Anatomy Exam 4
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
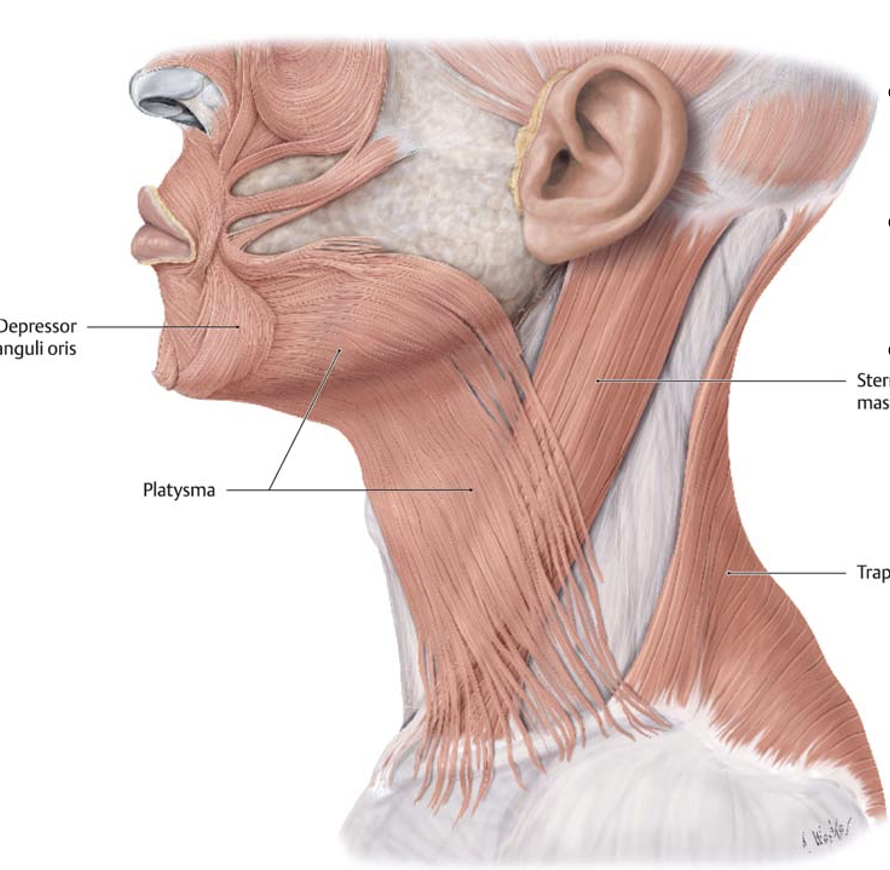
Action and innervation of the platysma muscle
tenses skin of inferior face and neck
facial nerve (CN VII)
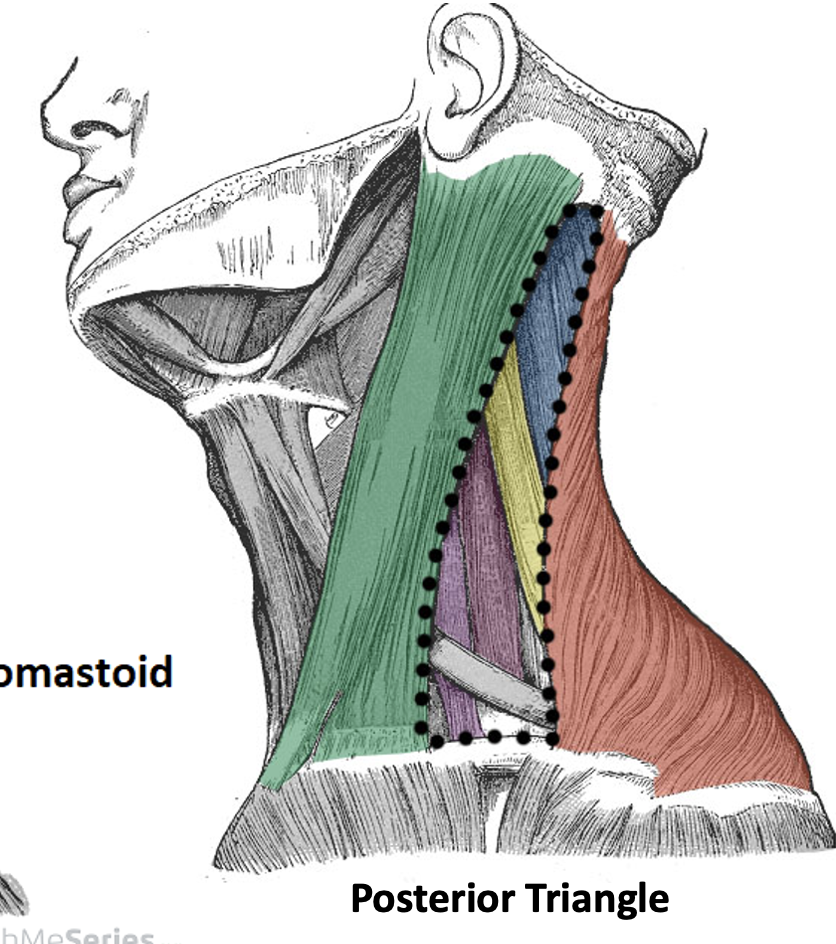
Borders of the posterior triangle
Anterior: sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
Posterior: Trapezius
Inferior: Clavicle
Floor: Prevertebral fascia, scalene muscles (anterior, middle and posterior), levator scapulae muscle, splenius capitis muscle
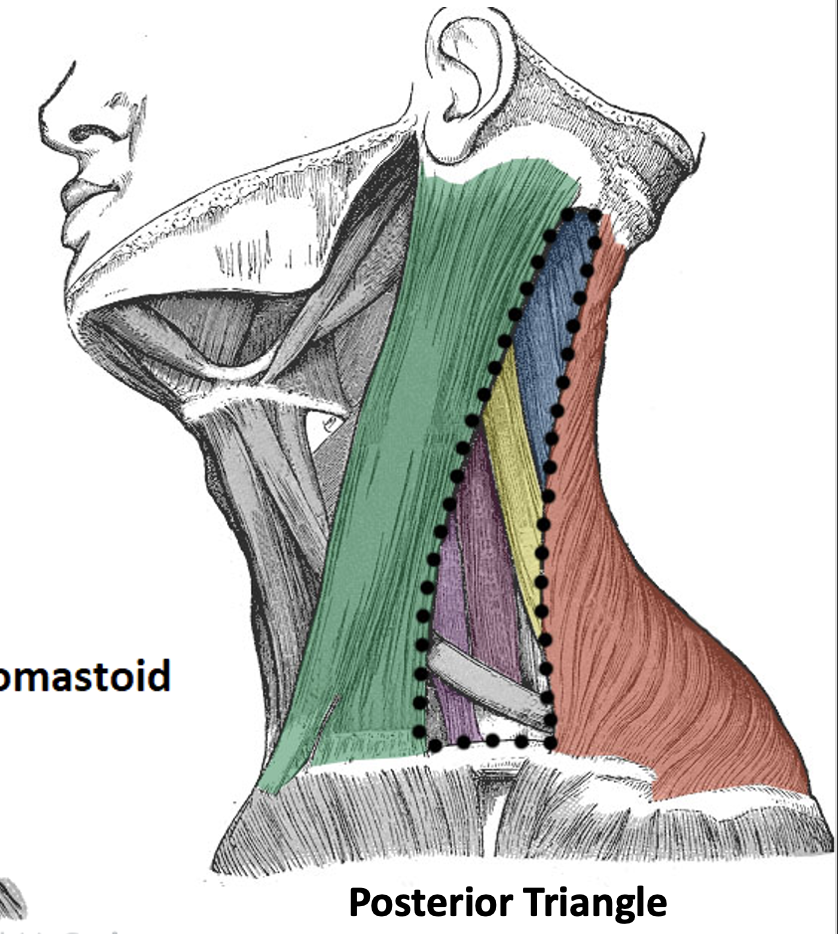
Content of the posterior triangle
inferior belly of omohyoid muscle, cervical plexus (C1-C4), roots and trunks of brachial plexus (C5-T1), phrenic nerve (C3-C5), accessory nerve (CN XI), external jugular vein, subclavian vein, subclavian artery and branches
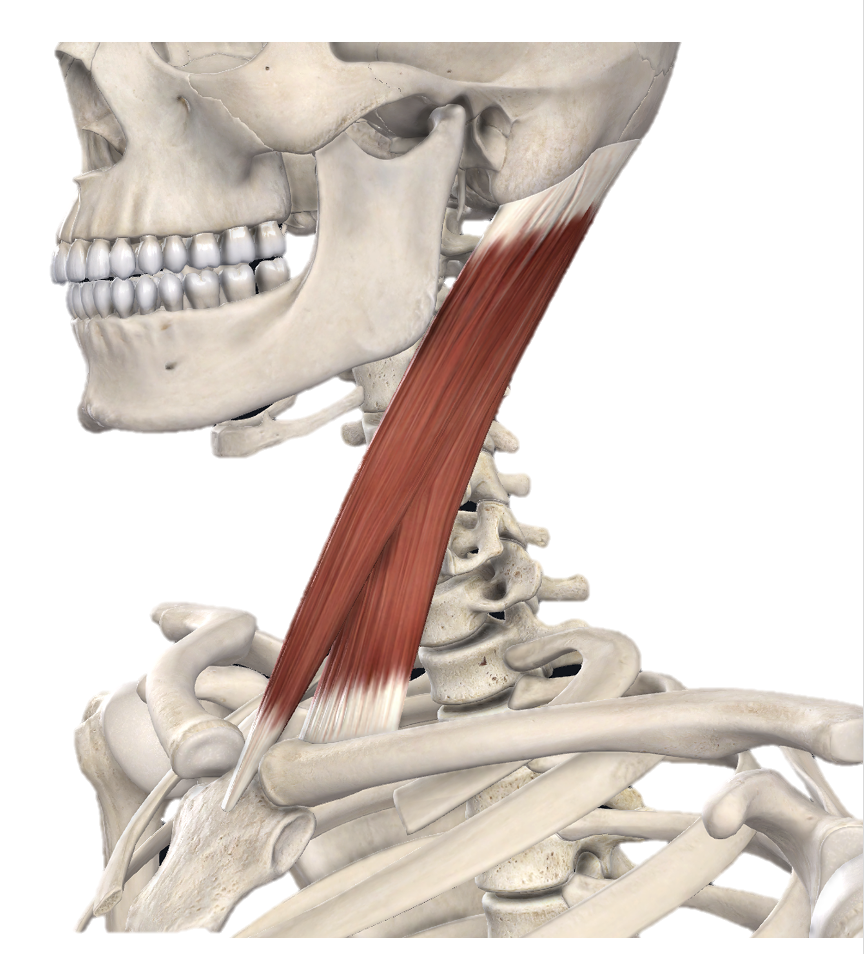
Action and innervation of Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle
together: neck flexion
individual: rotate head to opposite side, lateral flexion of head
accessory nerve (CN XI)
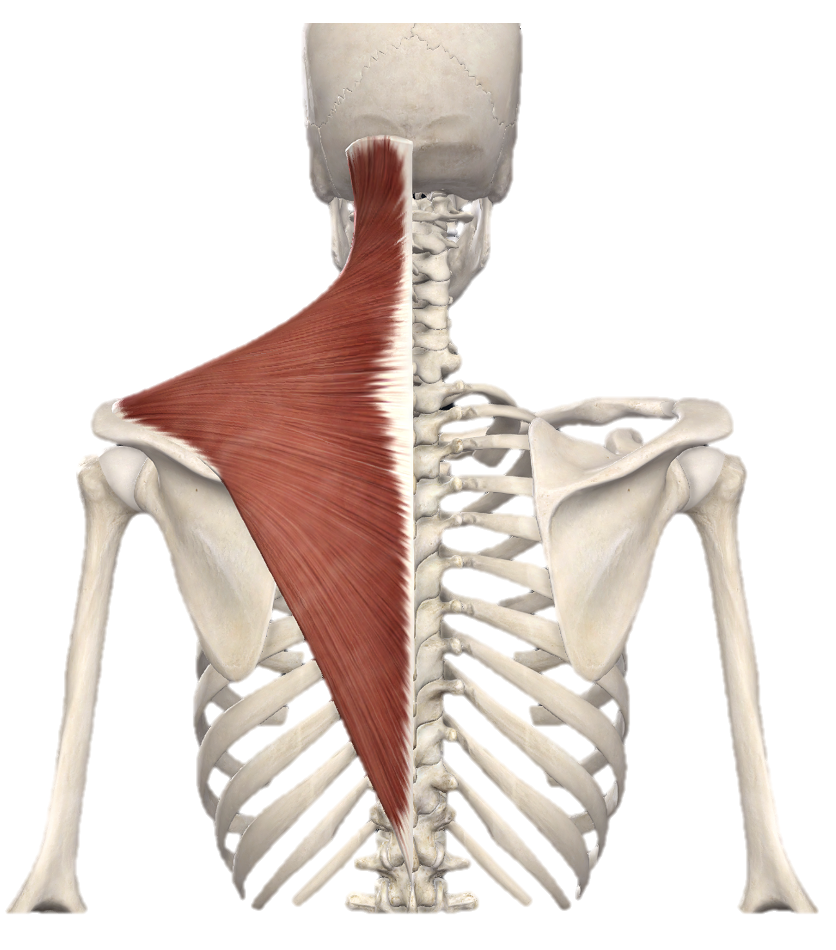
Action and innervation of Trapezius muscle
superior: elevate scapula
middle: adduct scapula
inferior: depress scapula
accessory nerve (CN XI)
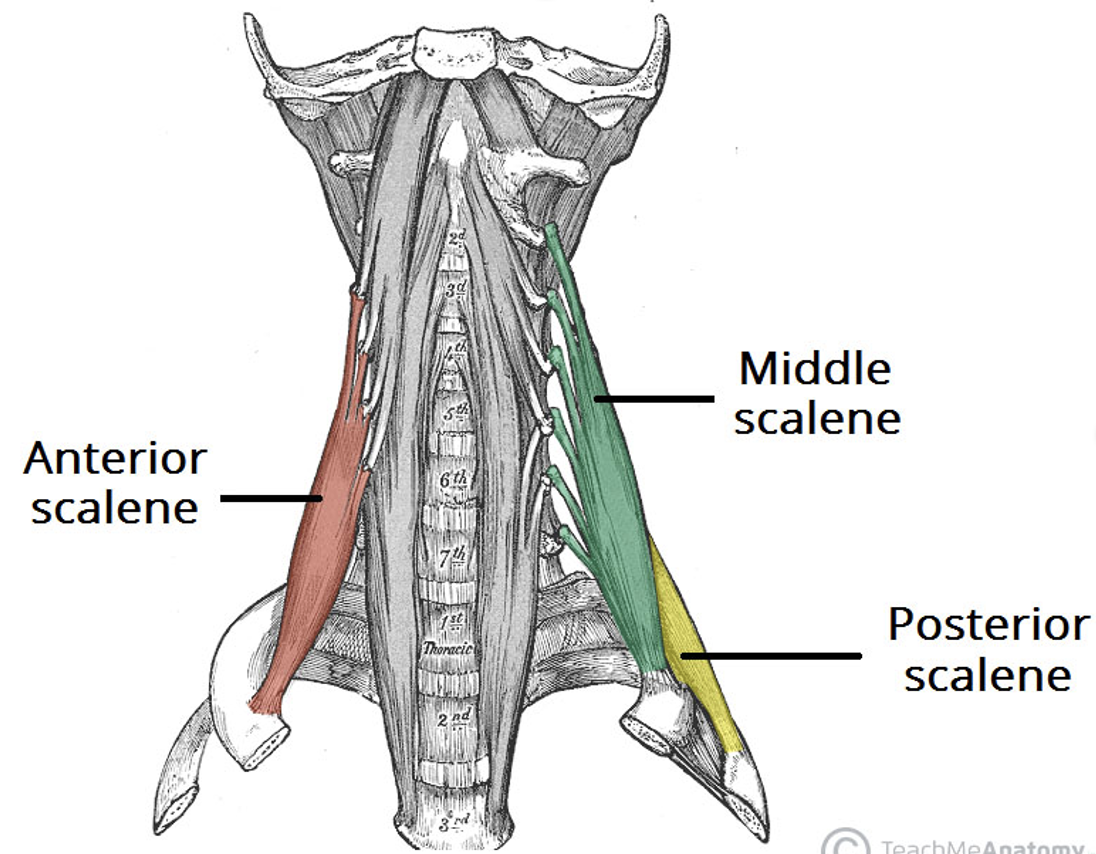
Action and innervation of Scalene muscle
elevation of ribs 1 and 2
anterior rami of C3-C7
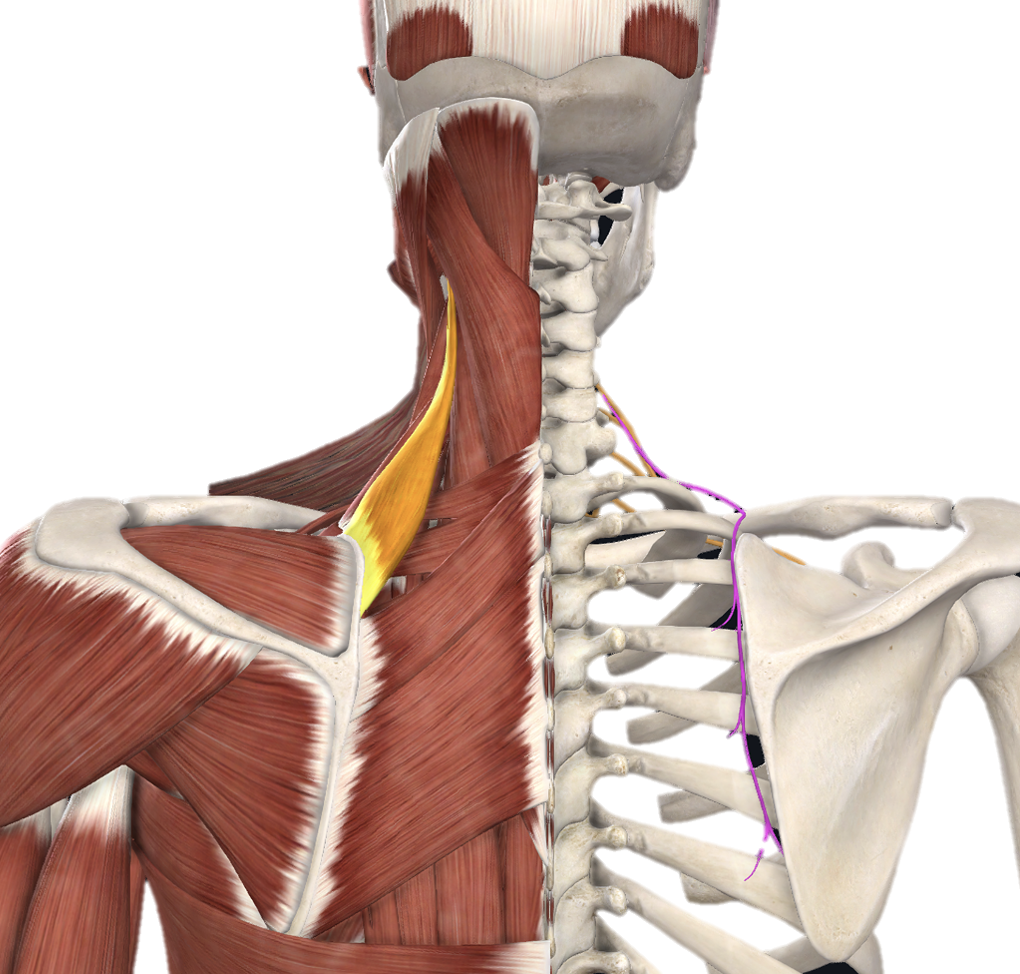
Action and innervation of Levator scapulae muscle
elevate scapula
dorsal scapular nerve
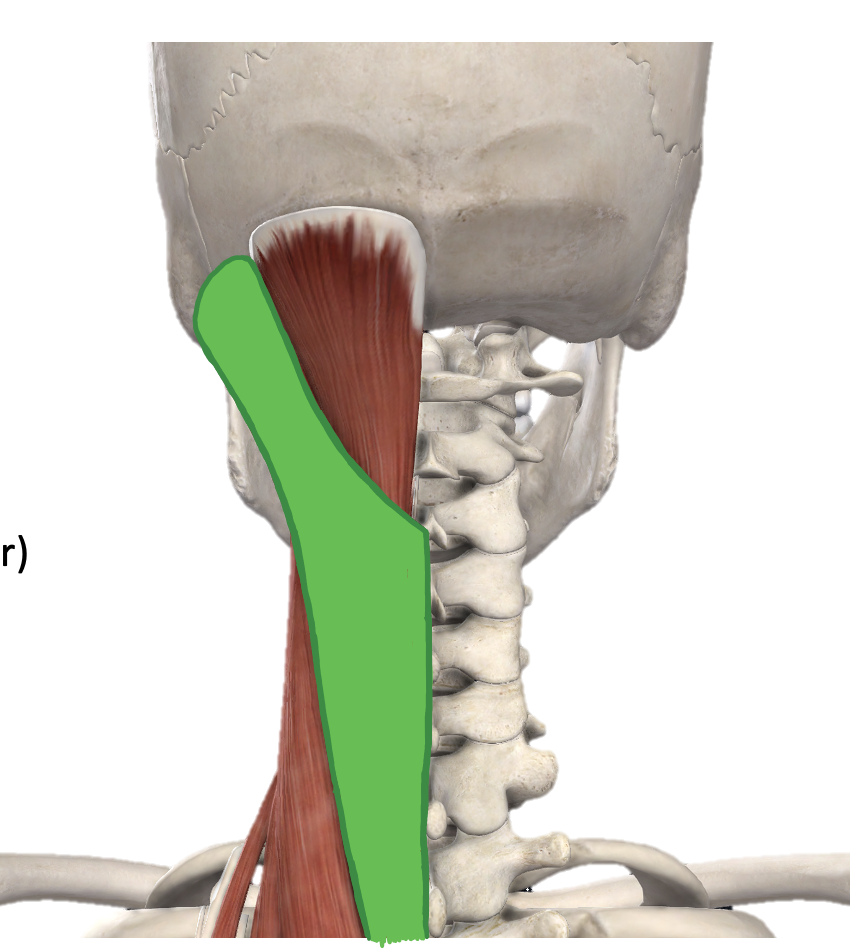
Action and innervation of Splenius Capitis muscle
together: extension of neck
individual: rotate head to same side
posterior rami of spinal nerves
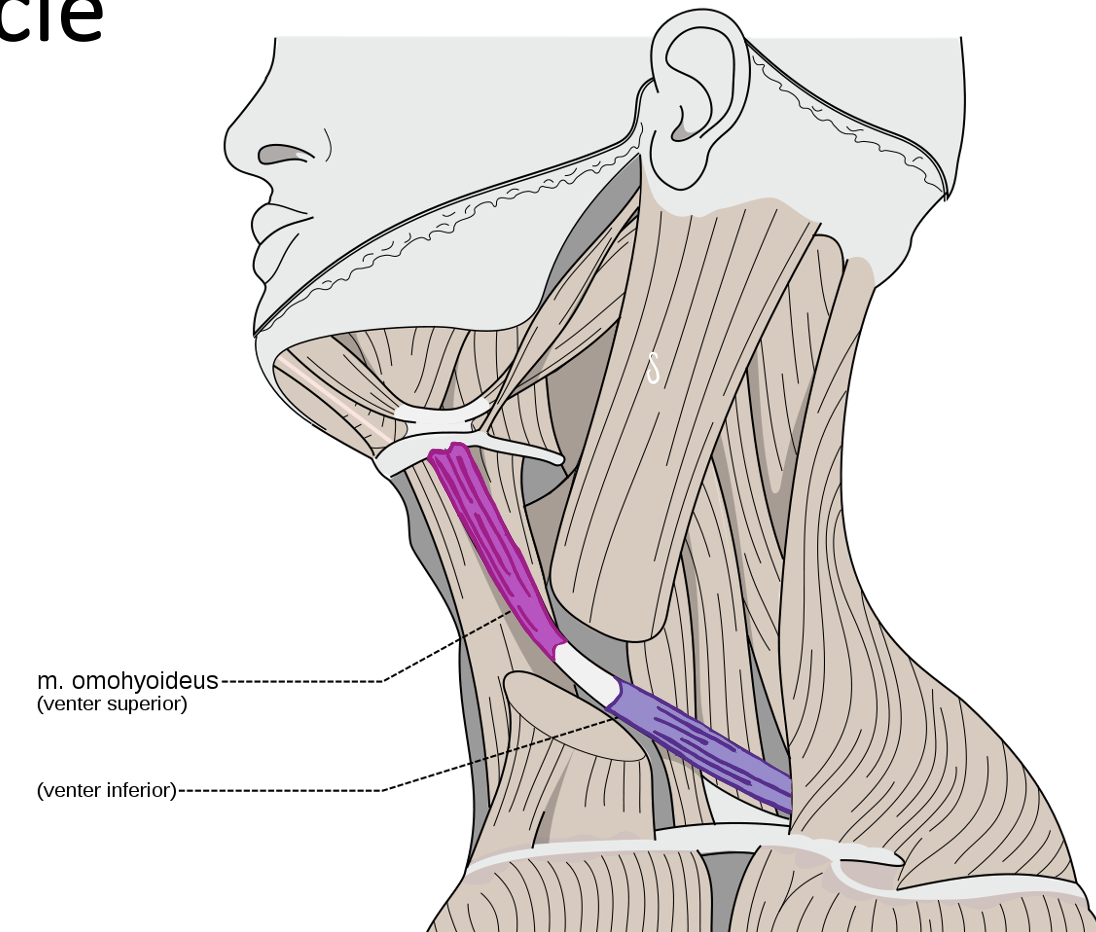
Action and innervation of Inferior Belly of the Omohyoid muscle
depresses hyoid bone
anterior rami of C1-C3 (ansa cervicalis)
What nerve runs on the anterior scalene muscle? What muscle does this nerve innervate? What cervical spinal nerves make up this nerve?
phrenic nerve
diaphragm
C3-C5
What structure is located between the anterior and middle scalene muscles?
roots of brachial plexus
What does the external jugular vein drain into?
the subclavian vein
What is the relationship between the subclavian artery and the anterior scalene muscles?
1st part of the subclavian artery is medial to the anterior scalene muscle
2nd part of the subclavian artery is posterior to the anterior scalene muscle
3rd part of the subclavian artery is lateral to the anterior scalene muscle
Identify the arteries (and their branches) that come off each of the parts of the subclavian artery.
1st part: vertebral artery, internal thoracic artery, thyrocervical trunk (branches = inferior thyroid, ascending cervical, transverse cervical, suprascapular)
2nd part: costcocervical trunk
3rd part: dorsal scapular artery
What cervical spinal nerves make up the cervical plexus?
anterior rami of C1-C4
What is the relationship between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and cervical plexus?
cervical plexus pierces the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
What is the ansa cervicalis? What muscles does it supply?
loop in the cervical, anterior rami of C1-C3
supplies the omohyoid muscle, sternothyroid muscle, and sternohyoid muscle
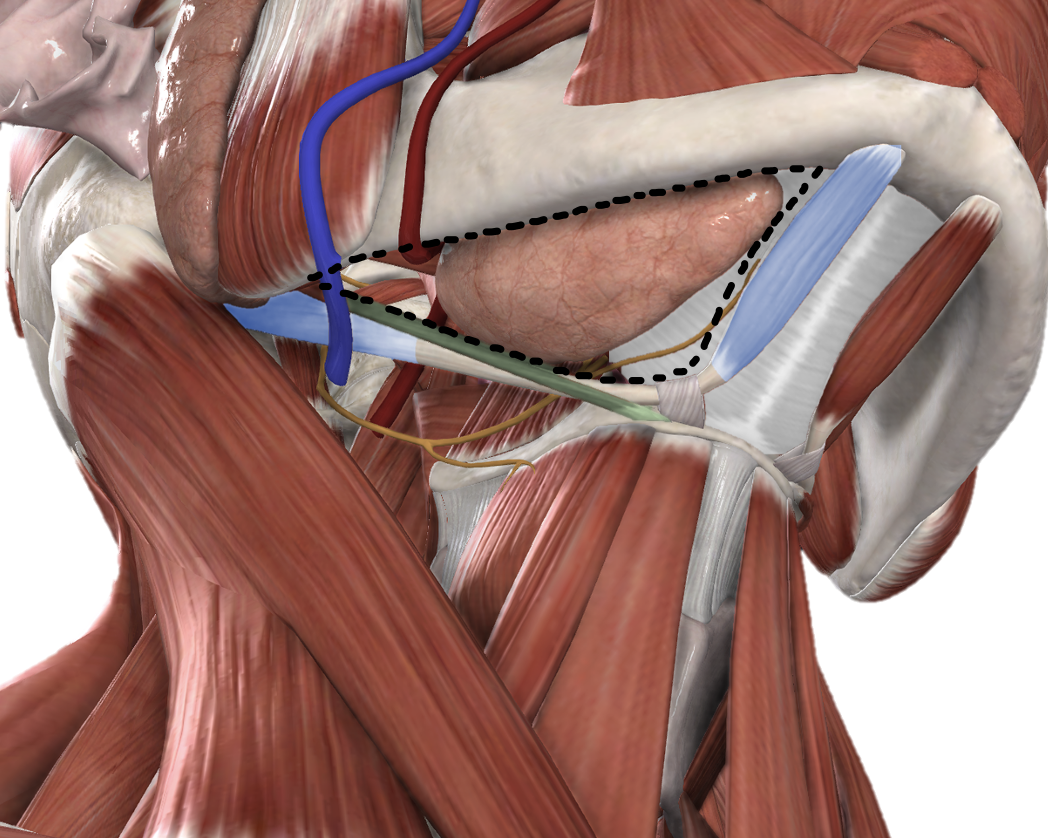
Borders and content of the Anterior Triangle - Submandibular Triangle
superior: mandible
anterior: anterior belly of the digastric muscle
posterior: posterior belly of the digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle
submandibular gland, lymph nodes, facial vein and artery, hypoglossal nerve and mylohyoid muscle
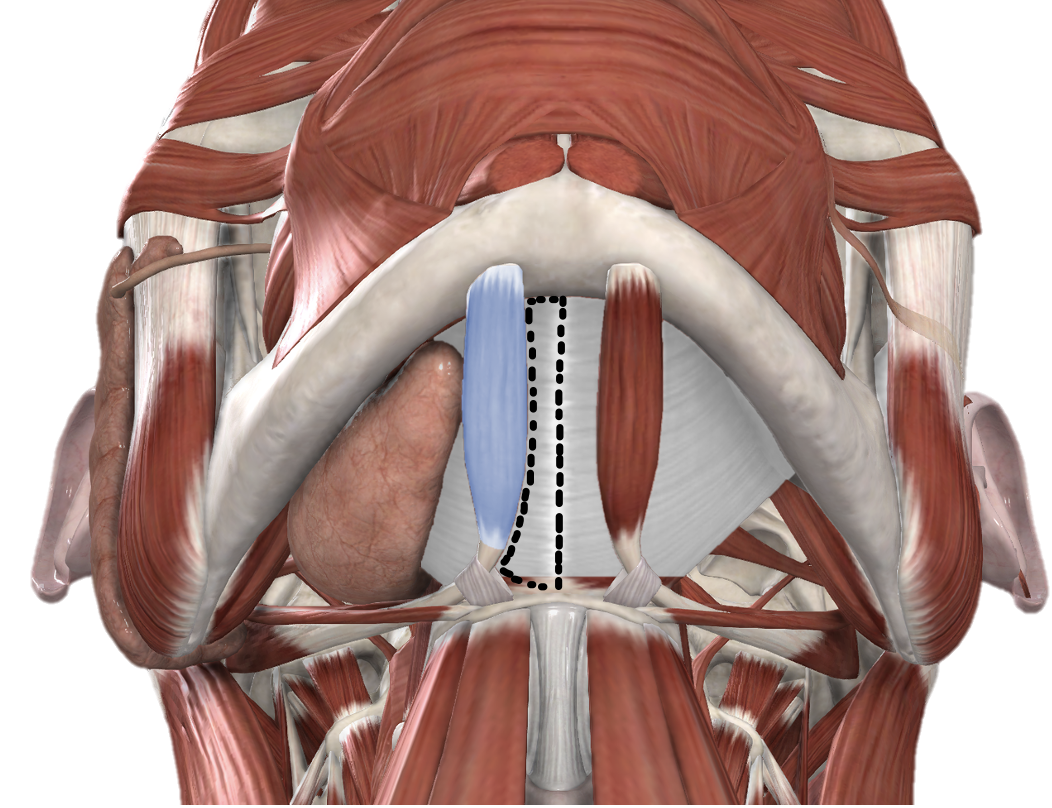
Borders and content of the Anterior Triangle - Submental Triangle
superior: mandible
inferior: hyoid
medial: midline of neck
lateral: anterior belly of digastric muscle
branches of facial artery and vein, branch of mandibular nerve (CN V3), mylohyoid muscles, lymph nodes
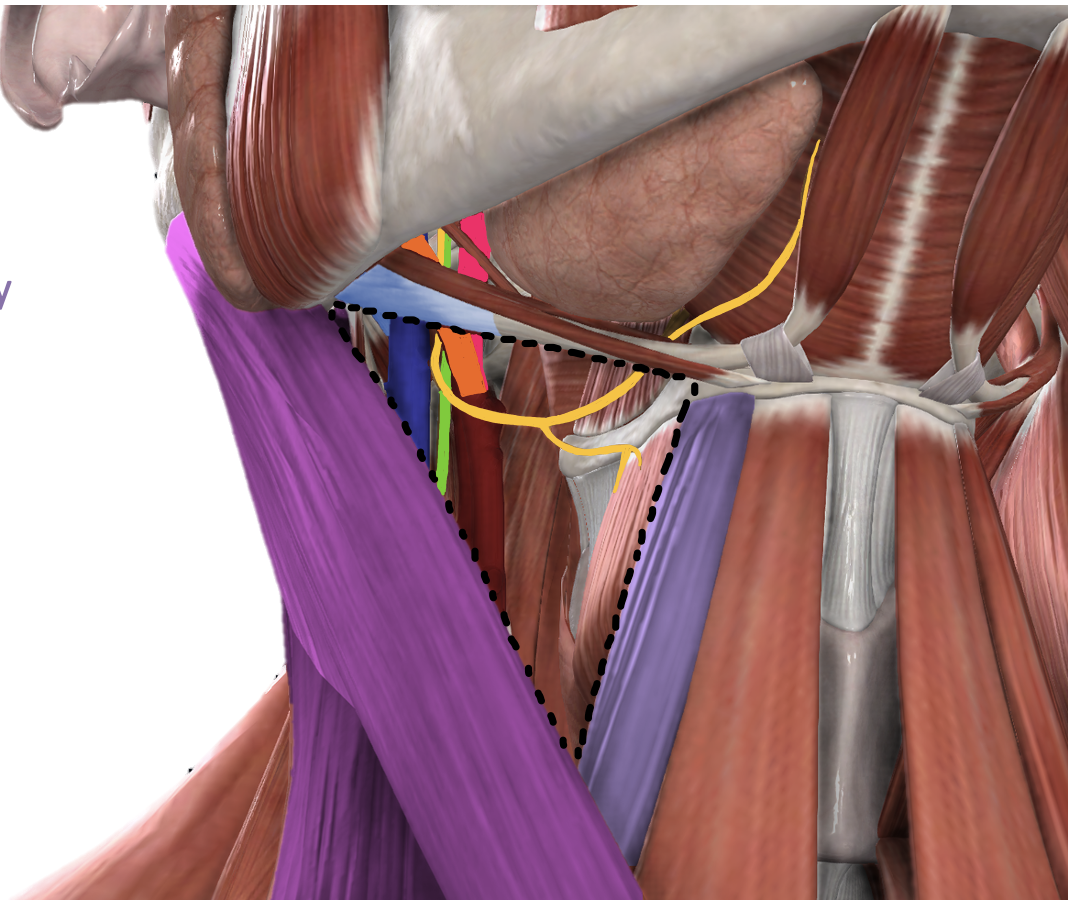
Borders and content of the Anterior Triangle - Carotid Triangle
superior: posterior belly of digastric muscle
anteroinferior: superior belly of omohyoid muscle
posteroinferior: SCM
common carotid artery, external carotid artery, internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve, hypoglossal nerve
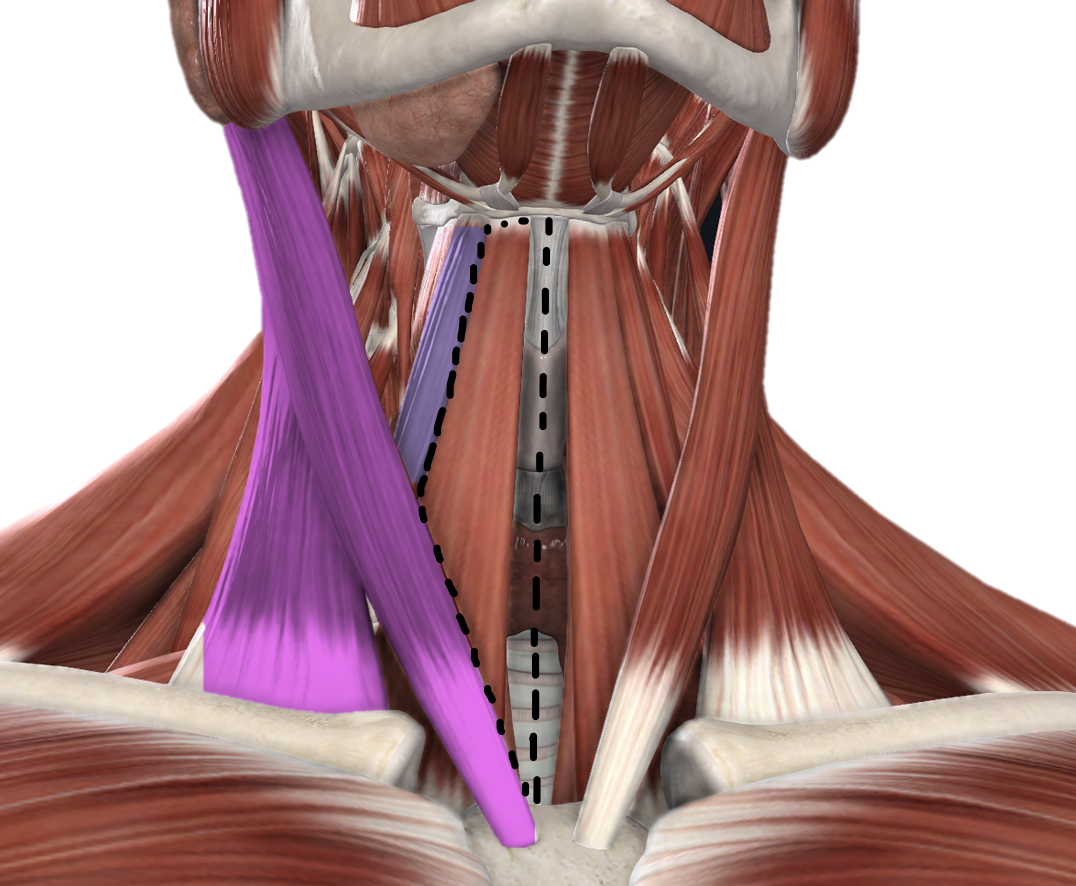
Borders and content of the Anterior Triangle - Muscular Triangle
superior: hyoid bone
medial: midline of neck
lateral: superior = superior belly of omohyoid muscle, inferior = SCM
infrahyoid muscles, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, larynx, trachea, pharynx, esophagus
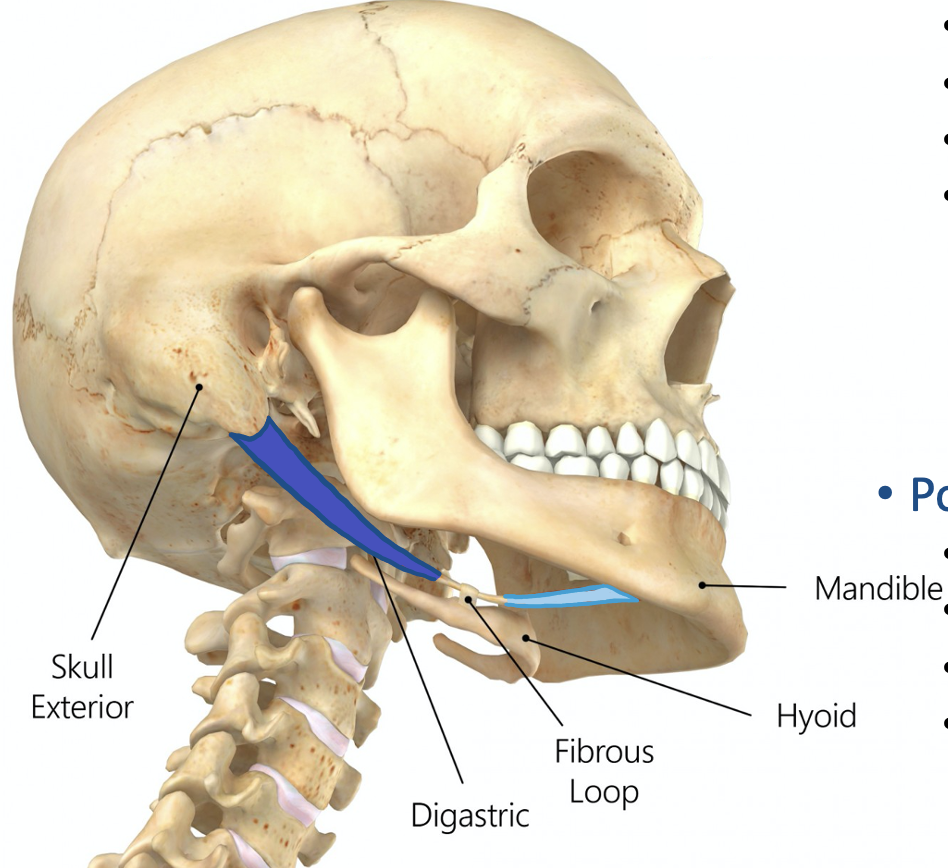
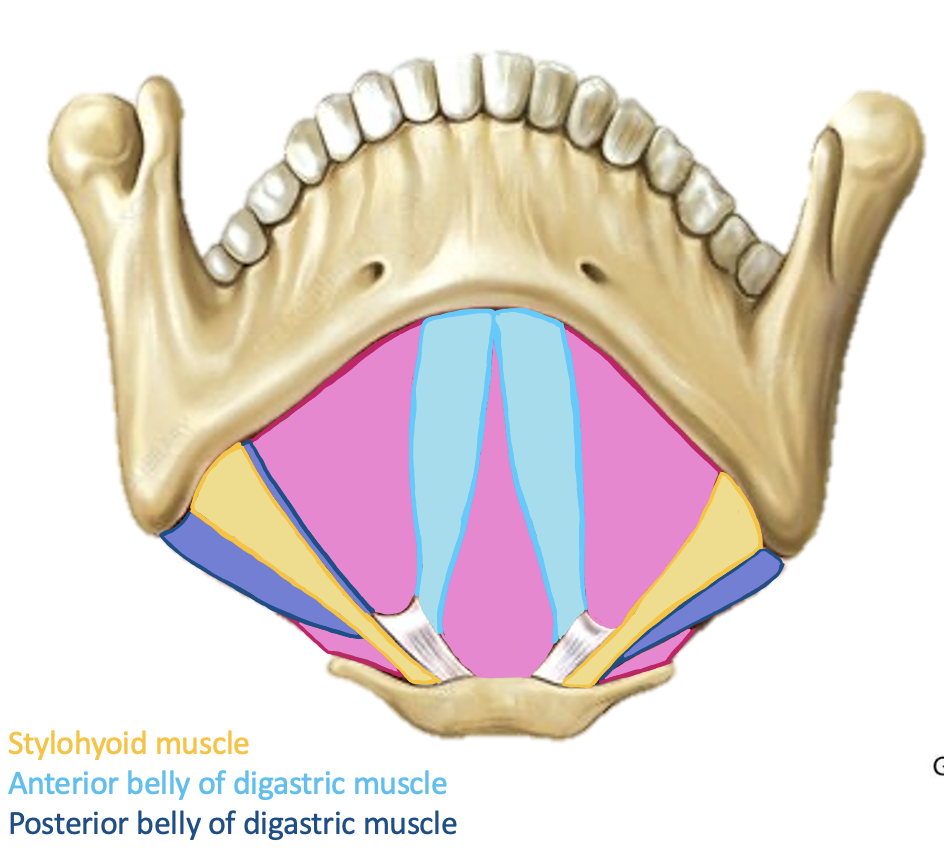
Action and innervation of Anterior Belly of Digastric Muscle
depress mandible
nerve to mylohyoid (branch of CN V3)
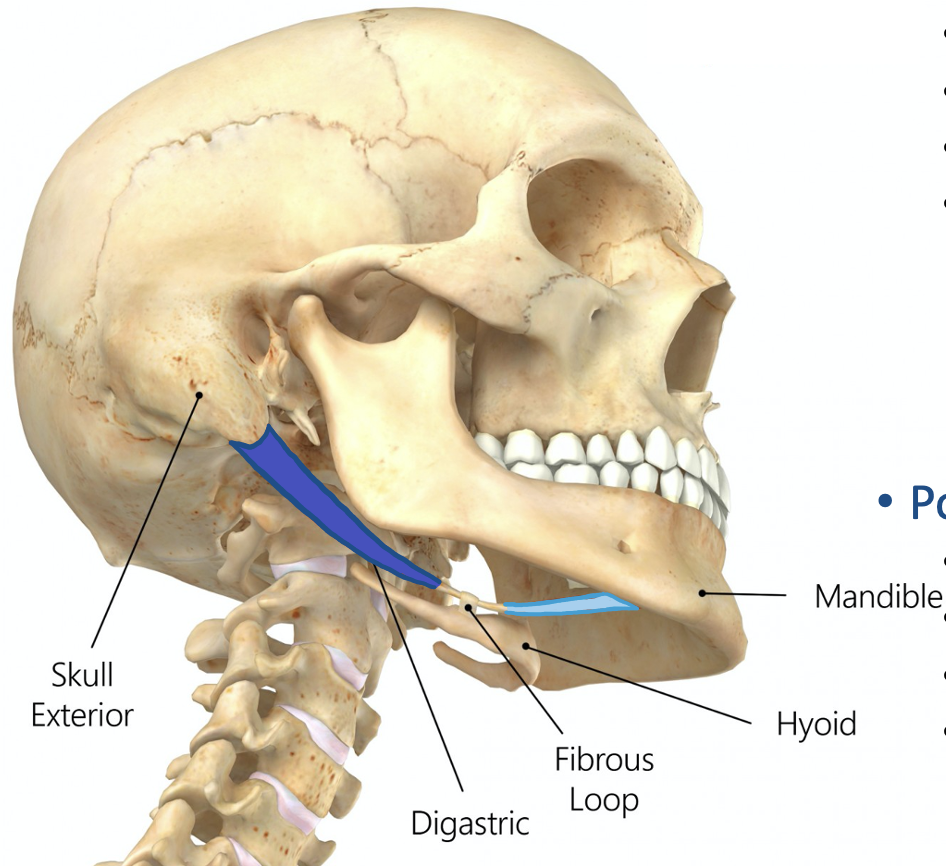
Action and innervation of Posterior Belly of Digastric Muscle
elevate hyoid bone
facial nerve (CN VIII)
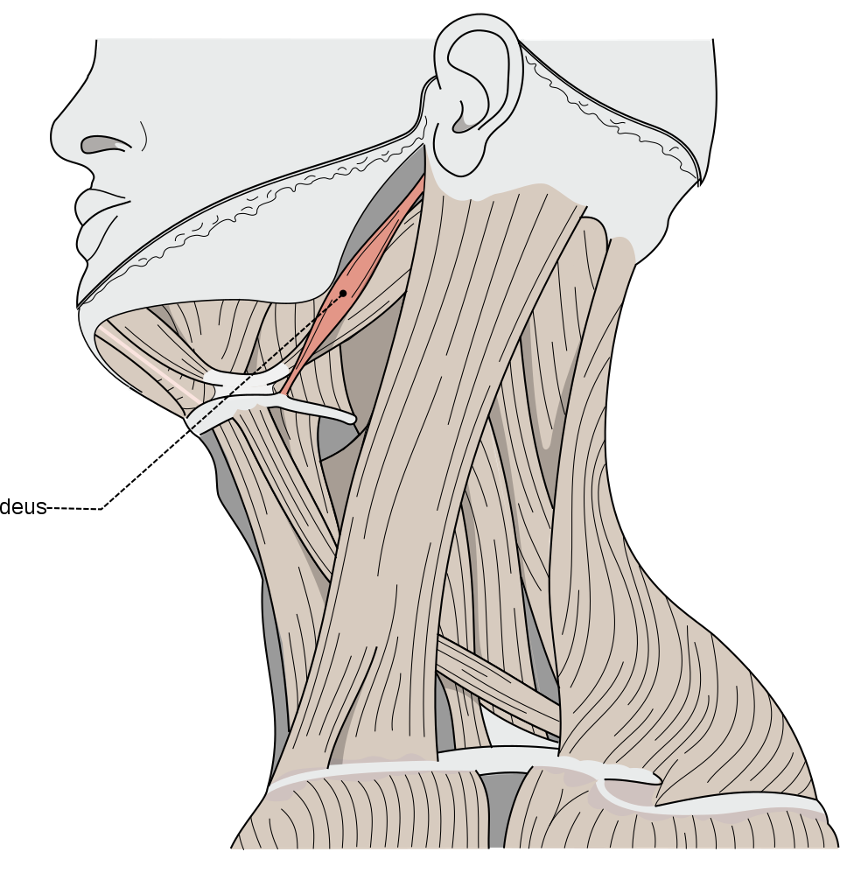
Action and innervation of Stylohyoid Muscle
elevates hyoid bone
facial nerve (CN VII)
Action and innervation of Mylohyoid Muscle
elevates hyoid bone and depresses mandible
nerve to mylohyoid (CN V3)
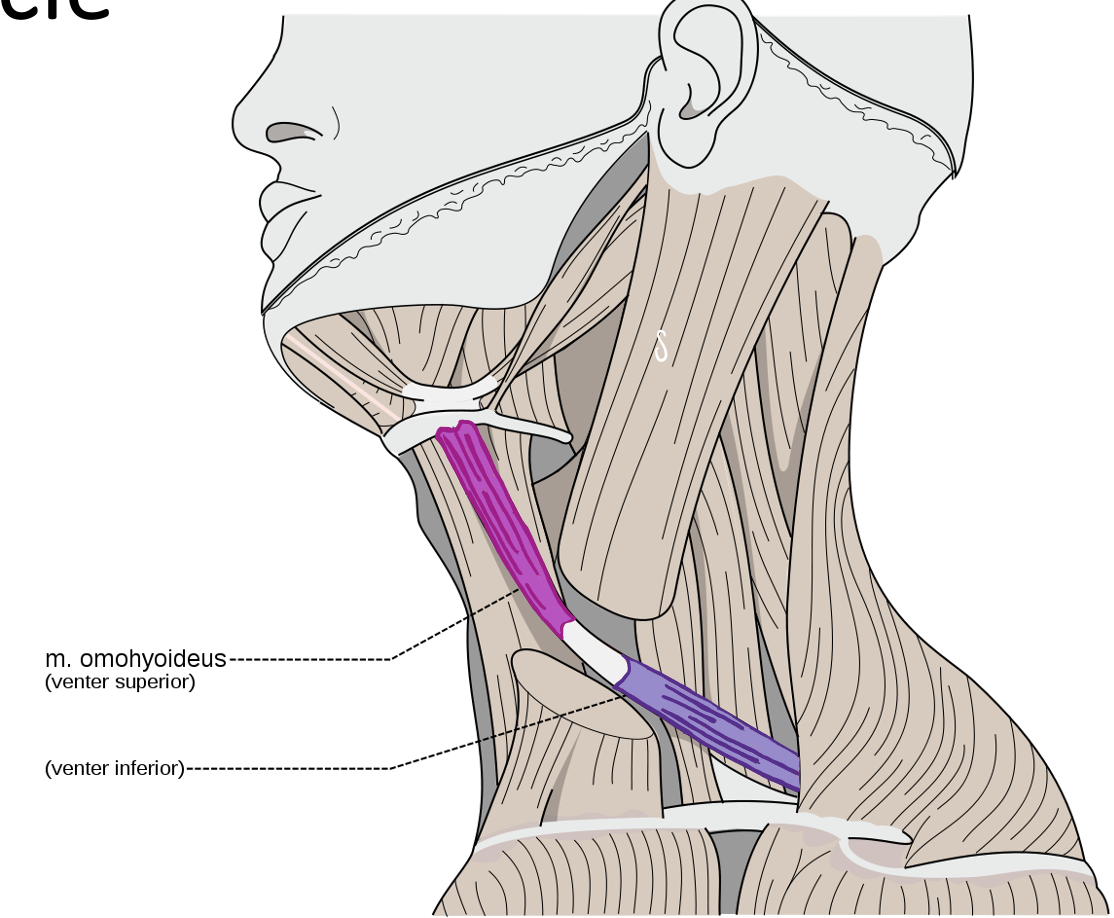
Action and innervation of Superior Belly of Omohyoid Muscle
depresses hyoid bone
anterior rami od C1-C3 (ansa cervicalis)
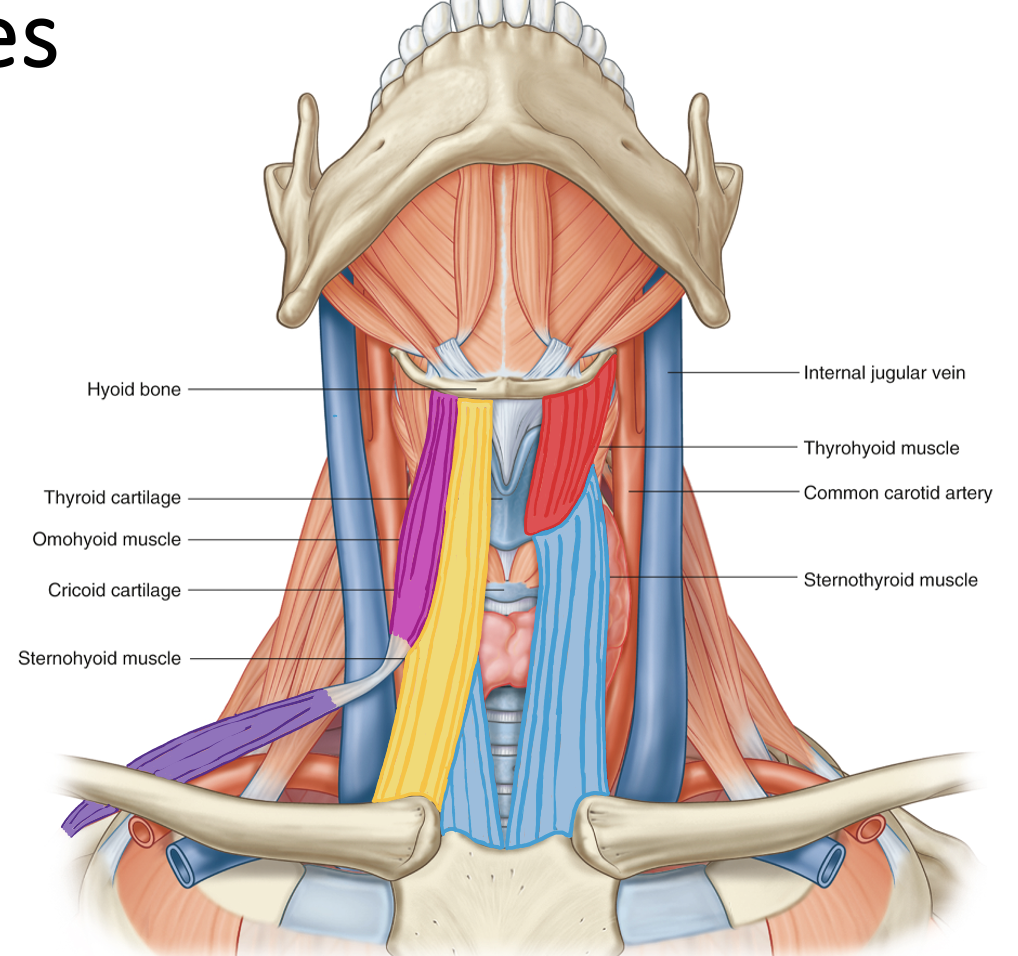
Action and innervation of Sternohyoid Muscle
depress hyoid bone
C1-C3 (ansa cervicalis)
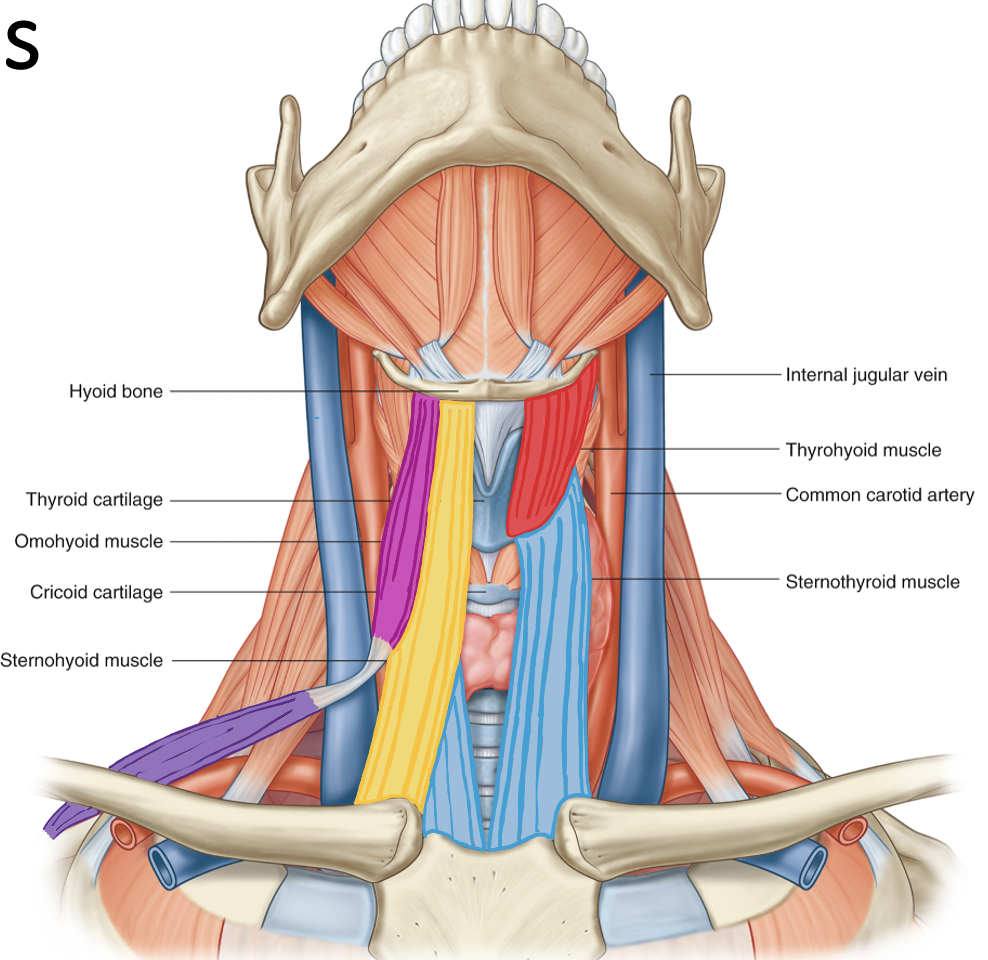
Action and innervation of Sternothyoid Muscle
depress hyoid bone
C1-C3 (ansa cervicalis)
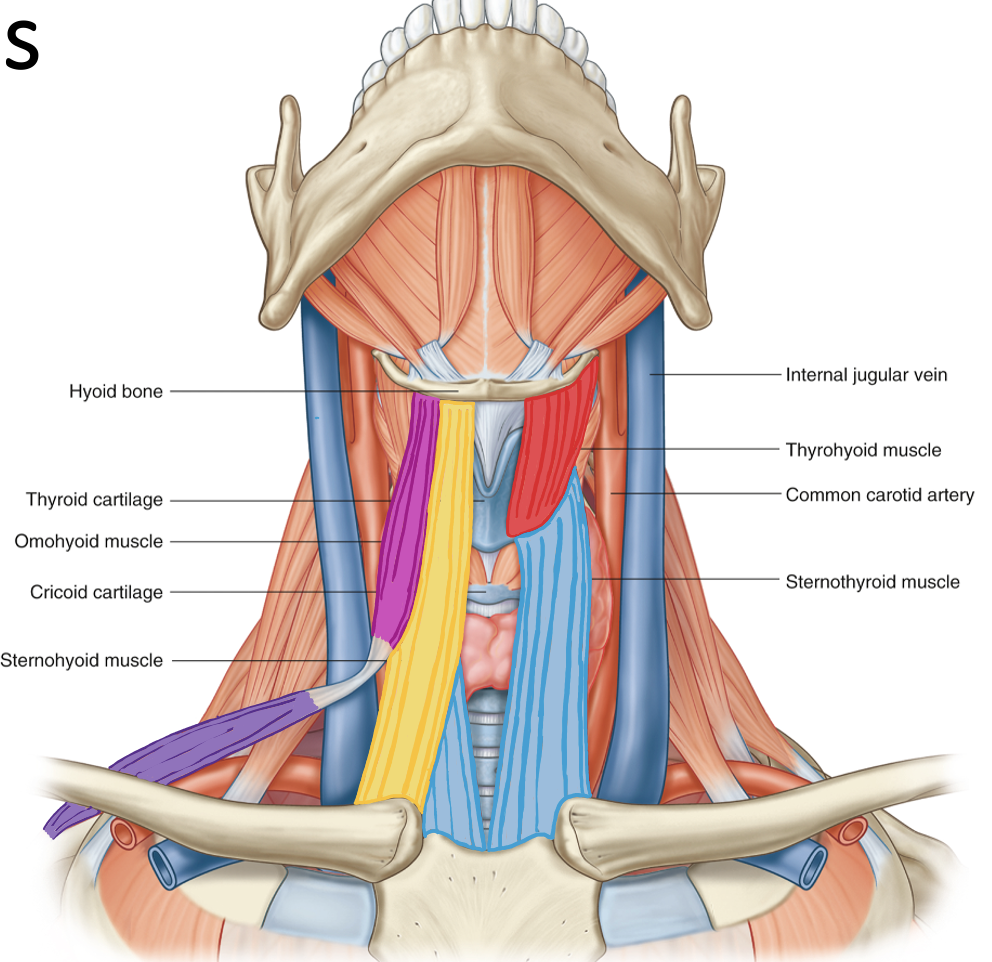
Action and innervation of Thyrohyoid Muscle
depress hyoid bone
C1 via hypoglossal nerve
What does the common carotid artery divide into? At what vertebral level does the division occur?
divides into external and internal carotid artery at C4
What are the contents of the carotid sheath?
medial to lateral: common carotid artery, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein
What are the branches of the external carotid artery? Know the basic routes they take. What is the terminal branch of the external carotid artery?
superior thyroid artery - goes towards thyroid
ascending pharyngeal artery - goes posterior and travels superiorly up pharynx
lingual artery - travels deep under tongue
facial artery - over mandible and vascularizes superficial face
occipital artery - vascularizes posterior skull
posterior auricular artery - travels behind the ear
maxillary artery - largest one, 3 divisions = mandibular, pterygoid, pterygopalatine
superficial temporal artery - temple, terminal branch
What does the internal jugular vein form when combined with the subclavian vein?
internal jugular vein + subclavian vein = brachiocephalic vein
Of the muscles discussed, which are considered suprahyoid or infrahyoid? How would you describe the relationship of these muscles with the hyoid bone?
suprahyoid = above the hyoid bone → anterior and posterior belly of digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle, mylohyoid muscle
infrahyoid = below the hyoid bone → superior and inferior belly of omohyoid muscle, sternohyoid muscle, sternothyoid muscle, thyrohyoid muscle
Where is the thyroid gland located? What are the parts of the thyroid gland?
thyroid gland located at C6
thyroid cartilage located at C4
2 lobes on the lateral sides, isthmus in the center connecting the 2 lobes, pyramidal lobe from isthmus up to hyoid bone
Where are the parathyroid glands located? How many parathyroid glands are there?
posterior side of thyroid gland
4
What is the arterial supply and venous drainage of the thyroid and parathyroid glands?
arterial supply: superior thyroid artery, inferior thyroid artery
venous drainage: superior, middle and inferior thyroid veins
Trace the drainage of the five groups of superficial lymph nodes
occipital nodes, mastoid nodes - superficial cervical nodes - deep cervical nodes - right and left jugular trunks - right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct
pre-auricular/parotid nodes, submandibular nodes, submental nodes - deep cervical nodes - right and left jugular trunks - right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct
The superficial and deep cervical nodes are located on which blood vessels?
superificial cervical nodes - external jugular vein
deep cervical nodes - internal jugular vein
List the twelve cranial nerves.
Identify which nerves are motor only, sensory only, or both.
For each nerve, what is the overall major function?
Olfactory (CN I) = sensory = smell
Optic (CN II) = sensory = vision
Oculomotor (CN III) = motor = extraocular and eyelid muscles
Trochlear (CN IV) = motor = extraocular muscle
Trigeminal (CN V) = both = V1 (ophthalmic): face sensation, V2 (maxillary): face sensation, V3 (mandibular): face sensation and mastication
Abducens (CN VI) = motor = extraocular muscle
Facial (CN VII) = both = facial expression, taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue, tear and salivary ducts
Vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) = sensory = balance and hearing
Glossopharyngeal (CN IX) = both = taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue, sensation to pharynx, swallowing
Vagus (CN X) = both = taste, sensory information to body viscera, glands to GI tract, swallowing
Accessory (CN XI) = motor = trapezius and SCM
Hypoglossal (CN XII) = motor = tongue muscles
What are the five terminal motor divisions of the facial nerve?
temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical
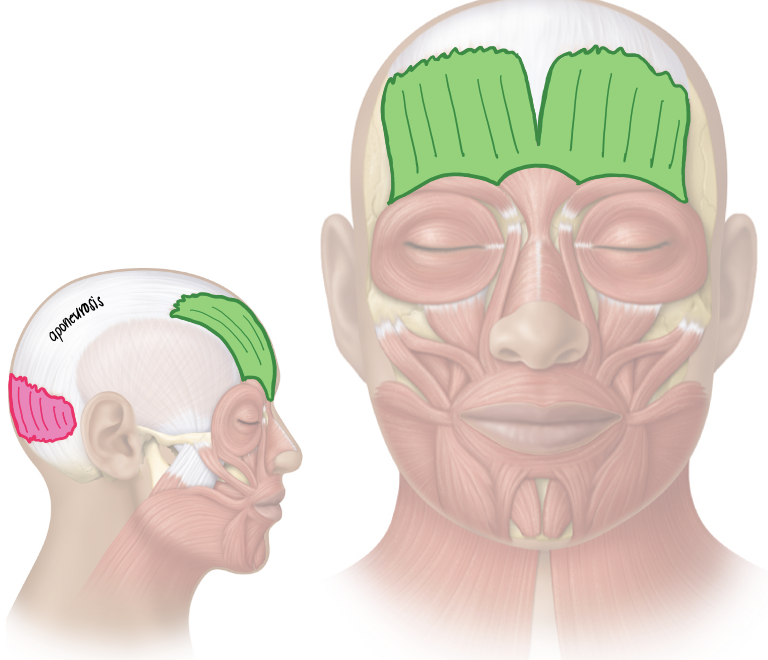
Action and innervation of facial expression muscle: Occipitofrontalis
frontal belly = raises eyebrow and wrinkles skin of forehead
occipital belly = pulls scalp posteriorly
facial nerve (CN VII)
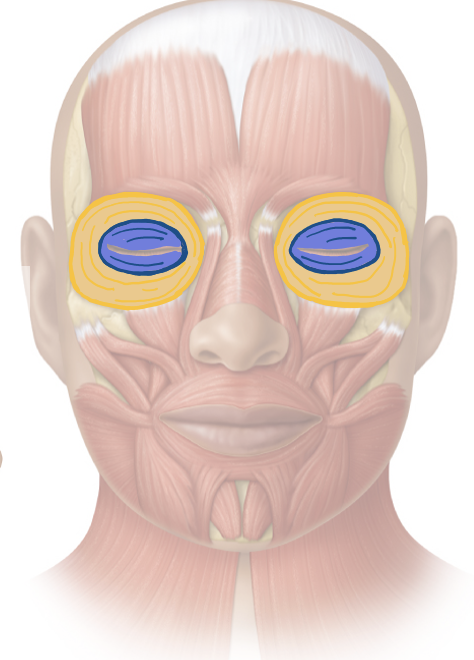
Action and innervation of facial expression muscle: Orbicularis Oculi
closes eye - palpebral = gently, orbital = tightly
facial nerve (CN VII)
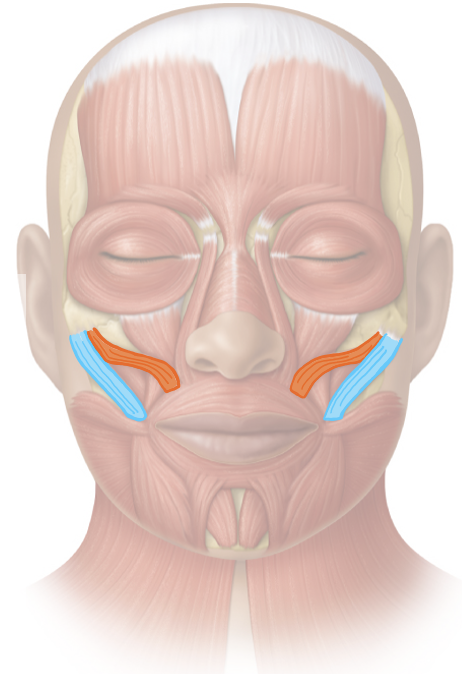
Action and innervation of facial expression muscles: Zygomaticus Major and Zygomaticus Minor
elevates corner of mouth
facial nerve (CN VII)
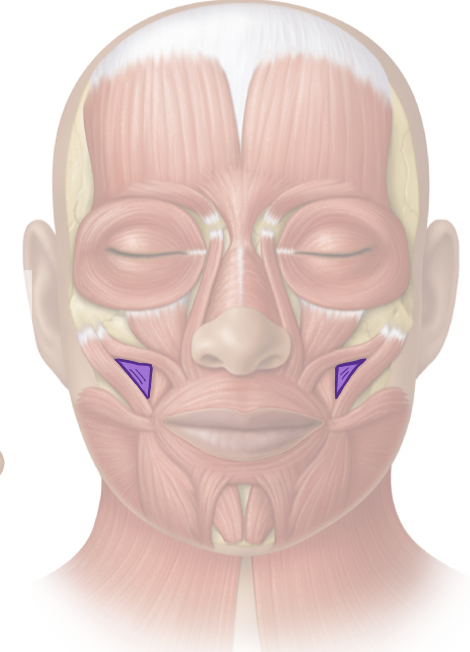
Action and innervation of facial expression muscle: Buccinator
compresses cheek against molars
facial nerve (CN VII)
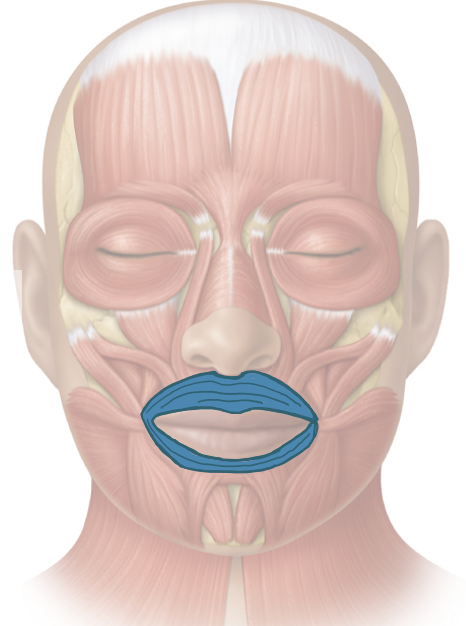
Action and innervation of facial expression muscle: Orbicularis Oris
closes lips
facial nerve (CN VII)
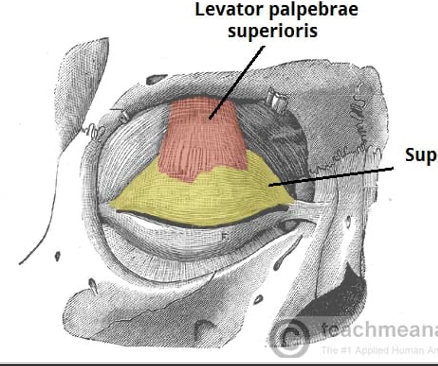
Action and innervation of facial expression muscle: Levator Palpebrae Superioris
elevates superior eyelid
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
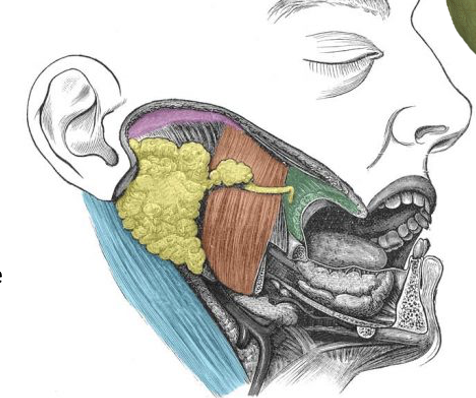
What is the parotid gland? Where is it located? What is its innervation? What structures pass through?
largest salivary gland located between the ear and masseter muscle
innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and auriculotemporal nerve (branch of CN V3 - mandibular nerve)
facial nerve (CN VII), external carotid artery and retromandibular vein pass thru parotid gland
What are the articulations of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)?
What separates the bony articulations from each other?
temporal bone and mandible
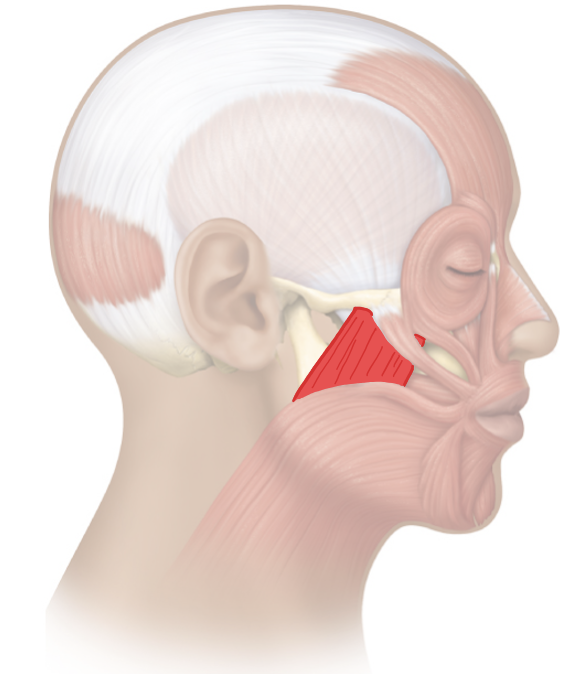
Action and innervation of the mastication muscle: Masseter
elevate (closing the mouth) and retract (moving mandible posterior) mandible
mandibular nerve (CN V3)
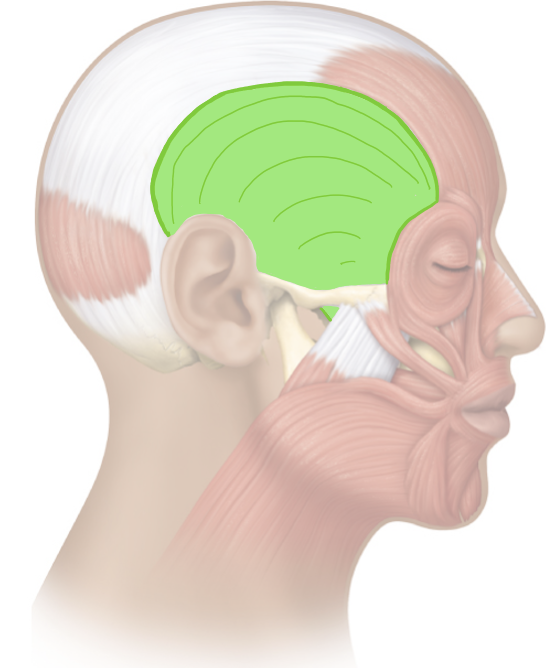
Action and innervation of the mastication muscle: Temporalis
elevate (closing the mouth) and retract (moving mandible posterior) mandible
mandibular nerve (CN V3)
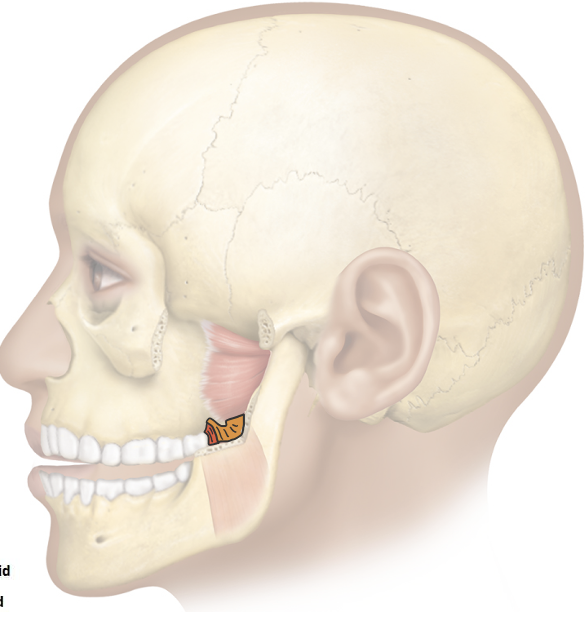
Action and innervation of the mastication muscle: Medial Pterygoid
elevate (close the mouth) and laterally deviate (side-to-side movement) mandible
mandibular nerve (CN V3)
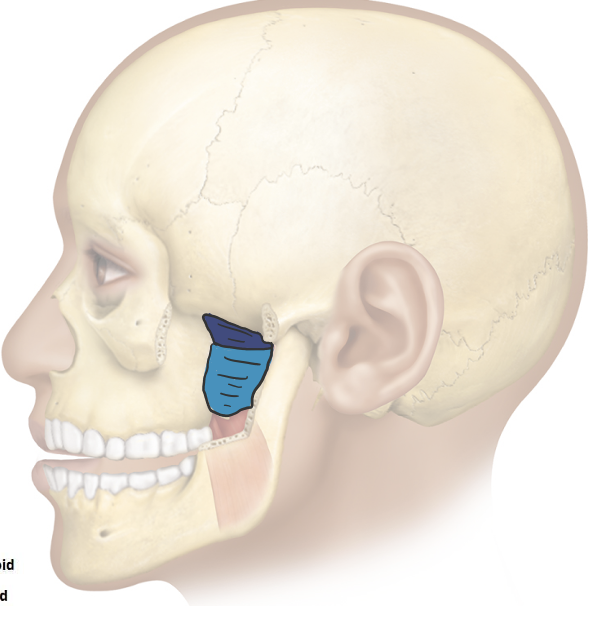
Action and innervation of the mastication muscle: Lateral Pterygoid
depress (open mouth), protract (moving mandible anterior), and laterally deviate (side-to-side movement)mandible
mandibular nerve (CN V3)
Which branches of the trigeminal nerve supply sensation to the face?
V1 = ophthalmic
V2 = maxillary
V3 = mandibular
What is the infratemporal fossa? What are its borders? What are its contents?
Wedge-shaped space located at the base of the skull, deep to masseter muscle
contains the 4 muscles of mastication
contains maxillary artery (branches = middle meningeal artery, inferior alveolar artery which exits mandible as mental artery)
contains pterygoid venous plexus which receives drainage from cavernous sinus via small emissary veins
contains mandibular nerve (branches = auriculotemporal nerve, inferior alveolar nerve which exits mandible as mental nerve and gives off the nerve to mylohyoid, lingual nerve)
What is the unique relationship of the auriculotemporal nerve and middle meningeal artery, and between the lingual nerve and chorda tympani nerve?
auriculotemporal nerve encircles the middle meningeal artery
chorda tympani nerve hitches a ride with the lingual nerve
The following nerves come off of which cranial nerve?
Auriculotemporal nerve
Inferior alveolar nerve
Lingual nerve
Chorda tympani nerve
Auriculotemporal nerve, inferior alveolar nerve,and lingual nerve come off of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Chorda tympani nerve comes off of the facial nerve (CN VII)
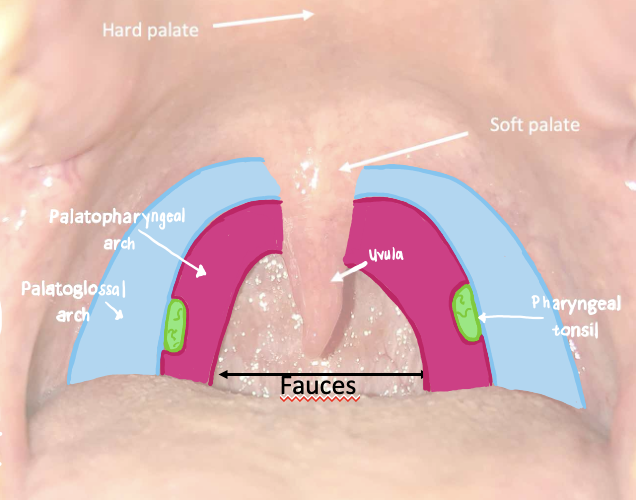
what does the palatoglossal arches connect and what muscle in found here
connects the soft palate and lateral aspect of the tongue
contains the palatoglossus muscle
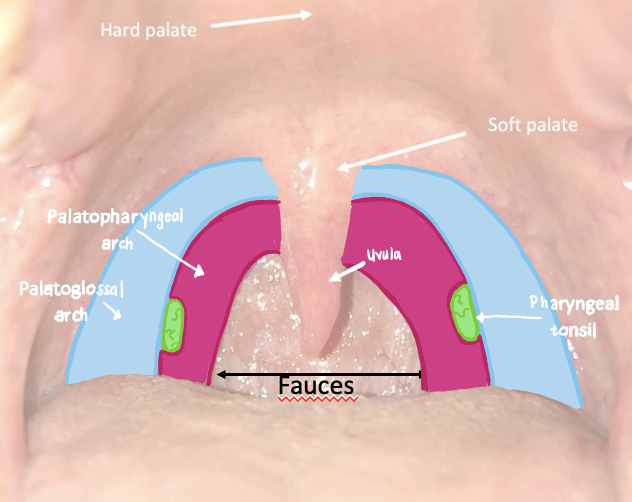
What do the platopharyngeal arches connect and what muscle can you find here
connects the soft palate and the pharynx
contains the palatopharyngeus muscle
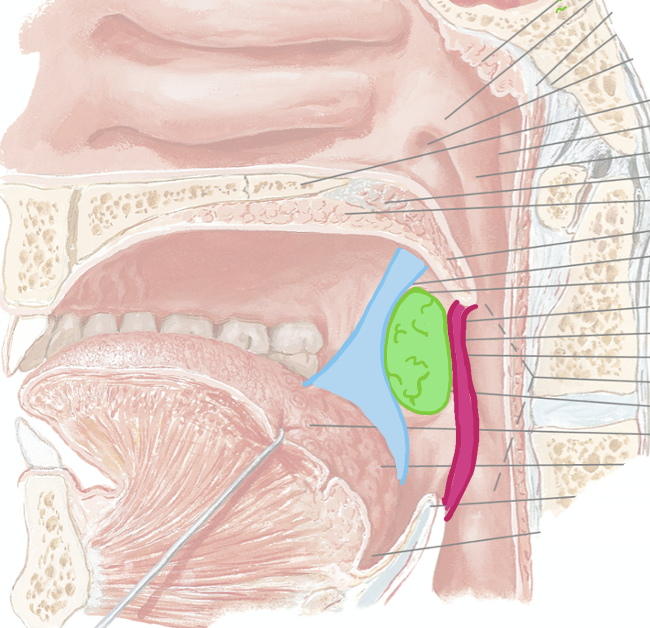
What is located between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches?
palatine tonsils
What are the five muscles of the soft palate? What is their innervation?
tensor veli palatini - CN V3
levator veli palatini - CN X
musculus uvulae - CN X
palatoglossus - CN X
palatopharyngeus - CN X
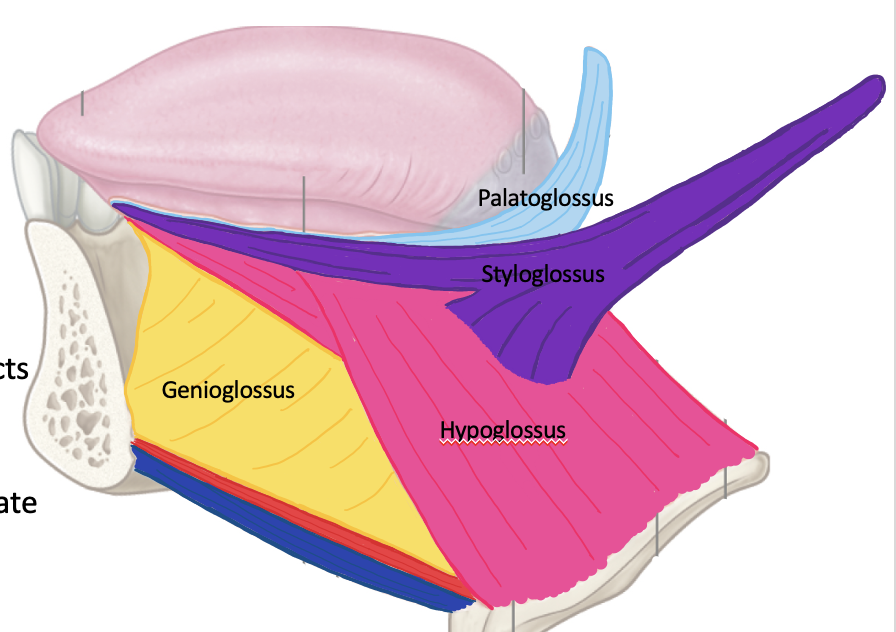
What muscles make up the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue? What is their innervation?
extrinsic muscles -
genioflossus = CN XII
hyoglossus = CN XII
styloglossus = CN XII
palatoglossus = CN X
What nerves allow for taste sensation? Be specific to which part of the tongue they innervate.
chorda tympani nerve (CN VII branch) = anterior 2/3 of tongue
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) = posterior 1/3 of tongue
What nerves allow for general sensation of the tongue? Be specific to which part of the tongue they innervate.
lingual nerve (CN V3 branch) = anterior 2/3 of tongue
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) = posterior 1/3 of tongue
What are the three divisions of the pharynx? Where are they located in relation to the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and larynx?
Nasopharynx - naval cavity is anterior
Oropharynx - oral cavity is anterior
Laryngopharynx - larynx is anterior
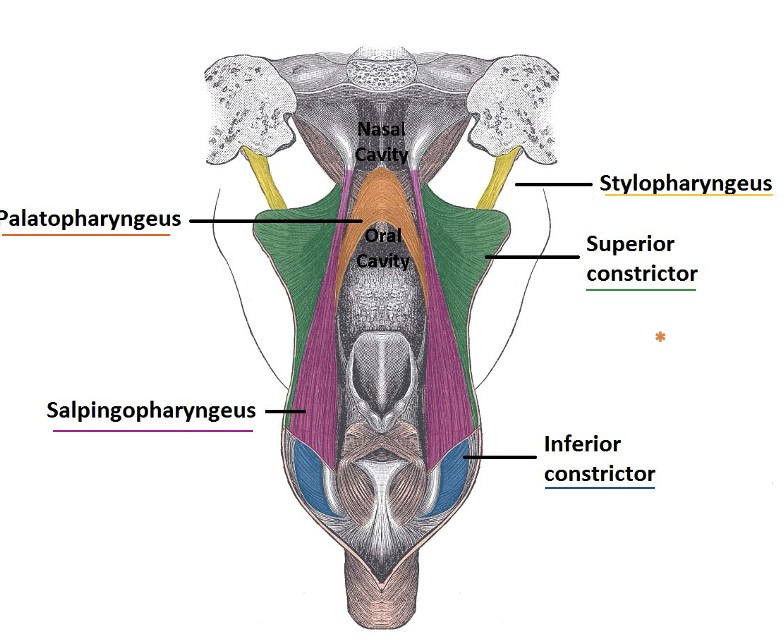
What are the muscles that make up the pharynx? What is their function? What is the innervation of these muscles?
Constrictor Muscles:
Superior Constrictor = CN X
Middle Constrictor = CN X
Inferior Constrictor = CN X
Longitudinal Muscles:
Stylopharyngeus = CN IX
Palatopharyngeus = CN X
Salpingopharyngeus = CN X
The muscles work together to facilitate swallowing and breathing by propelling food and air thru the pharynx
What is the sensory innervation of the pharynx?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Describe the following structures of the nasopharynx?
a. Pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids
b. Eustachian tube
c. Torus tubarius
Pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids = masses of lymphoid tissue located at the junction of the roof and posterior wall of the nasopharynx
Eustachian tube = located at the posterolateral wall of the nasopharynx, connecting the middle ear cavity to the nasopharynx
Torus tubarius = mucosal elevation in the lateral wall of the nasopharynx, formed by the underlying cartilage of the pharyngeal end of the Eustachian tube. It is located immediately posterior to the opening of the Eustachian tube
What are the boundaries of the larynx?
anterior = neck musculature
posterior = laryngopharynx
superior = hyoid bone, oropharynx
inferior = trachea
What are the three unpaired of laryngeal cartilage?
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
epiglottis
What is the function of the epiglottis?
epiglottis moves downward and covers the opening of the larynx
protect the airway by preventing food, liquid, or other foreign objects from entering the trachea
Where would you find the thyrohyoid and cricothyroid membranes?
thyrohyoid membrane = found between the hyoid bone and superior border of thyroid cartilage
cricothyroid membrane = found between the inferior border of thyrohyoid cartilage and superior border of cricothyroid cartilage
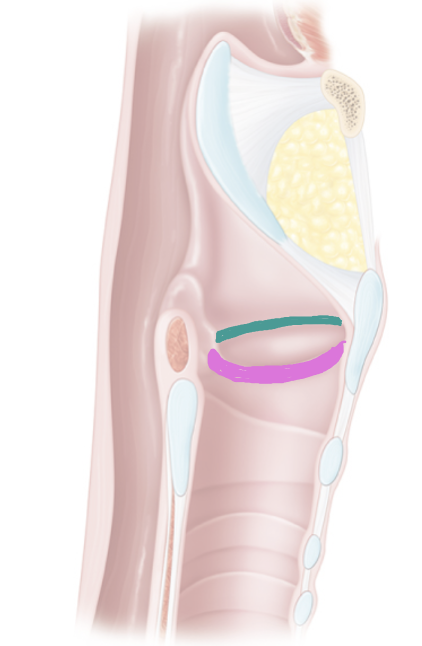
What is the difference between vestibular and vocal folds?
vestibular folds= false vocal cords, superior
vocal folds = true vocal folds, inferior
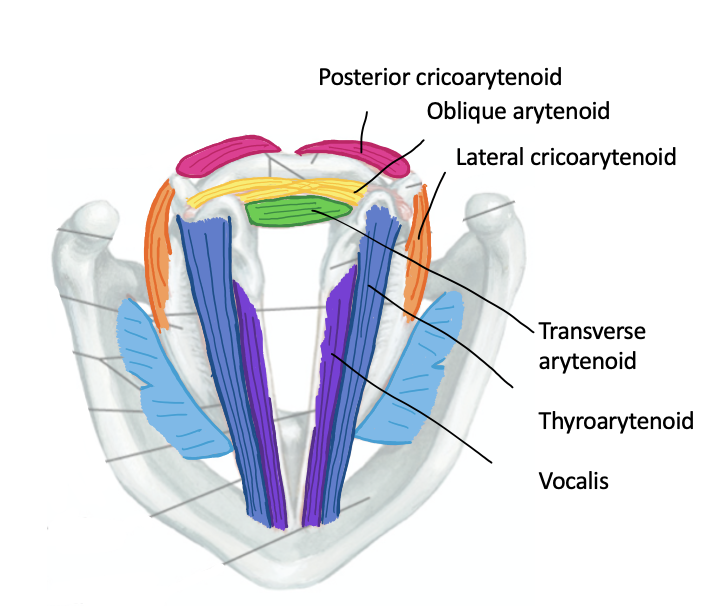
Action of the following intrinsic laryngeal:
Lateral cricoarytenoid
Transverse cricoarytenoid
Oblique cricoarytenoid
Posterior cricoarytenoid
Thyroarytenoid
Vocalis
Lateral Cricoarytenoid, Transverse Cricoarytenoid, Oblique Cricoarytenoid = adduction of vocal cords (produces higher tones)
Posterior Cricoarytenoid = abduction of vocal cords (produces lower tones)
Thyroarytenoid, Vocalis = relax/shorten vocal cords (produces lower pitch)
Innervation of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles
Vagus nerve (CN X) : superior laryngeal nerve and recurrent laryngeal nerve
What is the nasal septum? Formed from which bones or structures?
divides the 2 nasal cavities
formed by septal cartilage, vomer bone and perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
What is the pathway of airflow through the nasal cavities?
1) anterior naris (nostrils)
2) vestibule (open space)
3) nasal turbinates (superior, middle and inferior)
4) posterior naris (exits nasal cavity and enters nasopharynx)
What is the function of the nasal turbinates?
warm, humidify, and filter the air before it reaches the lungs
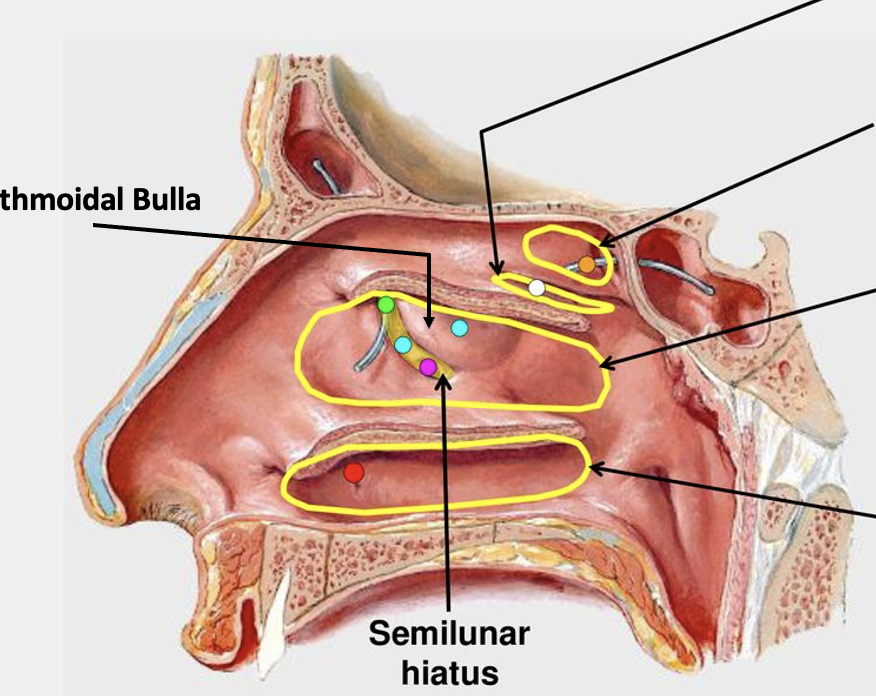
For each of the space (Inferior meatus, Middle meatus, Superior meatus, Sphenoethmoidal recess), what structures drain into each?
Inferior meatus = nasolacrimal duct
Middle meatus = frontal, maxillary, and anterior/middle ethmoid sinuses
Superior meatus = posterior ethmoid sinus
Sphenoethmoidal recess = sphenoid sinus
What are the major arteries of the nasal cavity (as discussed in class)?
terminal branches of maxillary and facial arteries
anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries
Kiesselbach’s area = anatomosis, common site of nosebleeds
What is the general innervation of the nasal cavity (as discussed in class)?
olfactory nerve (CN I) = special sensation (smell)
ophthalmic nerve (V1) and maxillary nerve (V2) = general sensation
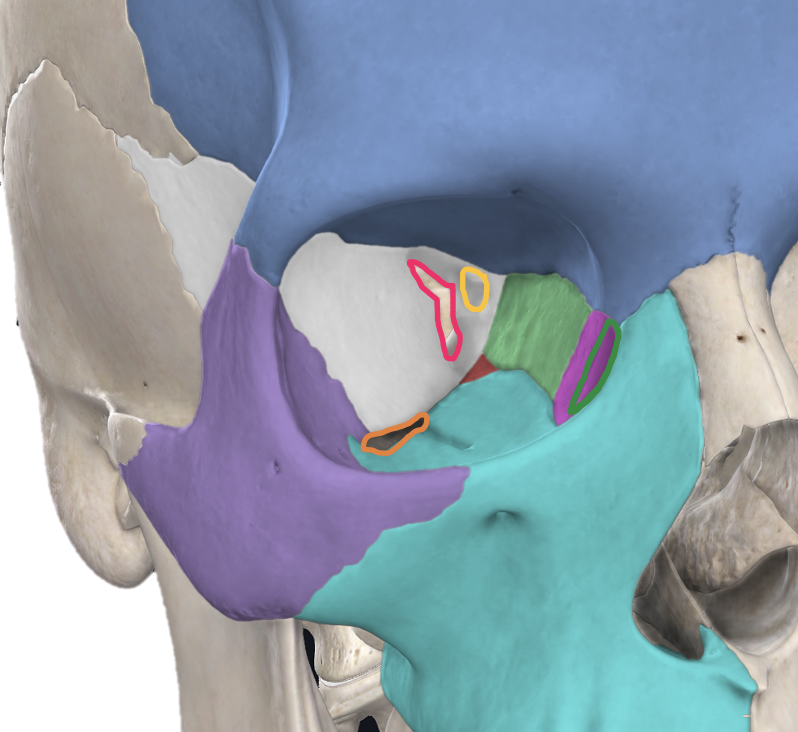
What major openings are found within the orbit? What structures pass through these openings?
optic canal = CN II, ophthalmic artery
superior orbital fissure = CN III, IV, frontal nerve (branch of V1), VI, superior ophthalmic vein
inferior orbital fissure = inferior ophthalmic vein
What are the components of the lacrimal apparatus?
Lacrimal gland
Lacrimal ducts
Lacrimal (serous) fluid
Lacrimal canaliculi - puncta
Lacrimal sac
Nasolacrimal duct
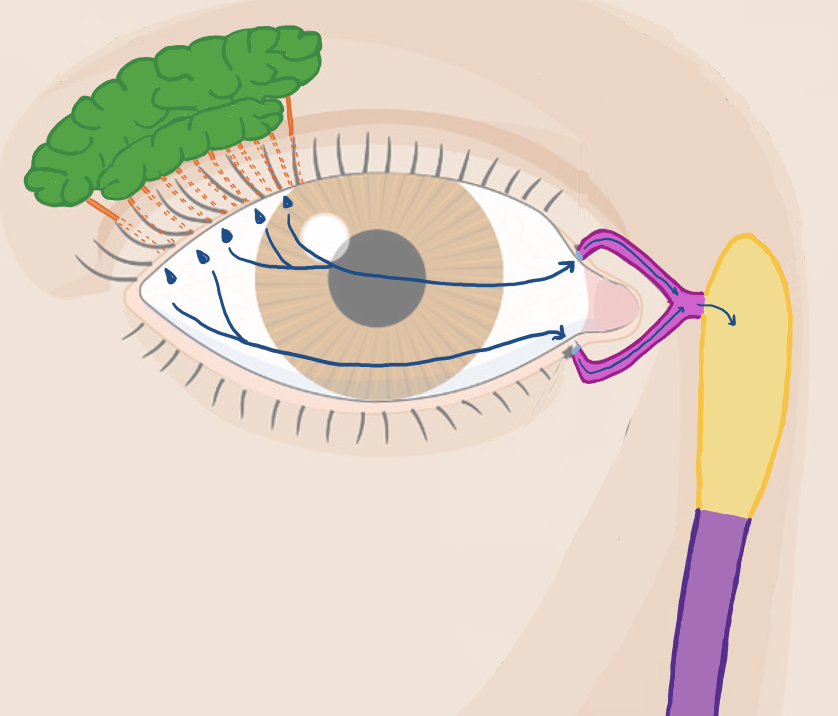
Where is the lacrimal gland located? What muscle divides it into two parts?
anterior, superotemporal part of orbit
divided by the levator palpebrae superioris
Trace the pathway of tear formation from the gland that produces tears to the nasal meatus that tears drain into.
lacrimal gland - lacrimal ducts - lacrimal fluid exits and blinking distributes fluid across the eye - fluid enters thru puncta into lacrimal canaliculi - lacrimal sac - nasolacrimal duct - drains inferior nasal meatus
What is the common tendinous ring?
fibrous ring in the back of orbit
origin for 4 rectus muscles of eye (superior, inferior, medial and lateral rectus)
List the extraocular muscles?
superior oblique, inferior oblique, superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus
What are the movements of the eyeball?
elevation (up), depression (down), adduction (to nose), abduction (away from nose)
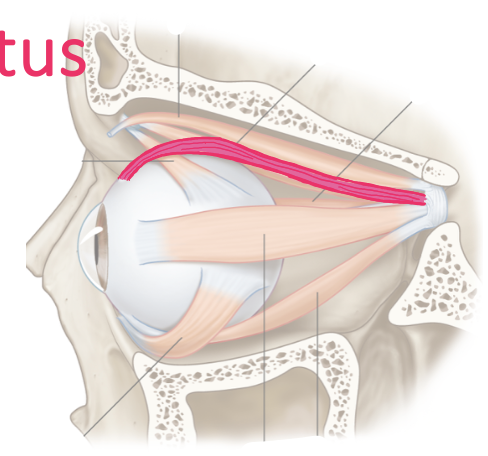
List their attachments, their function, and innervation: Superior Rectus
common tendinous ring
elevation, adduction
oculomotor nerve
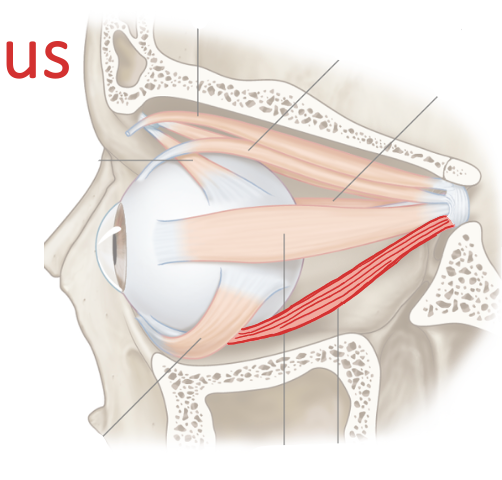
List their attachments, their function, and innervation: Inferior Rectus
common tendinous ring
depression, adduction
oculomotor nerve
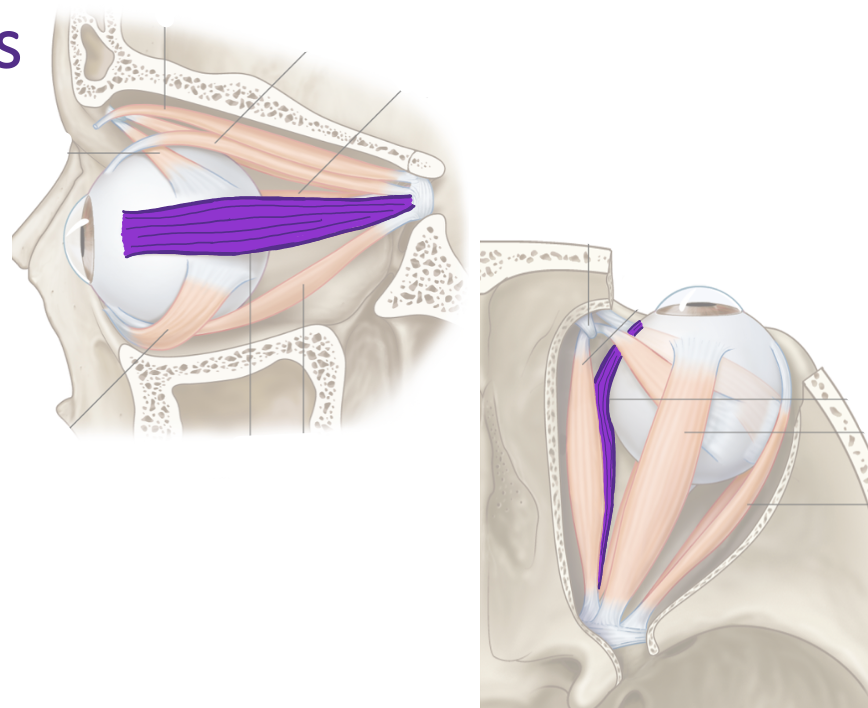
List their attachments, their function, and innervation: Medial Rectus
common tendinous ring
adduction
oculomotor nerve
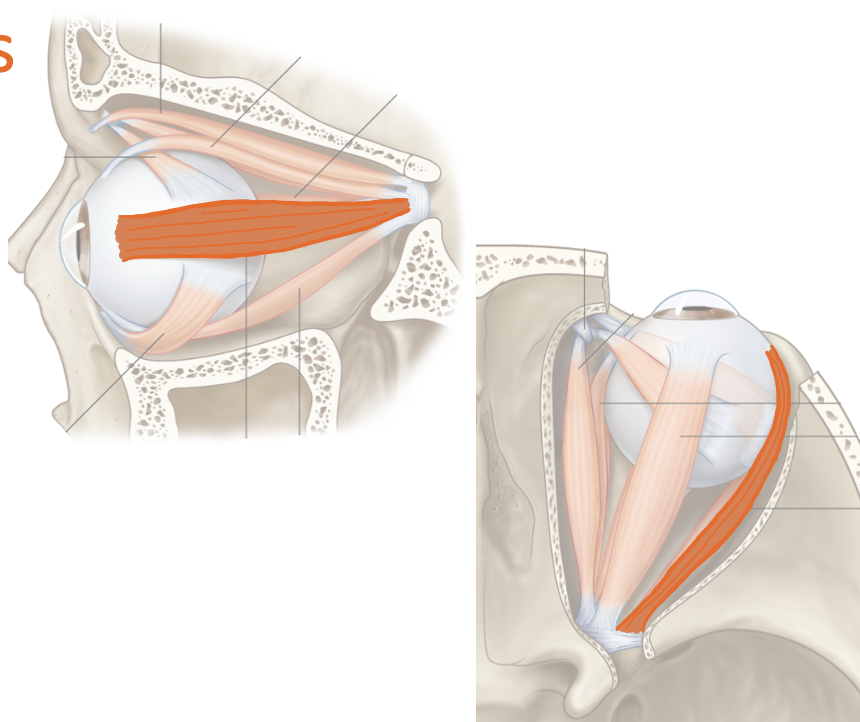
List their attachments, their function, and innervation: Lateral Rectus
common tendinous ring
abduction
abducens nerve
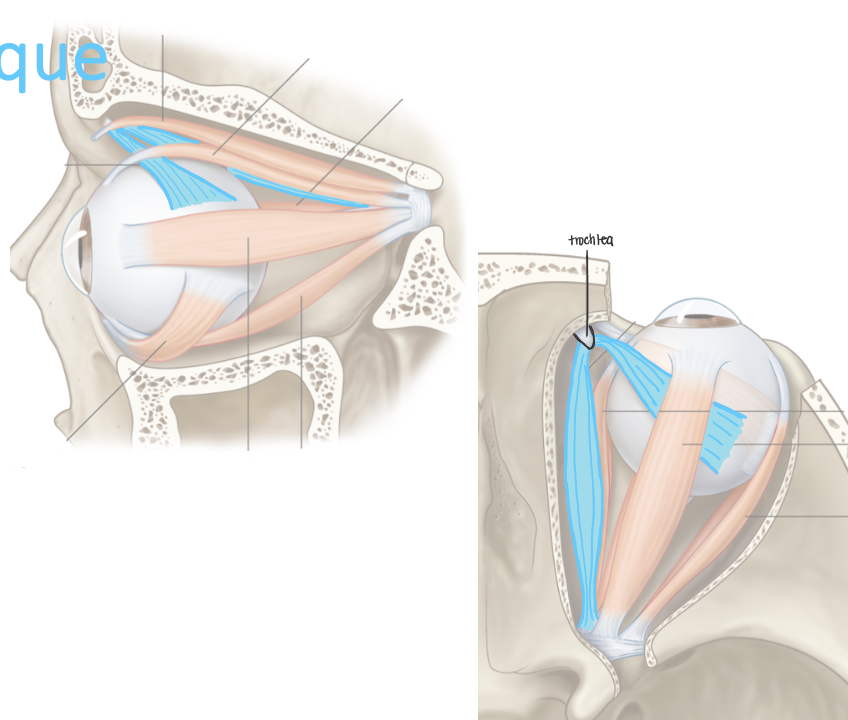
List their attachments, their function, and innervation: Superior Oblique
body of sphenoid bone
depression, abduction
trochlear nerve
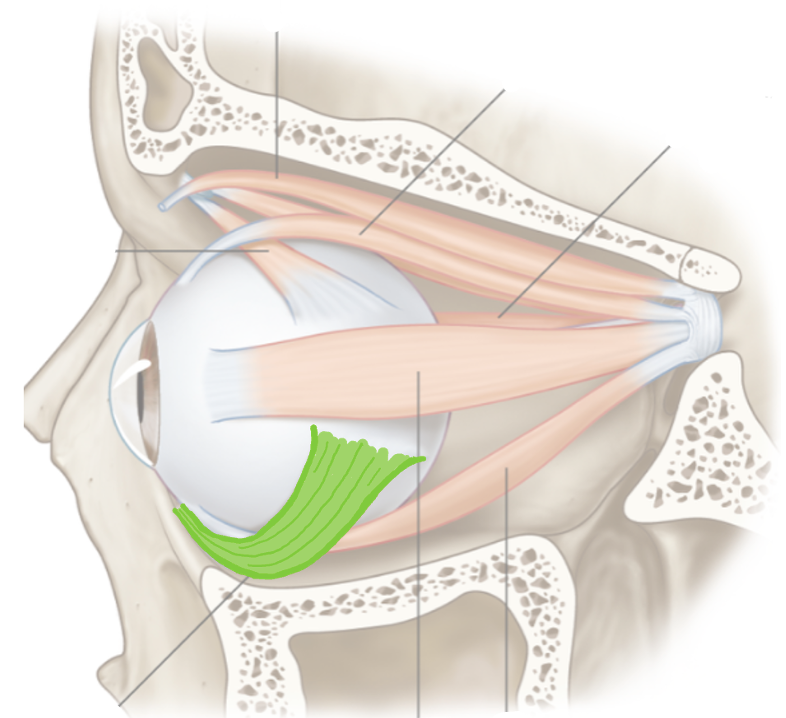
List their attachments, their function, and innervation: Inferior Oblique
floor of orbit
elevation, abduction
oculomotor nerve
Describe the autonomic innervation of the eye.
Ciliary ganglion:
Parasympathetic = pregangionic fibers branch of CN III, posterganglionic fibers travel in short ciliary nerve, innervates sphincter pupillae muscle (pupil constriction) and ciliary muscle (control shape of lens)
Sympathetic = has various paths, innervates dilator pupillae muscle (pupil dilation)