rules of tort law
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Liable
The judges decision that the case against the d is proved and that the d should pay compensation
Civil law
The law concerned with the relationship between individuals
Seeks to settle disputes
Tort
A civil wrongful and tort law compensates a person who has been injured or whose property is damaged.
Types of civil law
Tort law- allows people to claim compensation when injured or property damaged
Contract law-operates when goods or services are bought and sold
Family law-sets out rules governing family relationships
Employment law -rules operating between employer and employee
Claimant
The person who has suffered loss or damage and is bringing a claim for compensation
Defendant
Person who has caused the loss or damage
Damages
The payment of money by way of compensation. The aim of damages in tort is to put the claimant back in the position they were in before the tort so far as money can go
Injunction
An order of the court to stop doing something. Failure to follow the court order can lead to further sanctions including imprisonment. An injunction can order a positive action.
Courts
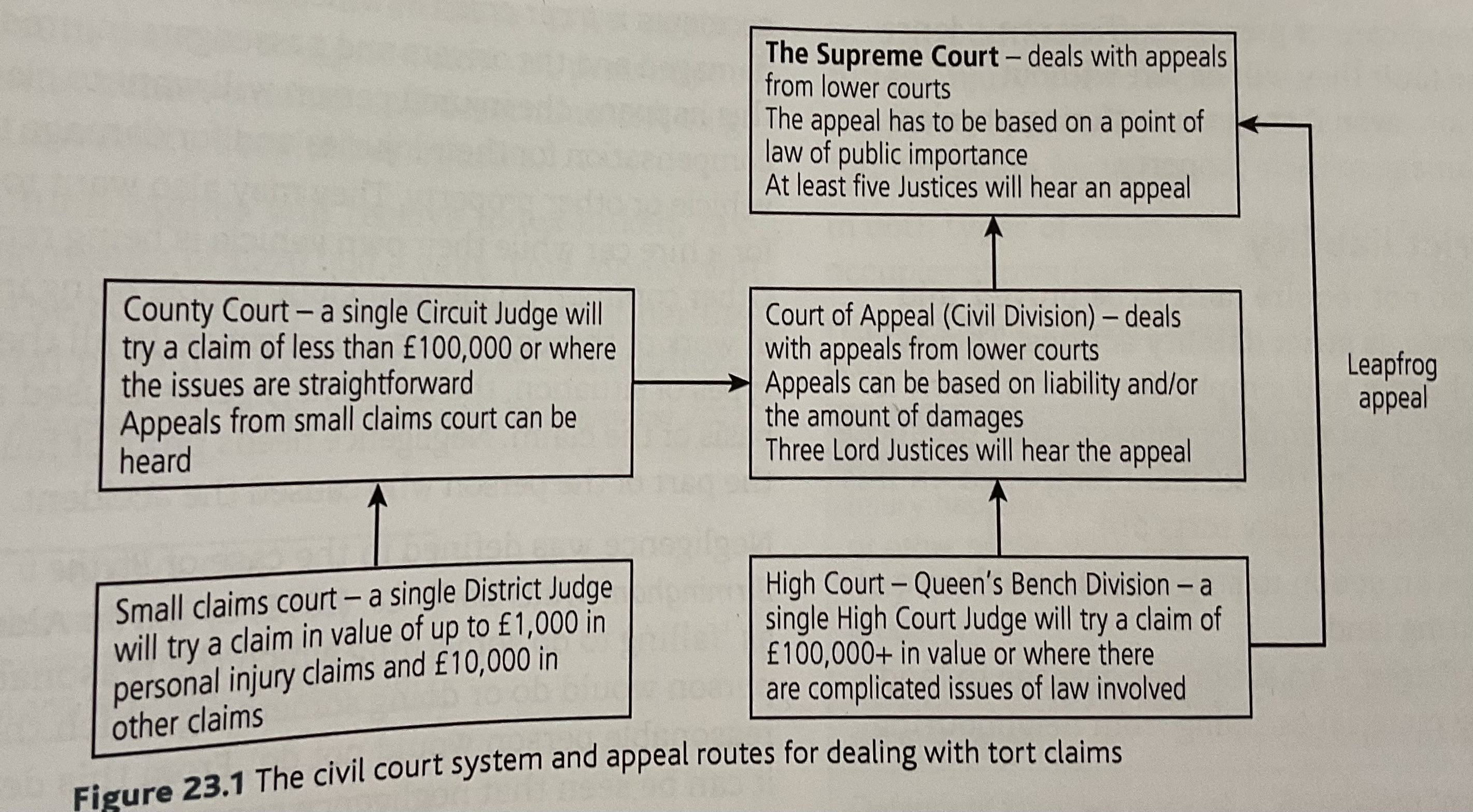
Procedure in courts
Claimant prepares claim and initial evidence to show they have a case + suggest the amount of damages they intent to claim
In civil courts judges sit alone to decide-the liability, how much damages should be paid, if the winning party is entitled to the payment of their legal costs by the losing party
General rule is that loser pays winners legal fees
One of the parties can appeal against the decision by
Against liability-who wins the case but on the grounds that the judge misdirected themself on the relevant law
Against the damages rewarded- excessive or insufficient
Burden of proof
Burden of proof is on the claimant
Standard if proof is the balance of probabilities
Fault
Means there is some wrongdoing by the defendant
Torts that require fault to be proved specifically:
Negligence
Occupiers liability
Psychiatric injury
Economic loss
Strict liability
A civil action where fault of the d need not be proved
Strict liability torts -nuisance-an action to stop unreasonable use of neighboruoughing land
Roland’s v fletcher- an action for damage to land caused by material escaping from neighbouring land
Vicarious liability-employee commits a tort in the course of their employment
Defences
Consent and contributory negligence
Dispute the claimants case and suggest claimant wholly or partly caused their own injury
Negligence
An act or failure to act due to the fault of the d which causes injury or damage to another person or their property
It’s a common law tort
Blythe v Birmingham waterworks co. 1856
Baron Anderson defined negligence
Failing to do something which the reasonable person would do or do something which the reasonable person would not do
Occupiers liability
Where claimant suffers personal injury on occupiers premisises
Occupiers liability act 1957-occupiers of premises owes a duty of care to lawful visisters (have permission of occupier). Common duty of care owed if duty broken and visitor injured they are entitled to receive compensation. V can also claim compensation for any property damages
Occupiers liability act 1984-allows claims by trespassers. They are also allowed a duty of care though different from a lawful visitor.
Remedy
Then way in which a court will enforce or satisfy a claim when injury or damage has been suffered and proved
Special damages
Cover the period up to the trail and cover claims that can be specifically calculated. For personal injury claim these include treatment cost + loss of wages
General damages
Cover the period after the trial and include the pain and suffering as a result of the accident, future loss of earnings, future medical costs and ny loss of amenity