Embalming II - Ch. 18-20
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i crave flesh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
An abnormal color in or on the skin of the human body:
Discoloration
In embalming, how are discolorations classified?
A.) Their time at which they appeared and location
B.) Their location and color
C.) Time at which they appeared and cause
D.) Their cause and location
Time at which they appeared and cause
What are the two classifications of discolorations?
Antemortem and postmortem
A discoloration that was present during life and remains after death is classified as a…
Antemortem discoloration
This type of discoloration results from changes in the blood composition, content, and location
Blood discoloration
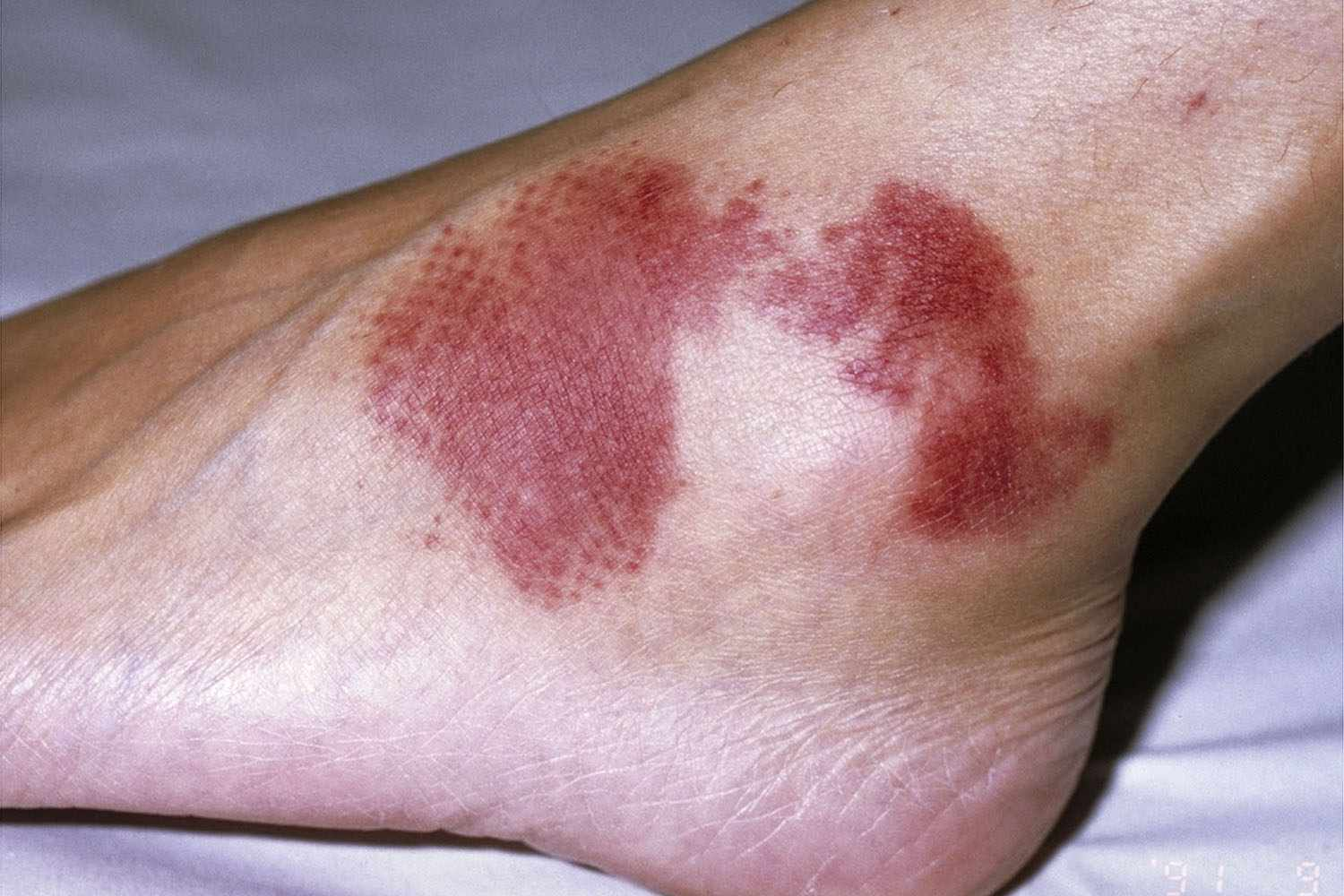
This type of discoloration is an antemortem discoloration resulting from administration of drug or chemotherapeutic agents:
Drug/therapeutic discoloration
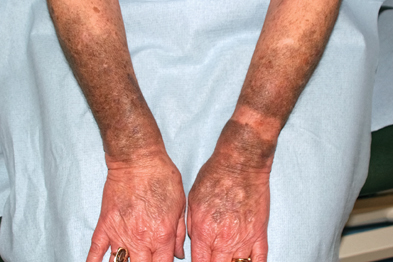
Antemortem discolorations that occur during the course of certain diseases:
Pathological discoloration
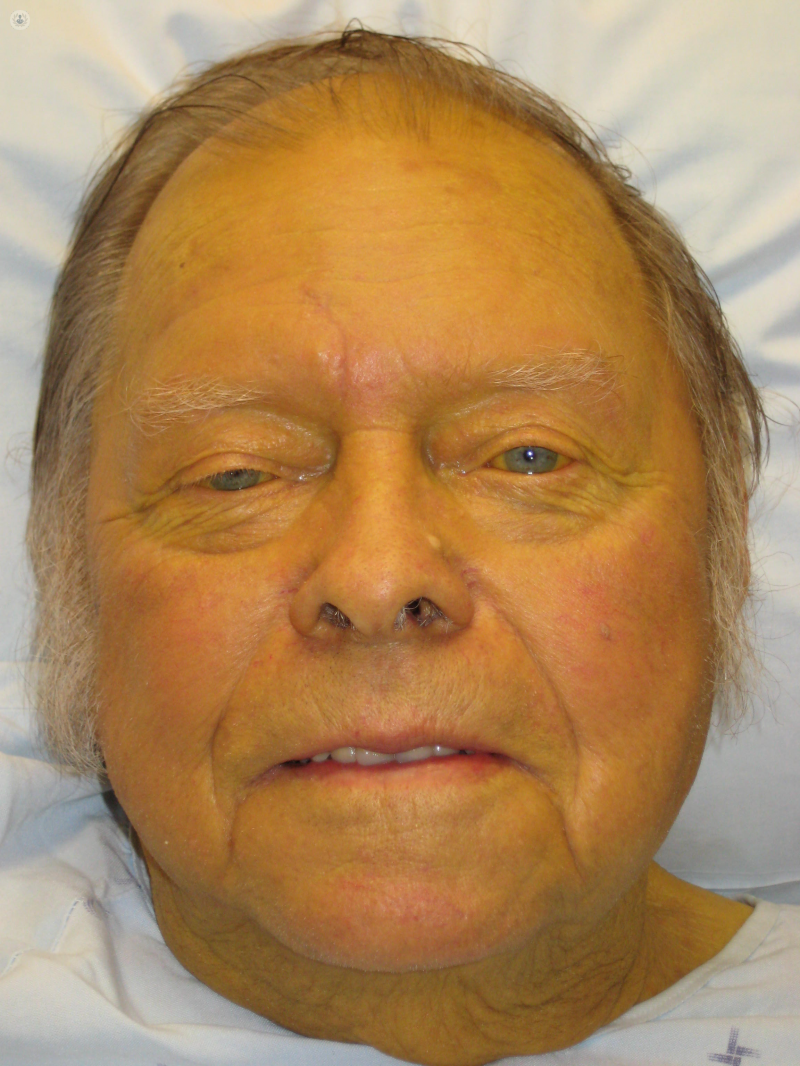
This discoloration can be antemortem or postmortem that can occur prior to or during embalming as the result of the deposit matter on the body surface:
Surface discoloration
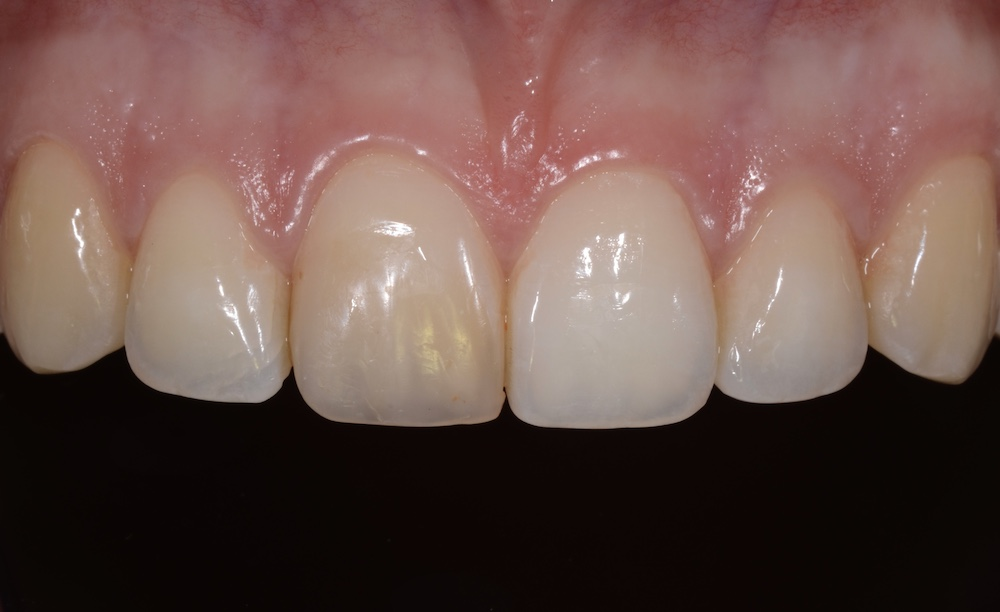
This is a postmortem discoloration brought about by the action of bacterial enzymes on the body tissues:
Decomposition discoloration
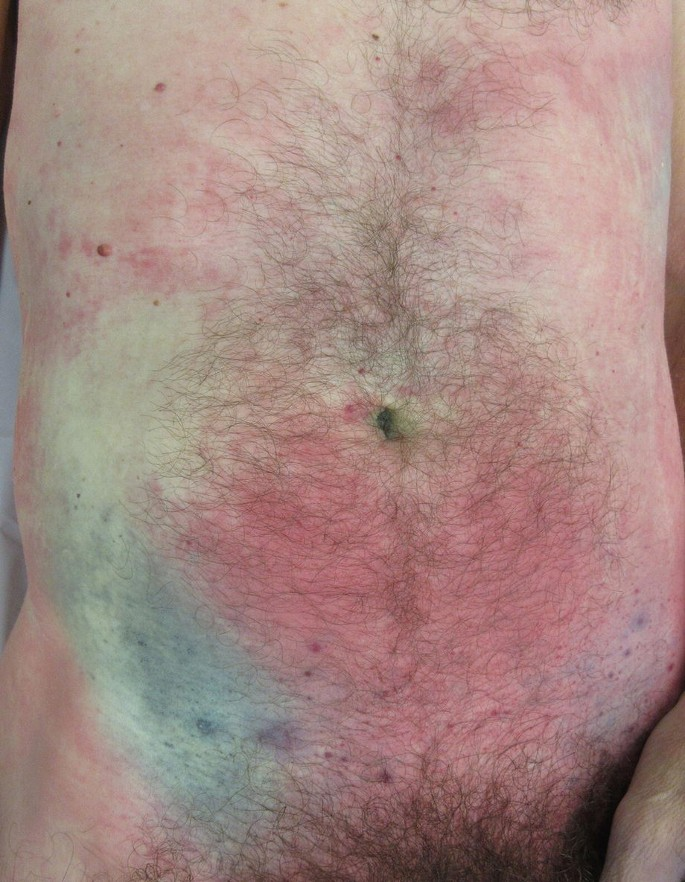
What color is hypostasis of the blood?
blue-black
What color is carbon monoxide poisoning?
Cherry red
When dealing with discolorations cause by drugs, these vessels breakdown and cause ecchymosis and purpura:
Capillaries
Wet gangrene brings on this color of discoloration:
red to black
Dry gangrene brings on this color of discoloration:
Dark red-brown to black
What color discoloration does Addison’s Disease bring about?
Bronze
What discoloration does leukemia bring about?
A.) Gangrene
B.) Hypostasis
C.) Petechiae
D.) Hyperemia
Petechiae
Intravascular blood discolorations respond best to what embalming treatments?
Hint: There’s two
Arterial injection and blood drainage
How long does livor mortis begin to take place?
20 minutes after death
How long does postmortem stain take to set in?
6 hours after death
What color discoloration can formaldehyde cause?
Gray
When HCHO and blood mix and causes a gray stain this is called…
A.) Methemoglobin
B.) Hemoglobin
C.) Aldehydeoglobin
D.) Urmomoglobin
Methemoglobin
This is a good sign of distribution:
A.) Clearing of the hair follicles
B.) Clearing of the nail beds
C.) Clearing of the retinas
D.) The decedent says “ouch!”
Clearing of the nail beds
Is carbon monoxide poisoning antemortem or postmortem?
Antemortem
When using hypodermic embalming, what are the two chemicals that can be used to treat discolorations?
Phenol (most preferred)
Formaldehyde (cavity fluid)
What are the three types of jaundice?
Toxic
Hemolytic
Obstructive
Healthy human blood serum contains approximately — to — milligrams of bile pigment bilirubin:
1.0 to 1.5
How many days to healthy red blood cells live?
120 days
Yellow jaundice is termed:
Bilirubin
Green jaundice is termed:
Biliverdin
Formaldehyde is what type of agent?
Reducing
The conversion of yellow jaundice to green jaundice is what kind of chemical reaction?
A.) Explosion
B.) Liquidation
C.) Deoxydation
D.) Oxidation
Oxidation
When working with a jaundiced body, should the embalmer use a lot of HCHO or a little of HCHO?
A little
What takes precedence over clearing discoloration when embalming a jaundiced body?
Preservation
One of the signs of chronic renal failure is described as this color:
A.) Sallow purple
B.) Sallow red
C.) Sallow blue
D.) Sallow yellow
Sallow yellow
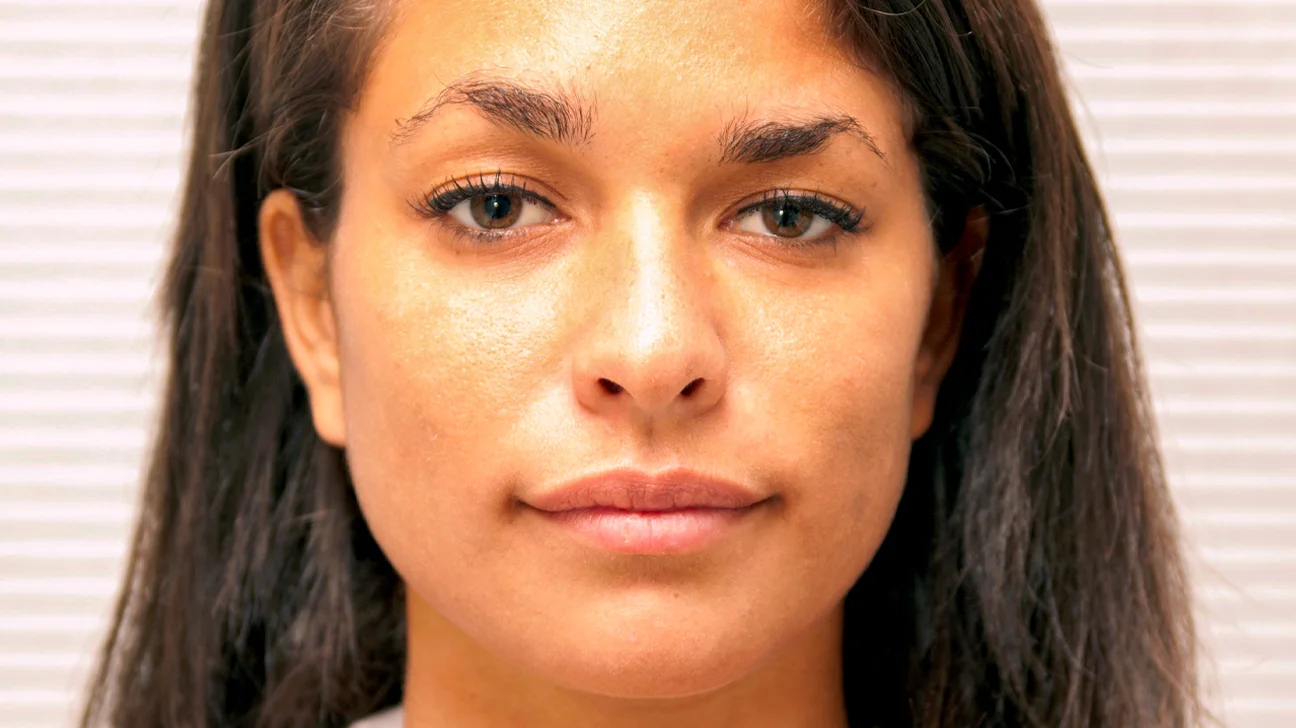

Out of these, what neutralizes formaldehyde?
A.) Bleach
B.) Ammonia
C.) Phenol
D.) Vinegar
Ammonia
What is a good solution to remove mold?
Mix of 1% phenol and 1% creosote
(Sadly Mayer makes a comback)
What are the normal discolorations of dehydration?
Yellow, brown, and black
How long does it take for formaldehyde gray to appear after embalming?
6 hours
What causes formaldehyde gray?
The failure to wash as much of the blood out of the body as possible
What is the best way to inject bodies that had previously been on blood thinners or elderly people who skin is thin?
Restricted cervical injection
What brings about decomposition discoloration?
Autolytic and bacterial enzymes
Where does the first discoloration of decomposition begin? And what color is it?
Lower right quadrant of the abdomen and a green color
Any traumatic or pathological change in the structure of skin:
Skin lesion
What color does raw skin turn when exposed to air?
Brown
Should you apply massage cream to an abrasion?
No
When dealing with a hanging case, the body is probably goin for an autopsy. When dealing with this delay it is best to use a arterial solution of —% to —%
2.0%-2.5%
This terms means the surface of the skin is red:
A.) Hyperemia
B.) Erythema
C.) Angina
D.) Cyanosis
Erythema
Blisters beneath or within the epidermis are called:
A.) Bullae
B.) Carbuncles
C.) Boils
D.) Pimples
Bullae
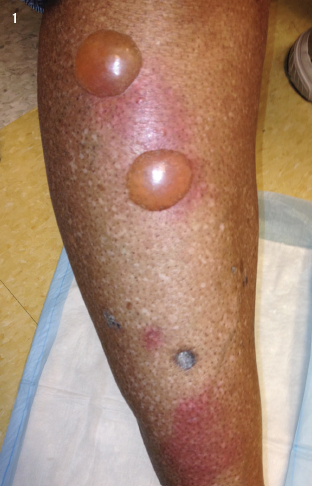
When dealing with an electrocution, what part of the body is usually affected?
Palms
What causes blood to be bright?
Carboxyhemoglobin
What are three common problems that come from delayed embalming?
Distribution problems
The body swells more easily
The body may need an increased preservative demand
What are some manual aids for achieving adequate distribution?
massaging, squeezing the sides of the fingers and nailbeds, rotating/flexing limbs, elevation, weights, compresses, pneumatic collars
What are some mechanical aids for achieving adequate distribution?
drainage tubes, controlled pressure and rate of flow, use of pulsation
What are some operative aids for achieving adequate distribution?
channeling, incising, excising
For under embalmed areas, the embalmer has three options to use. What are they?
Arterial injection
Hypodermic injection
Surface embalming
This type of injection involves the use of two carotid arteries
Restricted Cervical Injection
What part of the body should be injected first when using the restricted cervical injection:
Trunk and limbs
What arterial solution index is recommended when dealing with delayed embalming?
A.) 10 index or lower
B.) 15 index
C.) 25 index or lower
D.) 25 index or higher
25 index or higher
If the body has been delayed embalming, and has not been autopsied should you inject fast or slow?
Slow
Affects all body muscles when the body cannot replenish ATP
This rapidly occurs in bodies with high temperatures and where exertion or exercise have preceded death
Rigor mortis
Rigor mortis is recognized in the average body after how many hours?
A.) 2 to 4 hours
B.) 5 to 7 hours
C.) 8 to 10 hours
D.) Over 24 hours
2-4 hours
How many hours after death is rigor mortis fully established?
6-12 hours
How long does it take for rigor mortis to pass?
A.) 12 hours
B.) 24 hours
C.) 36 hours
D.) 48 hours
Generally 36 hours
What are the three stages of rigor mortis?
Primary flaccidity
The period of rigor
Secondary flaccidity
When a body is in rigor what type of injection may be best?
What vein is the best for drainage?
6 point injection
Right internal jugular vein
If a body has been refrigerated for a long time, should you inject slow or fast?
Slow
Post-mortem stain can make formaldehyde appear this color:
Gray
Should you pour warm water on a frozen body?
No
(Instead, one day blinding stew)
first discoloration is greenish on the — — quadrant and gradually outlines the large intestine
Lower right
Why is the lower right quadrant the first part of the body to become discolored?
This discoloration is the reaction between hydrogen sulfide produced in the colon after death and the breakdown of hemoglobin
Should you pre-inject an early decomp body?
No
Should a early decomp case be waterless?
Yes
Regarding a body in advanced decomp:
If possible, raise and inject the R Common Carotid with how many gallon(s) of undiluted high-index fluid?
1 gallon
The abdominal and thoracic cavities should be aspirated and filled with — or more bottles of undiluted cavity fluid
Hint: To pertains to delayed embalming cases
Three
Tissue donation involves the donation of…
skin, eye tissue, ligaments, bones
Organ donation involves the donation of…
kidney, heart, liver, etc.
enacted in all states and D.C. to provide regulations regarding postmortem organ and tissue donation. It allows any person 18 years or older to donate all organs and tissues of his/her body for transplantation, research, or educational purposes.
The Uniform Anatomical Gift Act
Donation of the human cornea:
Eye Enucleation
The most common issue after enucleation is
swelling and ecchymosis
To control swelling of the eyelids:
Use restricted cervical injection
Avoid pre-injection procedures
Use a stronger solution
If leakage occurs from the eye orbitals during injection, allow it to drain
Embalming complications that follow a vertebral donor:
possible leakage occurring from posterior region; loss of rigidity
What tissue recovery is considered the most dramatic:
A.) Skin
B.) Heart
C.) Long bone
D.) Eye
Long bone donation
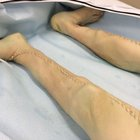
Should you use a pre injection for a long bone donation?
Yes
What arterial solution index should be used with a long bone donor?
25 or higher
This method of embalming a long bone donor involves leaving procurement sutures in place
The free flow method
the embalmer opens all procurement sutures, packs the legs with absorbent material saturated with undiluted cavity fluid and re-sutures the legs (sutures should be “locked down” every 5 inches)
Hint: This pertains to a long bone donor
Saturated packing
In the statured packing method sutures should be “locked down” every how many inches?
5 inches
procurement team uses a machine called a dermatome to peel or shave thin layers of the skin:
Hint: This is a type of skin donation
Partial thickness donation
procurement specialist removes the vascular layer of skin (down to the muscle layer) using a scalpel:
Hint: This is a type of skin donation
Full thickness donation
What is the best type of garment for skin donation?
A.) Cloth garments
B.) Plastic garments
C.) Embroidered garments
D.) Chiffon garments
Plastic garments