2.1 Molecules to Metabolism
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
metabolism
The totality of all enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism
Anabolism
The build up of complex molecules from more simple subunits (ie. monomers)
requires condensation reactions to proceed (water is produced as a by-product)
ex= Photosynthesis
Catabolism
The breakdown of complex molecules into more simple subunits (monomers)
requires hydrolysis reactions to proceed (water is consumed as a part of the reaction)
ex= Cell respiration
CATA BOOM
Organic vs Inorganic molecules
Organic molecules contain carbon & are synthesized by living organisms (anything else is INorganic). Exceptions include carbides, carbonates, oxides of carbon & cyanides
How the structure of carbon contributes to the formation of organic life
Carbon forms the basis of organic life due to its capacity to form large molecules. Carbon has 4 valence electrons & can form 4 covalent bonds. This allows it to function as a stable backbone in a wide variety of compounds
Theory of vitalism & how it was falsified
Vitalism proposed that organic molecules could ONLY be synthesized by living organisms.
It was falsified by Frederick Woehler in 1828. He was able to synthesize urea (organic molecule) from an inorganic salt under laboratory conditions
monomer
A recurring subunits within a more complex polymer
4 different types of Biomacromolecules
CARBOHYDRATE
Monomer: monosaccharide
Polymer: polysaccharide
Bond Involved: Glycosidic Linkage
LIPID
Monomer: Glycerol + fatty acids (3x)
Polymer: Triglyceride
Bond Involved: Ester linkage
PROTEIN
Monomer: amino acid
Polymer: polypeptide
Bond Involved: peptide bond
NUCLEIC ACID
Monomer: nucleotide
Polymer: DNA or RNA
Bond Involved: Phosphodiester bond
chemical formula for unsaturated fatty acid
CH3-(CH2)n-COOH
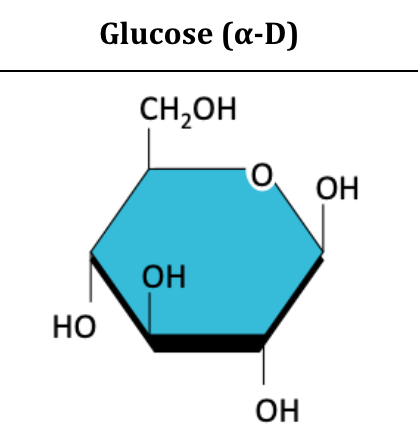
Glucose diagram
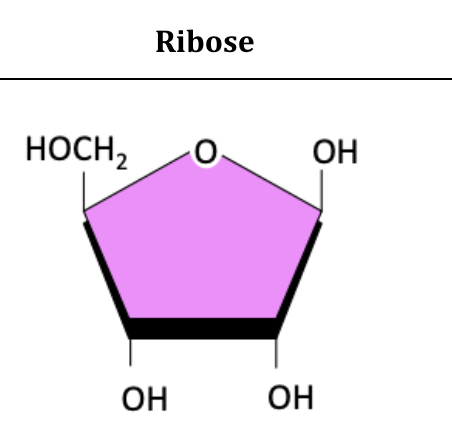
Ribose diagram
How the following may be identified based on their chemical formula
Carbohydrate: Have C,H,O in a common ratio according to formula (CH2O)n
Protein: May contain sulphur (some amino acids include sulphur)
Nucleic acid: Will contain phosphorous in relatively large amounts (nucleotides include a phosphate group)