6) Ocular Blood Supply
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
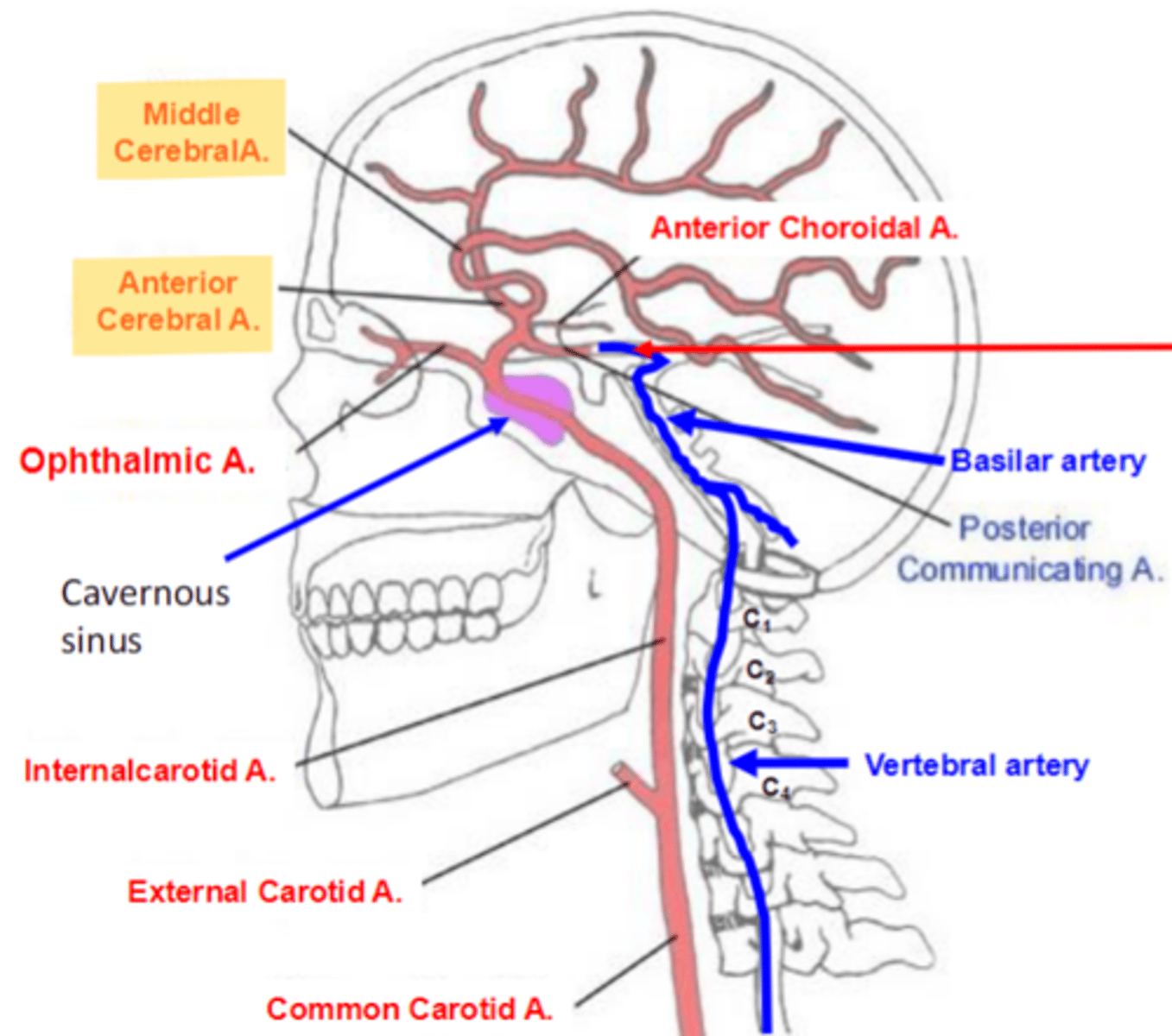
Internal carotid artery
supplies the anterior brain.
branches from the Common carotid artery.
enters the cranium through the Carotid canal, passes through the Cavernous sinus, and divides into the:
1. Ophthalmic artery
2. Posterior communicating artery
3. Anterior choroidal artery
4. Anterior cerebral artery
5. Middle cerebral artery
OPAAM
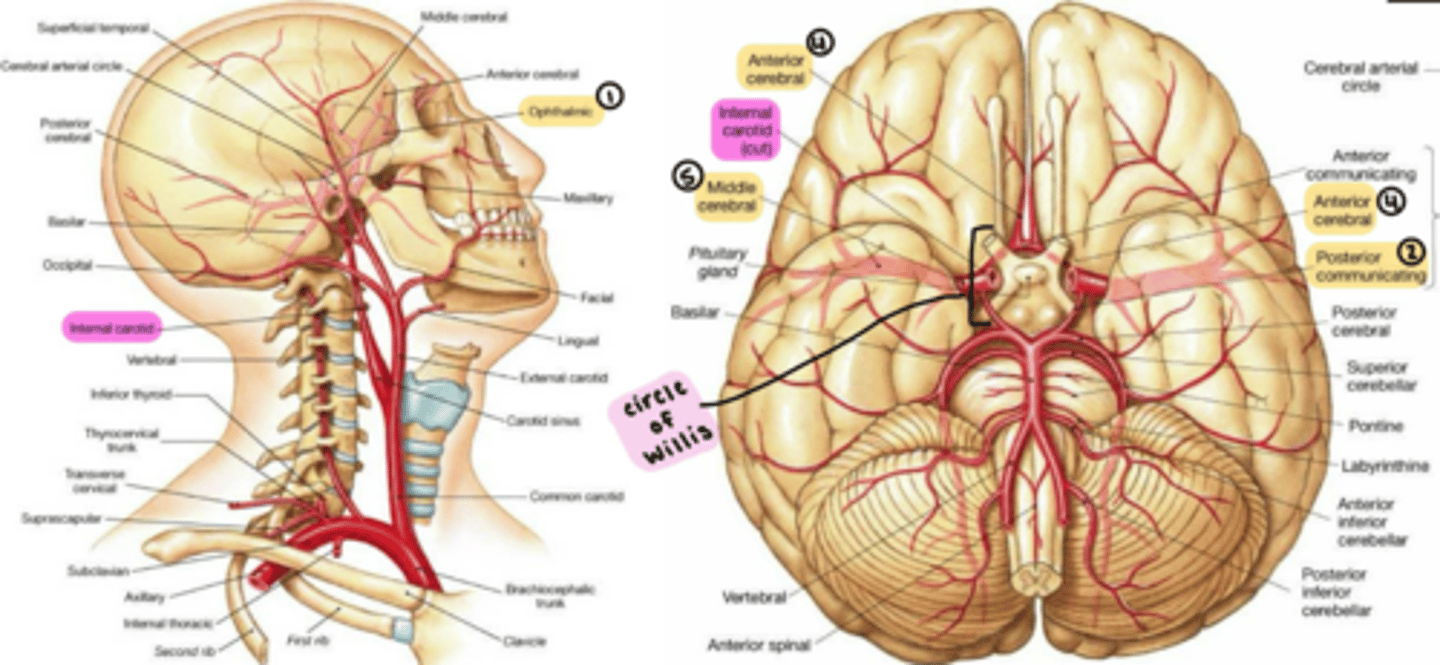
Vertebral artery
supplies the posterior brain.
branches from the Subclavian artery.
enters the cranium through the Foramen magnum.
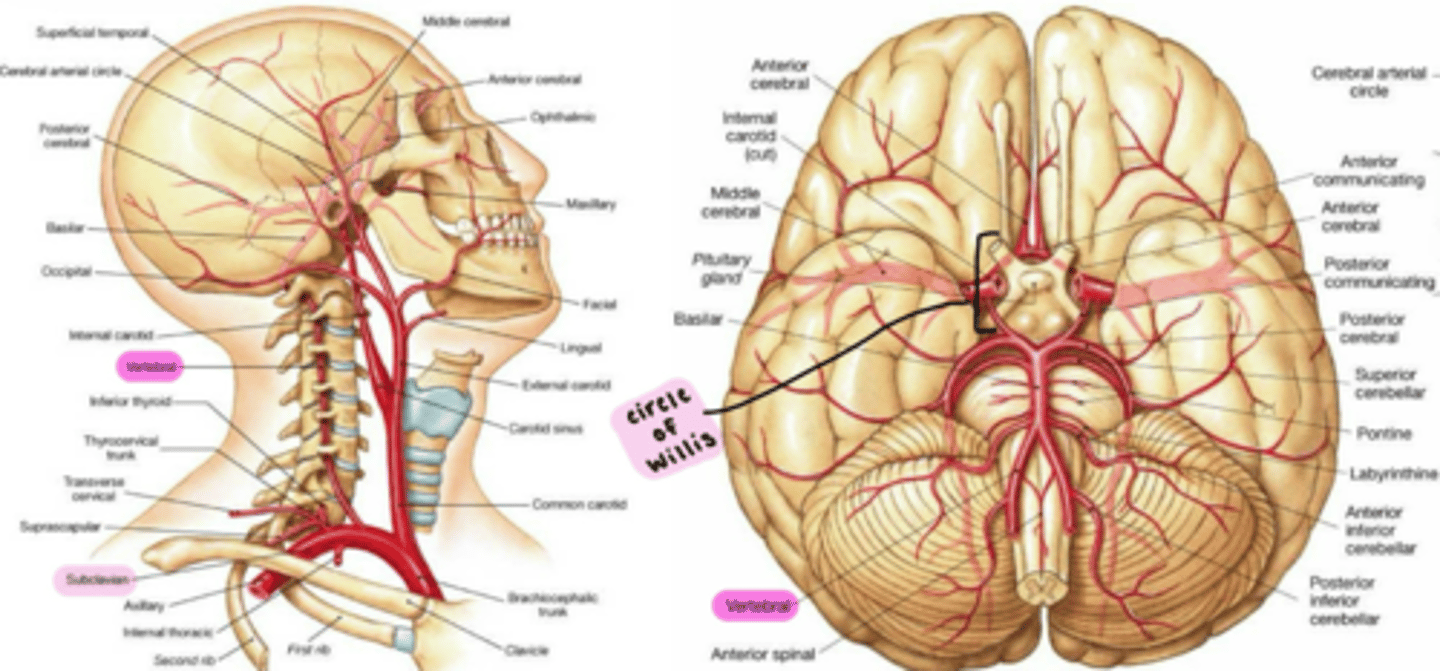
Basilar artery
Vertebral arteries fuse to form the Basilar artery
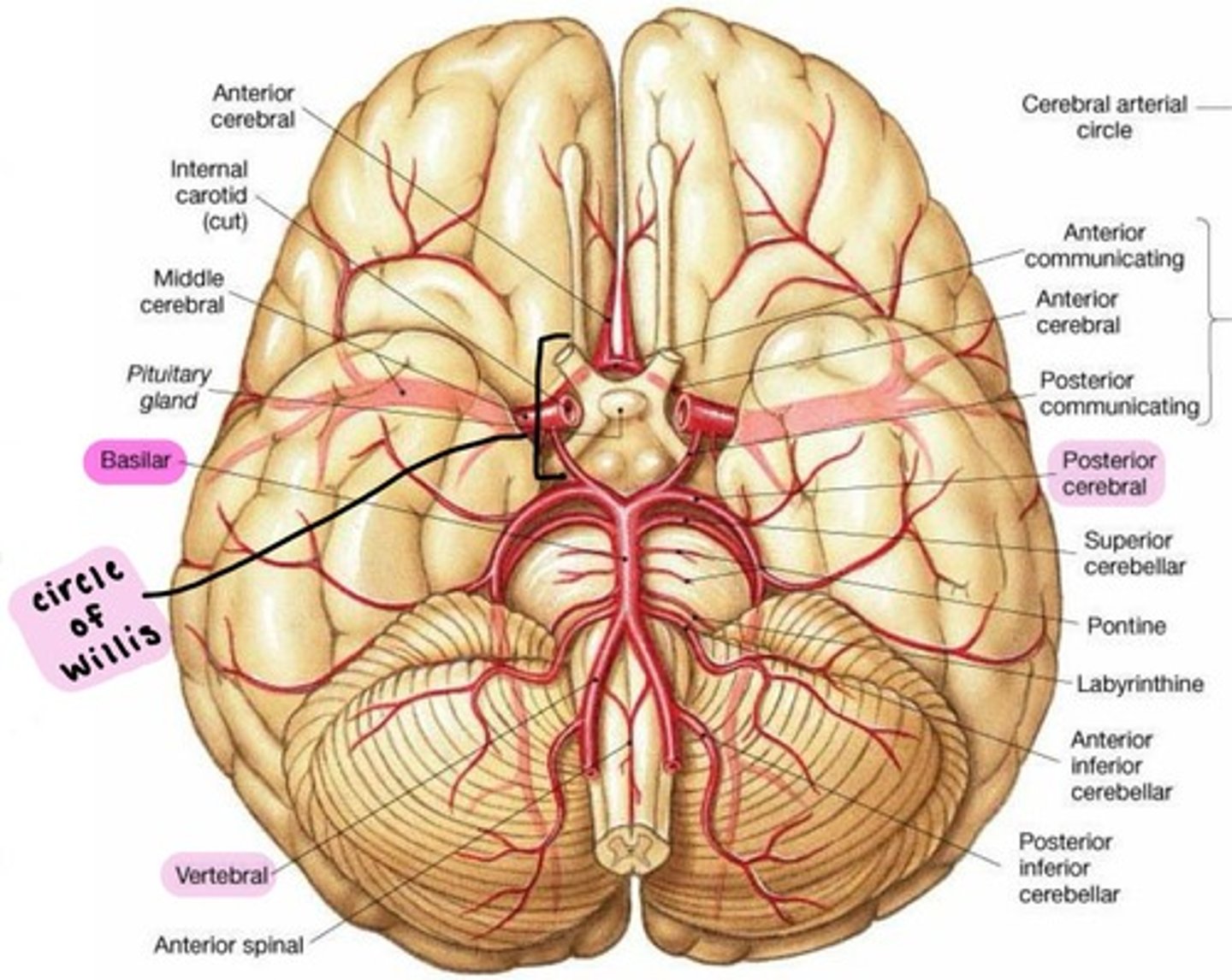
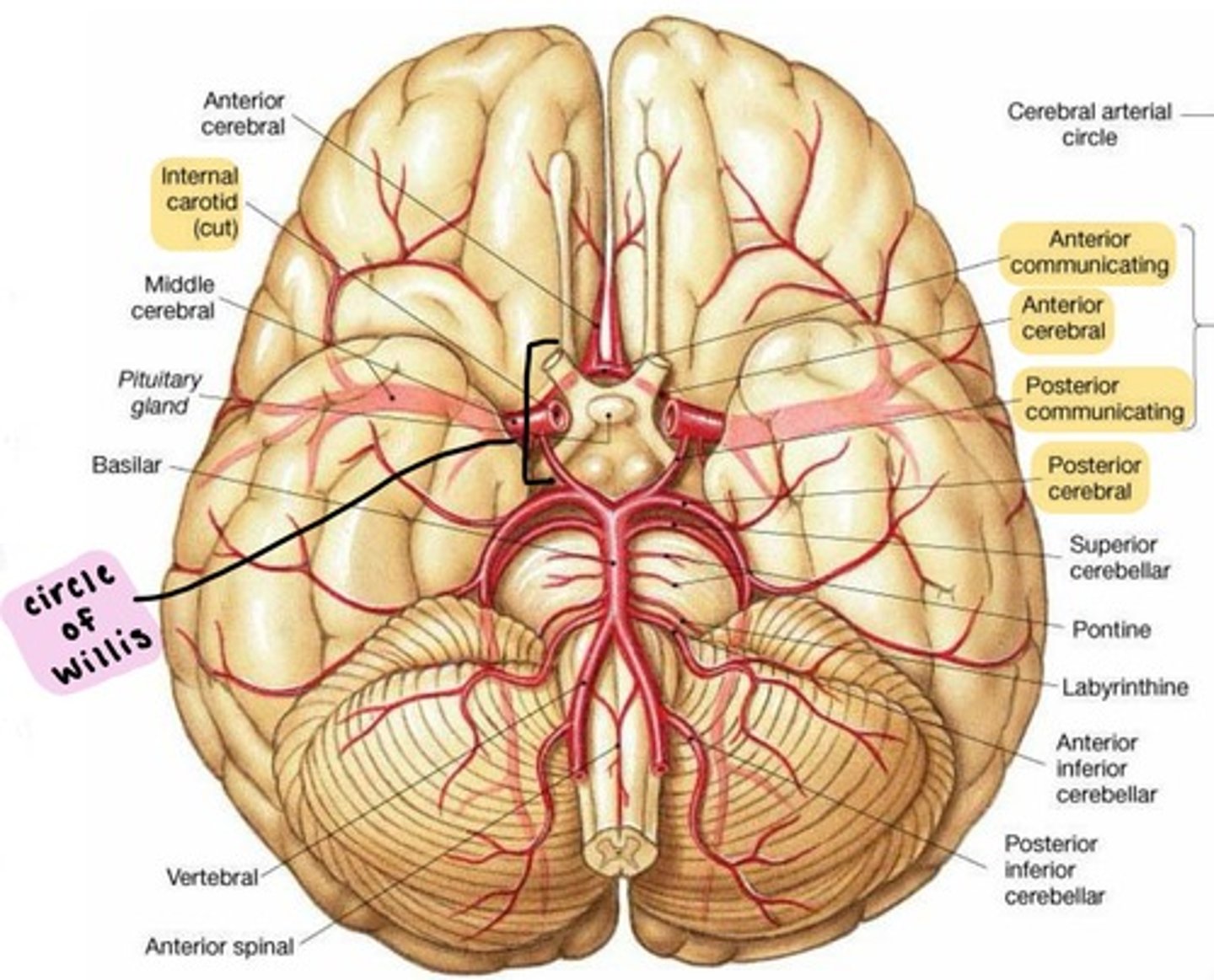
Cerebral arterial circle (Circle of Willis)
complex of anastomosing arteries that includes:
1. Internal carotid arteries
2. Anterior cerebral arteries, linked by
3. Anterior communicating artery
4. Posterior cerebral arteries, linked to Internal carotids by
5. Posterior communicating arteries
IPAPA
terminal branches of Internal carotid artery
-Anterior cerebral arteries.
-Middle cerebral arteries
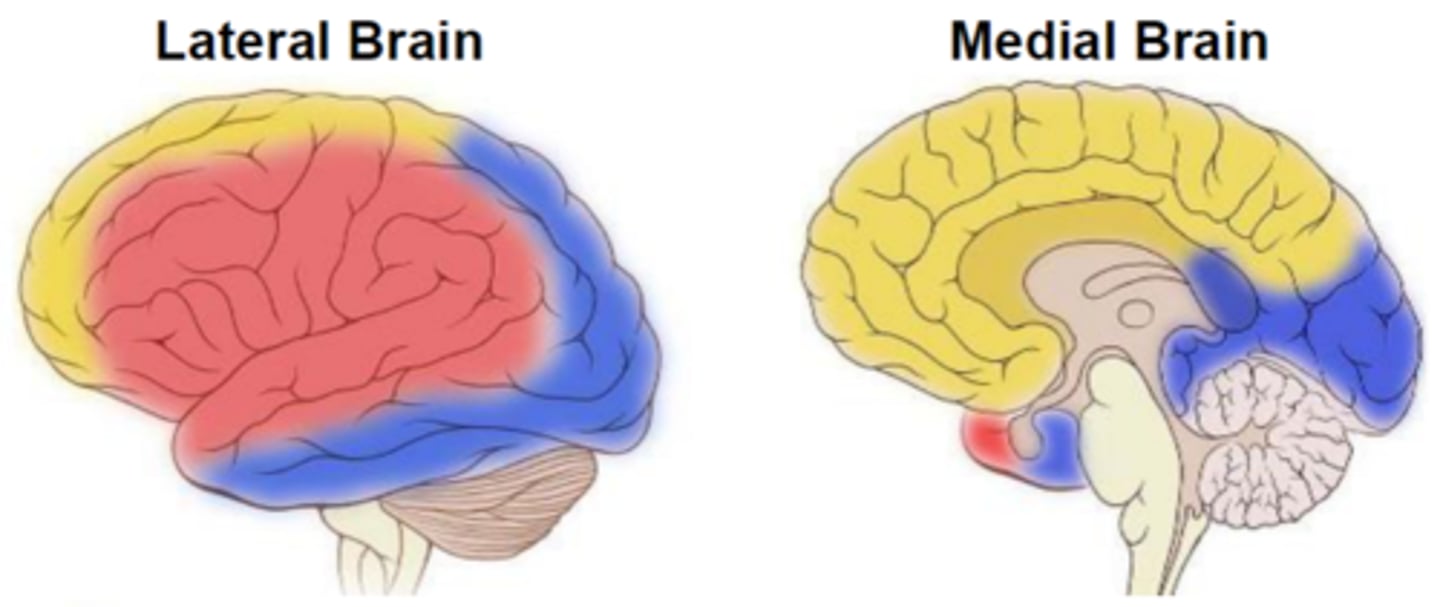
Anterior cerebral artery: where does it supply blood to?
anteriomedial portion of the cerebrum (in yellow)
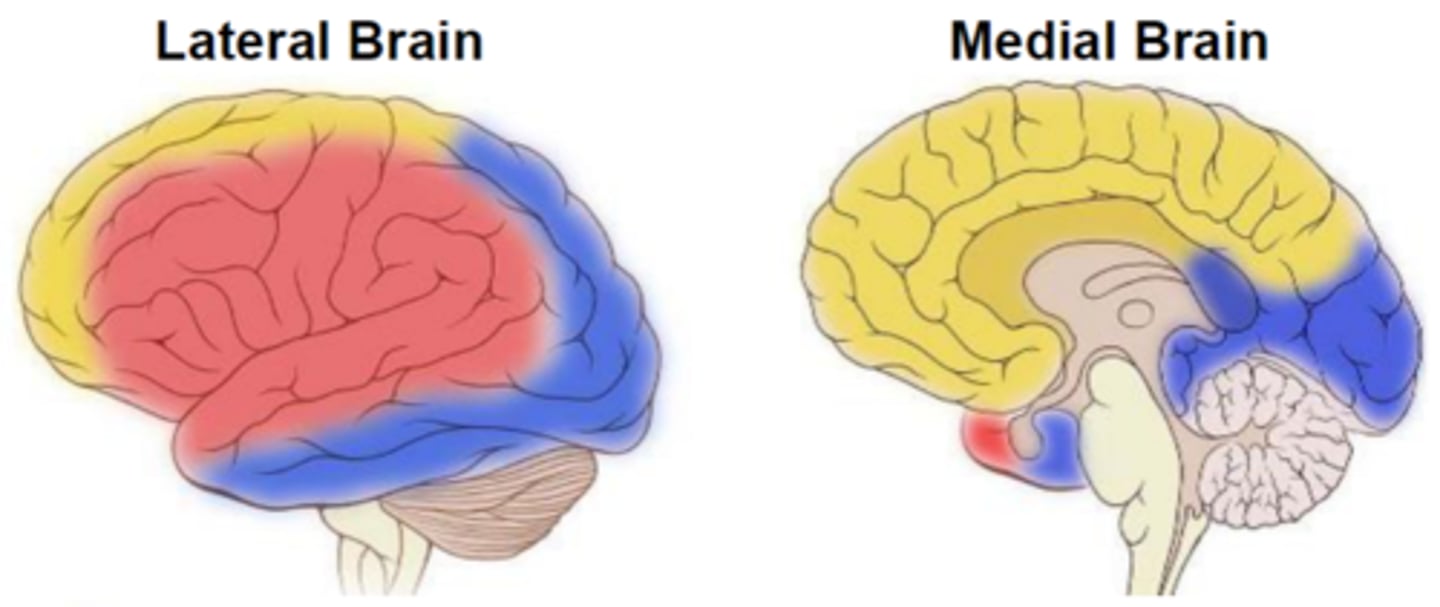
Middle cerebral artery: where does it supply blood to?
the majority of the lateral brain (in red)
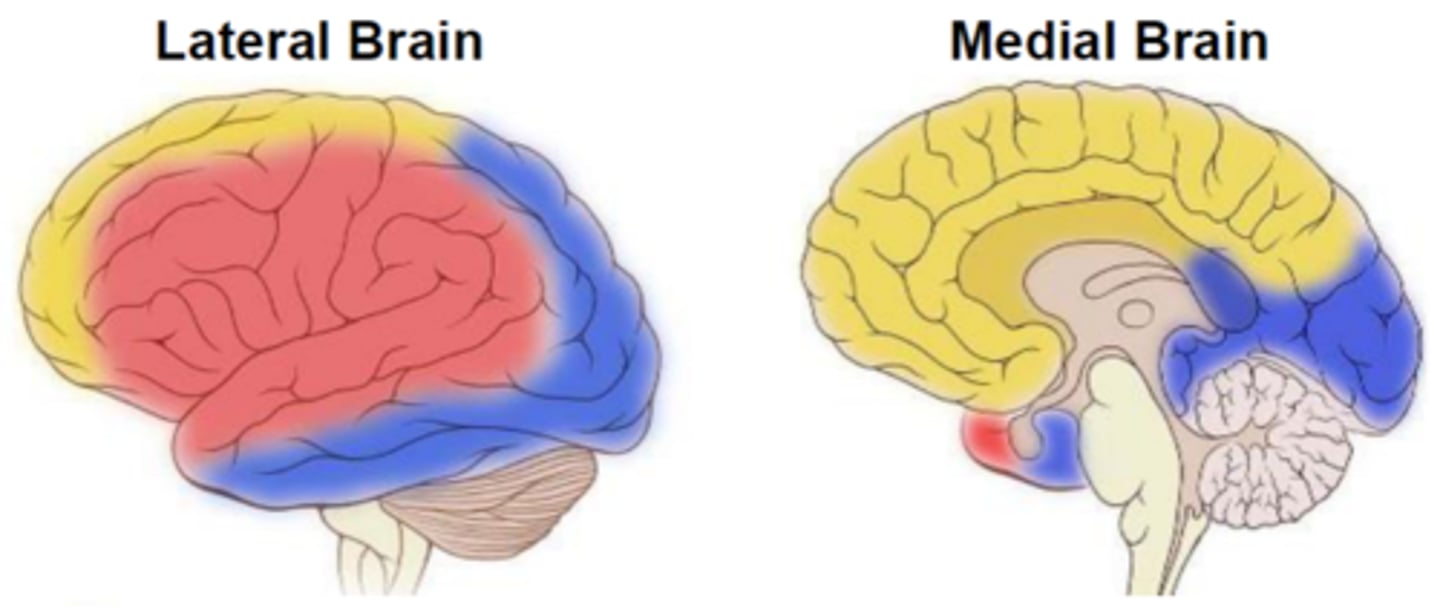
Posterior cerebral artery: where does it supply blood to?
medial & lateral parts of the posterior cerebrum (in blue)
***problems with the Posterior cerebral artery can affect vision/visual cortex!
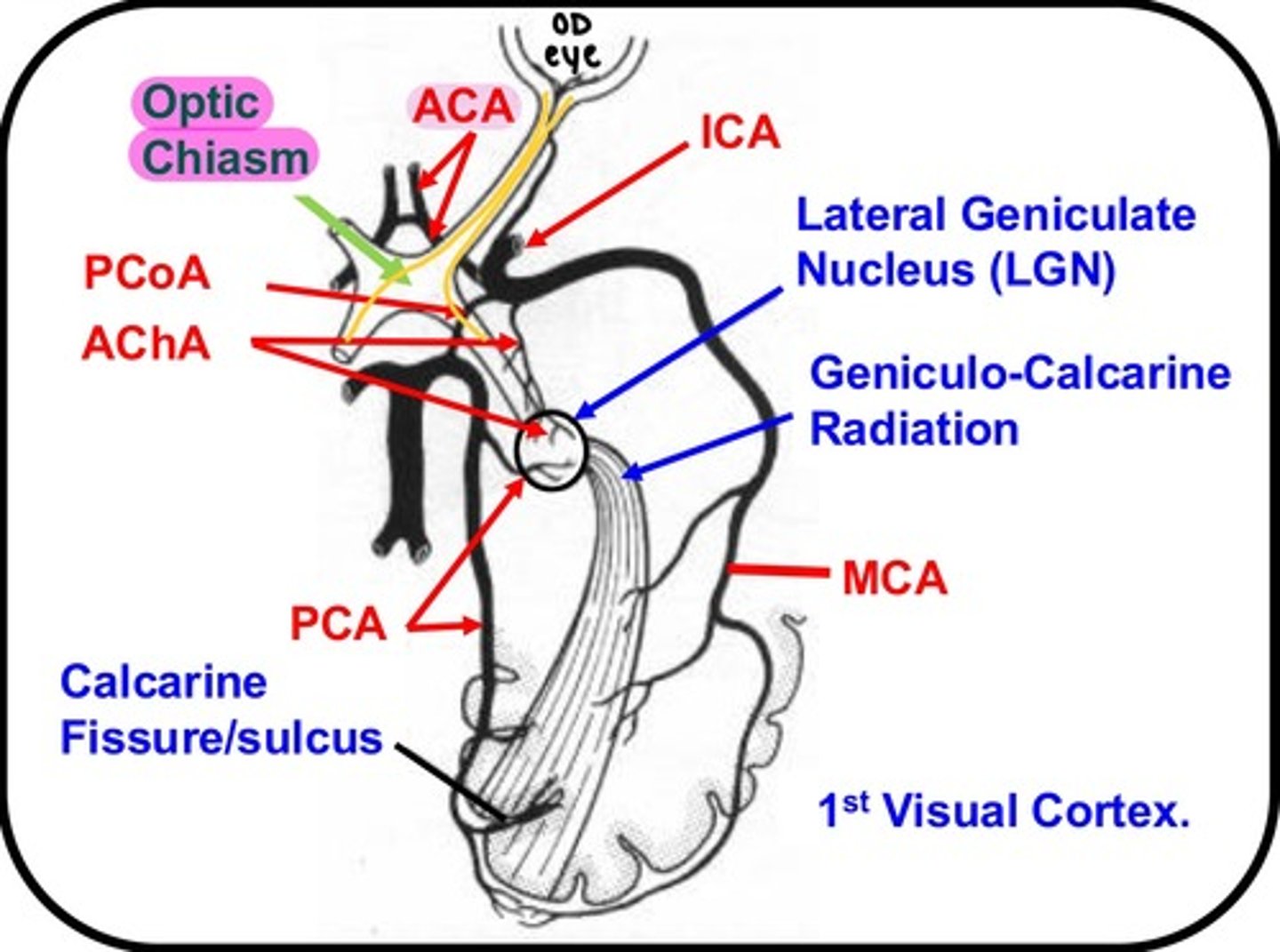
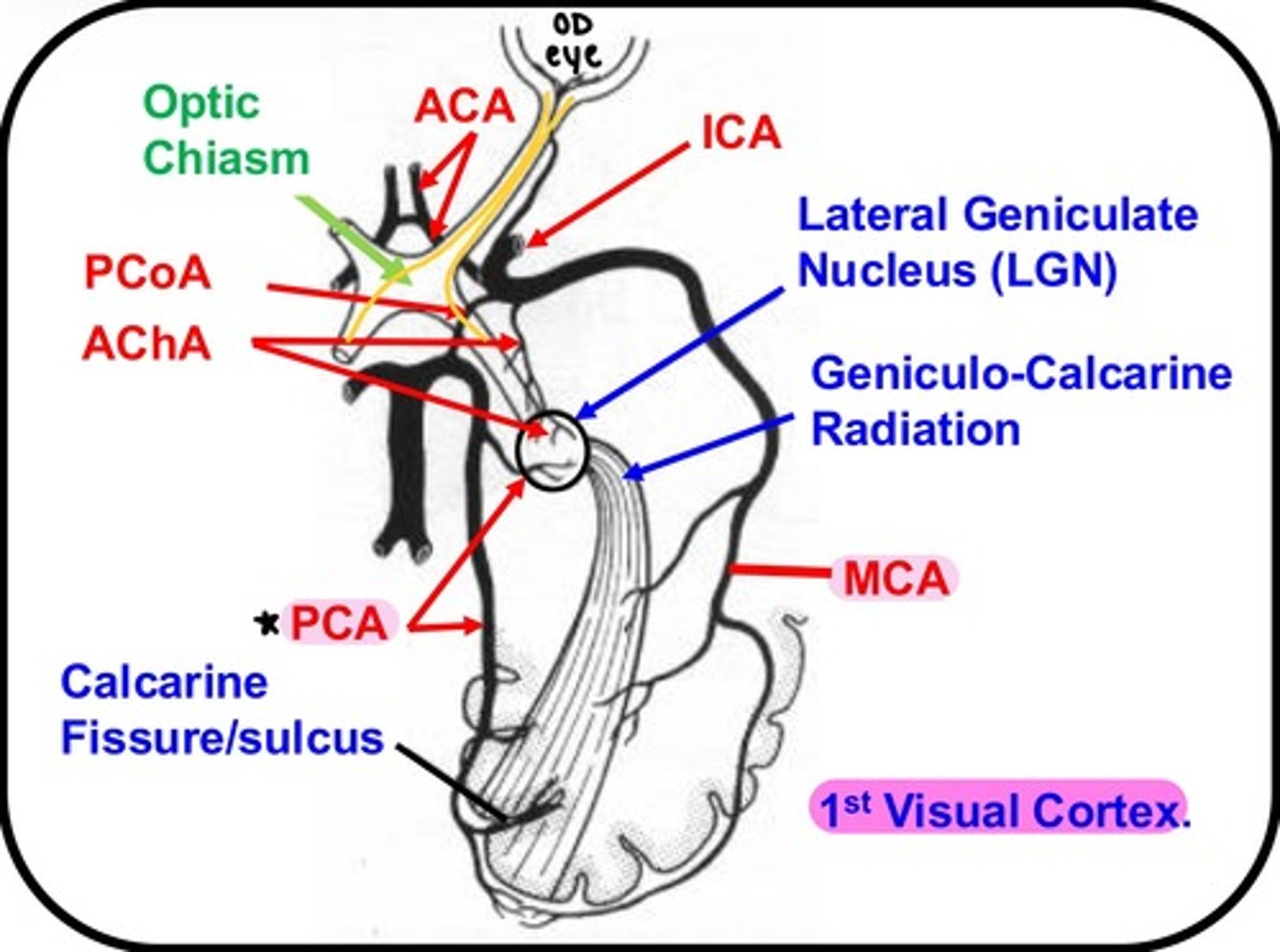
which artery/arteries supply the Optic chiasm?
Anterior cerebral artery
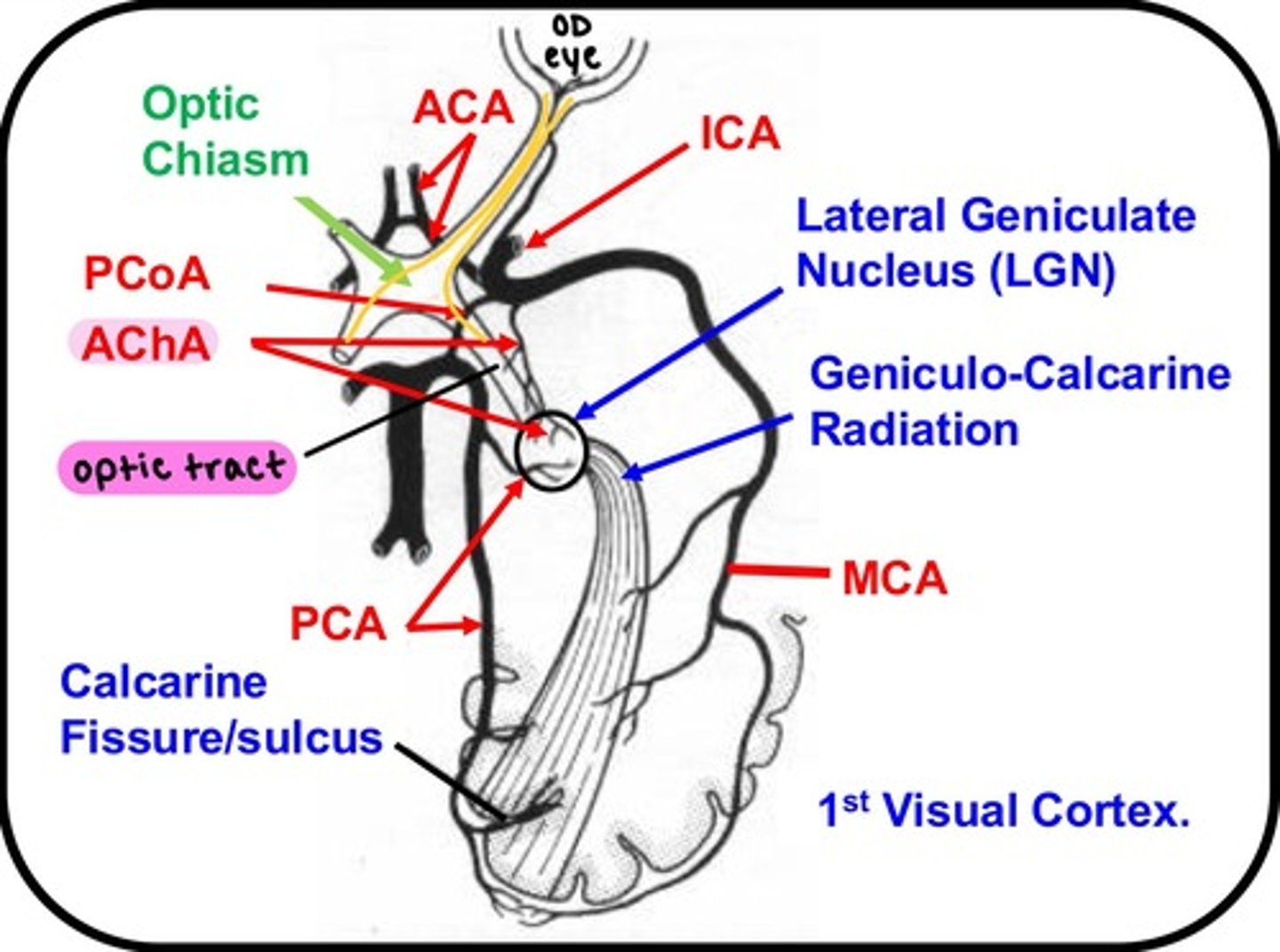
which artery/arteries supply the Optic tract?
Anterior choroidal artery
which artery/arteries supply the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)?
-Anterior choroidal artery
-Posterior cerebral artery
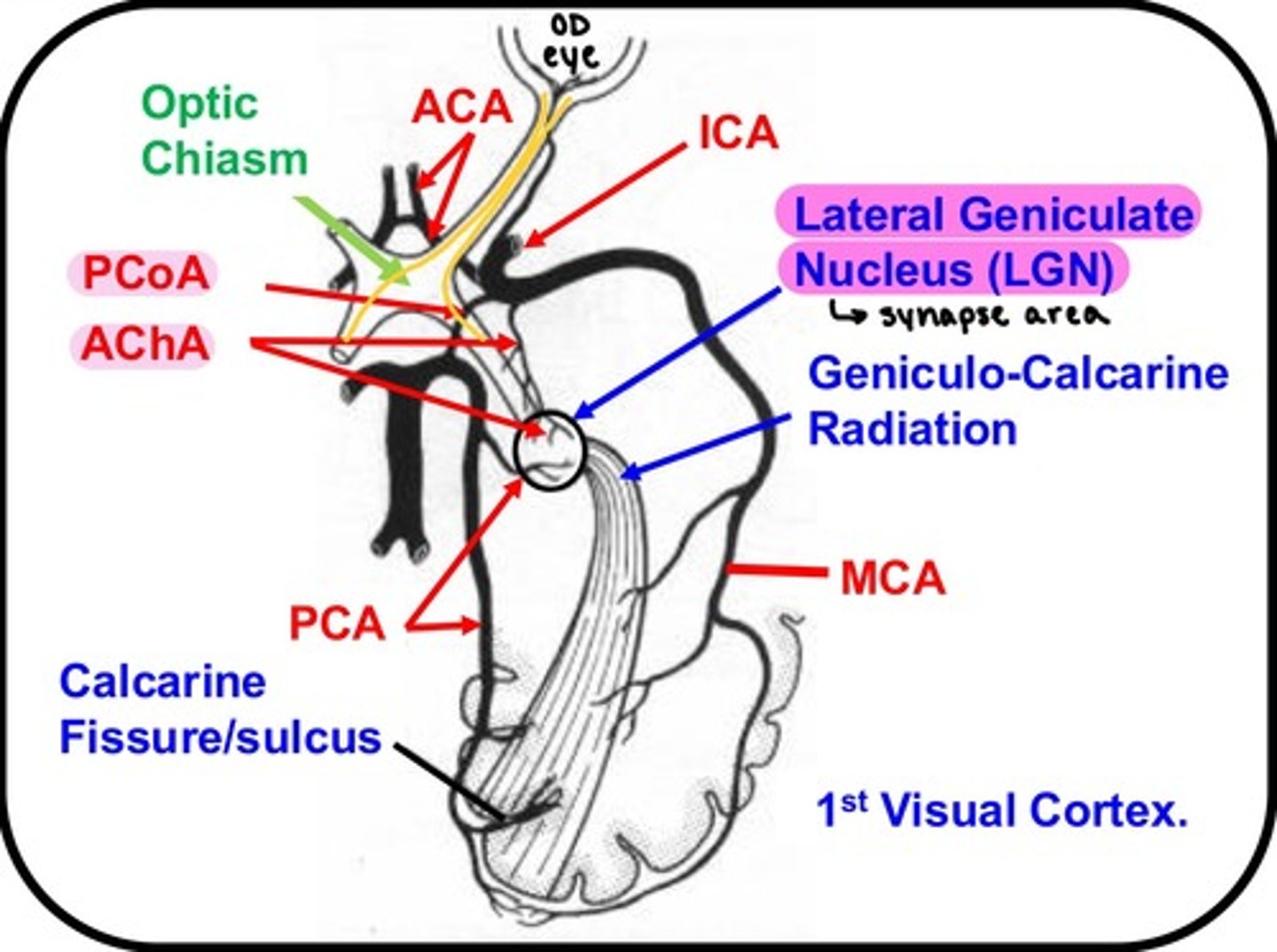
which artery/arteries supply the 1st Visual Cortex?
-Middle cerebral artery
-Posterior cerebral artery (!!!)
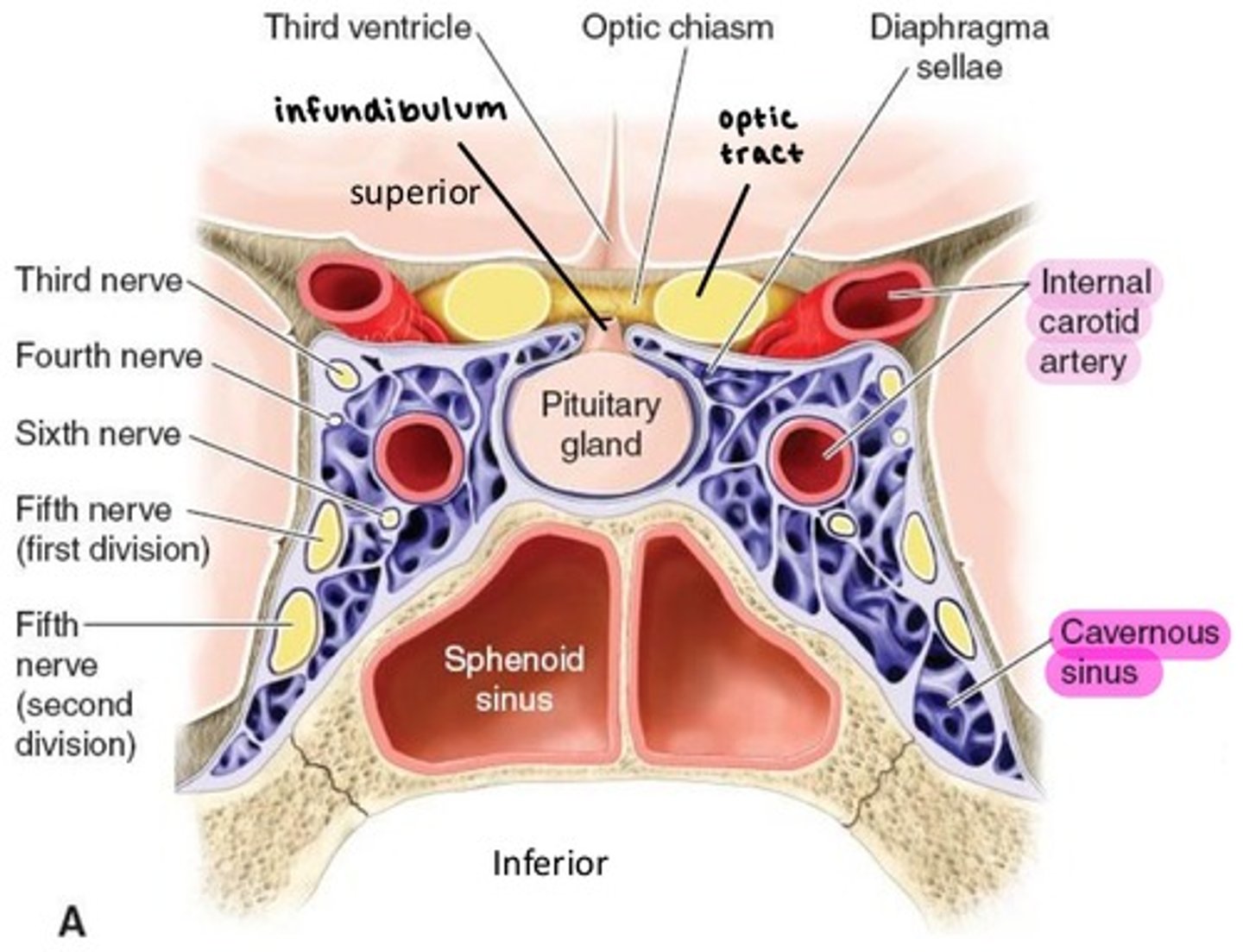
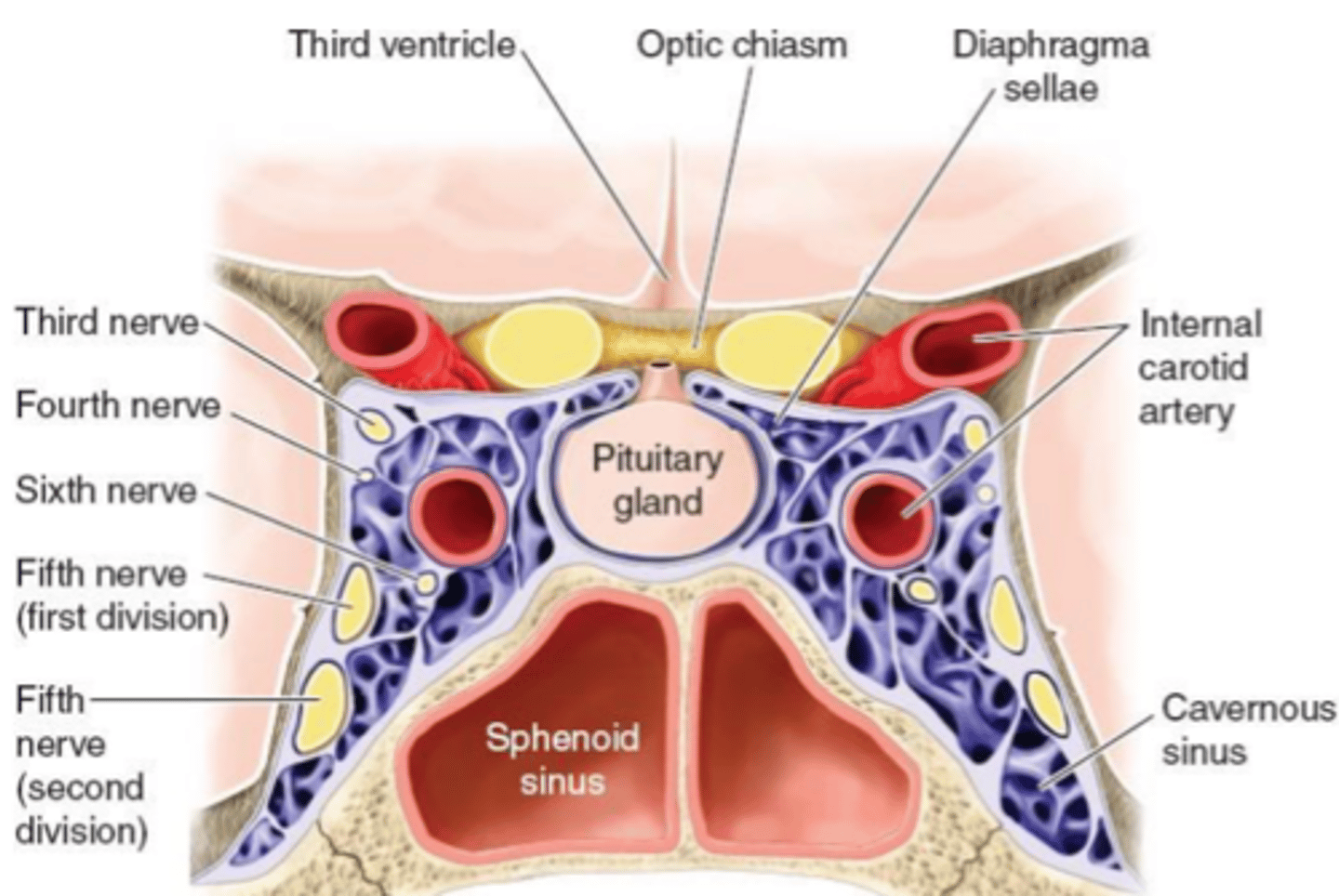
Cavernous sinus
Internal carotid artery enters the skull via Carotid canal, then enters the Cavernous sinus.
contains oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, ophthalmic, and maxillary nerves (3, 4, 6, V1, V2).
the Ophthalmic artery is the first branch of ICA as it leaves the Cavernous sinus.
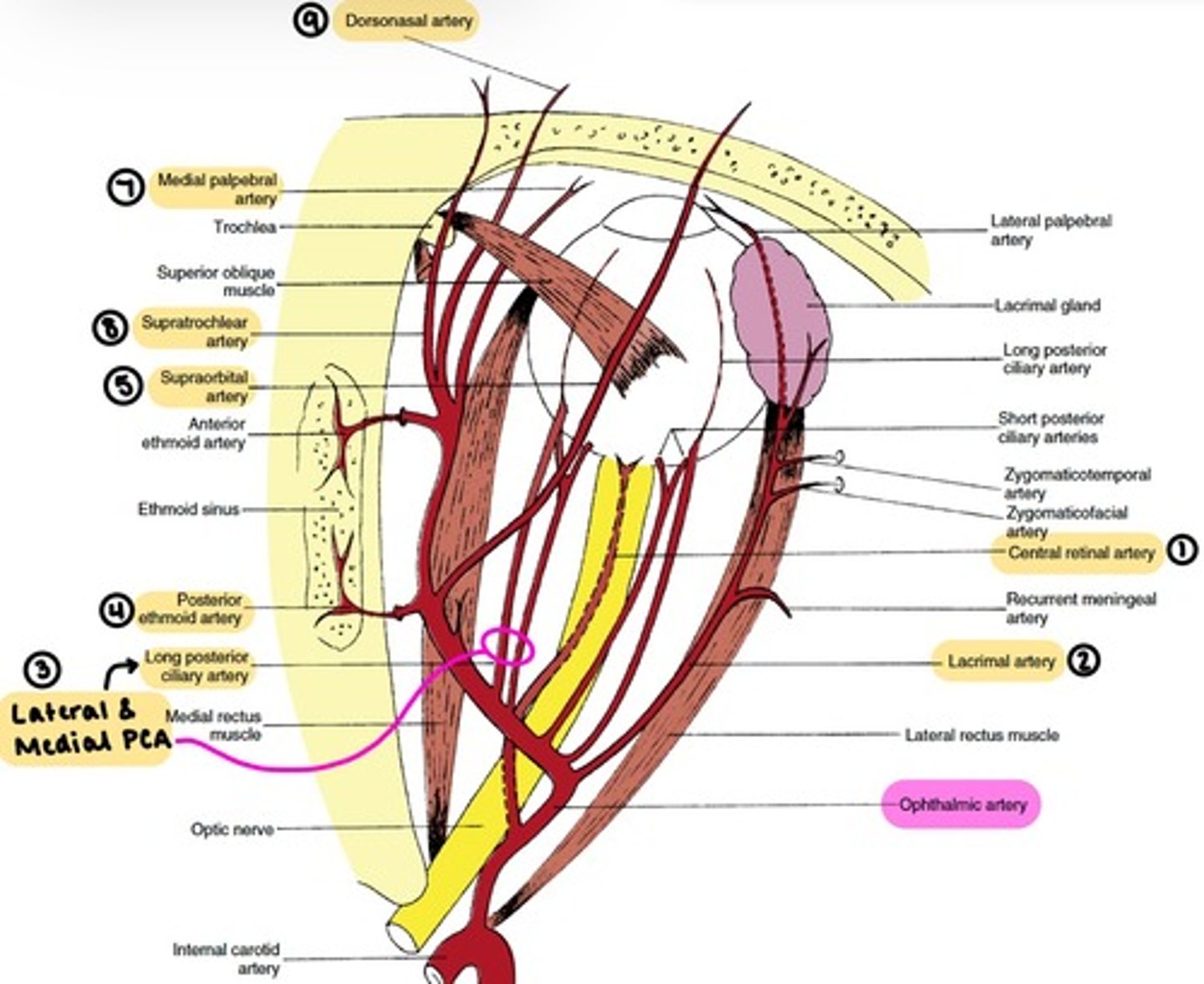
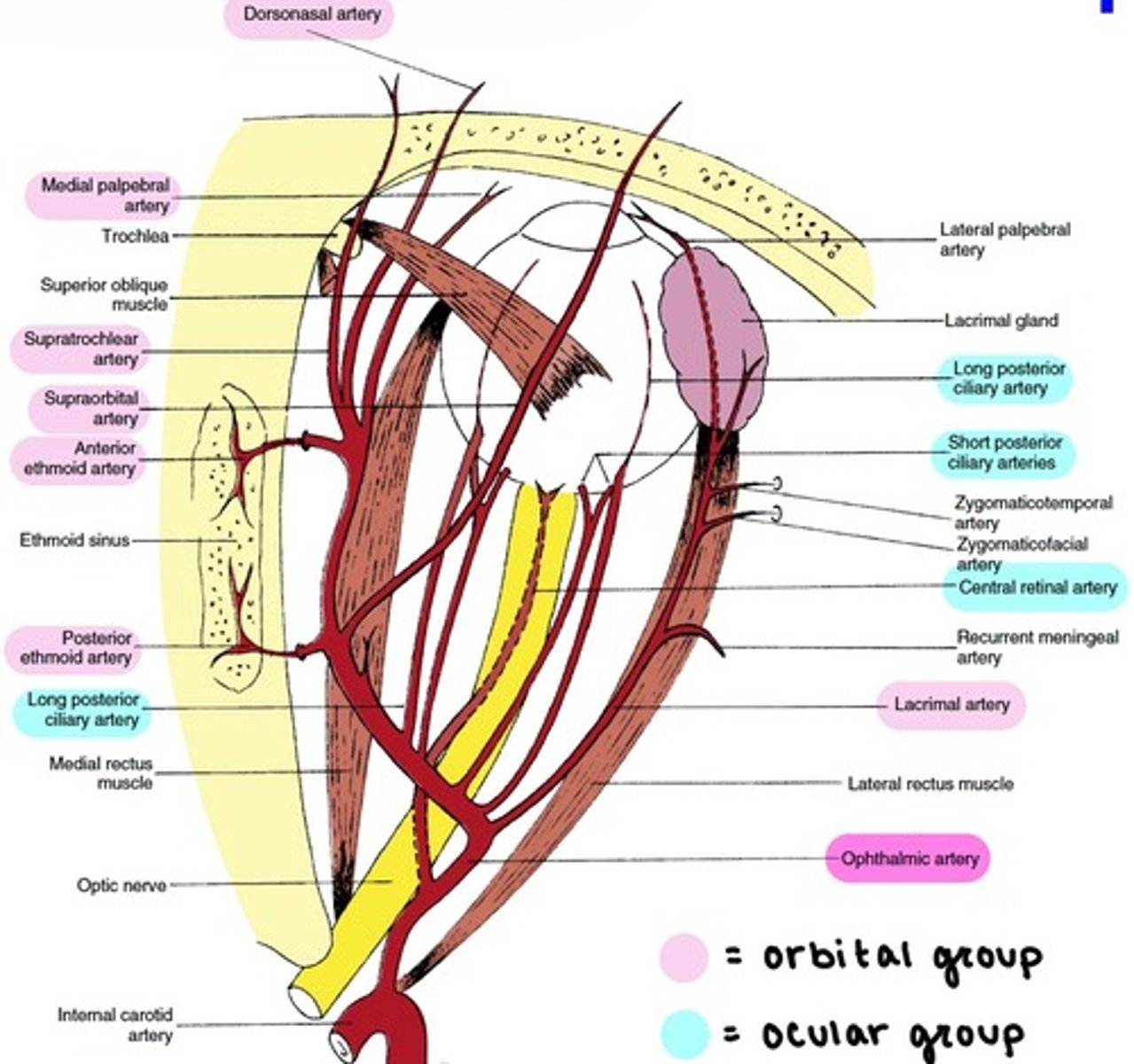
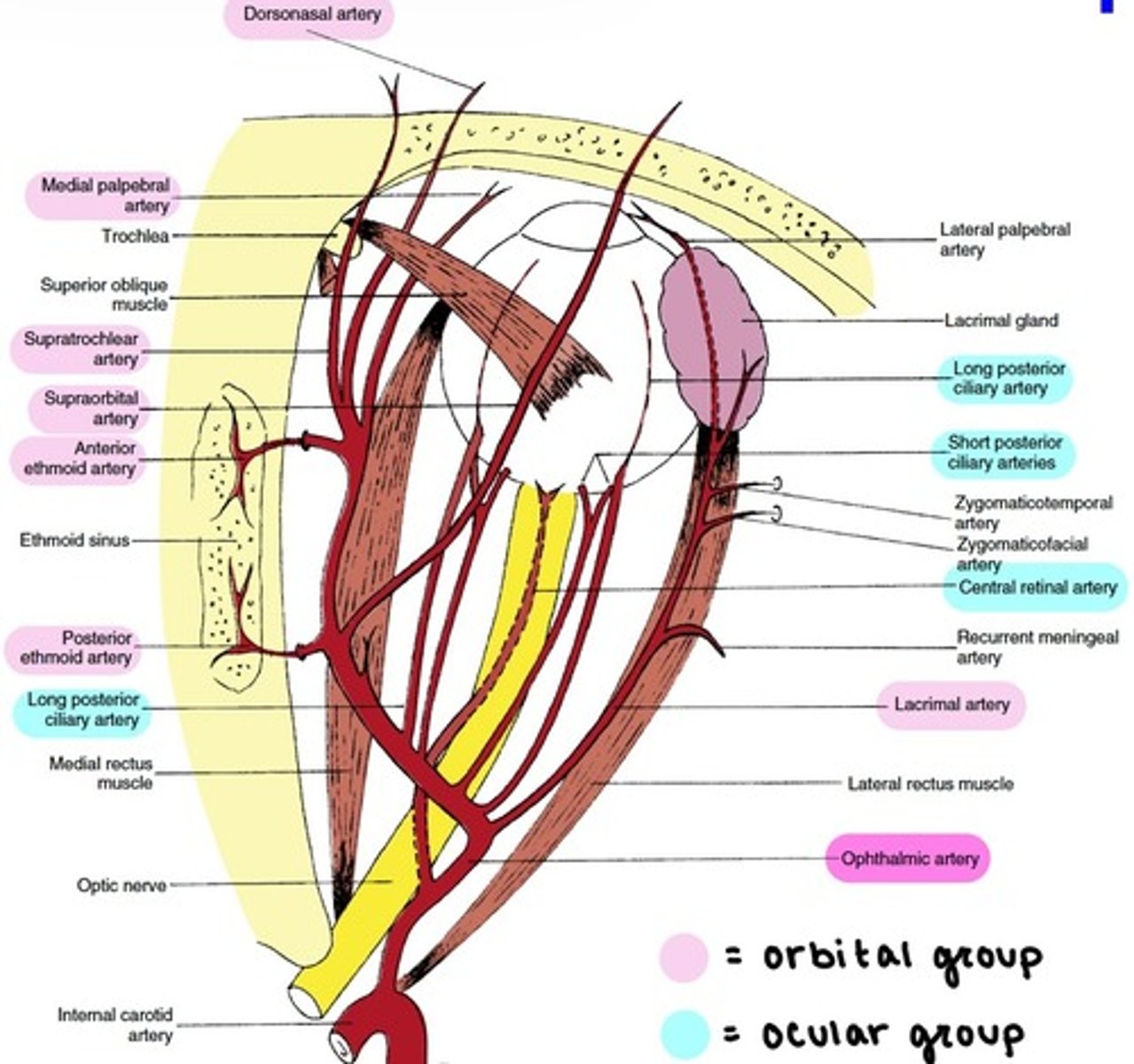
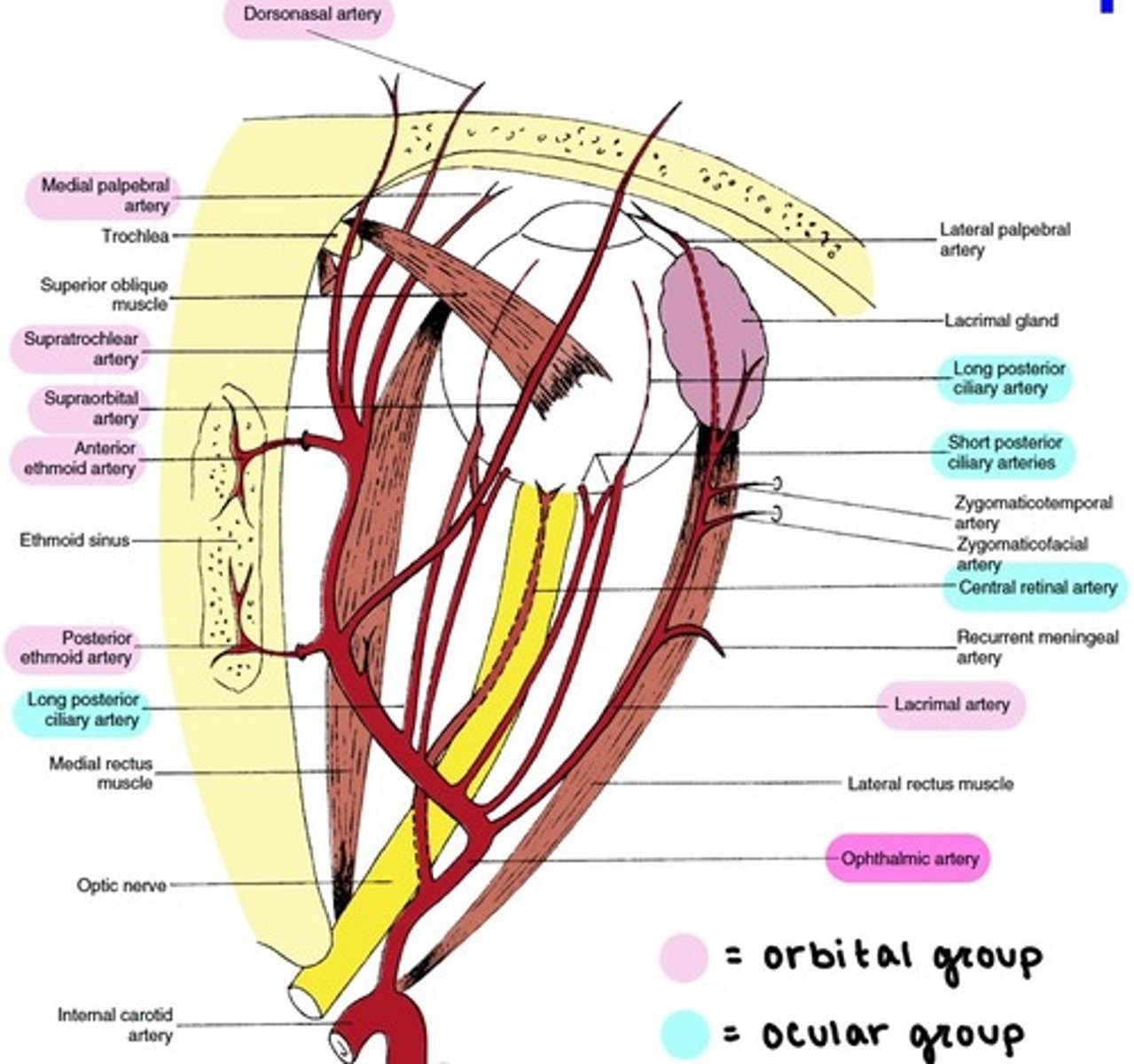
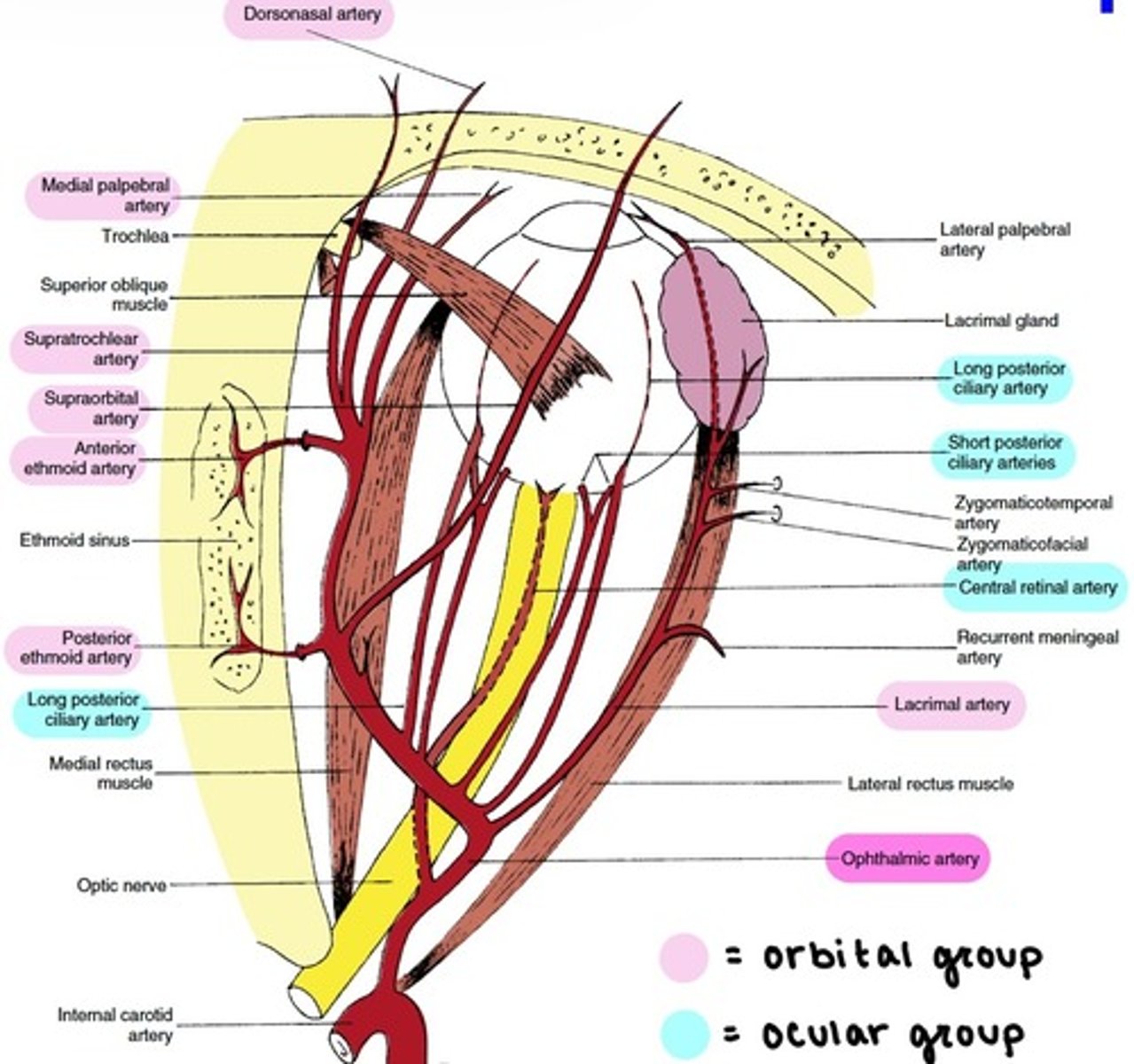
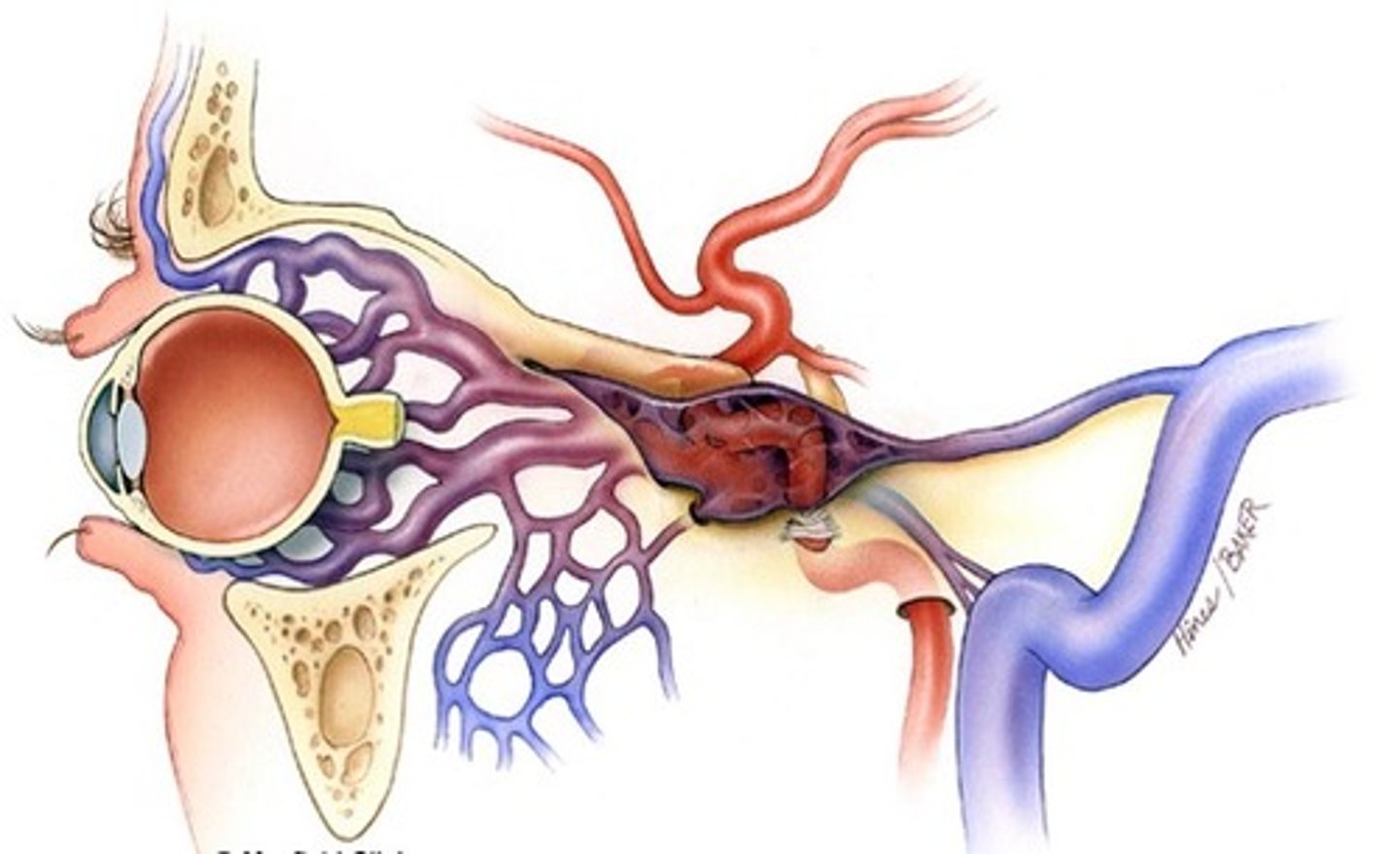
Ophthalmic artery
the main blood supply to the globe and ocular adnexa.
enters the orbit through the Optic foramen.
branches:
1. Central Retinal
2. Lacrimal
3. Lateral & Medial Posterior Ciliary (→Long & Short PCAs)
4. Ethmoidal
5. Supraorbital
6. Muscular (Lateral & Medial)
7. Medial Palpebral (Superior & Inferior)
8. Supratrochlear
9. Dorsonasal
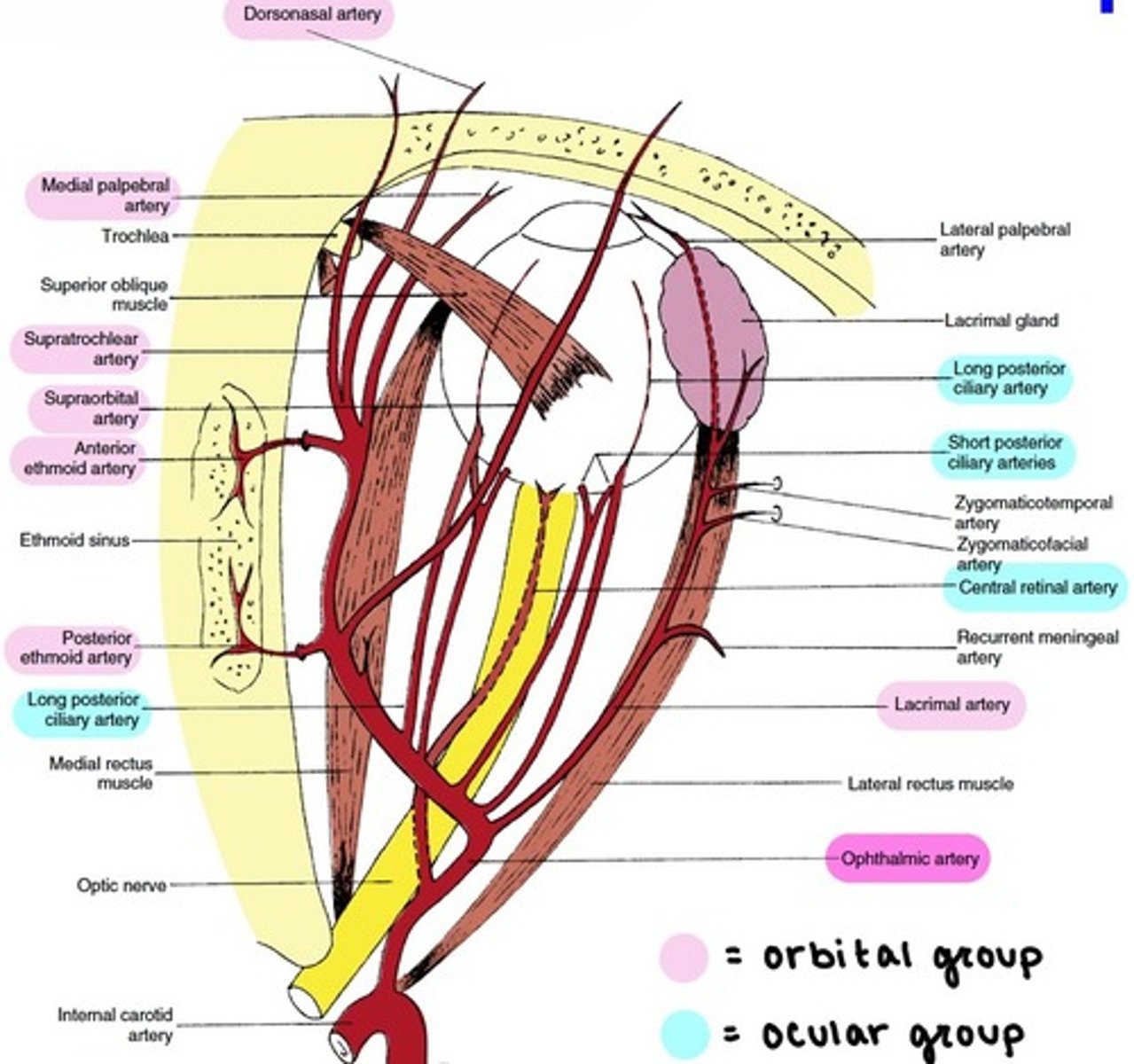
Branches of the Ophthalmic artery: Orbital group
distributed to the orbit and surrounding parts.
includes:
-Lacrimal
-Supraorbital
-Ethmoidal (Anterior & Posterior)
-Medial Palpebral
-Supratrochlear
-Dorsonasal
Lacrimal artery
runs along upper border of LR.
supplies the lacrimal gland.
terminates at lateral palpebral arteries.
Supraorbital artery
supplies SR, SO and levator.
supplies skin & muscles of the scalp.
Ethmoidal (Anterior & Posterior) arteries
supplies ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid sinuses.
supplies the nasal cavity & skin of the nose.
Medial Palpebral artery
branches into palpebral arcades.
supplies superior & inferior eyelids.
Supratrochlear artery
supplies the forehead.
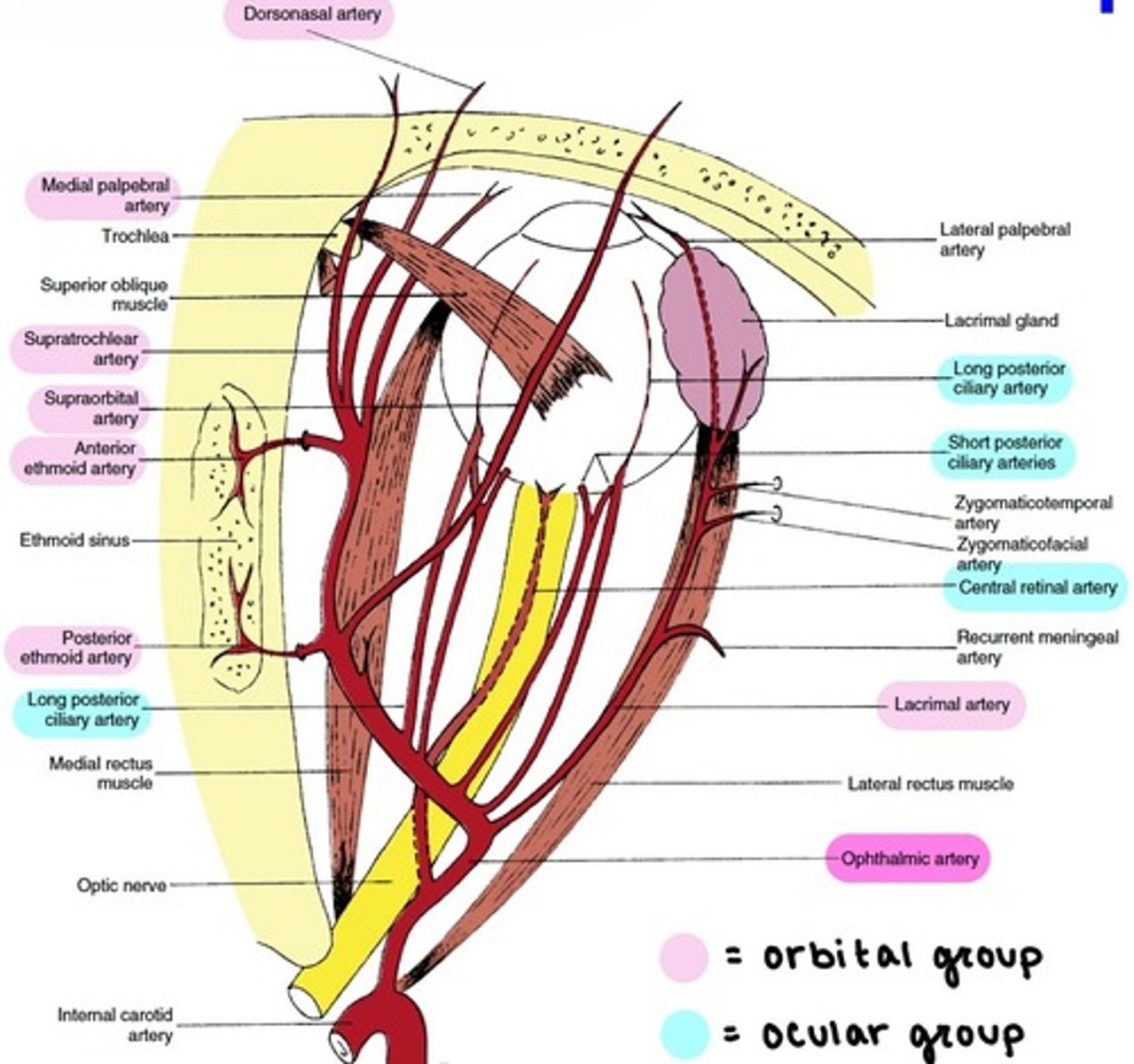
Dorsonasal artery
supplies the lacrimal sac.
supplies the outer nose.
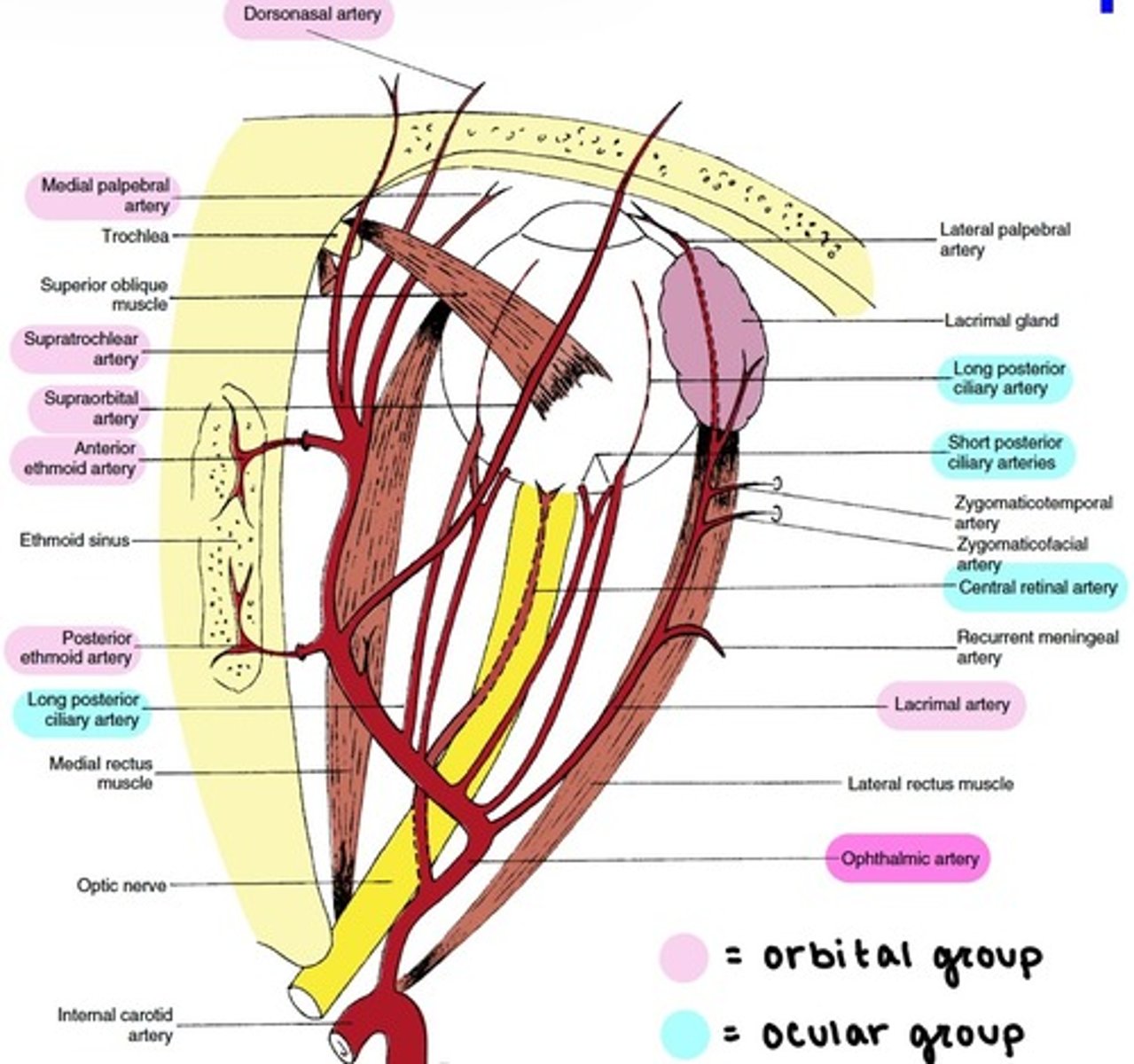
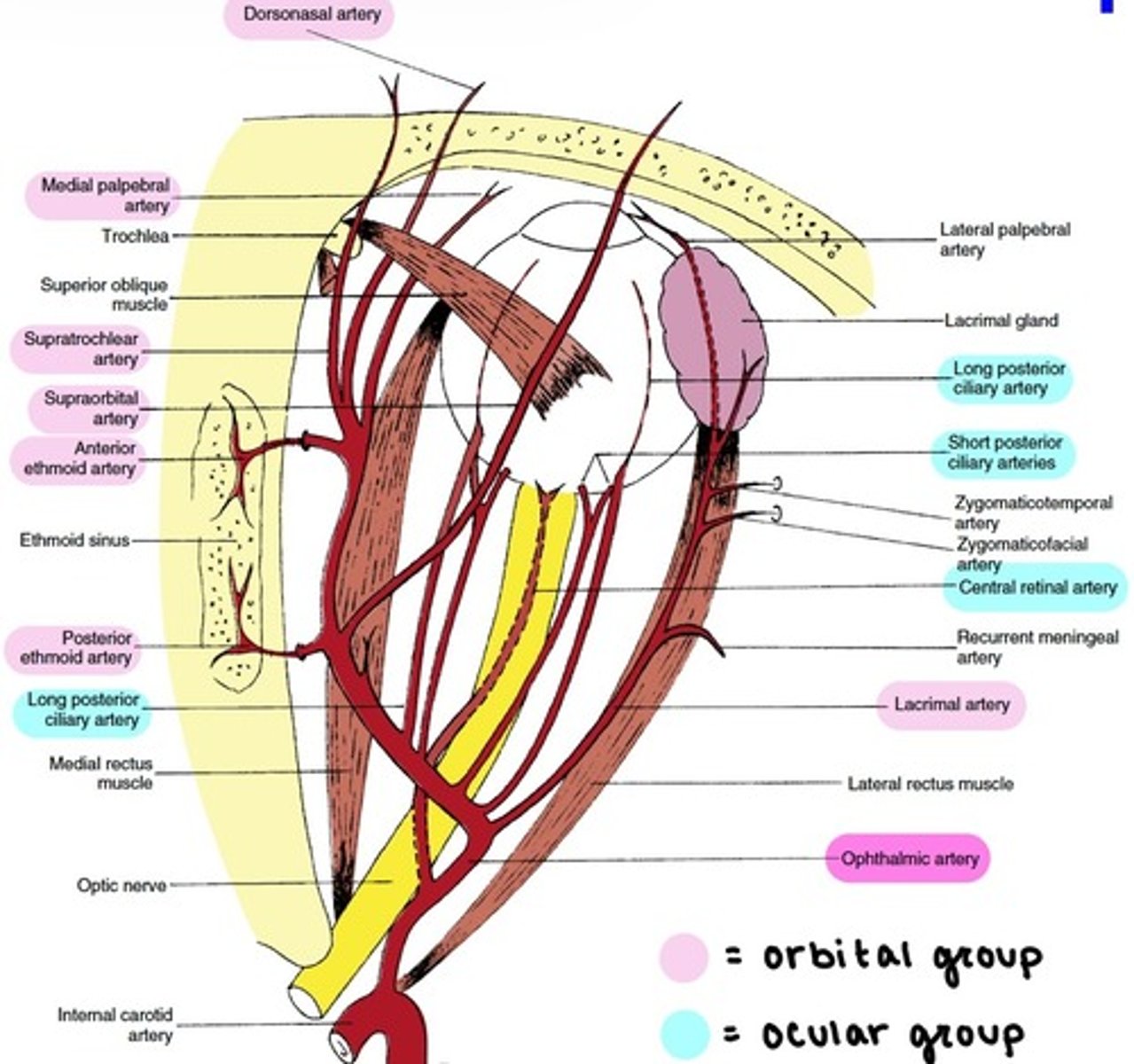
Branches of the Ophthalmic artery: Ocular Group
distributed to the muscles and bulb of the eye.
includes:
-Central Retinal
-Muscular
-Anterior Ciliary
-Long & Short PCAs
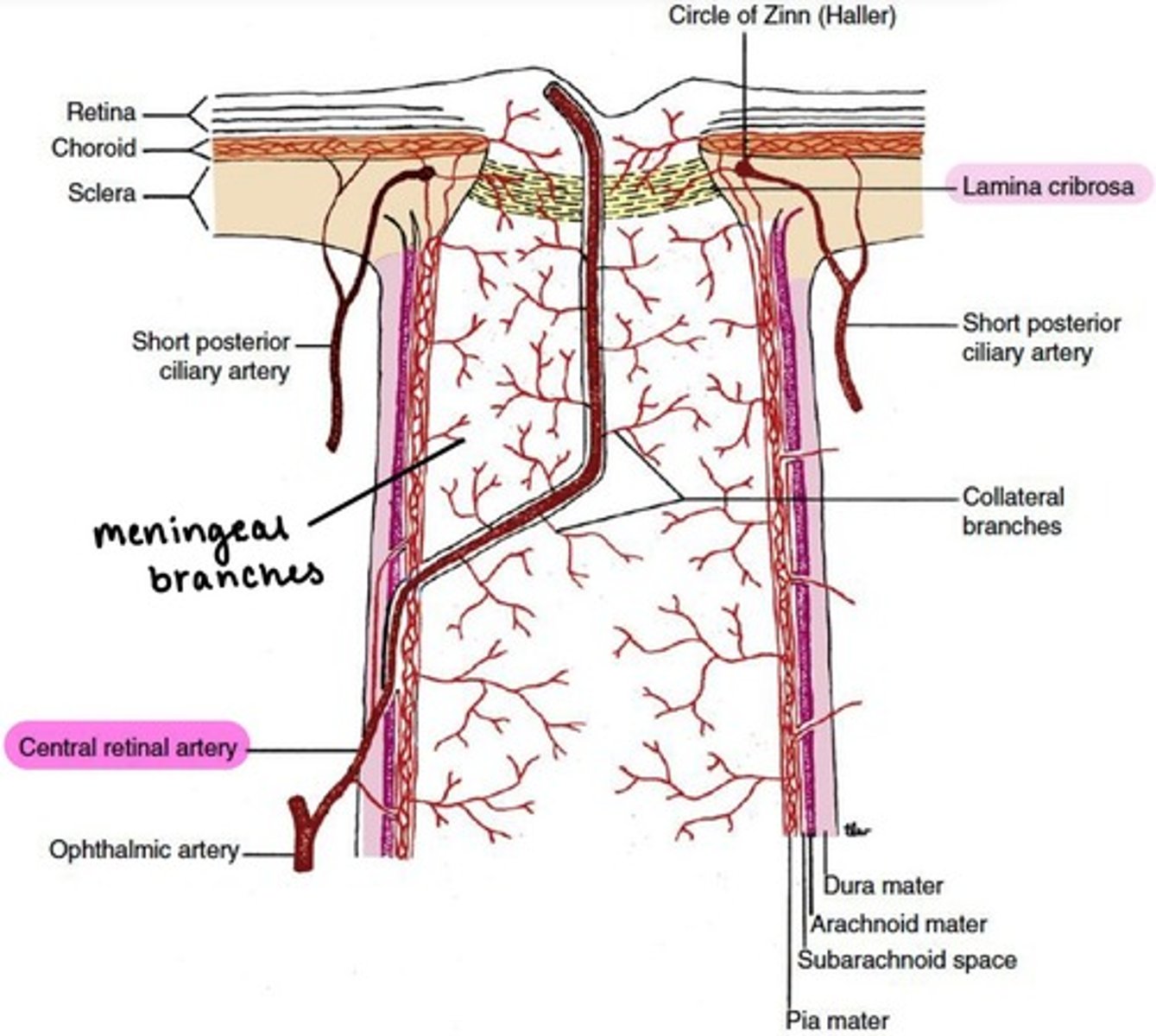
Central Retinal artery
pierces sheath and enters the optic disc on the nasal side.
branches into superior, inferior, nasal, & temporal.
gives off meningeal branches to supply the pia mater of the optic nerve.
Medial and Lateral PCAs (MPCAs & LPCAs)
the major blood supply to the globe.
branches into Long & Short PCAs
→ can have variable branching
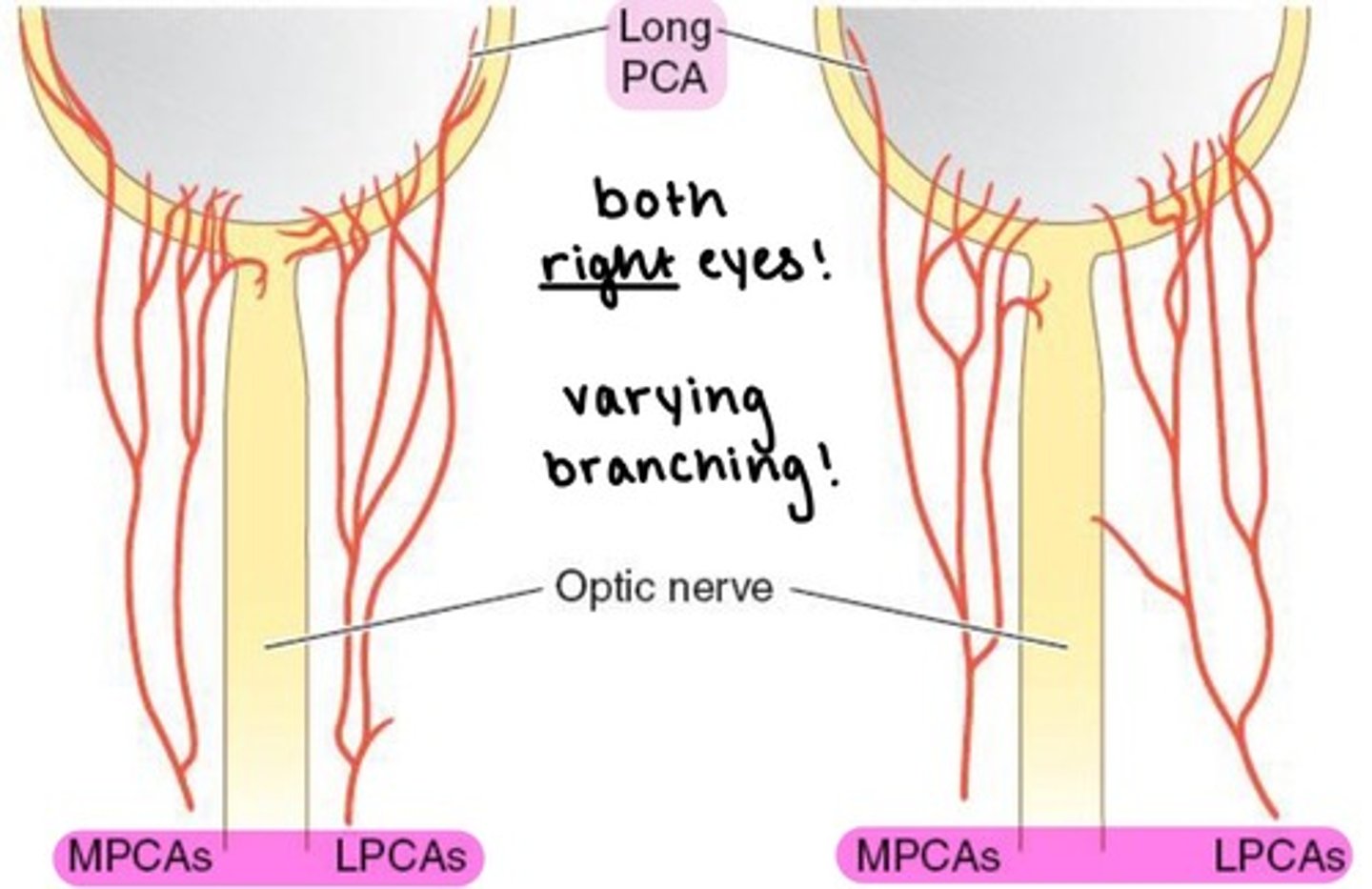
Long PCAs
paired (2) arteries that pierce the sclera and travel within the suprachoroidal space to the ciliary body.
supplies the choroid anterior to the equator.
combine with ACAs to form MACI
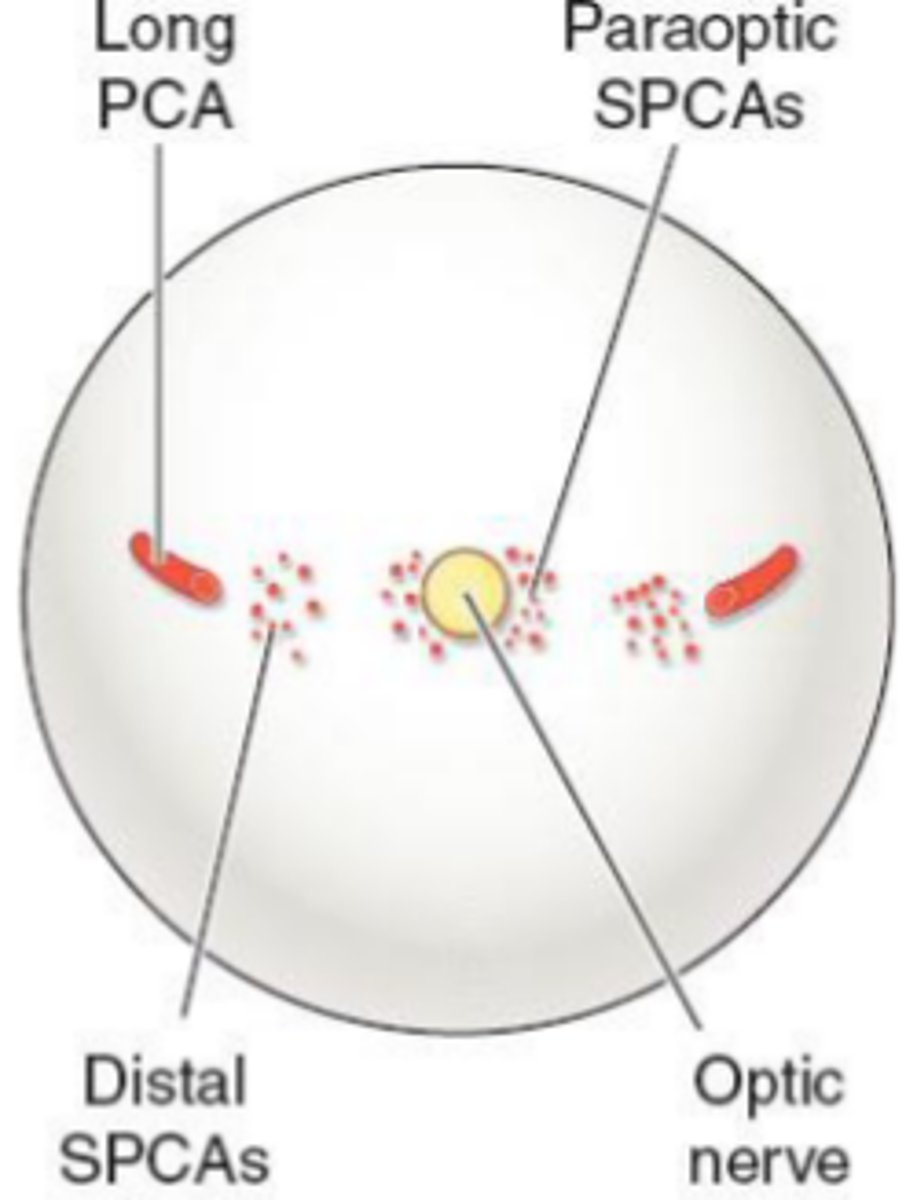
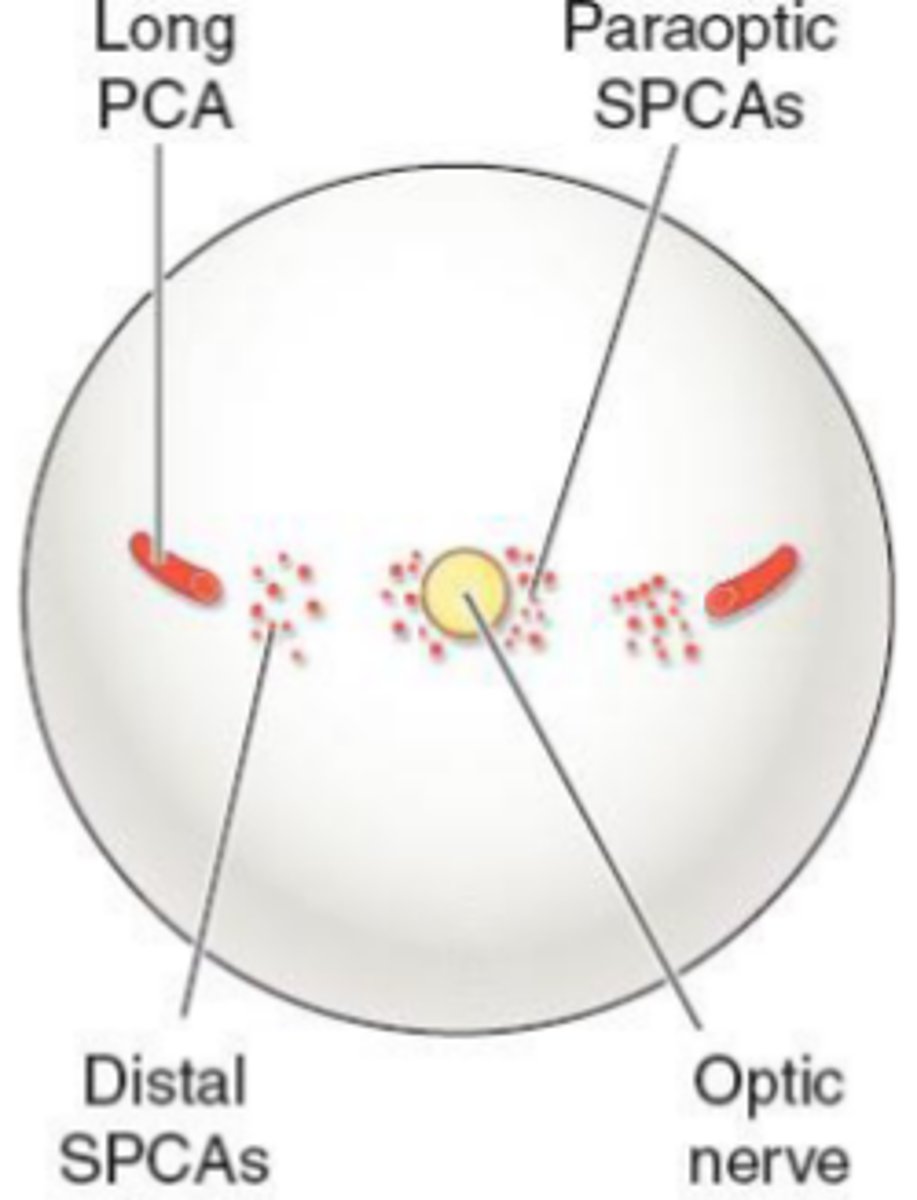
Short PCAs (SPCAs)
10-20 branches pierce the sclera around the optic nerve.
→ forms the circle of Zinn
supplies the optic nerve head
supplies the choroid posterior to the equator.
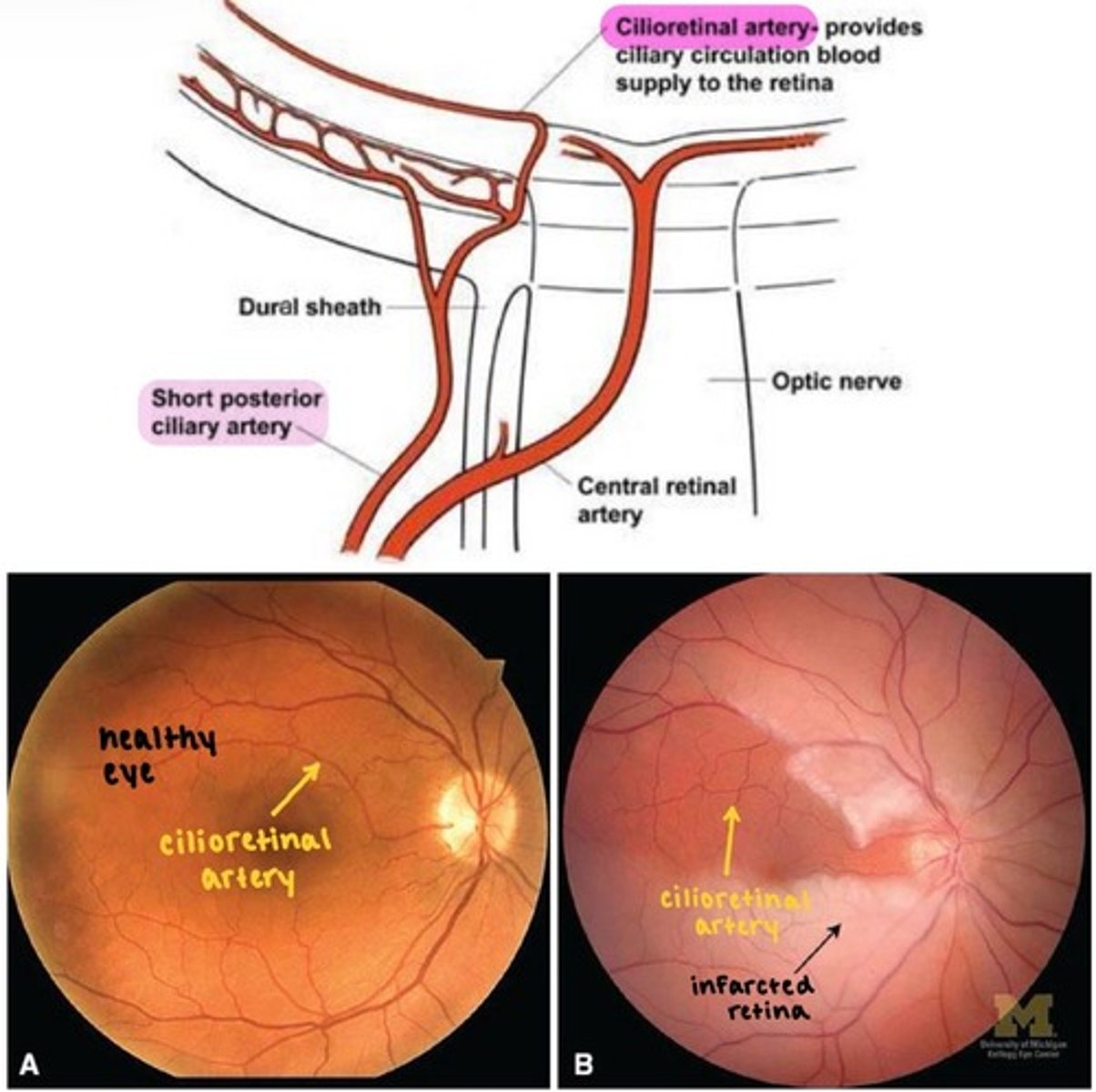
Cilioretinal artery
comes out of the temporal aspect of the optic nerve head and supplies the macula.
branches from short PCAs (not from CRA)
advantageous in cases of CRA occlusion
→ if there is CRAO, some blood flow to the macula is preserved via cilioretinal arteries.
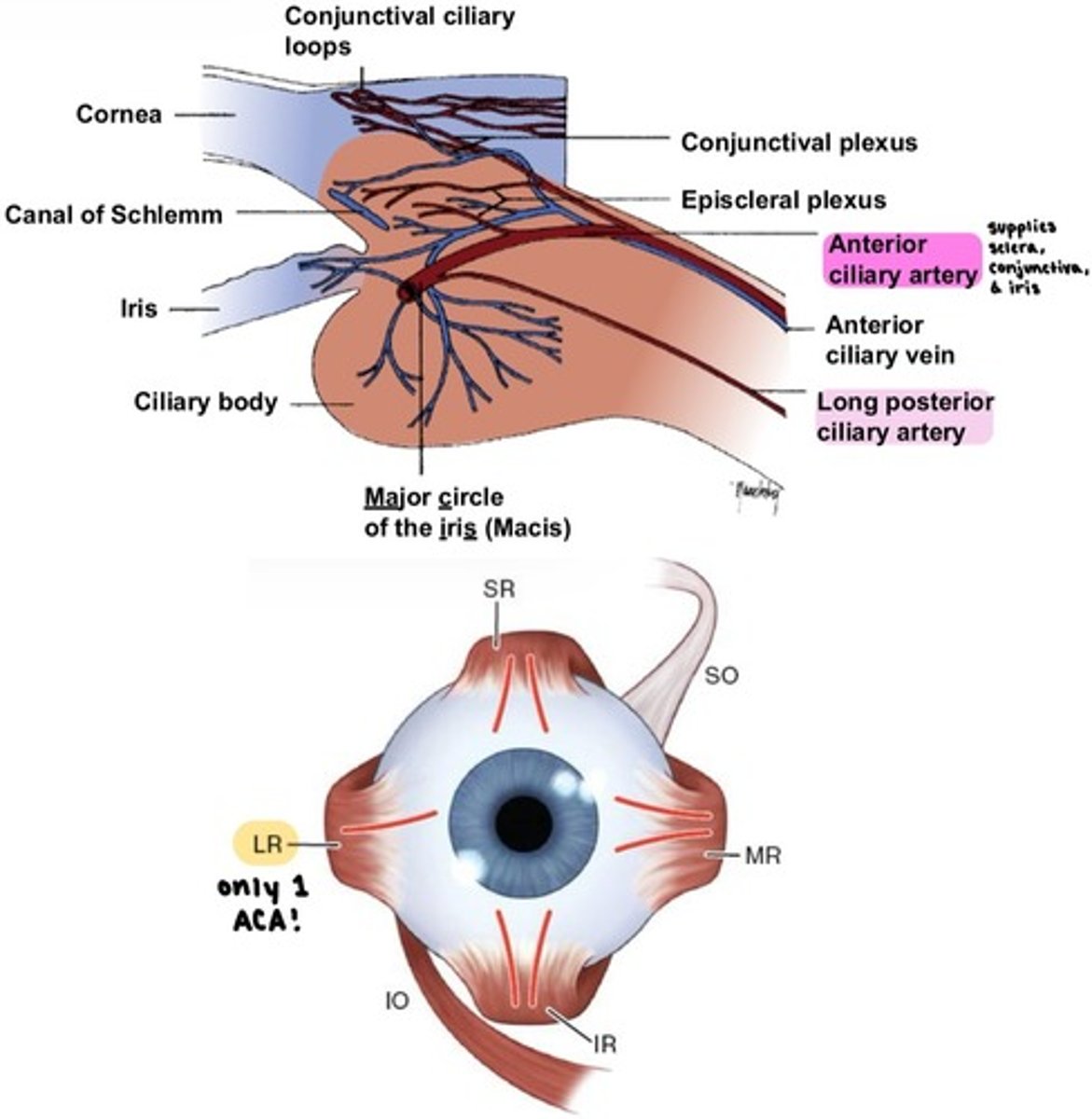
Anterior ciliary artery (ACA)
from the EOMs.
two ACAs for each rectus muscle
→ except LR muscle only has 1!
→ 7 ACAs total per eye
supplies the sclera, conjunctiva, and iris.
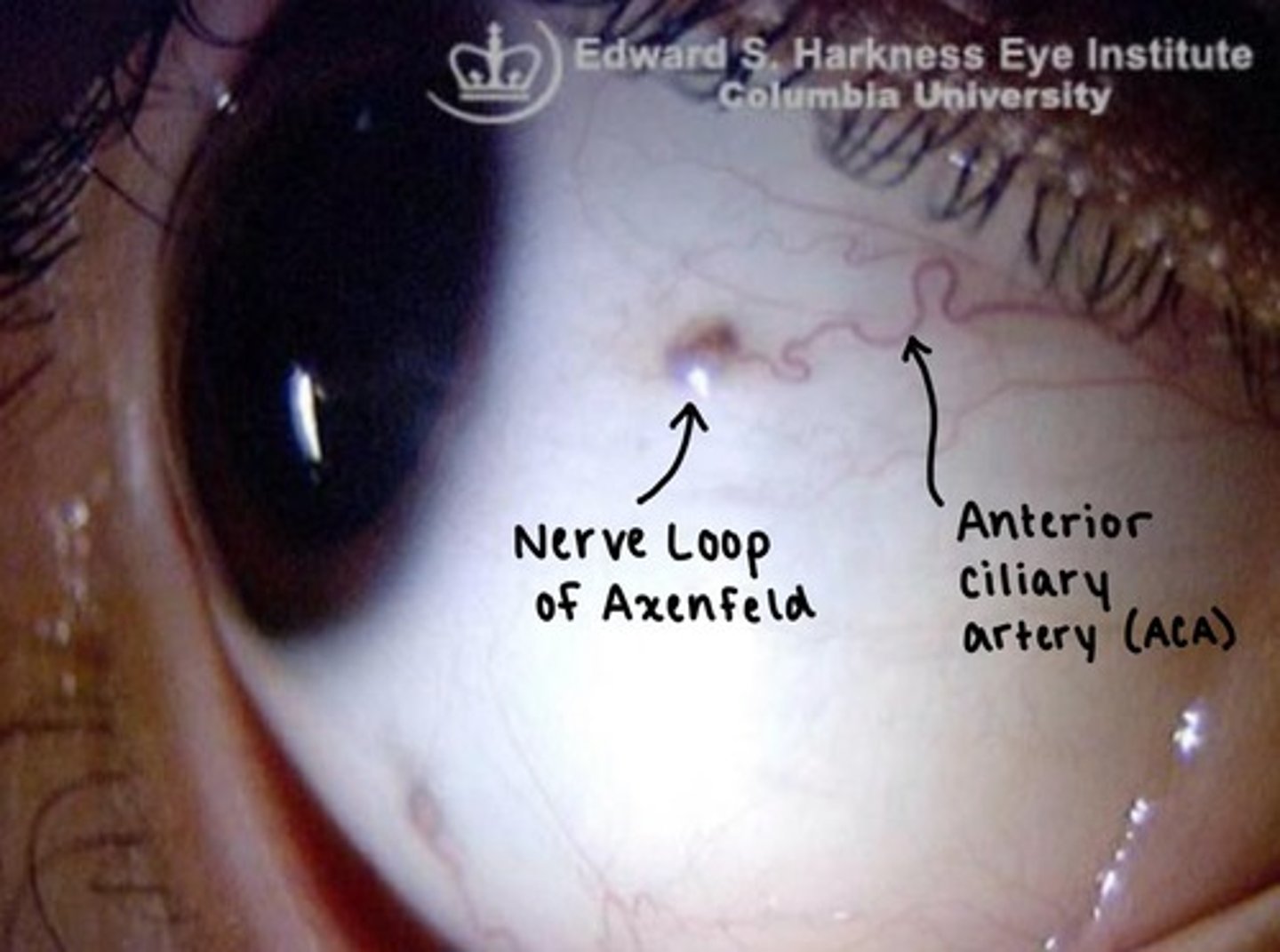
Nerve Loop of Axenfeld
a branch of the Long ciliary nerves reaches the surface of the sclera, forming a visible nodule.
the Anterior ciliary artery can be seen near the nerve loop.
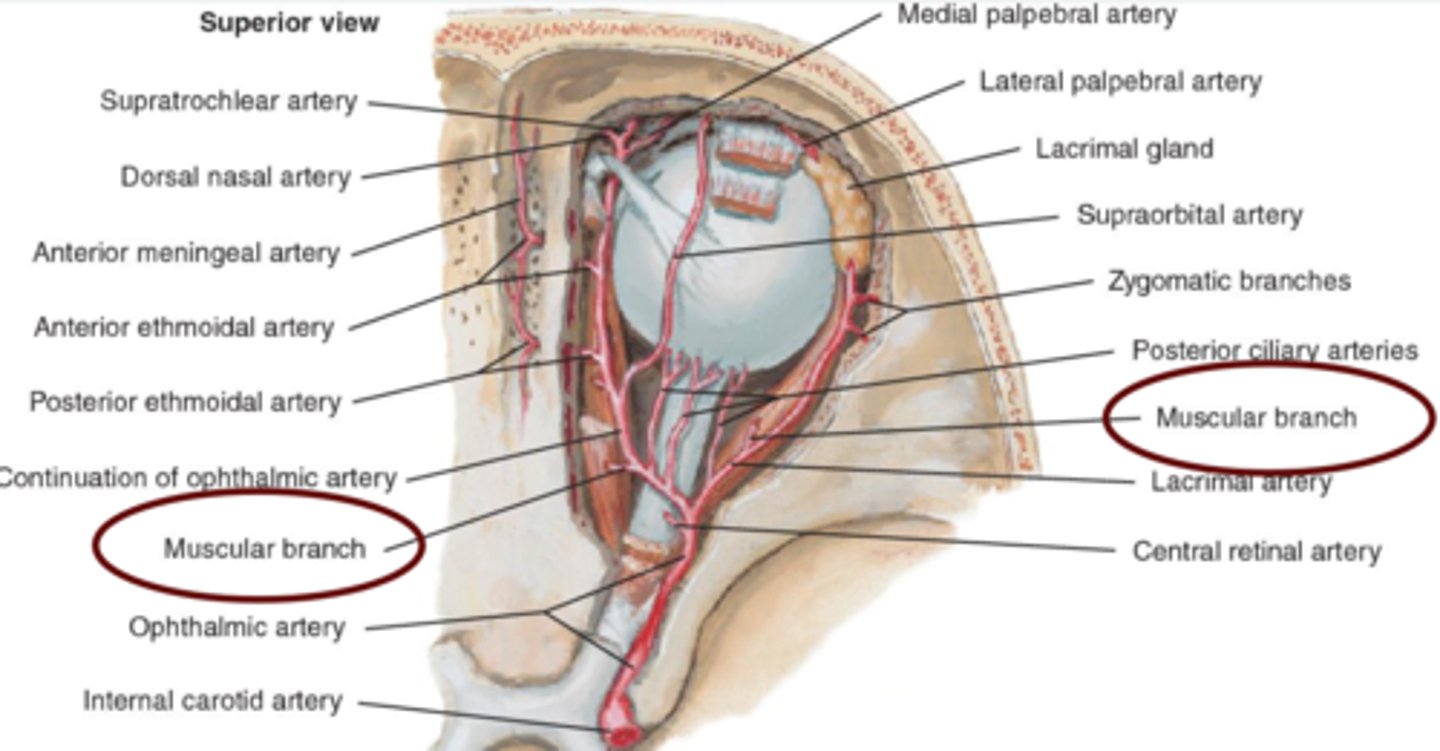
Muscular artery (Lateral)
superior artery.
supplies LR, SR, SO, and Levator muscles.
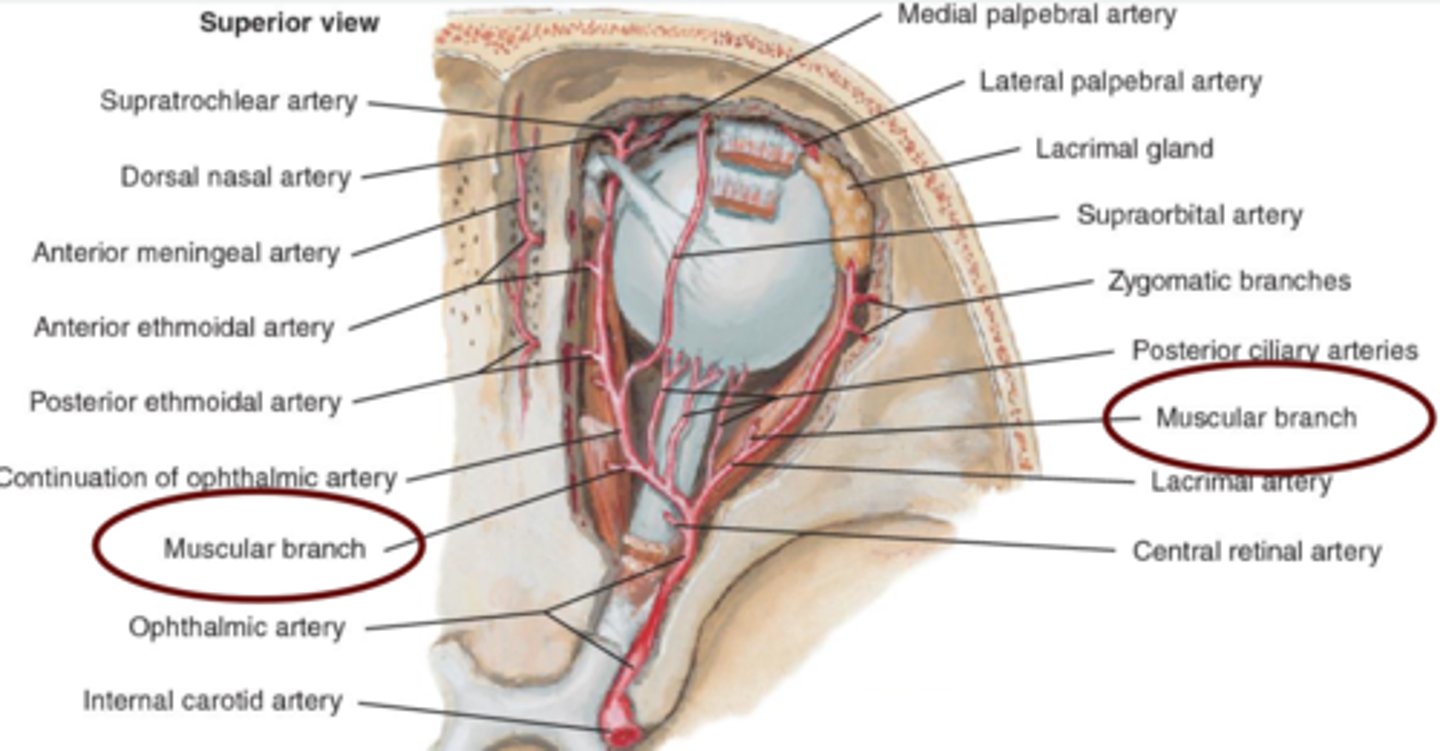
Muscular artery (Medial)
inferior artery.
supplies MR, IR, and IO muscles.
which EOM is the only one to receive blood supply ONLY from the Muscular artery?
Medial rectus
Medial rectus blood supply
Medial muscular artery ONLY
2 ACAs
Lateral rectus blood supply
Lateral muscular artery
Lacrimal artery
1 ACA
Inferior rectus blood supply
Medial muscular artery
Infraorbital artery
2 ACAs
Superior rectus blood supply
Lateral muscular artery
Supraorbital artery
2 ACAs
Inferior oblique blood supply
Medial muscular artery
Infraorbital artery
Superior oblique blood supply
Lateral muscular artery
Supraorbital artery
Supratrochlear artery
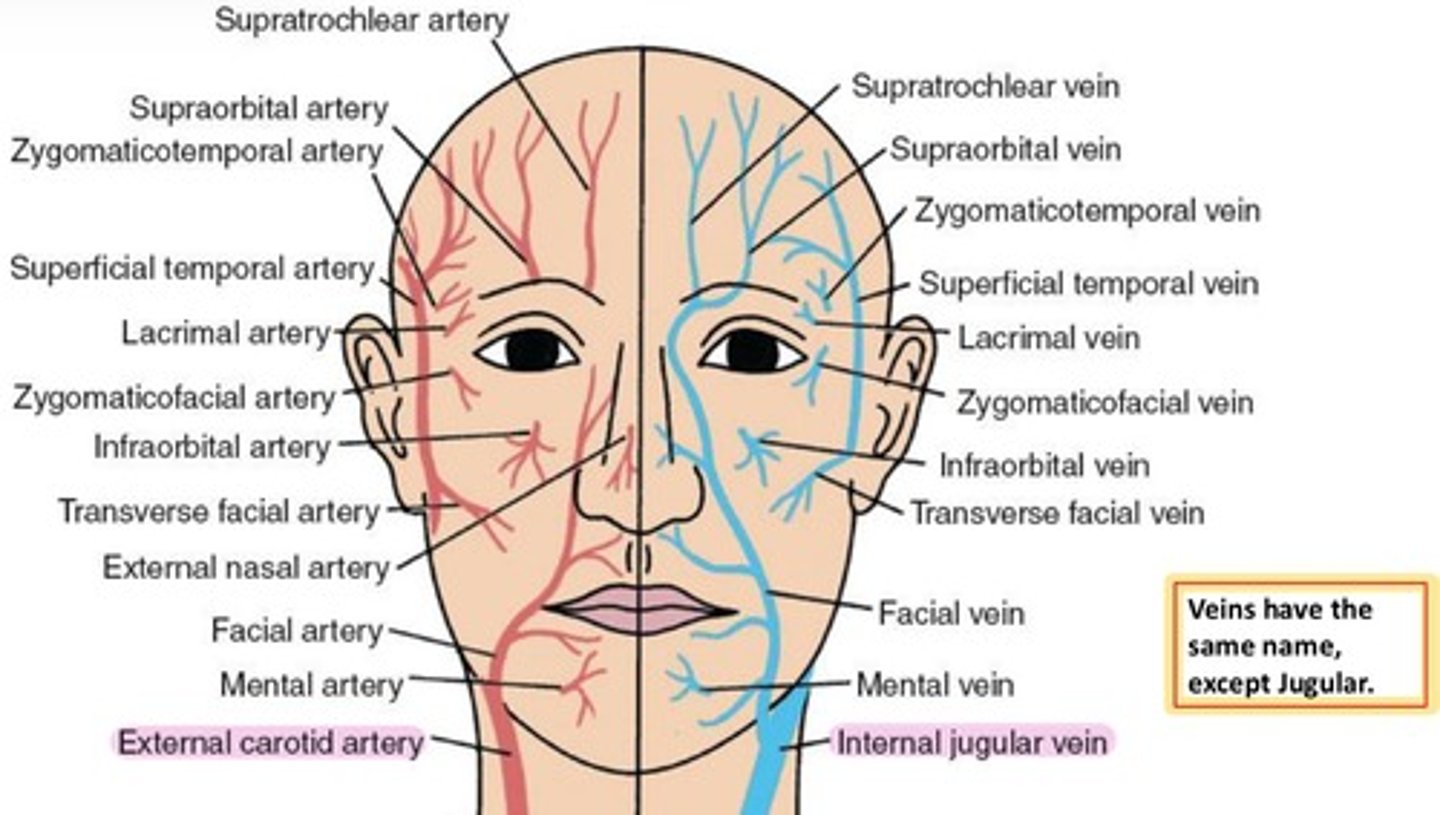
External carotid artery
supplies the ocular adnexa.
branches from the Common carotid artery.
branches into:
-Facial artery
-Superficial Temporal
-Maxillary artery
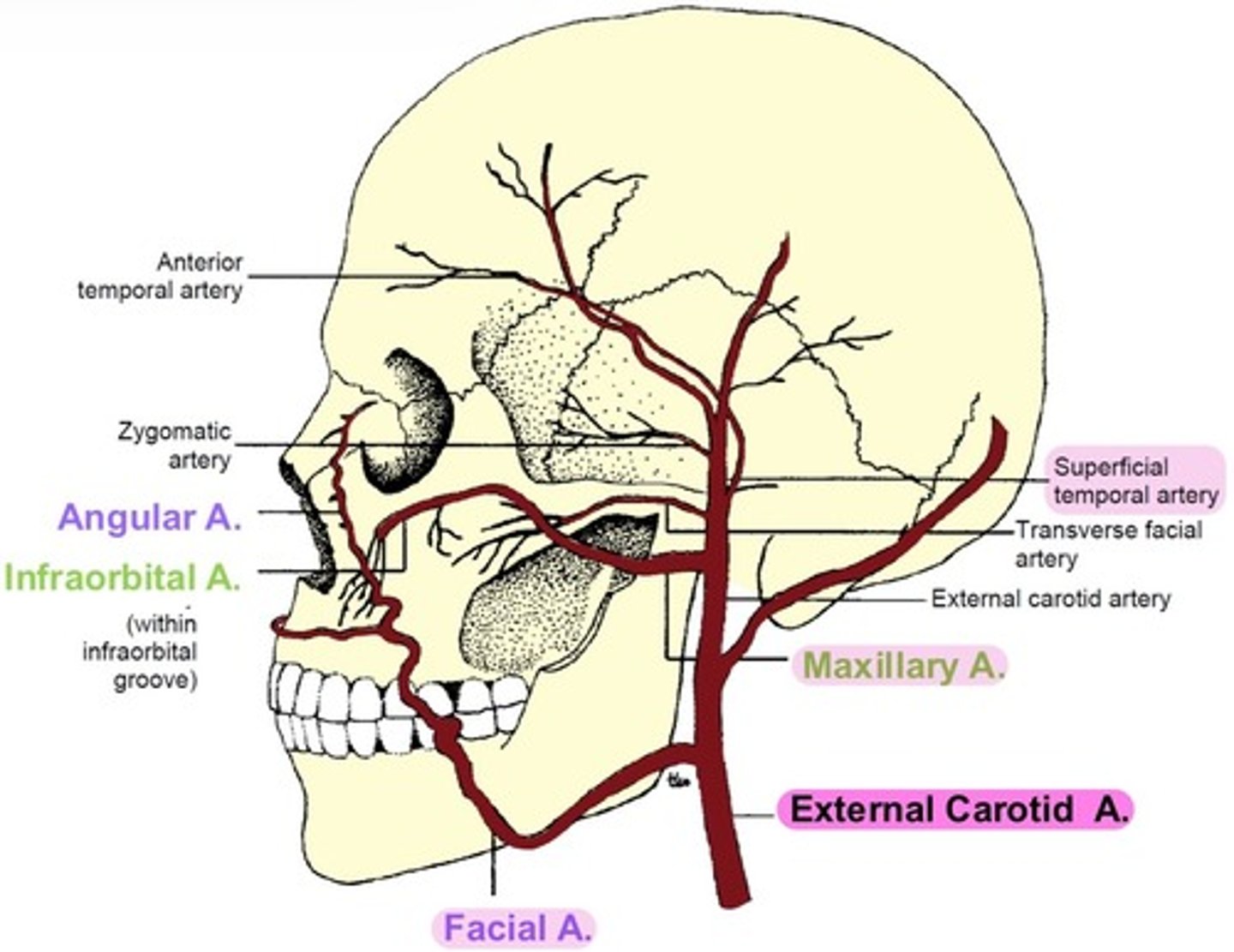
Facial artery
branches into Angular artery.
supplies the nose.
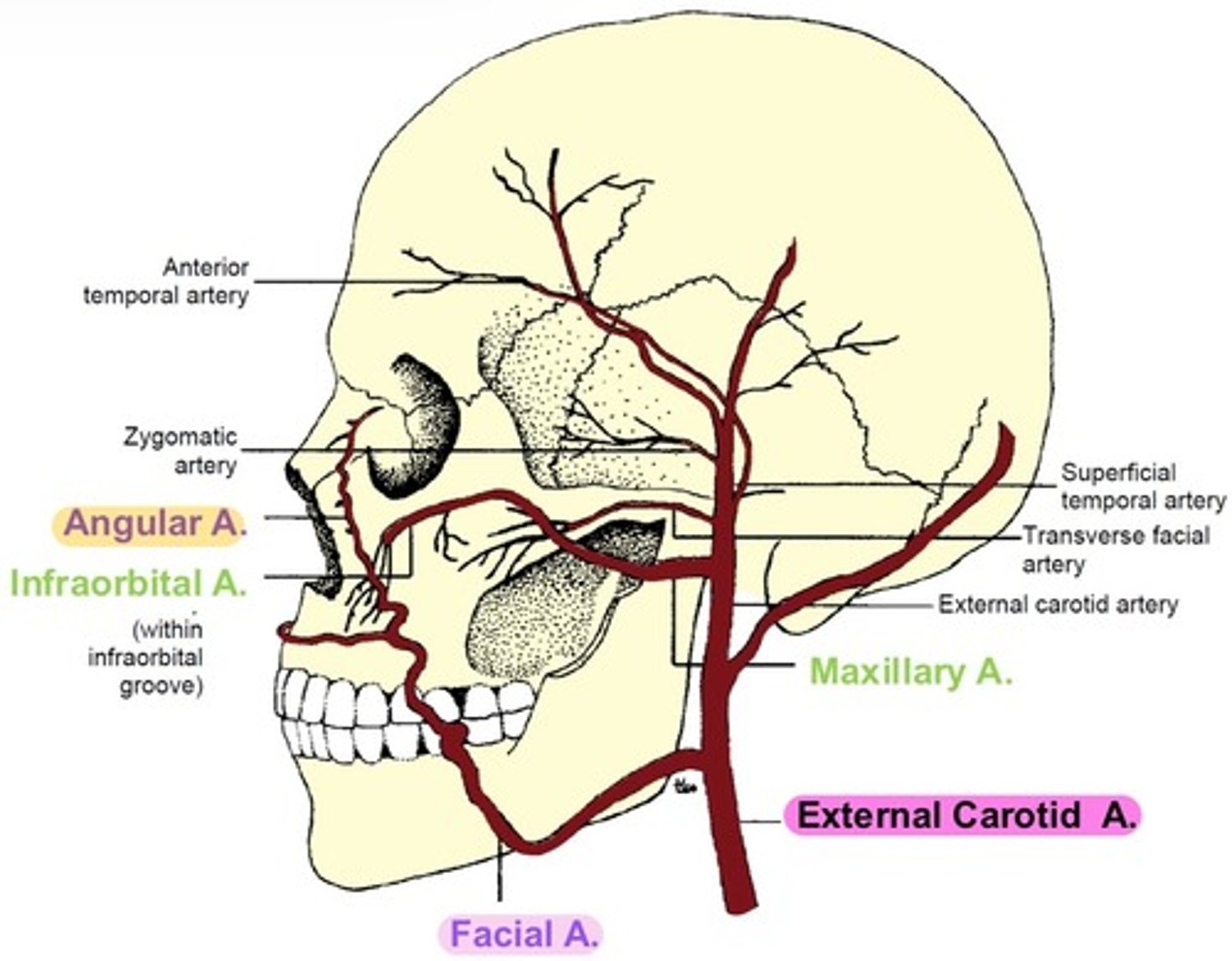
Superficial Temporal artery
branches into Anterior Temporal anastomoses.
→ contains Supraorbital & Supratrochlear arteries
branches into Zygomatic & Transverse Facial arteries
→ supplies orbicularis.
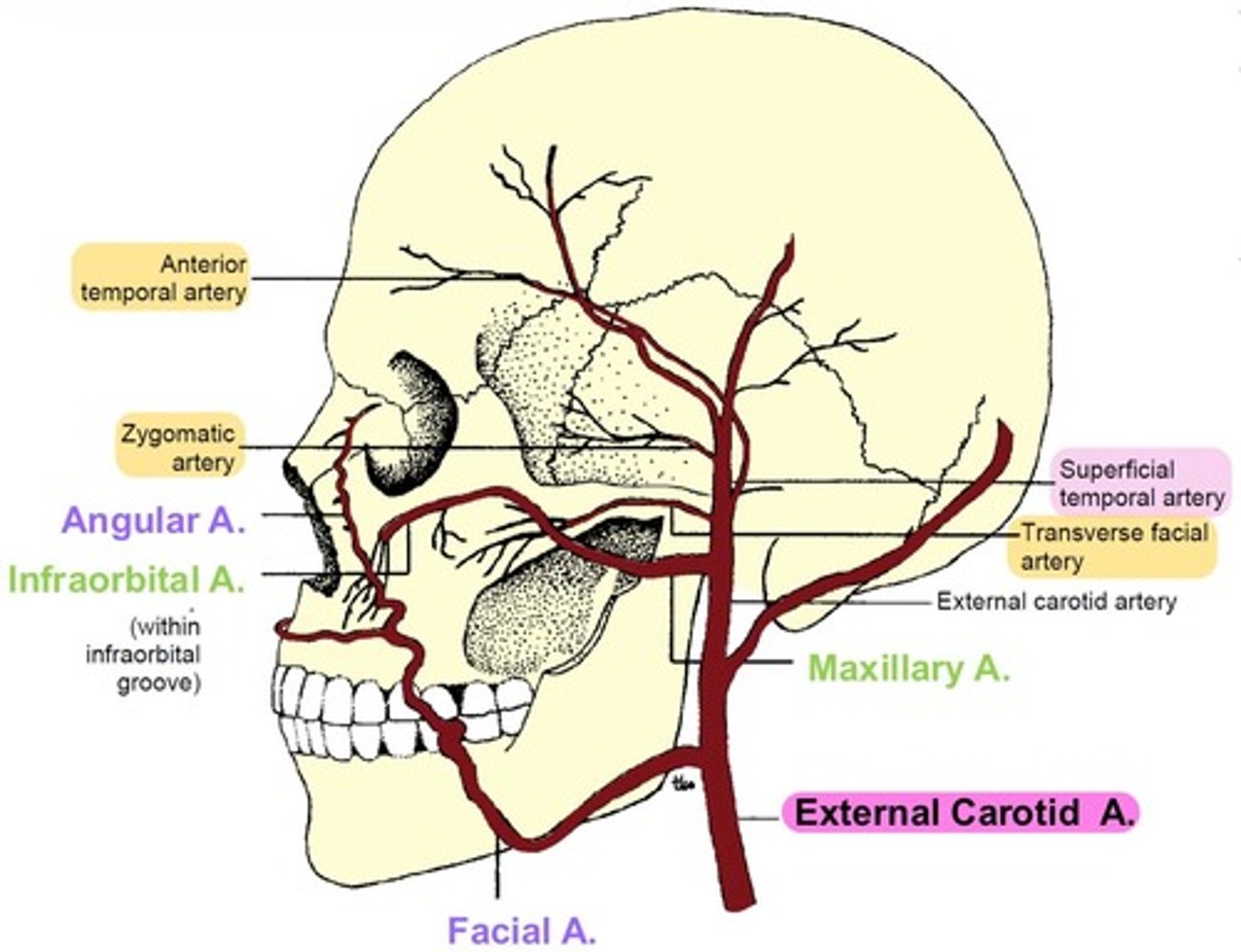
Maxillary artery
branches into Infraorbital artery.
→ Infraorbital groove → Infraorbital foramen → supplies IR, IO, and lacrimal sac
veins have the same name as their paired arteries, except for...?
External Carotid artery & Internal Jugular vein
how does venous blood leave the eye?
via four pathways:
-Central Retinal Vein
-Vortex veins
-Anterior Ciliary veins
-Episcleral veins
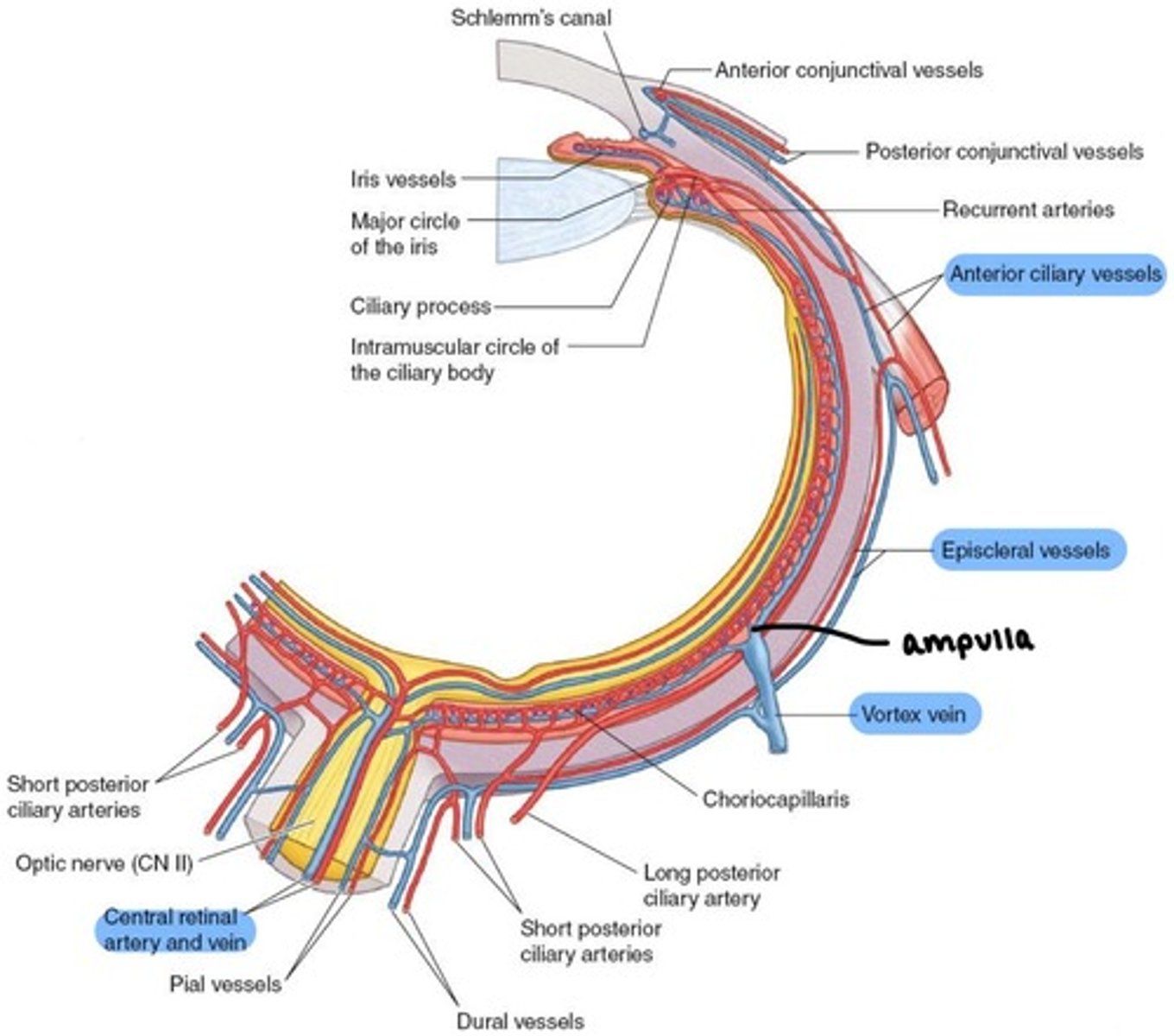
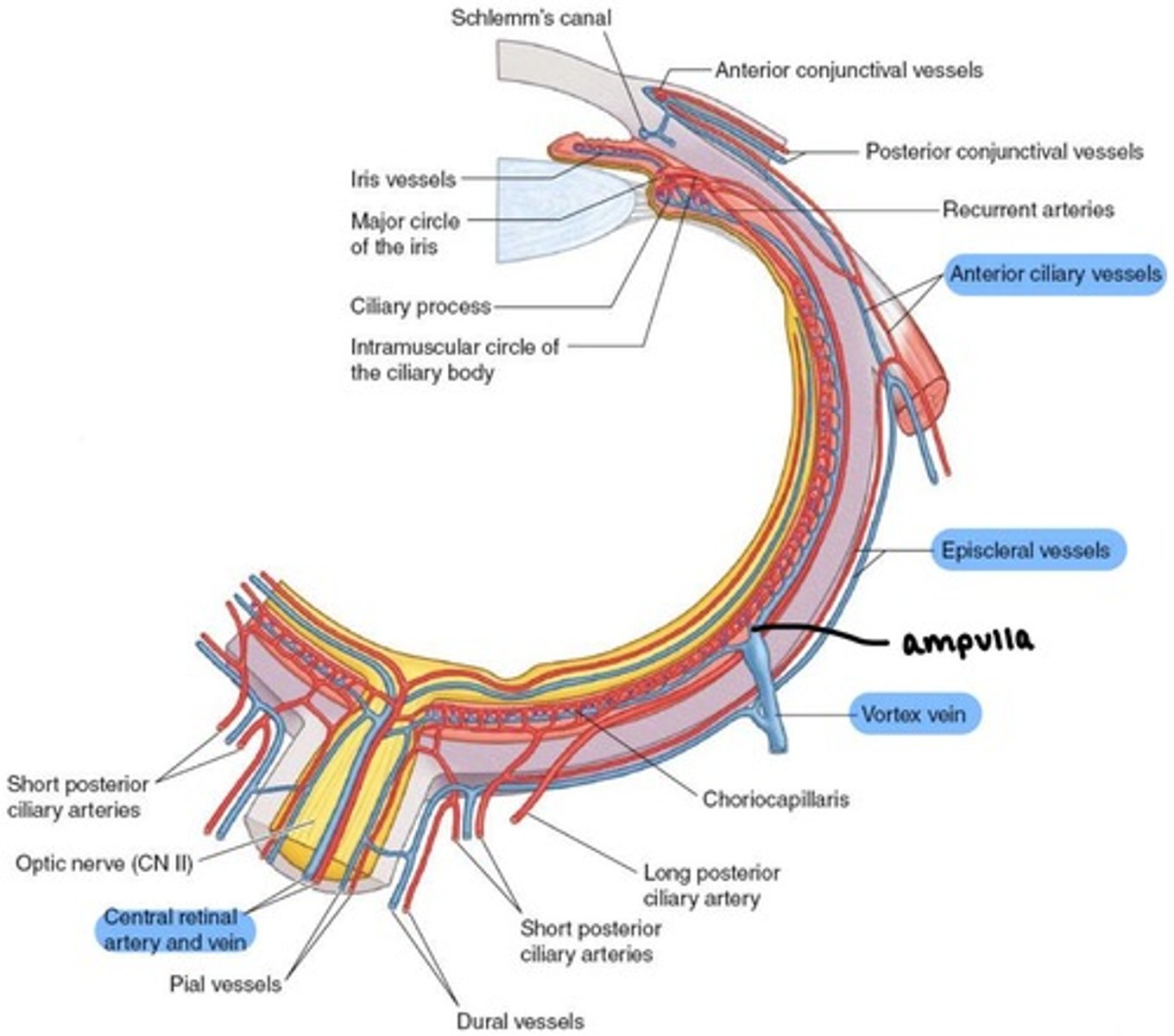
what does the Central Retinal vein drain?
inner retina
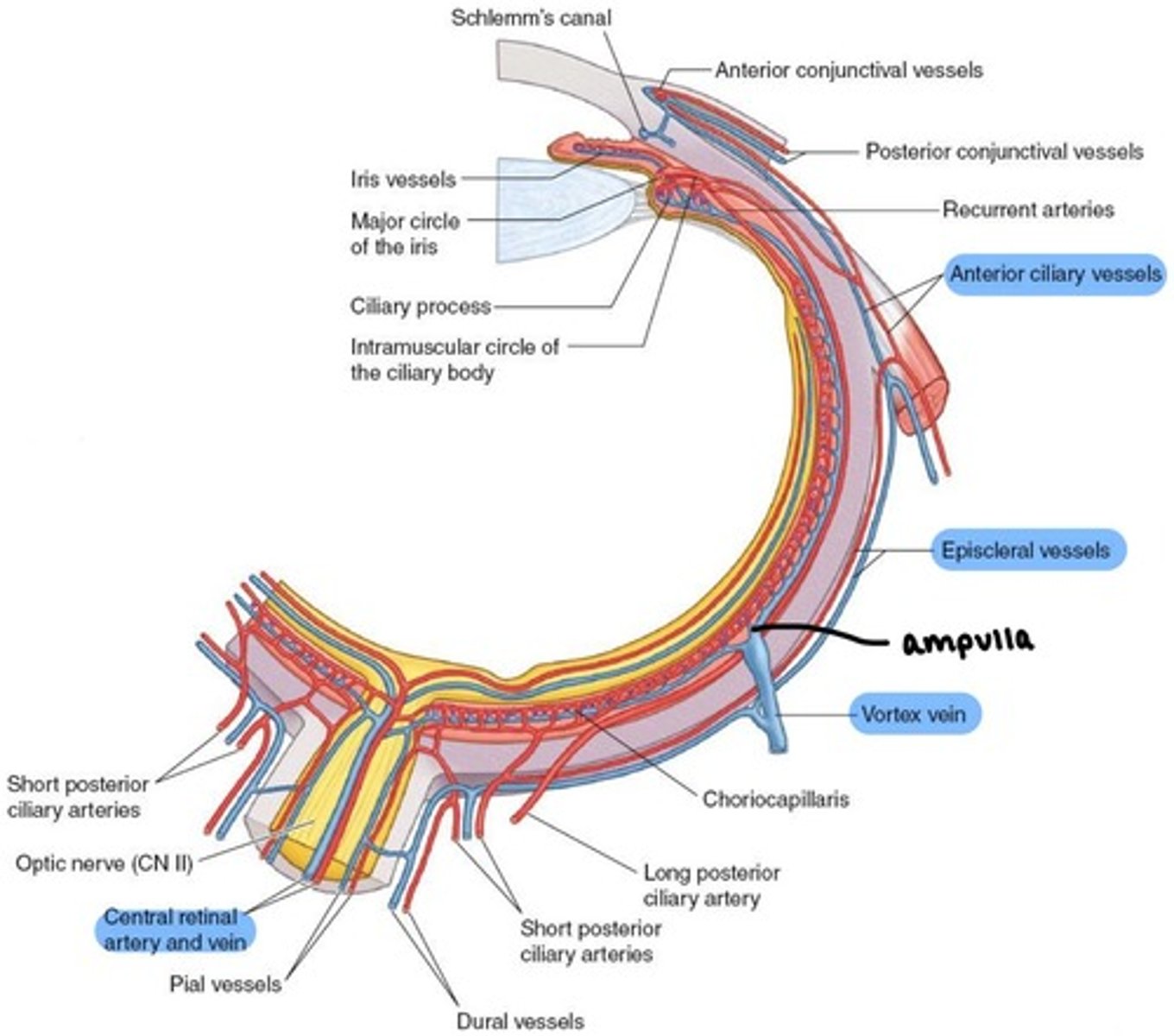
what do the Vortex veins drain?
choroid
what do Anterior Ciliary veins drain?
ciliary body
return via Muscular veins
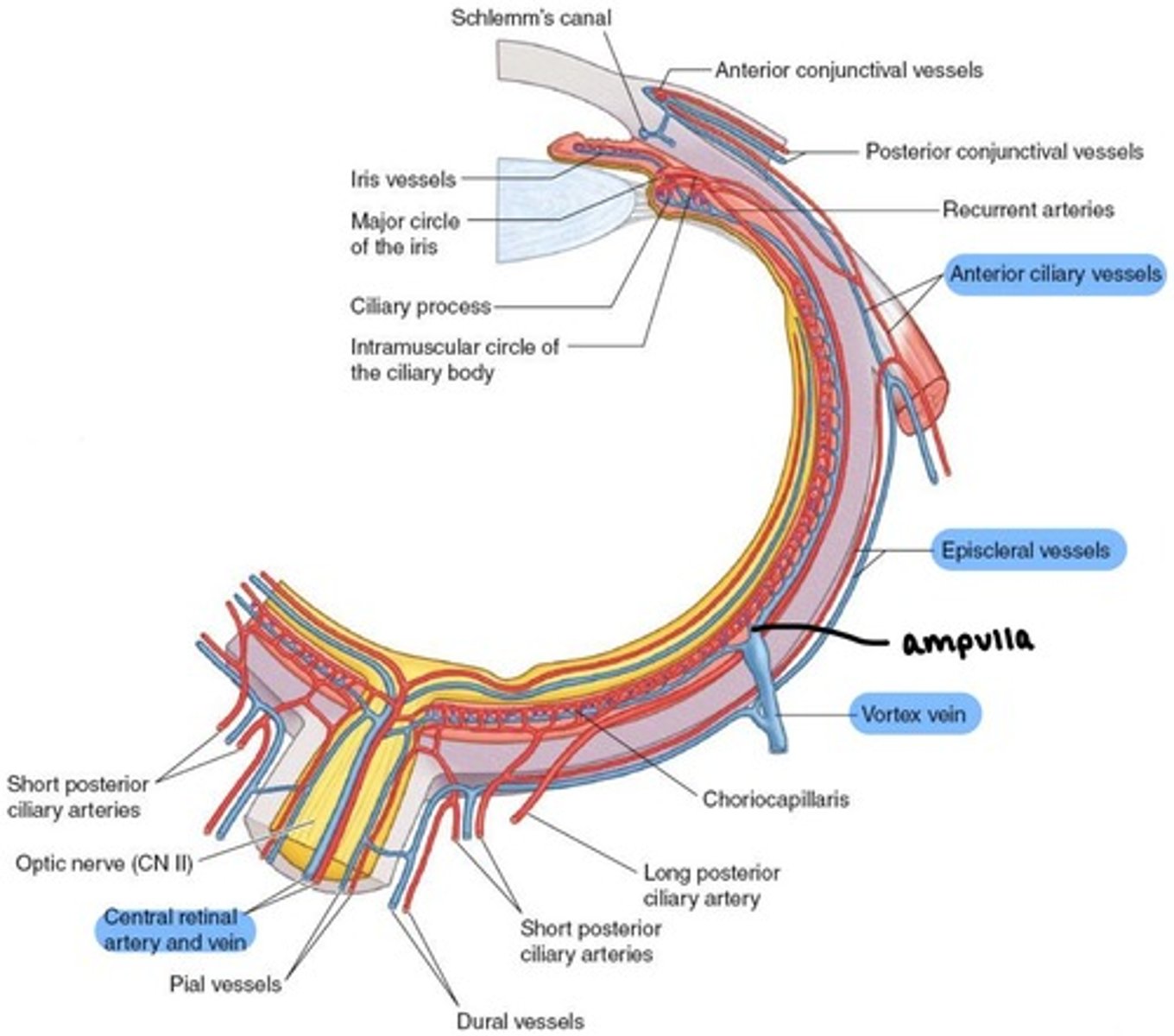
where do these veins drain to?
Superior & Inferior Ophthalmic veins, which combine behind the orbit and drain to the Cavernous sinus.
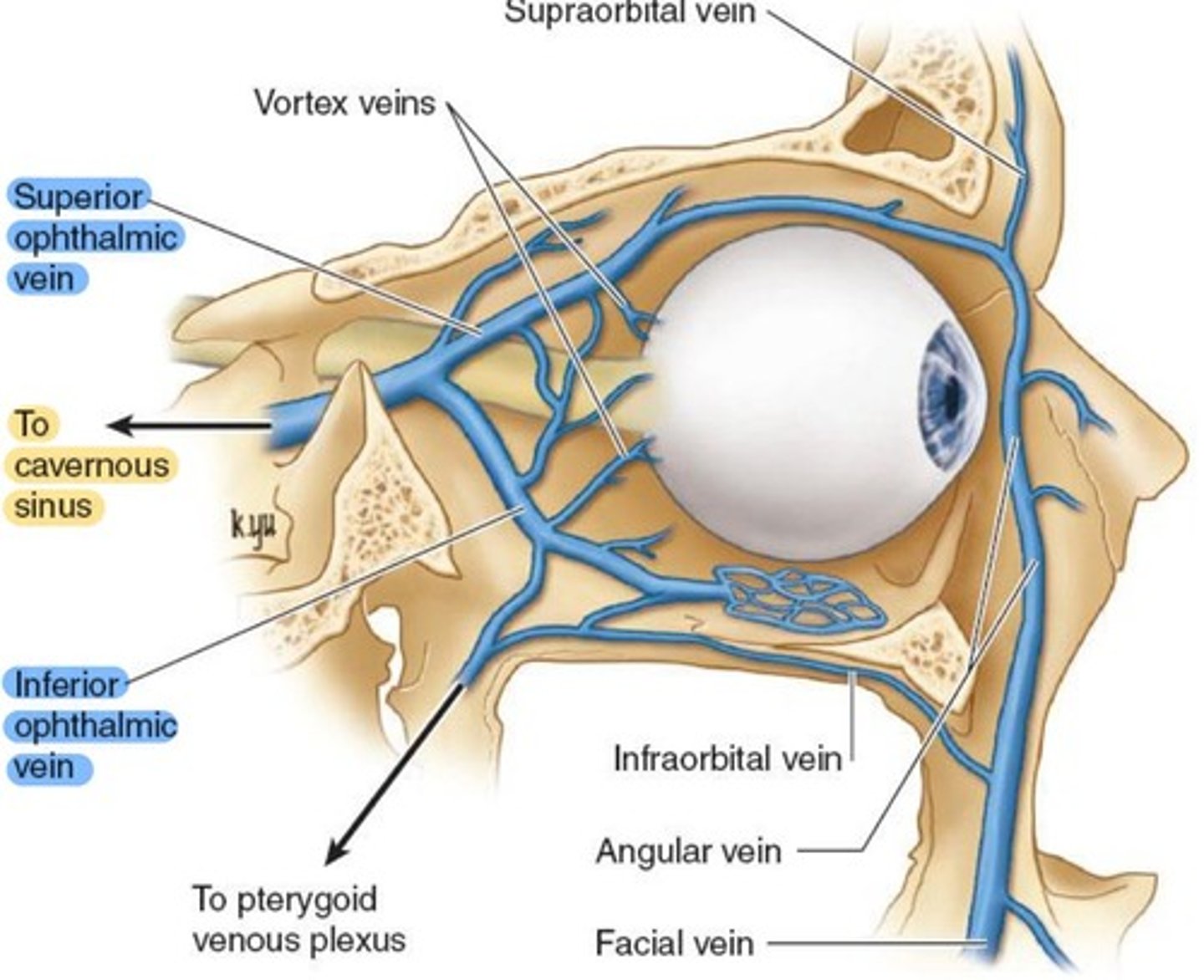
Superior Ophthalmic vein
drains superior orbit
exits the orbit through the Superior orbital fissure
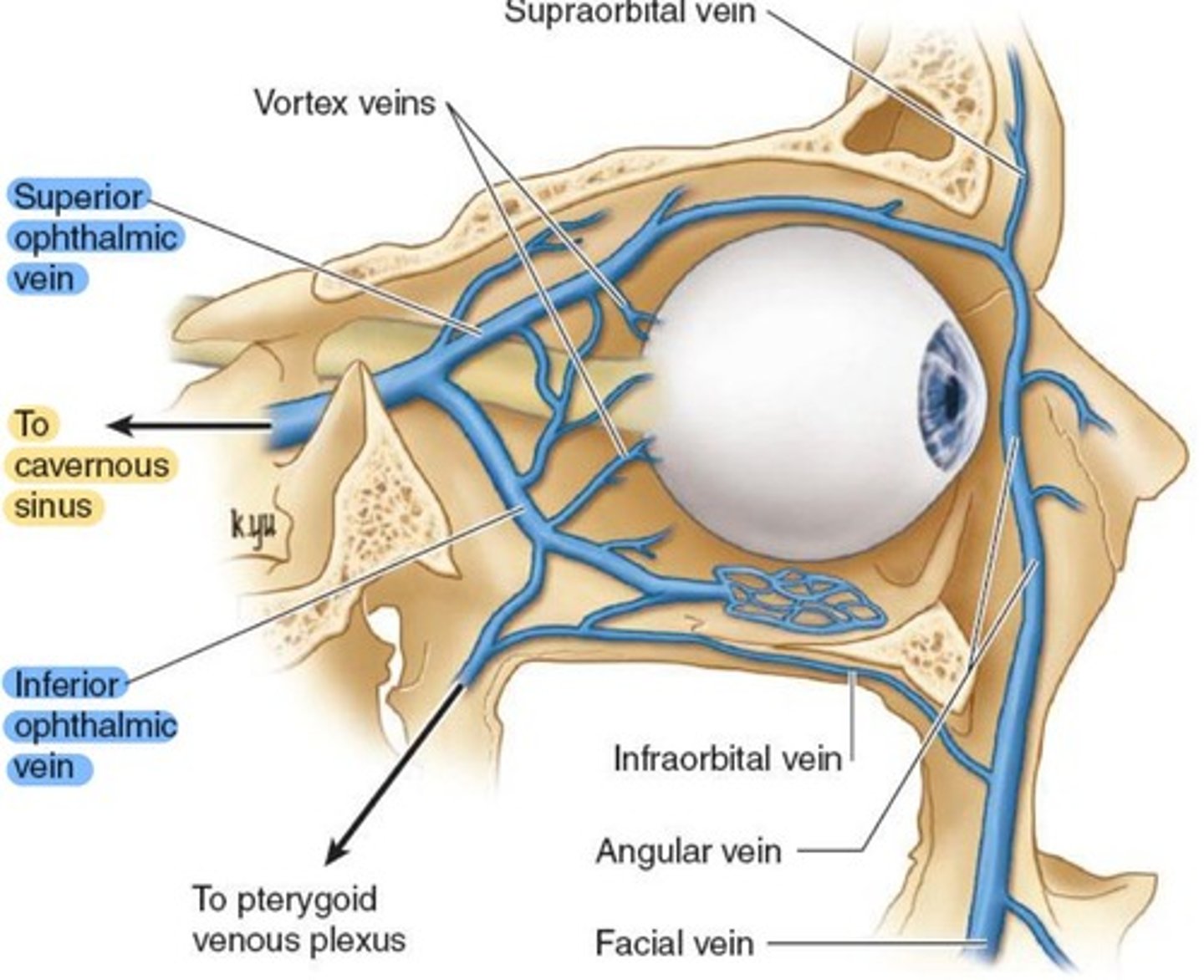
Inferior Ophthalmic vein
drains LR, conjunctiva, lacrimal sac, lower vortex veins.
exits the orbit through the Inferior orbital fissure
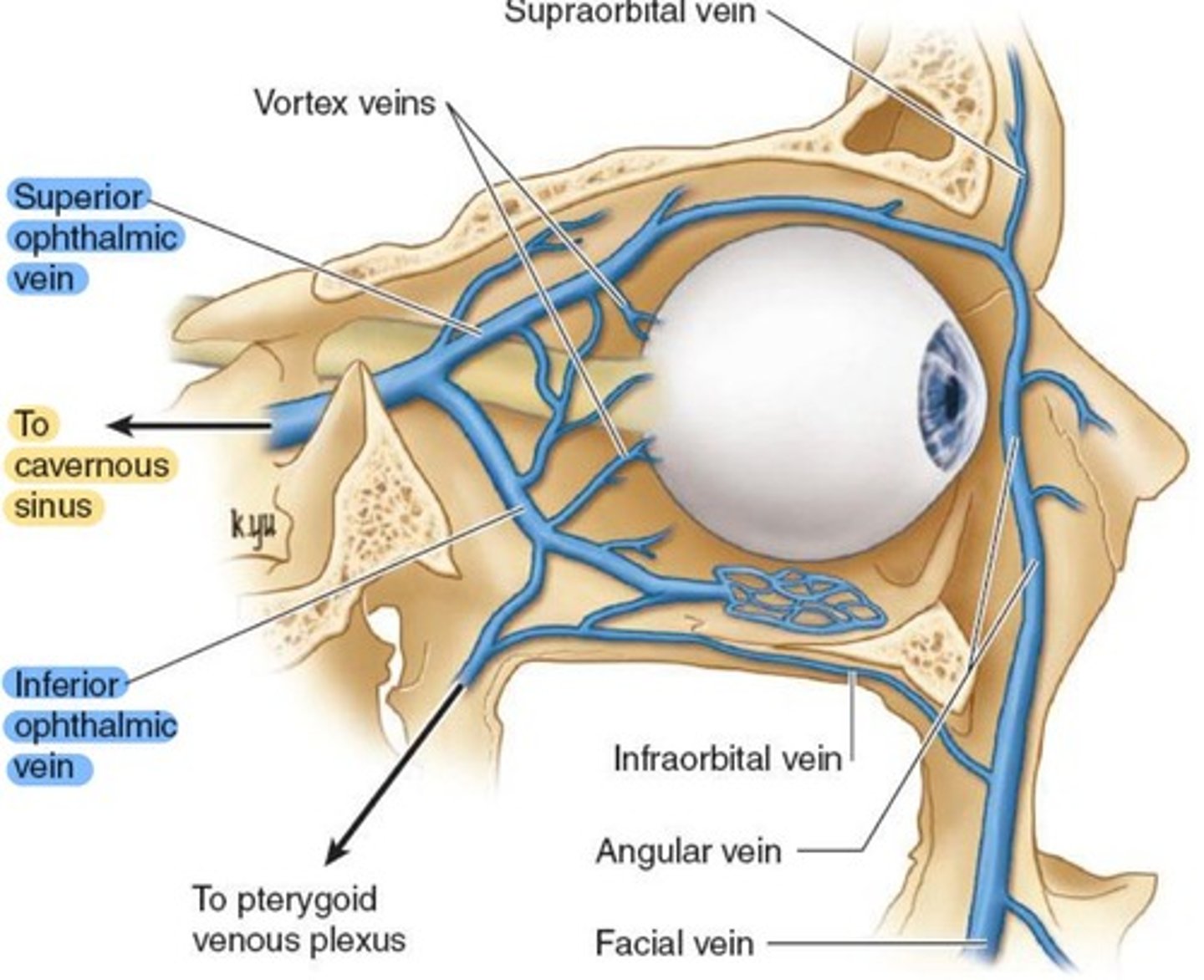
Central Retinal vein
either joins with Superior Ophthalmic vein, or drains directly to Cavernous Sinus.
where does Cavernous sinus drain to?
Cavernous sinus (and other brain veins) all drain to the Internal Jugular vein
what do Infraorbital veins drain?
the face
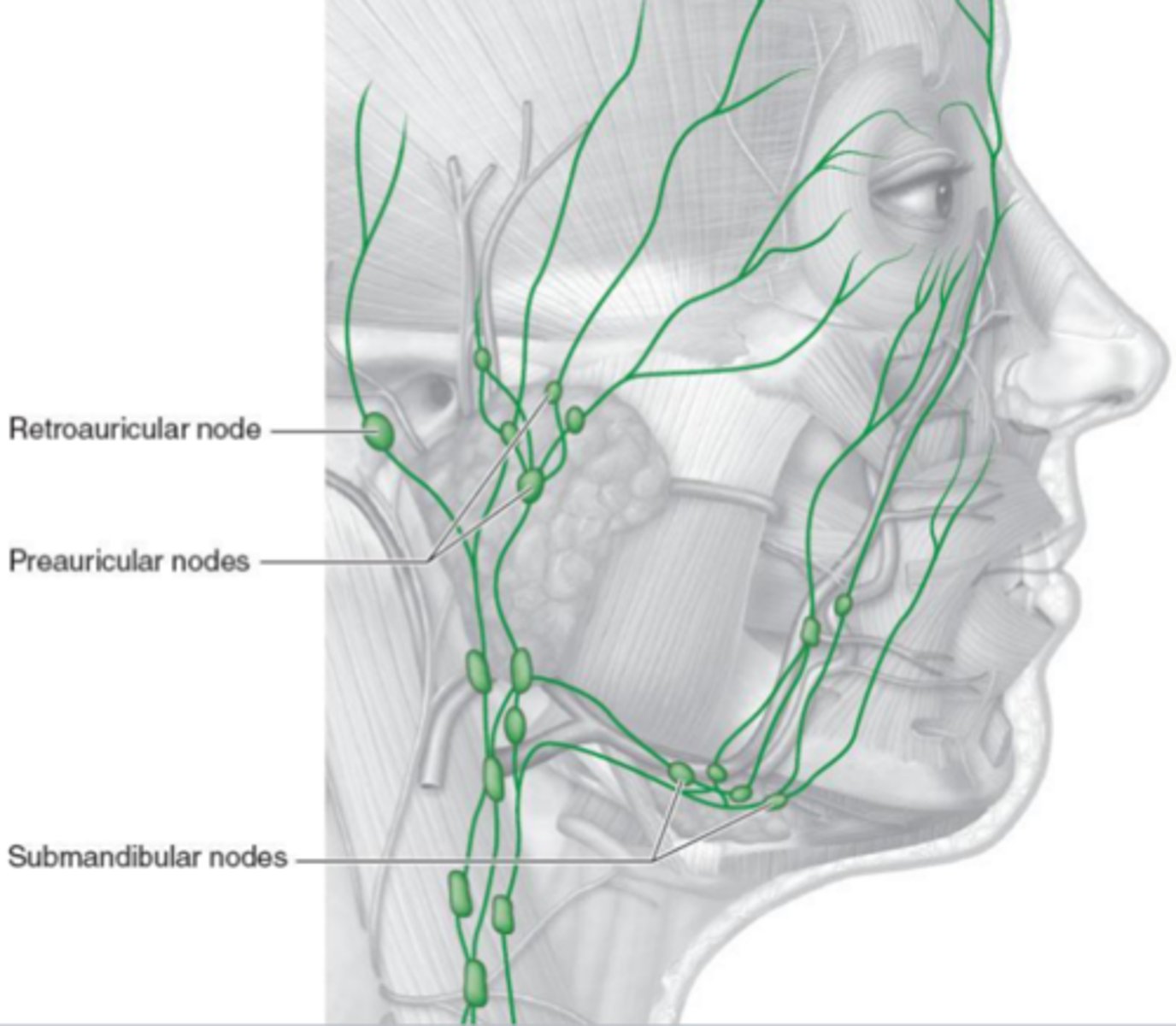
Lymphatic drainage system
immune function - activated when there is an infection.
Retroauricular nodes: behind the ear
Preauricular nodes: in front of the ear
Submandibular nodes: below the mandible
Spontaneous Venous Pulsation (SVP)
normal subtle pulsations of the retinal vein(s) as they cross the optic disc.
caused by variation in the pressure gradient between retinal veins and CRV.
IOP > CSF (intracranial) pressure
once CSF pressure increases, SVP will stop.

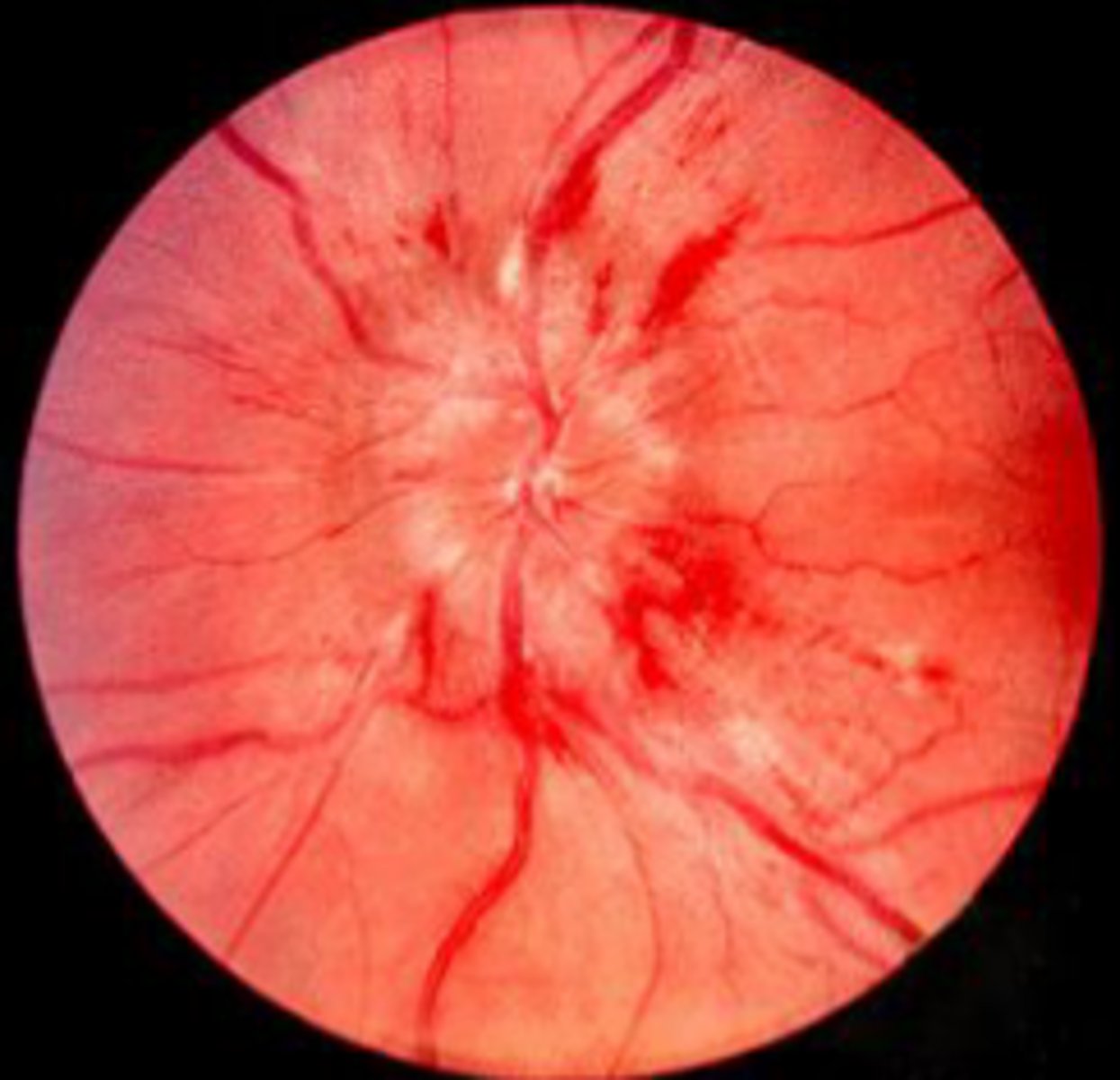
Papilledema
CSF (intracranial) pressure > IOP
increased intracranial pressure can compress CRV, causing a blockage, causing edema of the optic disc.
evident as blurred disc margins, sometimes with hemorrhages.
no venous pulsations
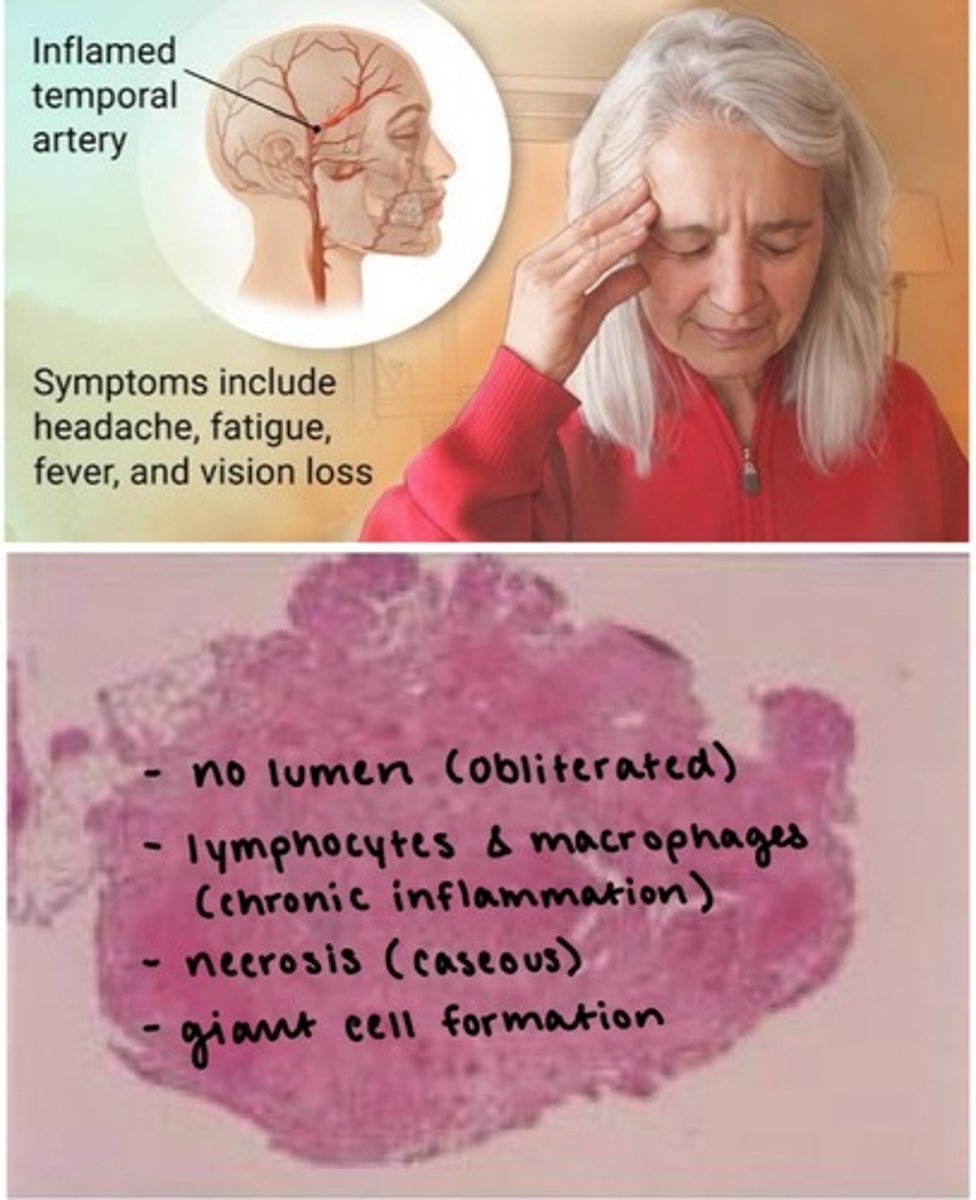
Giant cell arteritis (GCA)
aka Temporal arteritis.
most common form of systemic inflammatory vasculitis in adults/elderly.
inflammation of medium and large sized blood vessels
Prodrome Sx: HA, fatigue, fever, sudden blurry vision
Carotid-Cavernous Sinus Fistula (CCF)
abnormal communication between the ICA and Cavernous Sinus.
caused by a tear in the artery wall.
veins may become pulsatile.
can increase aqueous outflow resistance, leading to high IOP.
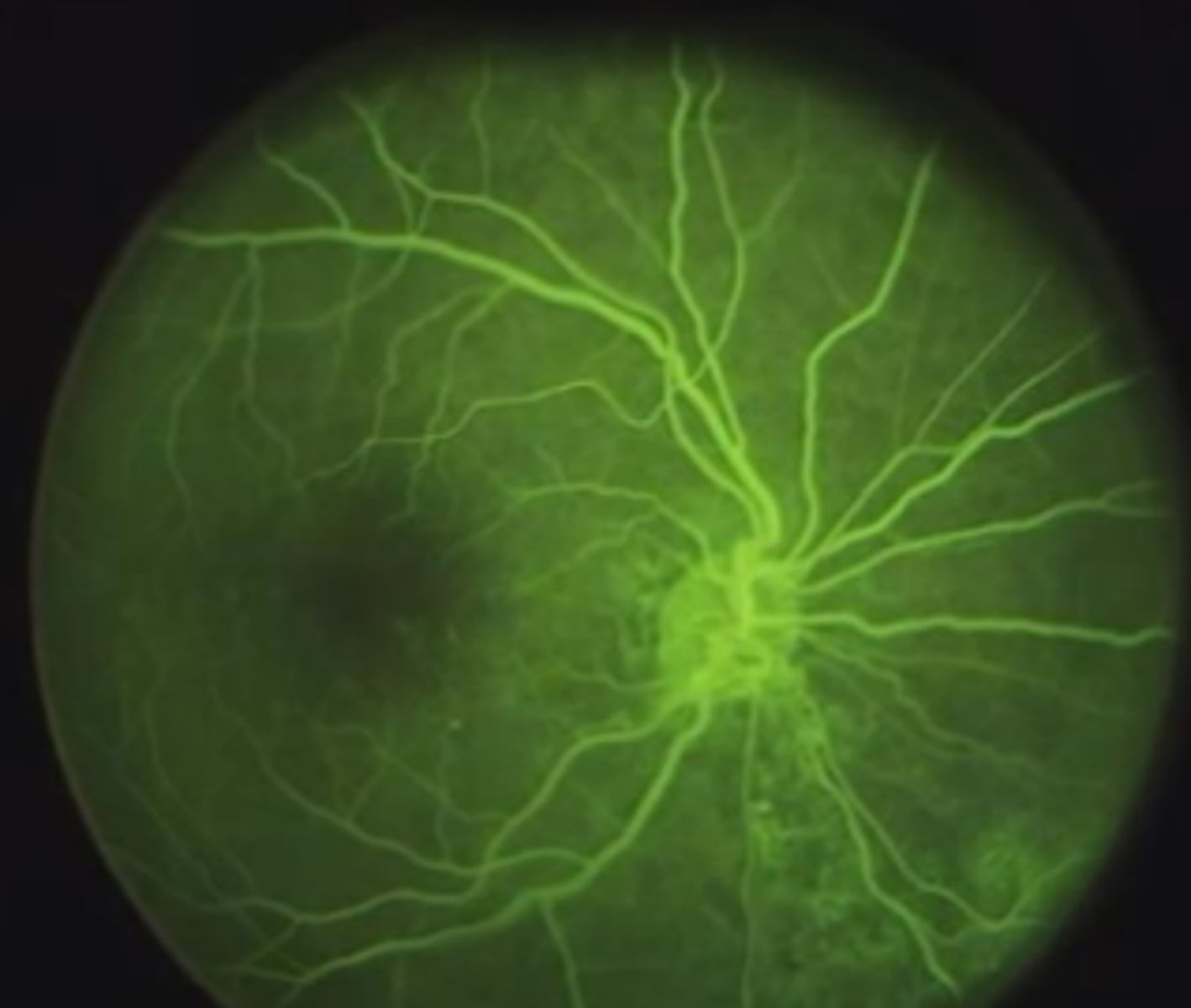
Fluorescein Angiography (IVFA)
fluorescein dye can be injected to examine choroidal and retinal circulation.
within 10 seconds, choroidal flush
→ dye leaks out of fenestrated choriocapillaris
→ dye should NOT leak into the retina because RPE is not fenestrated
within 12 seconds, retinal arteries fill, then retinal veins.
defects in the RPE can be seen if the dye leaks into the retina BEFORE the retinal vessels fill (during choroidal flush)
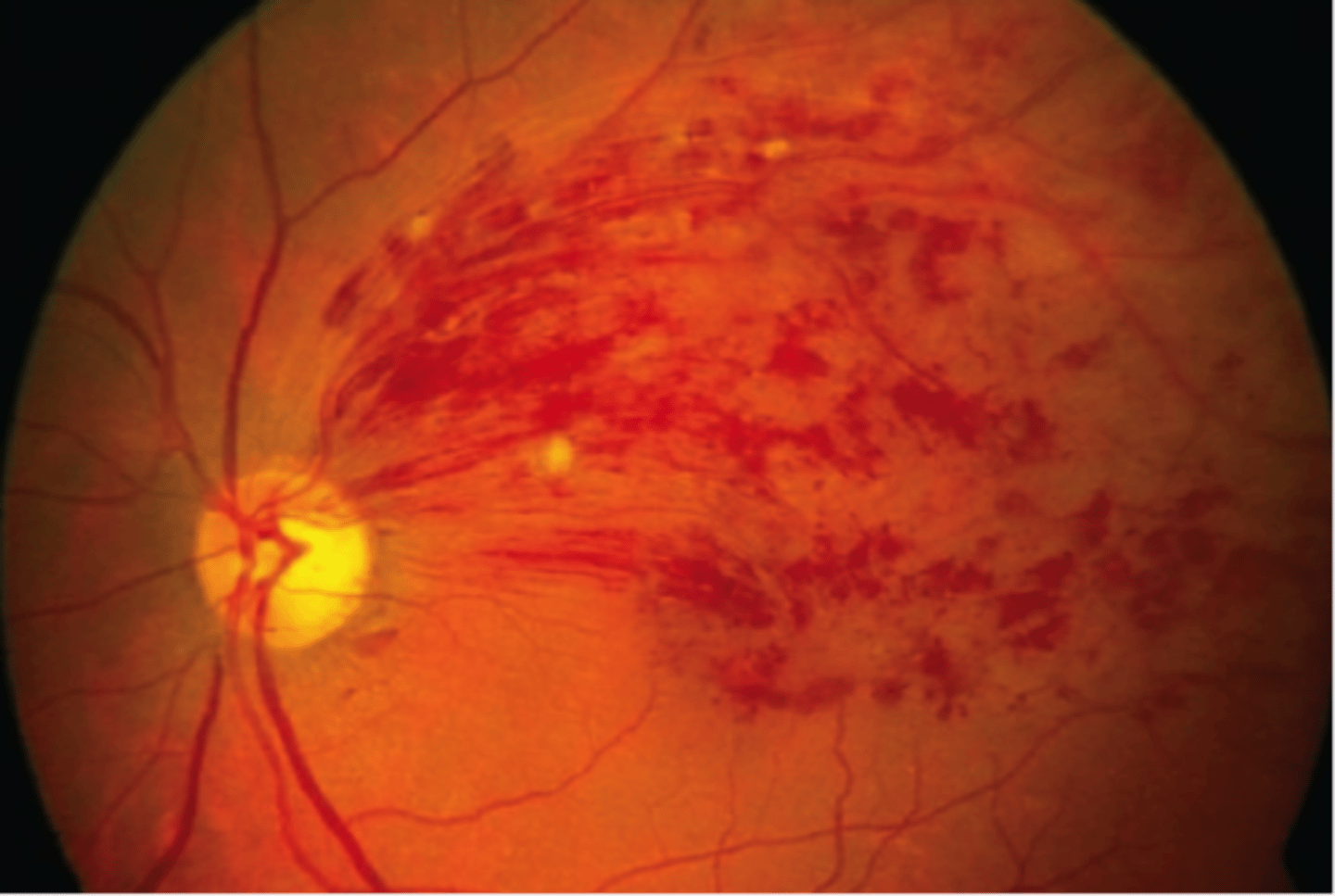
Branch Retinal Venous Occlusion (BRVO)
occurs when thickened or hardened retinal arteries cross over a retinal vein and block it.
when the vein is blocked, nerve cells within the eye may die.
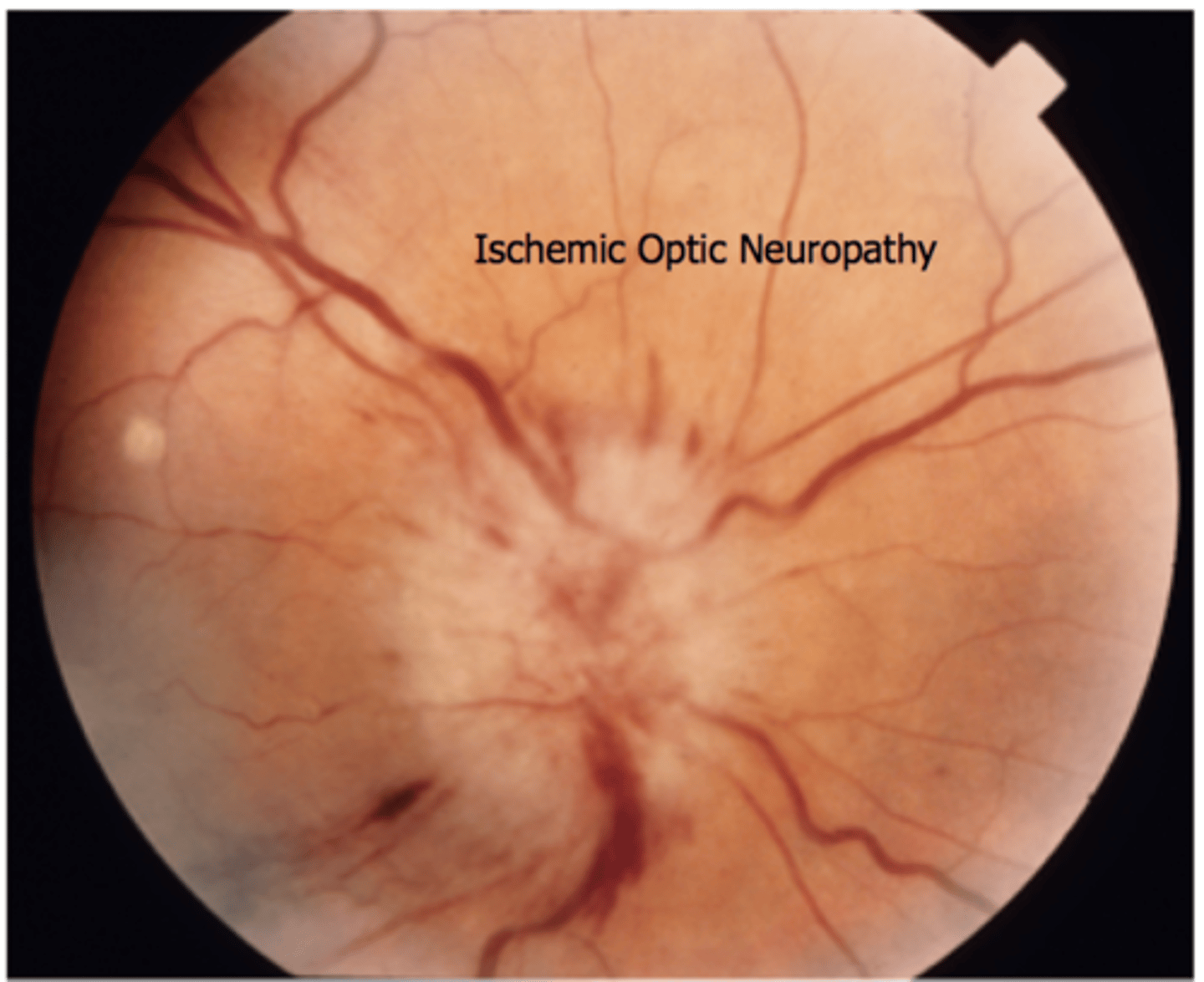
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION)
results from nonperfusion/hypoperfusion of the ciliary blood supply to the optic nerve head.
nonatheritic AION can cause altitudinal vision field loss.