U4 AOS2 - Aboriginal & Torres Strait Cultural Determinants of mental-wellbeing (cultural continuity & self-determination)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Factors that promote Cultural Continuity
Cultural awareness - understanding the role of cultural difference and diversity
Cultural respect - valuing Aboriginal & Torres Strait islander people and cultures
Cultural responsiveness - having the ability and skills to assist people of a different culture other than your own
Self-Determination
The ability to guide your own life path or destiny. It is cruicial for maintaining mental well-being.
9 Guiding principles
Health
Self-determination
Culturally valid understandings
Trauma & loss
Human rights
Racism stigma
Family & Kinship Ways of living
Strengths
Health as a guding principle
Viewed in a holistic context that encompasses mental, physical, cultural, and spiritual health. Land is central to wellbeing. When the harmony of these interrelations is disrupted, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander ill health will persist.
Culturally Valid Understandings as a guiding principle
Must shape the provision of services and must guide assessment, care, and management of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander (ATSI) people’s health in general, and mental health in particular.
Trauma and Loss as a guiding principle
Experiences of trauma and loss are a direct outcome of the disruption to cultural wellbeing. Trauma and loss of this magnitude (due to Eurpoean invasion) continues to have intergenerational effects.
Human Rights as a guding principle
Must be recognised and respected. Failure to respect these human rights constitutes continuous disruption to mental health. Human rights relevant to mental illness must be specifically addressed.
Racism, Stigma as a guiding principle
Environmental adversity and social disadvantage constitute ongoing stressors and have negative impacts on ATSI people’s mental health and wellbeing.
Family & Kinship as a guding principle
Must be recognised as well as the broader concepts of family and the bonds of reciprocal affection, responsibility, and sharing.
Strengths as a guding priciple
It must be recognised that ATSI have great strengths, creativity, endurance, and a deep understanding of the relationships between human beings and their environment.
Intergenerational/Transgenerational Trauma
Collective or historical memories of traumatic events that persist beyond the direct survivors of the event, continuing throughout time and if not healed, can negatively impact on subsequent generations.
Social and emotional wellbeing
Reflects the holistic understanding of wellness for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and includes intrinsic connections between the relational-self, mind-emotions, body, Country, community, culture, kinship and ancestry. These domains are situated in the broader social, political, historical and cultural determinants of health.
Human rights approach
An approach whereby oppression and discrimination are actively prevented and eliminated. This may include actions of equity where priority is given to marginalised individuals who face the biggest barriers in the realisation of their human rights.
Indigenous Psychology
A growing global movement and discourse of self-determination that strives to decolonise and emancipate people from the domination of Western psychology. Indigenous Psychology as a discipline promotes psychologies that have been developed and determined within a group’s cultural context.
Social & Emotional Wellbeing (SEWB)
Reflects the holistic understanding of wellness for ATSI peoples and includes intrinsic connections between the relational-self, mind-emotions, body-behaviours, country-land, community, culture, kinship-family, and spirituality-ancestry. These domains are situated in the broader social, political, historical, and cultural determinants of health.
Thus, it describes a collective and relational self that exists in the context of the other domains and determinants of health.
SEWB - Connection to Body & Behaviour
Includes physical health and considers the importance of optimal functioning through diet and exercise - your body, health, spirit, and mind being at their best.
Protective Factors
Sports, exercise, hunting & gathering, and other activities on country, traditional diets & medicines, and access to culturally safe services.
Risk Factors
Smoking, alcohol, drug misuse, junk food, chronic and communicable diseases, exclusions from health + well-being + and other essential services.
SEWB - Connection to mind & Emotions
Extends beyond mental health to include recognising culture-bound disorders and the importance of positive emotions, self-confidence, and experiencing joy, rather than just the absence of disorder.
Protective Factors
Belonging, mindfulness, accessing support to manage stress, overcome trauma, and/or recover from other mental health illnesses. Truth-telling.
Risk Factors
Threats to safety, social disadvantage, intergenerational trauma, experience of racism, misdiagnosis and mislabelling.
SEWB - Connection to Family & Kinship
Includes family and kinship relations, systems of reciprocity and caring, gender and age roles, including respect for Elders and heritage
Protective Factors
Learning about and connecting with family history, sharing experiences with other Aboriginal people, and being part of healthy relationships/family connections.
Risk Factors
Removal of children from families, incarceration, family violence, grief and loss, and lack of cultural education.
SEWB - Connection to Community
Includes cultural structures of responsibility and obligation, social inclusion, and relationships.
Protective Factors
Self-determination and having community control. Having Aboriginal mentors, role-models, advisors, and Elders. Cultural revitalisation. Participation in community activities. Community harmony.
Risk Factors
Social exclusion and systematic racism, lateral violence, family feuding, disconnection and isolation.
SEWB - Connection to Culture
Includes cultural expressions and activities (yarning, ceremony, camping, fire, art, dance, song, storytelling, funerals); cultural knowledges (language, protocol, lore, ethical practice), and cultural identity (pride, values, belonging).
Protective Factors
Learning about, involvement with, and participation in cultural activities and knowledge to build cultural identity. Passing on cultural activities and knowledge to young people who have been disconnected from culture.
Risk Factors
Cultural dislocation, cultural genocide, cultural clash between two worlds, disconnection from language, country, and family, and assimilation policies.
SEWB - Connection to Land & Country
Includes experiences of belonging to Country, a traditional spiritual connection to kin and culture through Country, and a yearning to heal Country.
Protective Factors
Returning to the country as a way of healing the body, mind, and spirit, and reconnecting with community, cultural renewal. Traditional medicine and diet. Land rights.
Risk Factors
Removal from the country, dispossession of land, destruction of sacred sites, and environmental degradation.
SEWB - Connection of Ancestors & Spirituality
Includes Indigenous knowledges and belief systems. Traditional and cultural healing practices, sacred sites and men’s and women’s lore grounds. Values of wisdom and hope.
Protective Factors
Accepting traditional and evolving expressions of indigeneity and spirituality that coexist with other religions and mindfulness practices that enable peace and balance.
Risk Factors
The impact of mission life, religion, assimilation policies such as Stolen Generations, and cultural genocide. Symptoms of trauma, such as misuse of drugs.
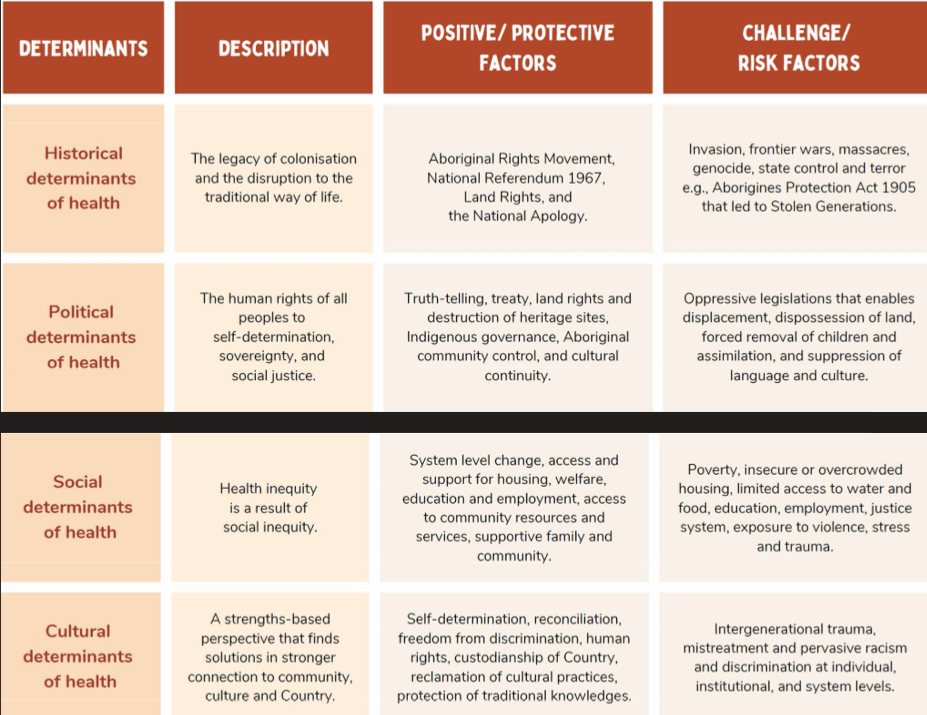
Determinants of health