Phosphorus
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 4 in Lecture Manual
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Labile P
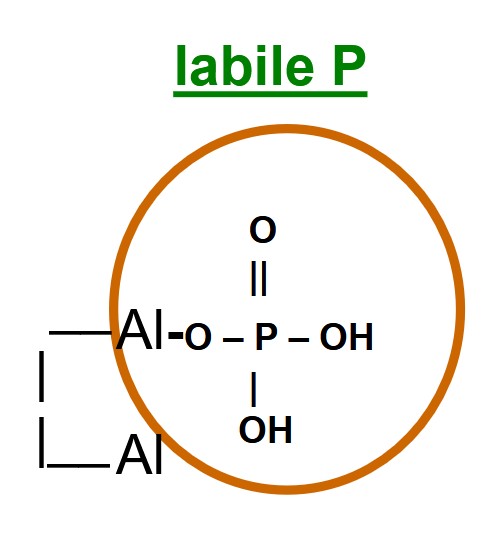
the portion of Orthophosphate-P loosely associated with clay mineral surfaces and is available to crops during the growing season
Non-labile P
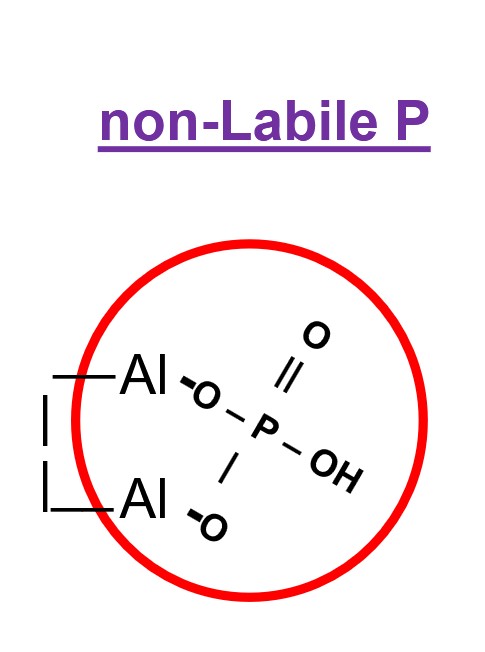
the portion of orthophosphate-P tightly associated with clay mineral surfaces and is not available to crops during the growing season
Erosion
the movement of soil and nutrients from their placement position due to wind and water
What are the P forms in nature?
Orthophosphate (PO4³-)
is found in both organic and inorganic forms
Use of orthophosphate-P and forms used by plants
Plants uptake P as Orthophosphate Ions
H2PO4-,H3PO4, HPO4²-
Form depends on pH of soil
Ortho P used for energy storage (ADP/ATP), nucleic acids (DNA/RNA), and enzymes in cell membranes (phospholipids)
Ortho-P movement in soil
Highly immobile, moves by diffusion
Fixation with Fe and Al in acidic soils or with Ca in calcareous (high-pH) soils reduces P movement.
High clay soils also have reduced P movement
P nutrient cycle differences from N cycle
N Cycle: main loss is leaching & denitrification, nitrate is very mobile, has a large gaseous phase
P cycle: main loss is erosion, very low mobility, no gaseous phase, no biological fixation, organic forms (crop residue, manure, soil O.M.) must mineralize to release plant-available ortho. P
Status of Ortho-P Ion in Soil
solution ortho-P is a small fraction of total soil ortho-P
Most of ortho-P is associated with soil components (labile and non-labile P)
What factors influence soil ortho.-P availability to crops?
Influence of clay content in soils (quantity and clay type)
As soil clay content increase, labile and non-labile ortho-P increases (Soils with more clay hold P tighter)
Clay types - age (degree of weathering) is more impactful than structures, as total surface area increases, more ortho-P can be sorbed and fixed by Al and Fe minerals
Soil pH - maximum ortho-P availability occurs in a pH range of 6-7
With time, ortho-P forms compounds that become less available to crops
Identify popular synthetic fertilizer materials and chemical formula
Crushed Apatite - chemical form is orthophosphate-P
N-P combinations (most common used in SD)
MAP - Mono-Ammonium Phosphate (11-52-0)
DAP - Di-Ammonium Phosphate (18-46-0)
NH4-polyphosphates (10-34-0)
Effective management of fertilizer P applications
Always use soil test results to determine amount needed
Delay P application 3 weeks after liming (Ca in lime will bind to the P fertilizer)
Subsurface application is ideal, can apply surface for perennial crops
Use tillage, starter P bands and strip till to place P fertilizer in root zone
Environmental risks associated with soil ortho.-P
Erosion: causes eutrophication in lakes, lowers profitability, threatens the enviroment
erosion loss is the greatest risk associated with P use
What can minimize soil ortho.-P erosional losses?
Minimize runoff, reduce tillage, use cover crops, manage runoff and drainage areas
chemical changes for labile ortho.-P
ortho. P ions form a single ‘covalent’ O-P bonds with clay mineral surfaces
chemical changes for non-labile ortho.-P
ion forms two ‘covalent ‘O-P bonds with Al or Fe on clay mineral surfaces