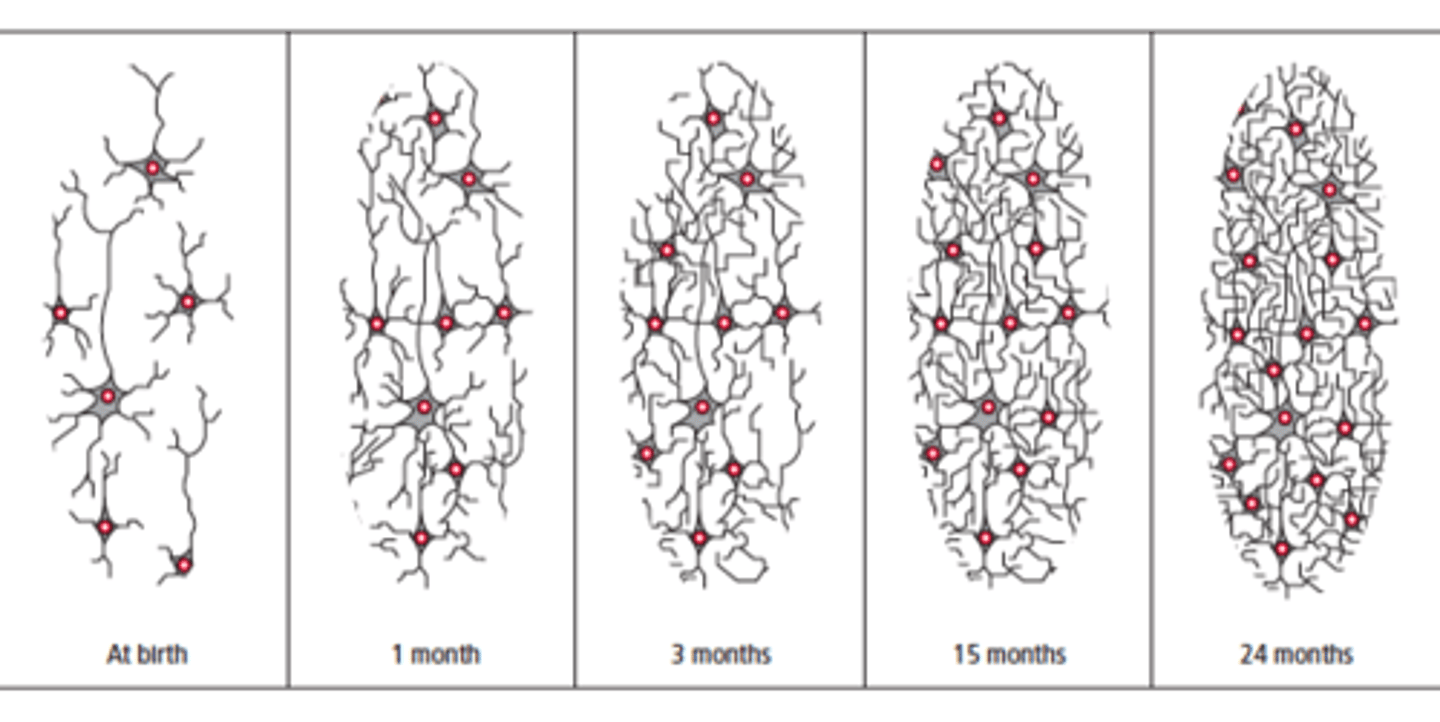
neuroplasticity
The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
synaptic plasticity
the ability to adjust synaptic connections between neurons
grey matter
dendritic branching
the neurons connecting to create a new trace in the brain.
synaptic pruning
the elimination of neurons as the result of nonuse or lack of stimulation
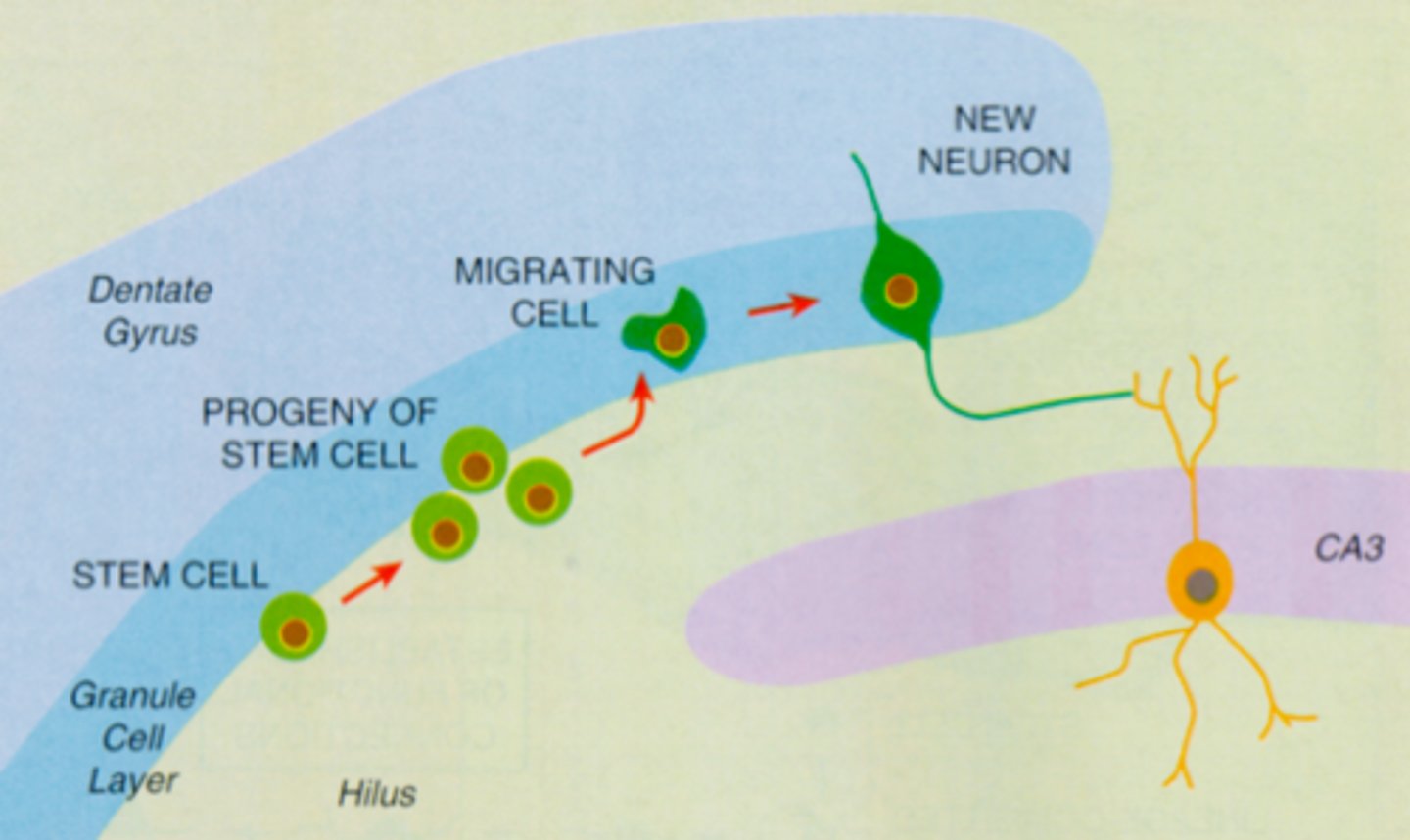
neurogenesis
formation of new neurons
Localisation of function
The theory that different areas of the brain are responsible for different behaviours, processes or activities.
Still learning (14)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!