Biol 2051 - MICRO - Luzan Exam 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
The use of Gram stain microbiology is important because they differentiate __________
bacterial cells with different cell walls
The cytoplasmic membrane could be best described as __________
a highly selective permeability barrier
Differential selection and descent with modification occurs during a process called ________
evolution
If delta G is negative, the reaction is ________
exergonic
The rigid layer that is present in the cell walls of Bacteria that is primarily responsible for the strength of the wall is known as __________
peptidoglycan
T/F: Microbial sterilization is used to kill all microbes in or on objects
True
Which of the following would be used by a chemoorganotroph?
C2H3O2-
T/F: Activation energy is the energy required for a chemeical reaction to begin.
True
When does endospore formation commence?
when bacterial growth ceases due to limitation of an essential nutrient
Cells move polar molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient using
Energy and transport proteins
The change in free energy for a particular reaction is the most useful in determining ________
Whether there will be a requirement or production of energy
Based on the functional roles of phosphate in various microbial metabolisms, which of the following compounds most likely contain phosphate?
Both inorganic and organic
Which of the following is false?
Most available nitrogen is in organic forms.
T/F: A pure culture contains a population of identical cells
True
You have discovered a new coccoid-shaped microorganism with no nucleus, a rigid cell wall, and a diameter of 2 micrometers. Chemical tests reveal that its cell wall does NOT contain peptidoglycan. The new microorganism is ___________
most likely an archaeon
Electron microscopy has greater _________ than light microscopy, because the wavelength of visible light is much larger than the wavelength of electrons.
resolution
Biological catalysts involved in the acceleration of the rate of chemical reactions are called ___________
enzymes
Based on your understanding of metabolism, generalize when an enzyme's rate of activity can be charged.
AFTER enzyme production
The terms "run" and "tumble" are generally associated with __________
chemotaxis in bacteria and archaea
Using phase contrast microscopy on a wet mount of live cells, you observe motile bacilli moving rapidly and randomly through the field of view, changing directions after a brief tumble and taking off in a different direction. These cells are exhibiting ___________ motility.
swimming
Compared to Eukaryotes, Bacteria and Archaea have _________ surface-to-volume ratios, causing __________ nutrient exchange.
higher; higher
All eukaryotic cells contain ________
a membrane-enclosed nucleus.
While examining cellular material, you find that organelle DNA is present. What organelle(s) must be within the sample?
chloroplasts or mitochondria
The sum of all biosynthetic reactions in a cell is known as ___________
anabolism
Which of the following statements is correct?
Microorganisms are significant contributors to the total biomass on Earth.
Exam 1 Practice (part 2)
-------
Common descent with modification (acquisition of genetic changes and passing them on to offspring resulting in better adaptation to their environment over generations) occurs during a process called
natural selection
A pure culture ______
is a population of identical cells
Pathogenic bacteria that are able to grow in humans and cause disease would be classified as _______________ (think of what is the average human body temp)
mesophiles
A type of medium that has at least one component that does NOT have an exact chemical formula is called ____________
complex
The codon on the ____________ matches with the anticodon on the _____________ to direct the addition of the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain
mRNA;tRNA
During DNA replication, the synthesis of the leading strand occurs continuously; the synthesis of the lagging strand is discontinuous, and requires frequent RNA primer formation and extension. Which of the following is formed on the lagging strand during DNA synthesis?
Okazaki fragments
Which metabolic strategy does NOT include proton motive force and generation of hydrogen ion gradient for energy conservation?
fermentation
A chemical that denatures proteins and kills living bacteria is most likely to be classified as a(n) ______________ agent.
bactericidal
A bacteriophage whose DNA is integrated inside its bacterial host genome is called ___________, and is known to enter a ___________ cycle.
prophage; lysogenic/lytic
When a virus enters a host cell which it can replicate, the process is called a(n) ________.
infection
Which of the following statements about cellular appendages is TRUE?
Fimbriae are usually shorter than flagella, whereas pili are involved in genetic exchange.
Which scientists and their contributions are MISMATCHED?
Robert Koch - disproved spontaneous generation
What are the order of enzymes during DNA replication?
DNA helicase > RNA primase > DNA polymerase, > DNA ligase.
What is the role of DNA helicase?
It separates the double strand into single strand allowing them to be copied
During DNA replication, what is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA primer?
Function?
Primase - adds new nitrogen-containing bases to single strands brought about by helicase
Main polymerase enzyme of DNA replication? Function?
DNA Polymerase III - adds nucleotides to the growing DNA chain on 3' OH end , incorporating only those that are complementary to the template
During DNA replication, what enzyme introduces negative supercoiling into DNA by making and re-sealing the double strand breaks in DNA?
DNA Gyrase
__________________ is a DNA-joining enzyme. If two pieces of DNA have matching ends, this enzyme can link them to form a single, unbroken molecule of DNA.
DNA Ligase
When a solution composed of bacteria and infectious virions are mixed and spread on an agar plate, ___________ form where viruses lyse the host cells.
Plaques
When packaged in the virion, the complete complex of nucleic acid and protein is known as the virus ____________.
nucleocapsid
One of the many types of proteins found in the cytoplasmic membrane that is involved in the chemotactic response in bacteria by binding the attractant and/or repellant molecule is called a ____________
Chemoreceptor
Bacterial plasmids often encode for proteins that ___________
confer resistance to antibiotics and ability to degrade xenobiotics (like petroleum-derived hydrocarbons)
Gram negative bacterial envelop contain ___________ membrane with the unique molecules called ______ which can act as potent endotoxins and cause overreactive immune response in humans
double; LPS (lipopolysaccharides)
During protein synthesis, what happens at the P site of the ribosome?
The P site holds a tRNA that carries a growing polypeptide (the first amino acid added is methionine (Met)
During protein synthesis, tRNA is released from the ribosome at the _____________.
E site
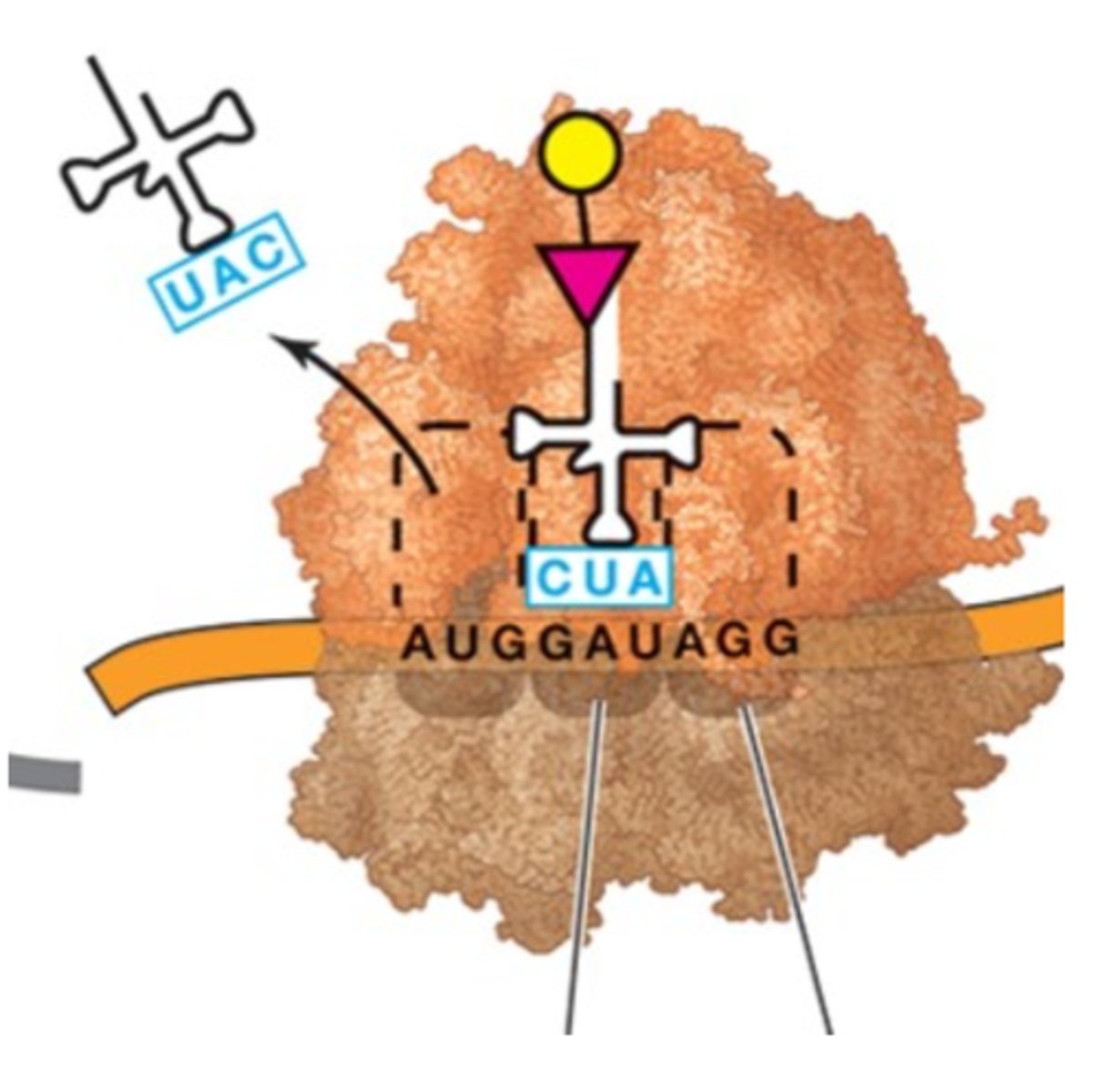
During protein synthesis, what happens at the A site of ribosome?
The A site (acceptor site), binds to the aminoacyl tRNA, which holds the new amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain
In microbial population growth, the stage, when population grows exponentially is called the _________ phase.
log phase
The portion of an enzyme to which substrates bind is referred to as the ___________
active site
A drop of a pure culture of a bacterium possessing an enzyme called ___________ will produce O2 bubbles when mixed with hydrogen peroxide.
catalase
Viral reverse transcriptase enzyme is a(n) ______________
RNA-dependent polymerase (synthesizes DNA based on RNA template)
Cells move polar molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient using _____________
energy of ATP and transport proteins
From the standpoint of fermentative microorganisms, the most important product in glycolysis is ___________ (think how microbe would think)
ATP and regeneration NAG+; the fermentation products like lactic acid and ethanol, are waste products to a microbe
______________ is a survival structure found in some bacteria (like clostridium), and is surrounded by a very tough outer coating that protects bacterial cell content from UV light, desiccation and abrasion
an endospore
In general, lipids in Archaeal cytoplasmic membranes lack true fatty acids
True
Which type of microscopy allows to visualize cells as brightly colored glowing structures on a black background by the use specific dyes?
Fluorescent microscopy ?
Acetyl Co-A is utilized in
gluconeogenesis
How does the proton motive force lead to production of ATP?
Movement of protons through the F1 (transmembrane compartment) of ATP synthase into cell down the concentration gradient drives the F0 component of ATPase, which in turn spins and phosphorylates one ADP into ATP.
Flagella - "run"
Counterclockwise rotation
Flagella - "tumble"
clockwise rotation
Polar Flagella Bacteria
many do not tumble; just reverse; some stop and rely on Brownian motion (random movement)
How do you measure chemotaxis?
Capillary tube
Mitosis
results in 2 diploid daughter cells
Meiosis
results in 4 haploid gametes
What are folded membranes that contain enzymes needed for respiration and ATP production?
Cristae
What is the innermost membrane of mitochondria?
Matrix
What is the cytoskeleton made of?
Microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
Anabolic/Anabolism
Endergonic; requires energy; biosynthesis of cellular macromolecules
Catabolic/Catabolism
Exergonic; generates free energy; depends on electron flow
Electron donor
Transfers electrons; OXIDIZED
Electron acceptor
Accepts; REDUCED
What does the fermentation of glucose involve?
Substrate level phosphorylation and redox balance via pyruvate reduction and excretion as waste.
NO acceptors.
What does respiration involve?
Electrons transferred from reduced electron donors to external acceptors
Where does reoxidation occur?
ETC (electron transport chain)
Respiratory electron transport vs. photosynthetic electron transport?
Electrons are RETURNED in photosynthesis
What is a chemostat?
Most COMMON CONTINUOUS culture device. Maintain exponential growth for weeks or months
In PROKARYOTES where does protein synthesis take place?
the cytoplasm
What are the steps of protein synthesis in Prokaryotes?
TWO steps: translation and transcription
Where does protein synthesis occur in Eukaryotes?
the Nucleus
What are the steps of protein synthesis in Eukaryotes?
THREE steps: Initiation, Elongation, and Termination
Exam 1 Practice Part 3
---------
Which of the following statements about microbial flagellum is false?
Flagellar rotation generated ATP
During DNA replication, Okazaki fragments formed on lagging strand are linked together by ________ , enzyme that creates phosphodiester bonds, the main type of covalent bonds, between separate fragments of DNA.
DNA Ligase
General steps of viral life cycle are similar. One major exception, however, is entry to the host cell. How does this step differ between an animal cell and E. coli?
The entire virion is taken into the animal cell, but only the genome enters E. coli.
Gram-positive cell wall consists of thick ______ layer.
peptidoglycan
T/F: Added rigidity of cellular structures such as more beta pleaded sheets in enzymes and higher amount of saturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids, is important molecular adaptation of thermophiles and hyperthermophiles that helps them thrive in extreme hot environments.
TRUE
Enveloped viral membranes are generally ________ with associated virus-specific ________.
lipid bilayers; proteins
In microbial growth, the time between inoculation and the start of growth is usually called the _________
lag phase
T4 is a common lytic bacteriophage that infects E. coli cells. What would be the consequence of deleting the late T4 genes?
T4 capsid proteins would NOT be made.
For bacteriophages and animal viruses ________ is the step in the viral life cycle that determines host cell specificity.
attachment
In the process of transcription, promoters are specific sequences of ________ that are recognized by ________.
DNA; sigma factors
Which is the biggest difference between anaerobic and aerobic respiration?
The nature of electron ACCEPTOR
What does topoisomerase do in DNA replication?
unwinds the DNA, relaxes supercoiling
Which scientist and contribution is mismatched?
Winogradski - first to propose three domains of life
The LPS (a potent endotoxin) is found ONLY in the cell walls of _____________
gram-negative bacteria