Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is acute renal injury
a sudden decline in renal excretory function over hours or days that can result in failure to maintain fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance
How do you diagnose acute kidney disease?
acute increase in serum creatinine and a reduction in urine output (oliguria)
risk factors for acute kidney injury
aged 65 years or over.
history of AKI or urological obstruction.
history of CKD, heart failure, liver disease, or diabetes mellitus
taking NSAIDS, ACEi
sex: female
ethnicity: black
causes of pre renal AKI
volume depletion
reduced ECV
renal hypoperfusion
renal artery stenosis
altered renal autoregulation by drugs
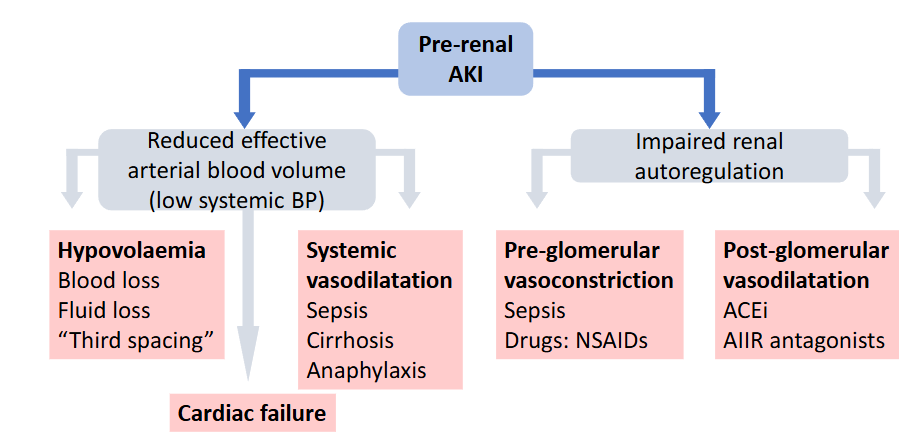
What is Prerenal Acute Kidney Injury?
Results from decreased renal perfusion, causing impaired oxygenation of renal tissue
reverses rapidly once renal perfusion is restored
Not associated with structural renal injury
Causes of renal AKI
ischaemic injury
nephrotoxic injury
immune-mediated injury
vascular disease
** structural damage to the kidneys!

causes of post-renal AKI
partial or complete obstruction of the urinary collecting system
How does Drug-induced prerenal acute kidney injury happen?
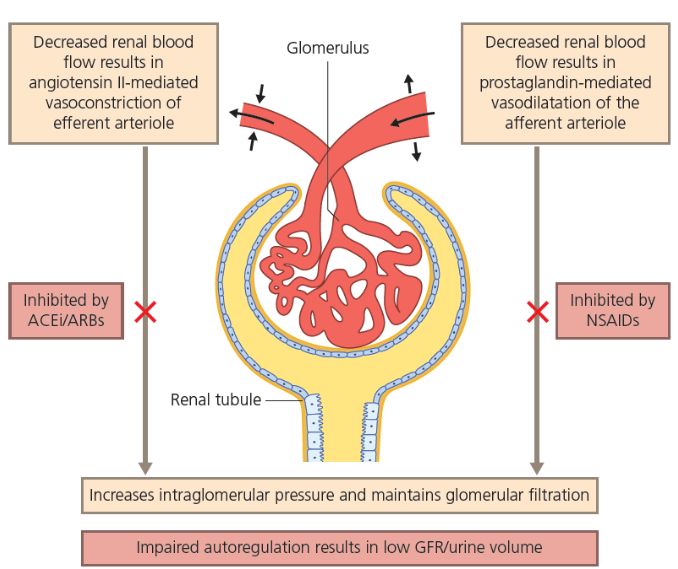
what can cause Acute Tubular Necrosis?
result of ischemic or nephrotoxic injury or a combination of both
• Trauma
• vascular and cardiac surgery
• severe burns
• pancreatitis
• sepsis
• chronic liver disease
** uncomplicated ATN is recovery over 2 to 3 weeks
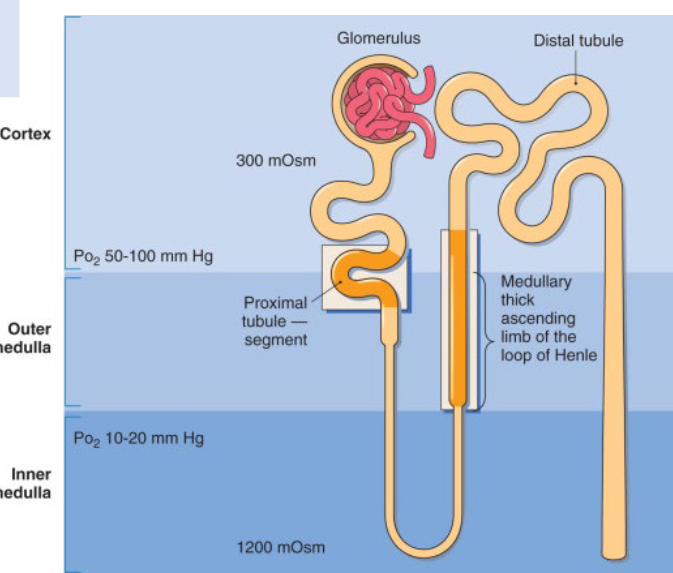
what part of the tubule is vulnerable to hypoxic injury and why?
S3 segment of proximal tubule cells and distal
medullary thick ascending limb
Countercurrent oxygen exchange leading to a progressive fall in PO2 from cortex to medulla
High tubular energy requirements for ion pumps
What happens in Acute Tubular Necrosis?
Tubular Cells death:
• Loss of brush border
• Disruption of actin cytoskeleton
• Abnormal translocation Na + K + -ATPase
• Loss of cellular polarity
Cast Obstruction
Back leak of filtered tubular fluid
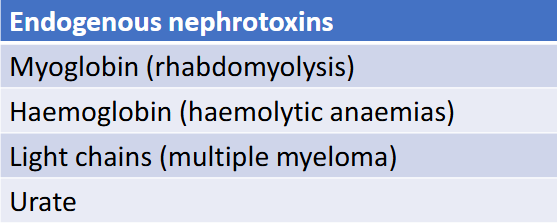
Endogenous nephrotoxins
Exogenous nephrotoxins

what caused Rhabdomyolysis and why does it cause kidney injury?
Due to muscle injury - release of myoglobin
Myoglobin filtered at glomerulus and toxic to tubule cells
Can also cause obstruction
symptom of Rhabdomyolysis
It causes red-brown colored urine (urine dipstick positive for heme but negative
for RBCs)
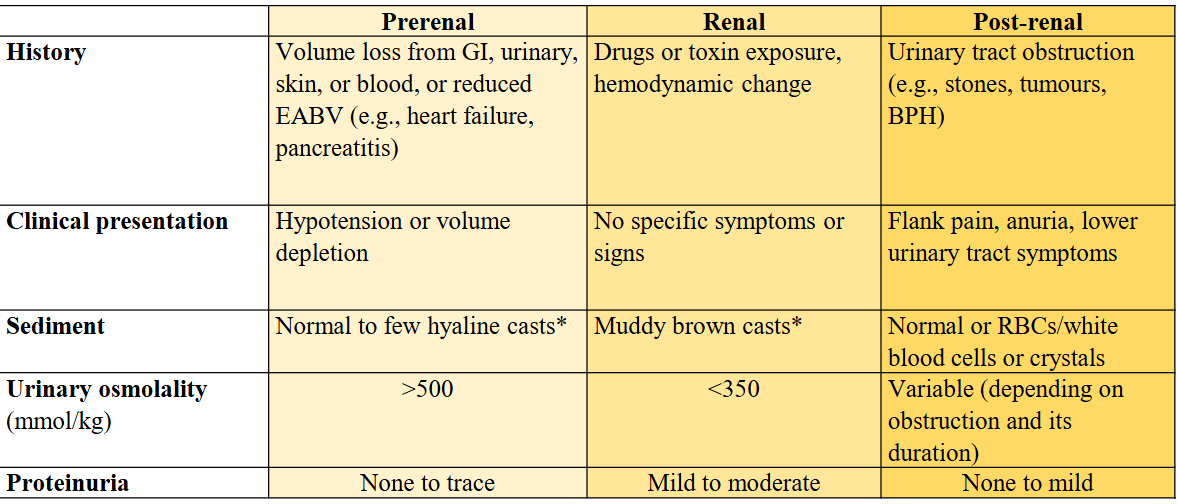
prerenal vs renal vs postrenal
Primary prevention of AKI
manage/ prevent:
hypovolaemia
hypotension
nephrotoxic drugs/ nephtoxic contrast media
sepsis
Clinical evaluation of AKI
history: look out for risk factors
Physical examination: evaluation of fluid status, signs for acute and chronic heart failure, infection and sepsis
Lab: urine output and serum creatinine, urea, electrolytes (particularly potassium), Urine analysis and microscopic examination
Imaging tests: ultrasound
AKI complications
(1)Hyperkalaemia.
(2) Other electrolyte imbalances: hyperphosphataemia, hyponatraemia, hypermagnesaemia, hypocalcaemia.
(3) Metabolic acidosis.
(4) Fluid overload (peripheral and pulmonary oedema); heart failure; lung injury; liver injury.
(5) Uraemia.
(6) Chronic kidney disease and kidney failure
Treatment of AKI
Treating any underlying cause
Temporarily stopping or reducing specific medications
Fluid and electrolyte management
Supportive measures: glycaemic control, BP control and nutrition
If urinary tract obstruction: urological intervention to re-establish urine flow
Renal replacement therapy
What patients wit AKI need renal replacement therapy?
No response to treatment with:
Hyperkalaemia
Metabolic acidosis
Fluid overload
Pulmonary oedema
Symptoms of uraemia (pericarditis or encephalopathy)