Physio Lect 25 - Microcirculation Part Two: Solute Flux
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
_______ is the key factor in providing the exchange of solutes such as gases, nutrients, and waste products between the capillary and the cells in tissues.
Diffusion
How do we define flux using ohm’s law?
Flux = conductance*driving force

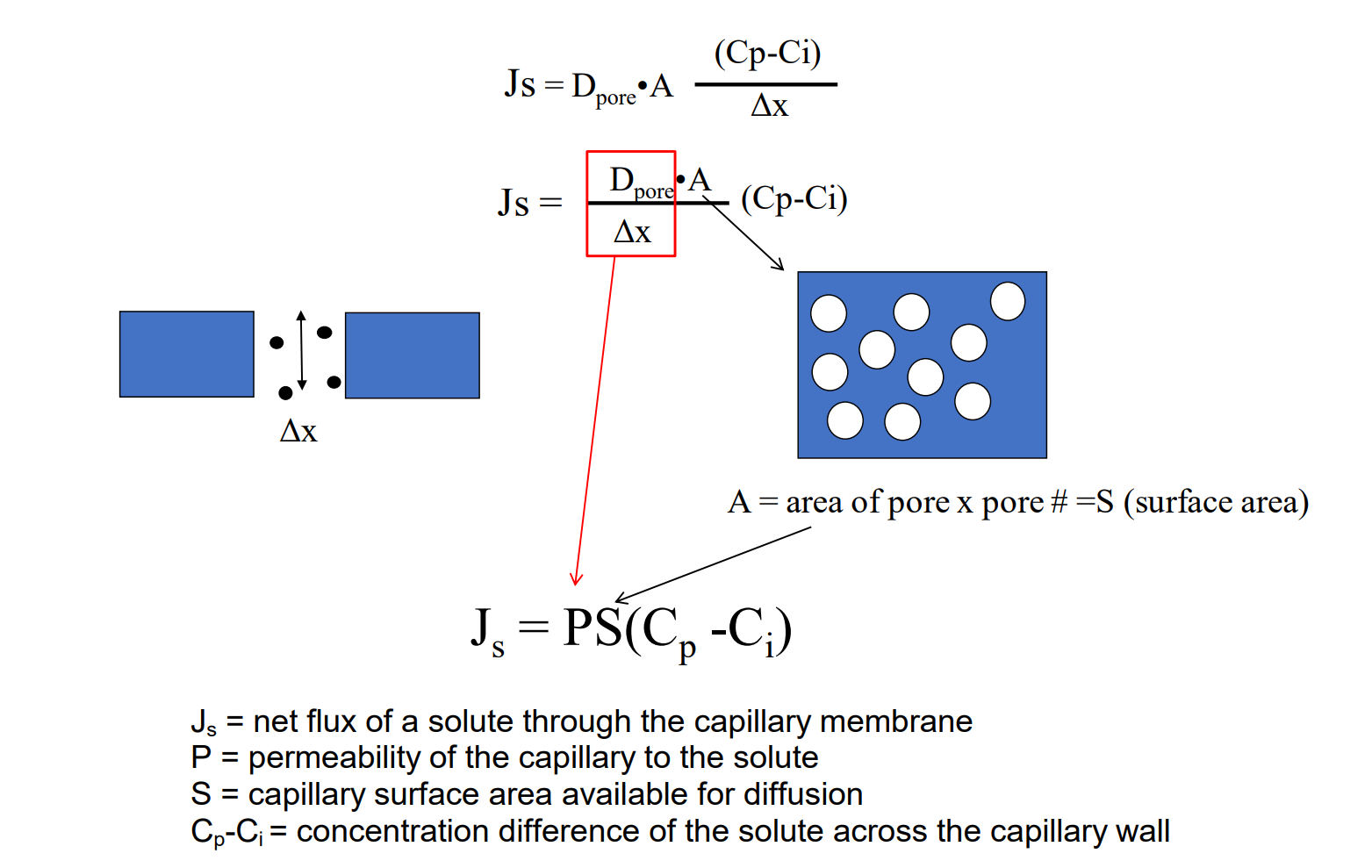
What is the solute flux equation? What does each variable in the equation mean?
Js = net flux of a solute through the capillary membrane
P = permeability of the capillary to the solute
S = capillary surface area available for diffusion
Cp-Ci = concentration difference of the solute across the capillary wall
What are the 3 factors that effect transvascular exchange of macromolecules?
Surface area, blood flow, and permeability
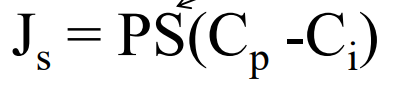
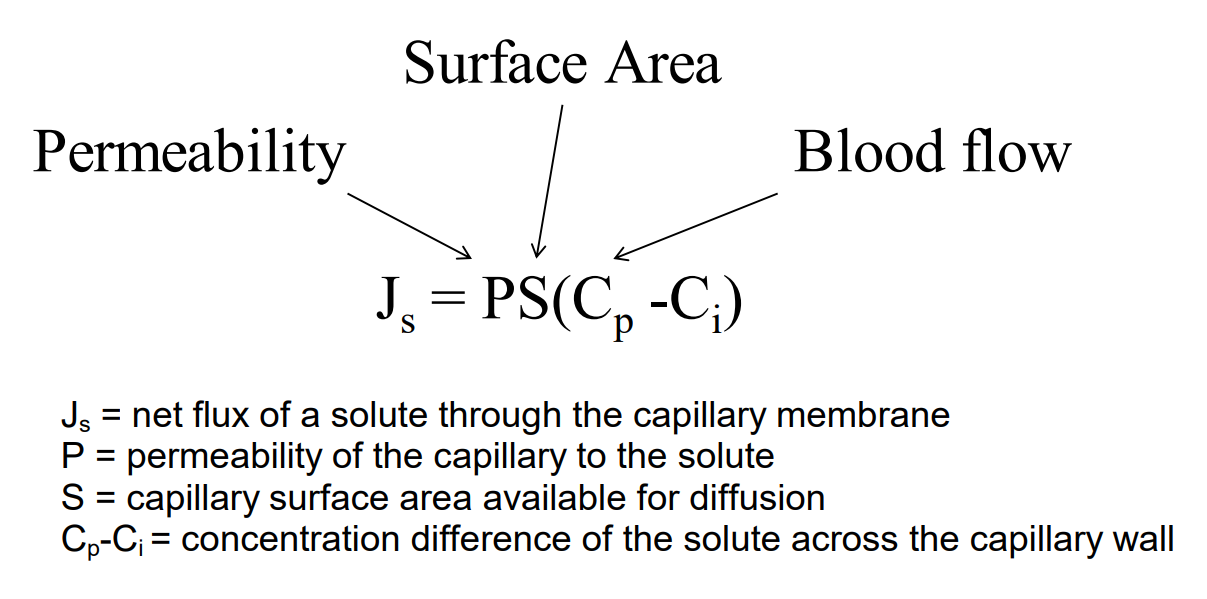
What do the 3 factors (surface area, permeability, and blood flow) correspond to in our equation for solute flux?
Permeability - permeability of the capillary to the solute
Surface area - capillary surface area available for diffusion
Blood flow - Cp-Ci = concentration difference of the solute across the capillary wall
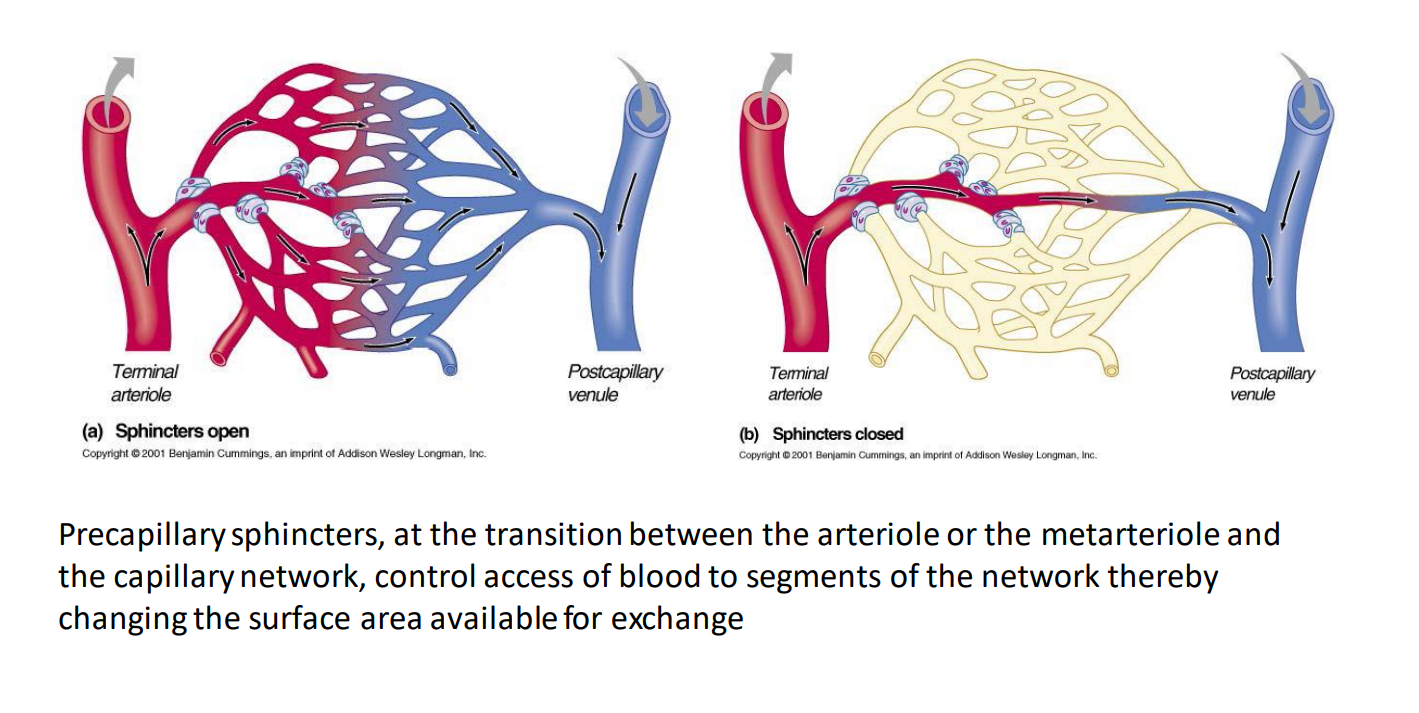
When we are referring to surface area what do we mean?
how much capillary surface area is exposed to blood and available for exchange
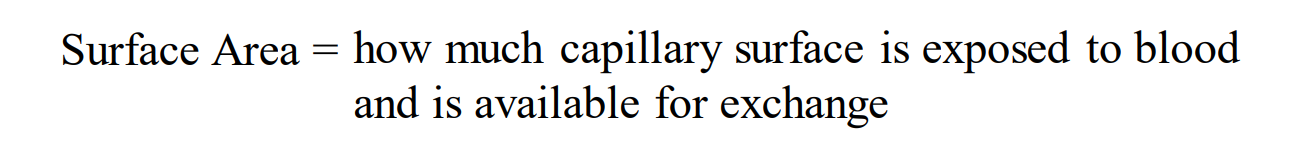
How does our body control the amount of capillary surface area exposed to the blood?
through the use of capillary sphincters
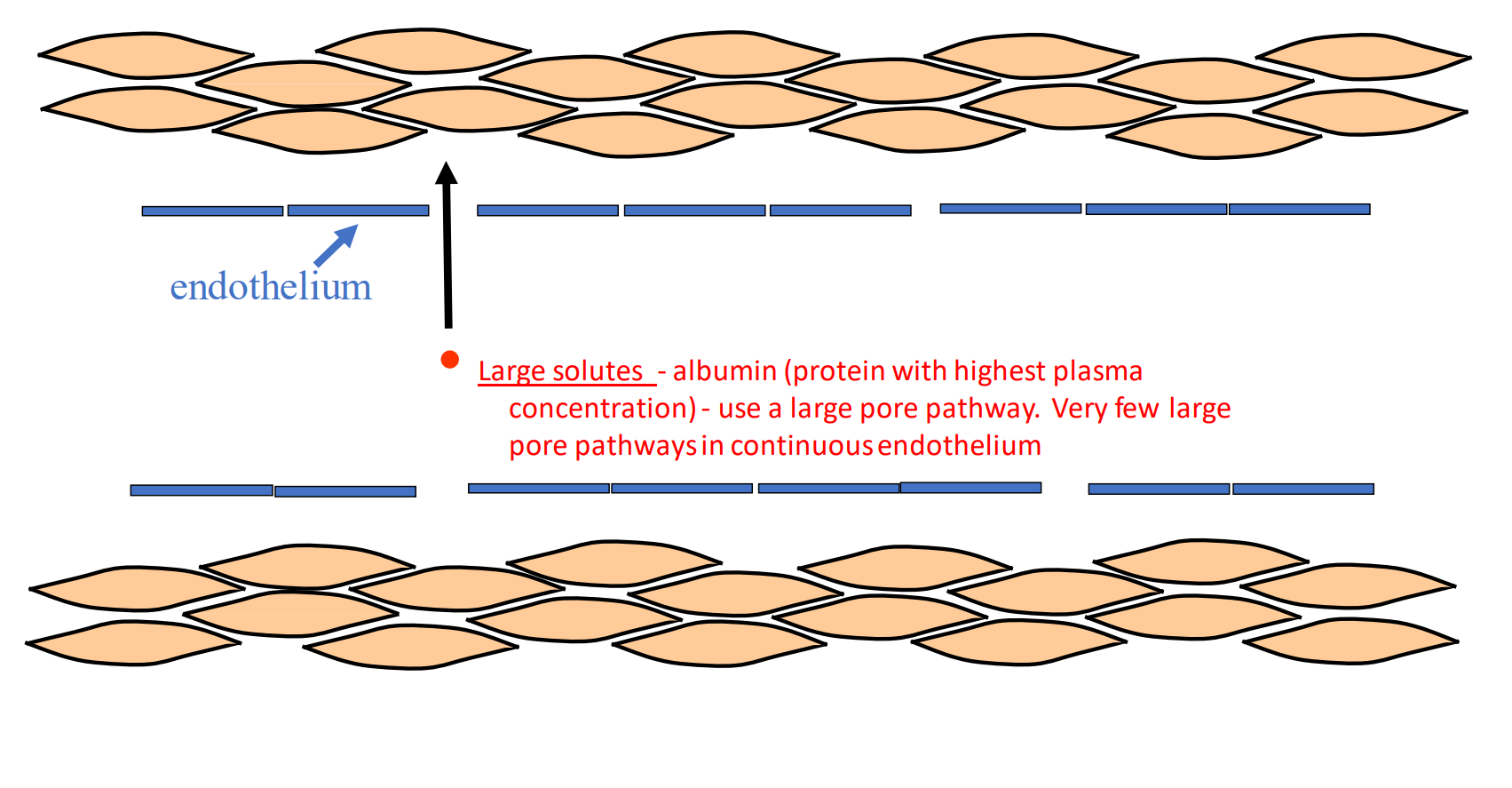
What are we talking about when we discuss permeability in the solute flux equation?
large solutes
Large solutes - albumin (protein with highest plasma concentration) - use a large pore pathway. Very few large pore pathways in continuous endothelium
What does it mean to be permeability limited?
too big of a solute/not enough pores to filter through - being diffusion limited
What are we talking about when we discuss blood flow in the solute flux equation?
Talking about small solutes like O2 and CO2
They are very soluble in the lipid membrane and will pass through the endothelial layer with ease
Also talking about Na+ Cl- and glucose - but they get in through a small pore pathway, there are many of these
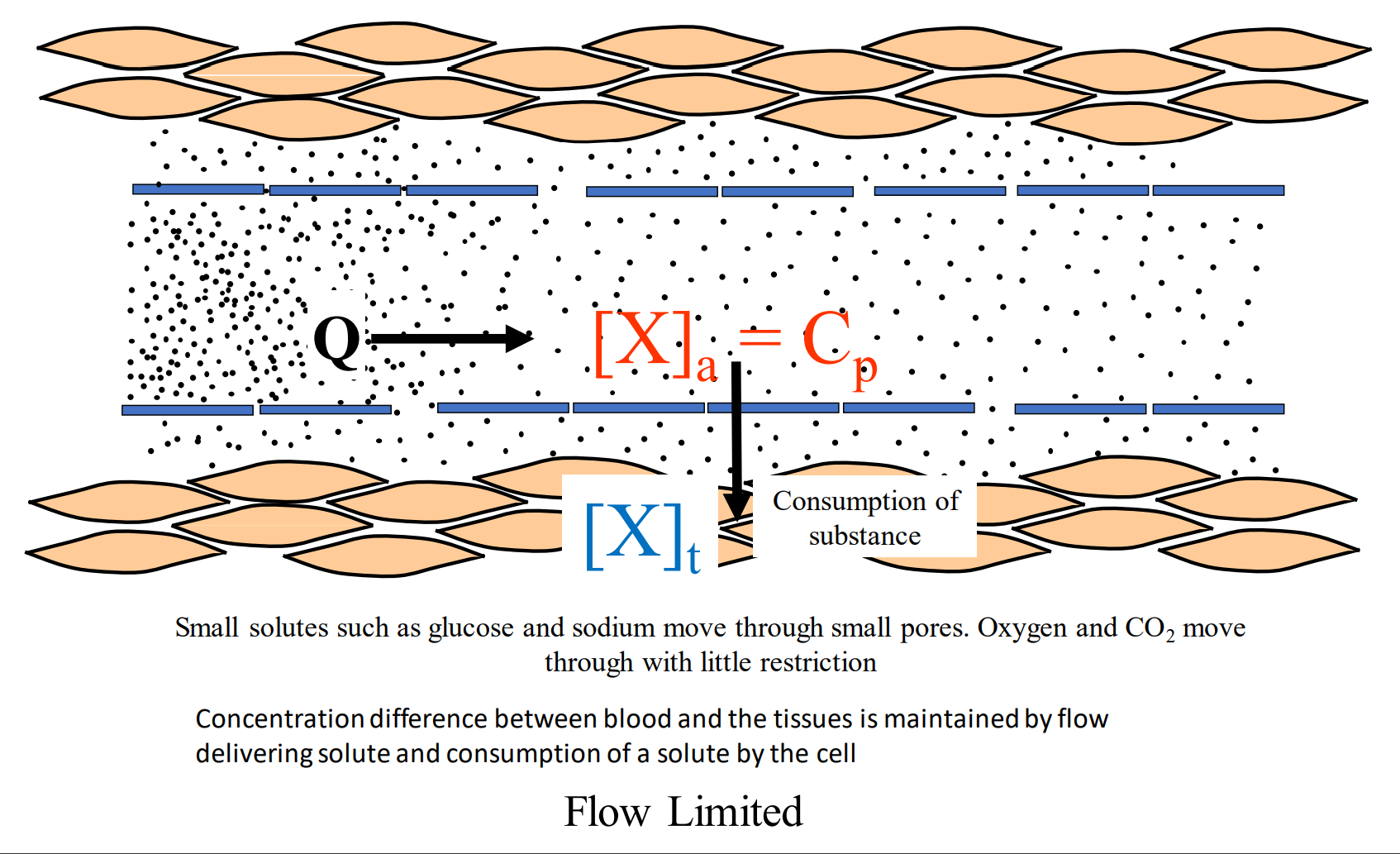
Explain the distribution of the solute on this slide.
They are tight packed in the beginning and it serves as a large driving force, but as the solutes travel down the capillary the driving force reaches equilibrium quickly because permeability is not a limiting factor.
All of these molecules are limited by blood flow - hence why they are termed flow limited