College Chem
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Matter
The physical material of the universe; it is anything that has mass and occupies space.
Gas
No fixed volume or shape. Uniformly fits its container. Can be compressed.
Liquid
Distinct volume assuming the shape of the portion of the container it occupies. Non-compressible.
Solid
Defined volume and shape. Non-compressible.
Physical change
Changes in appearance not composition. (Water changing states/melting/freezing/evaporating)
Chemical change
Transformation to a chemically different substance (reaction/bonding/breaking bonds)
Pure Substance
Consists of 1 type of atom or chemically bonded atom. Defined and constant composition.
Element
Pure substance with only 1 type of atom (on periodic table)
Compound
Pure substance with multiple bonded atoms/elements
Mixture
2 or more substances physically combined not bonded.
Hetero mixture
Can see that it’s not bonded/not uniform. Ex: salsa, cereal, gravel
Homo mixture
Uniform/ can’t see that it’s not bonded). Ex: Kool-aid, brass, steel
Significant Figure
Not a zero, a zero between non-zeros, at the end of a decimal, in the coefficient of a number written in scientific notation.
Mass
Amount of matter (g,kg,lb)
Volume
The amount of space. (L,mL,gallons,etc)
When multiplying to get an answer with significant digits report the answer with…
The fewest s/d
When adding or subtracting significant digits report the answer with…
The fewest place value/decimal points
Proton
Positive charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom. 1 weight
Neutron
Neutrally charged particle with largest mass in an atom also found in the nucleus.
Electron
Negatively charged particles with NO mass found in the orbitals of an atom.
Atomic Number
Number of protons
Mass number
Number of protons + number of neutrons
Isatopes
Atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers. (Different number of neutrons but same number of protons)
Democritus
First man to theorize that the world is made up of “tiny invisible units”. (Atoms) No evidence for his theories.
John Dalton
1808 theorist who said atoms can’t be broken to smaller pieces and created the Law of Definite Proportions: A chemical compound always contains the same proportion of a particular element.
JJ Thomson
1897 theorist who discovered Cathode Rays by using a vacuum tube to isolate 2 particles, one negatively charged and one positive, and shot them to create the ray which could be deflected with a magnet. Discovered the Electron
Ernest Rutherford
Student of JJ Thomson who tested to find out that an atoms mass is spread evenly throughout a volume. Aimed a Cathode Ray through a sheet of gold and found that some went through but some didn’t concluding that atoms are denser in the middle/ nucleus.
Period
A horizontal row in the periodic table
Group
The vertical line of elements on the periodic table. Has the same number of valence electrons
Metal properties
Shiny, malleable (can be hammered into sheets), conducter, ductile (can be drawn into wires).
Nonmetal properties
Dull, brittle solids that are poor conductors
Metalloid Properties
Shiny, brittle solids that are semi-conductors. Can have some metal+nonmetal properties.
Ion
An atom with a charge due to a difference in protons and electrons
Cation
A POSITIVE ion with more protons then electrons
Anion
A NEGATIVE ion with more electrons then protons
Polyatomic ions
A group of elements with a charge (golden ticket)
Ionic compounds
Metals+Nonmetals (poly), on golden ticket, Roman numerals, cross cross, NO prefixes
Molecular compounds
Nonmetal+Nonmetal, use prefixes
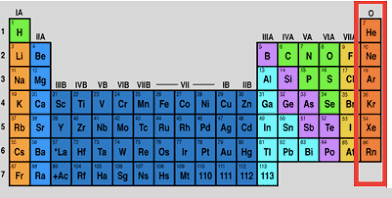
Noble gases
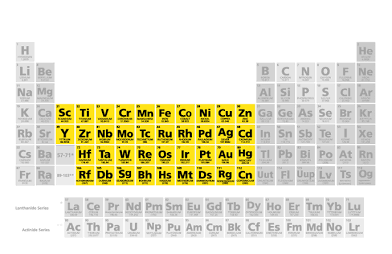
Transition Metals
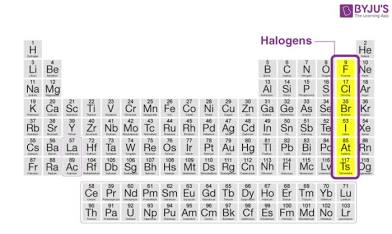
Halogens
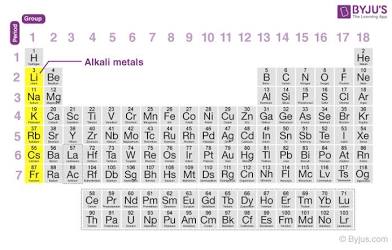
Alkali Metals
Lanthanides

Actinides
Nonmetals
Basic Metals
Metalloid
Acids
Compound that starts with H
Molecular formula
The actual number of atoms in a molecule
Empirical formula
The simplest reduced form of a molecule