Ch 21 Placenta, UC, and AFI
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Umbilical cord forms from the fusion of the yolk sac stalk and omphalomesenteric duct at ____ gestation.
7 weeks
Outpouching from the urinary bladder forms ____.
urachus
Urachus projects into connecting stalk to form _____.
allantois
Allantoic vessels become the ____ ______.
umbilical vessels
Intestines grow at a ____ rate than the abdomen.
A) faster
B) slower
faster
Intestines herniate into proximal umbilical cord at _____.
7-8 weeks
When does the umbilical hernia resolve itself?
at approx. 10 weeks
What’s the latest an umbilical hernia returns back to the abdomen?
12 weeks
What does the umbilical cord include?
2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein
What substance is the umbilical cord surrounded by?
Wharton’s jelly, all surrounded by amnion
What kind of blood does the vein carry to the fetus?
oxygenated
What kind of blood do the arteries carry to the fetus?
deoxygenated
Arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the _____.
placenta
Which vessel(s) in the umbilical cord is longer and winds around the other vessel(s)?
arteries
Cross section of cord correlates with gestational age until ______.
32 weeks
At term, the average length of the fetal cord is ______ with a mean circumference of ____.
51.5-61 cm, 3.8 cm
Routine images of the ____, _____, and _____ should be taken.
fetal cord insertion, placental cord insertion, documentation of 3VC
The 3VC should not be confused with what other vessel(s)?
umbilical arteries
What does LUS stand for?
lower uterine segment
Why is it important to look at the cervix and LUS?
to look for evidence of cervical incompetence or placenta previa
Who usually gets their cervix length measured?
HX of premature labor or PROM, uterine anomalies, multiple gestations
What should the cervical length be to be considered normal?
3 cm or greater
T/F: An empty bladder can create a false placenta previa.
false (full bladder)
Which ultrasound approach lets you get an accurate measurement of the cervix?
endovaginal
What is cervical incompetence?
painless cervical dilation
What is a cervical cerclage?
a stitch that prevents further dilation and allows the pregnancy to continue
What is the sonographic appearance of a cerclage?
several bright echoes within the muscle of the cervix
What is the placenta composed of?
maternal and fetal portions
What is the term used to describe the functional layer of the endometrium in the gravid woman?
decidua
What part of the decidua lies deep to the conceptus and develops into maternal side of the placenta?
decidua basalis
What part of the placenta overlies the conceptus?
decidua capsularis
What part of the decidua encompasses the remaining decidua?
decidua parietalis (or vera)
What are the functions of the placenta?
respiration, nutrition, excretion, protection by placental barrier, storage, hormone production
What hormones does the placenta produce?
hCG, estrogen, progesterone
How much does the placenta weigh at term?
480-600 grams
Where does attachment of the placenta occur?
anywhere
What side of the placenta has a fused layer of amnion and chorion (chorionic plate) with underlying vessels?
fetal side
What side of the placenta has about 20 functional lobes cotyledons composed of maternal sinusoids and chorionic villous structures?
maternal side
Describe the placenta.
480-600 grams, 20 functional lobes/cotyledons, discoid shape, central cord insertion, normal placenta 2-4 cm thick
True/False: Maternal and fetal circulations are separate.
true
Oxygenated maternal blood is pumped through ____ _____ within the ____ ____ and enters the ____ _____ surrounding ana bathing the villi.
spiral arterioles, decidua basalis, intervillous spaces
Deoxygenated fetal blood carried to the placenta from the ___ _____, circulates through ____ in the ___ ___ within the ____ ____.
umbilical arteries,capillaries, chorionic villi, placental lobes
Oxygenated blood within the ____ ____ returns to the fetus through the ___.
umbilical vein, placenta
True/False: During pregnancy, maternal blood volume decreases.
false, it increases
Many vascular channels and sinusoidal structure of the placenta create a ____ impedance system. (high or low)
low
Doppler investigation of maternal and fetal vessels demonstrates the ___ resistance nature of the placenta. (high or low)
low
Increased resistance in placental circulation increases _____ _____.
placental insufficiency
The placenta consists of about 20 tree-like structures called ____.
cotyledons
How does the fetal surface look like on the placenta?
smooth, glistening, and covered by amnion
How does the maternal surface look like on the placenta?
red and flesh-like and is divided into many cotyledons
What are teratogens?
any substance that is harmful to the fetus
Vascularity. The two circulations ____ in the placenta but do not mix.
intertwine
Maternal venous channels in the placenta are hypoechoic or anechoic spaces called ____ ____.
venous lakes
What prevents most pathogens from entering fetal circulation?
placental barrier
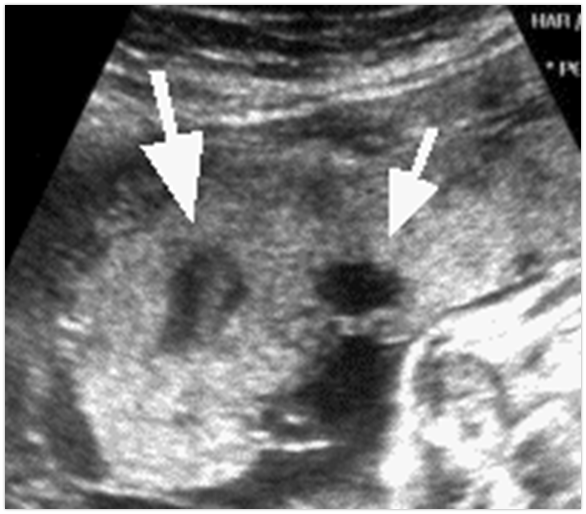
What are these?
placental lakes
An over distended bladder may cause a ___ ____.
false positive
What are some placental locations?
anterior, fundal, posterior, (right/left) lateral
What should placental thickness be?
less than 4 cm
True/False: Placental calcium deposition is abnormal.
false, it is a normal physiologic process
More than 50% show some degree of calcification after ____ weeks.
33
How many categories are used to grade placental maturity?
4
What are the categories for placental maturity called?
grades
Yes/No: Does a Grade 0 placenta have calcifications?
no
Yes/No: Does a Grade I have calcifications?
yes
What is the zone that is composed of the decidua basalis and portions of the myometrium including veins that drain the placenta called?
retroplacental complex (or retroplacental zone)
How does the retroplacental complex look like and when does it show and much does it measure?
hypoechoic, 14 weeks, 1-2 cm
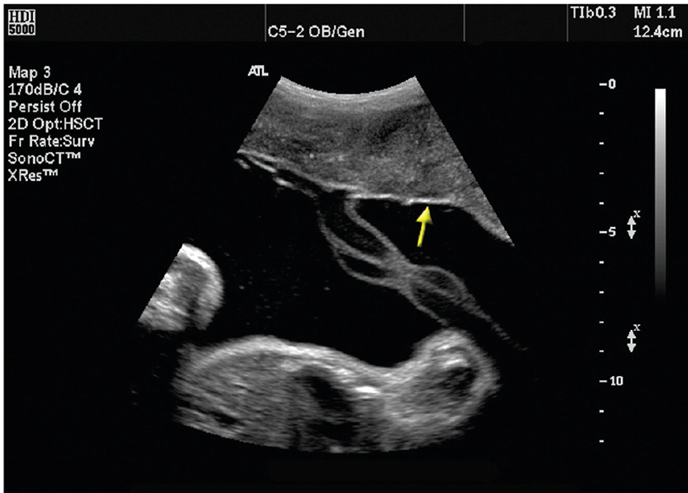
What is this?
chorionic plate
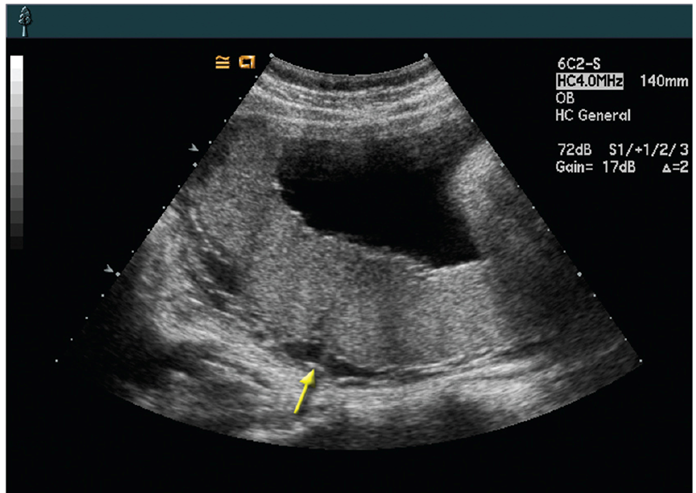
What is this?
retroplacental complex
What is the proper name of these uterine contractions that are normal, spontaneous, painless?
Braxton-Hicks contractions
In which trimester do Braxton-Hicks contractions occur?
it occurs in all trimester starting from the first to the end
True/False: Amniotic fluid is essential to the development of a fetus.
true
True/False: Amniotic fluid may have floating echogenic particles in the 1st and 2nd trimesters.
false, it is normally anechoic
True/False: In the 3rd trimester, it is normal to see floating echogenic particles within the amniotic fluid.
true
_______ ________ is a fatty material found of the fetal skin late in pregnancy and can be see floating within the AF late in pregnancy.
vernix caseosa
What are some of the functions of amniotic fluid?
cushion to protect fetus, allows embryonic and fetal movements, prevents adherence of the amnion to the embryo, allows symmetric growth, maintains temperature, contributes to lung development, acts as reservoir
Amniotic fluid volume increases until _____ weeks.
36-38
_____ of the _____ produces amniotic fluid early in pregnancy.
Epithelium, amnion
After ____ weeks, most of the fluid is through fetal urine.
16
Abnormalities of the GU or GI tract can affect _____ _____.
amniotic fluid
Occasionally, a membrane may be seen after _____.
16 weeks
Is seeing a membrane after 16 weeks normal?
no, the chorion should merge by 16 weeks
Subjective assessment of amniotic fluid can be performed by the sonographer using a _______ evaluation.
“eye-ball“
What method is used most frequently to asses amniotic fluid levels?
AFI
What are the normal ranges for AFI?
8 cm - 22 cm
What is it called when there is decreased amniotic fluid? How much should it measure to be considered decreased?
oligohydramnios, less than 5cm, less than 2 cm in one pocket
What is it called when there is increased amniotic fluid? How much should it measure to be considered increased?
polyhydramnios, more than 24 cm, greater than 8 cm in one pocket