U of U PA School Intro to Neuroanatomy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are the parts of the neuron? (4)
Dendrites
Cell body + nucleus
Axon
Axon terminal
What are the parts of the axon?
Myelin sheath
Schwann cell
Node of Ranvier
Where do the body of neurons live?
In the CNS
What are the parts of the brain? (7)
Cerebrum
-Cortex (gray matter)
-Myelinated axons (white matter)
Brainstem
-Cranial nerves
Basal ganglia and thalamus
Cerebellum
What is included in the PNS? (5)
Spinal root
Plexus
Peripheral nerves
Neuromuscular junction
Motor nerve ending
How should a diagnosis be approached in neurology?
Characterize
-Sensory
-Motor
-Both
Localize
-What function is located where (CNS/PNS/both)
Differential
Diagnostic testing for differential
How do upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons differ?
Upper
-Cell body and axon reside in CNS
Lower
-Cell body in CNS
-Axon in PNS
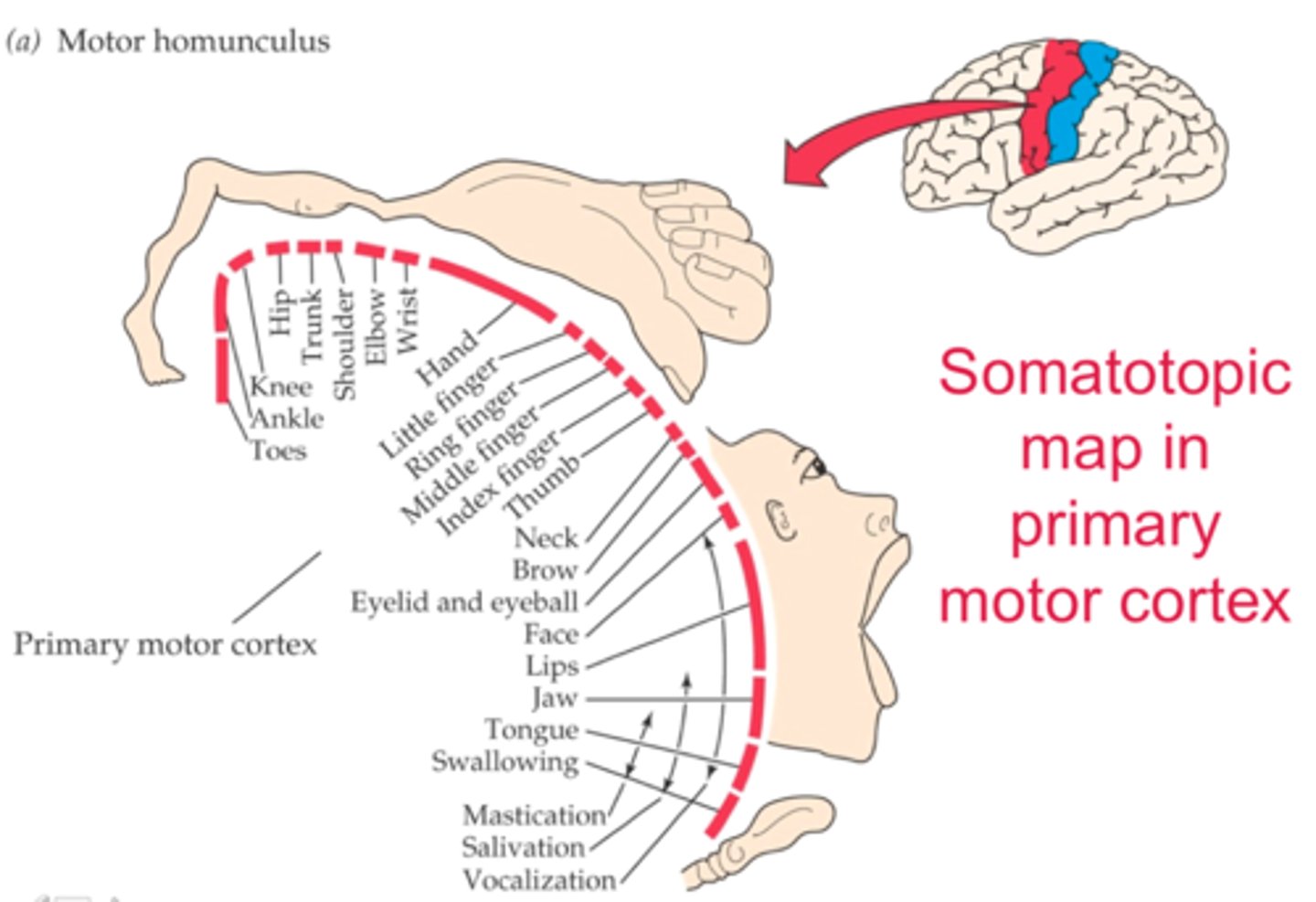
What is somatotopic organization?
Correspondence of a specific point in the body to a specific point in the primary motor and sensory cortexes for controlling motor or sensory info
Organized into homunculus
Largest areas for face and hands
What is the internal capsule?
It consists of ascending and descending tracts (motor and sensory) that connect the thalamus and the cerebral cortex.
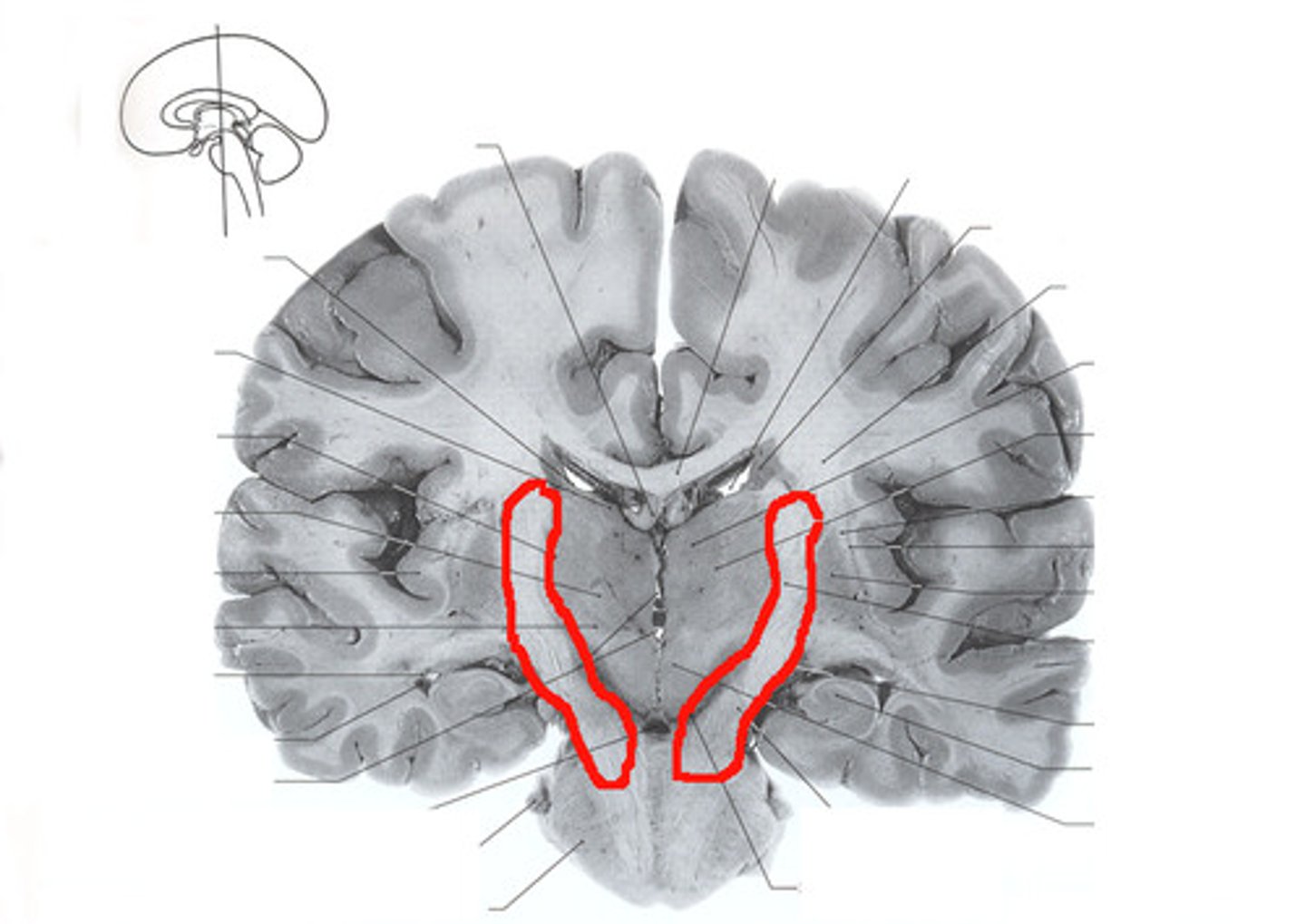
Why can smaller lesions that are deeper in the brain cause more issues?
Can interfere with internal capsule where tracts come together affecting more areas of the body
How does muscle movement occur?
Cortex -> brainstem -> spinal cord -> synapse at LMN nerve root -> plexus -> peripheral nerve -> NMJ -> muscle -> movement
How does sensory information travel to brain?
Sensory signal -> peripheral nerve -> plexus -> dorsal root ganglion at level of spinal root -> spinal cord -> brainstem -> thalamus -> cortex
What are the sensory tracts for sensory information? What is transmitted with each?
Spinothalamic tract
-Pain
-Temperature
Dorsal column
-Vibration
-Position sense
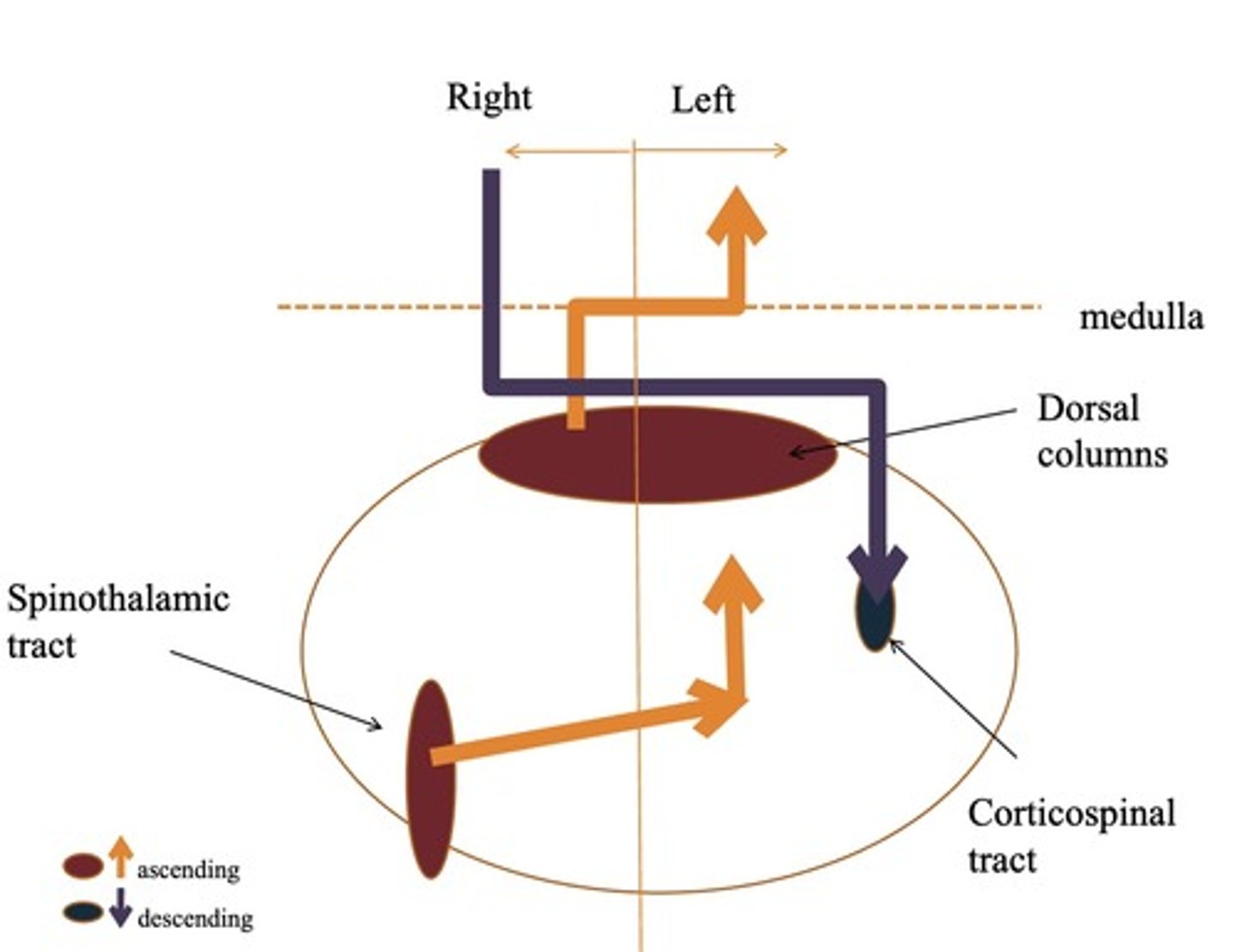
When does sensory information for each spinal tract cross to the opposite side?
Spinothalamic tract
-Crosses immediately in spinal cord
Dorsal column
-Medial lemniscal pathway - crosses in medulla
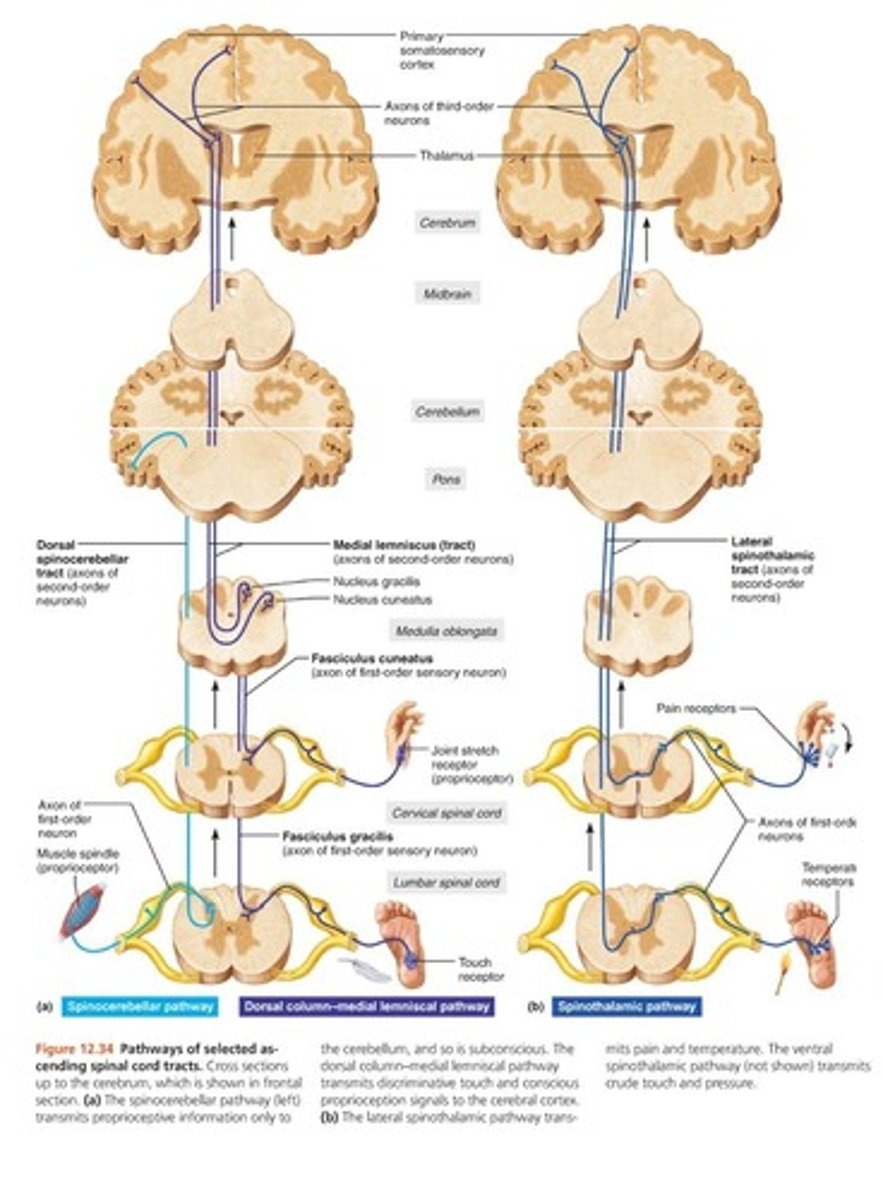
How is sensory/motor information processed in the brain?
Info from one side of body is processed in contralateral cortex
Most motor activity on one side of the body originates in contralateral cortex
Left hemisphere dominant for most people
What are the areas of the frontal lobe (4)? What do they do?
Primary motor cortex
Brocas area in left frontal lobe
-Produces language
Frontal eye fields
-Horizontal conjugate gaze
Prefrontal cortex
-Executive function
-Emotional regulation
What does a deficit in Brocas area cause?
Expressive aphasia
-Patient understands what is said but cant produce speech that is appropriate
What does a deficit in the prefrontal cortex cause? (4)
Loss of executive function
-Emotional instability
-Impulsivity
-Aggressive
-Change in social behavior, planning, and reasoning
What are the areas of the temporal lobe and what does it do?
Auditory cortex
Wernickes area in left temporal lobe
-Language comprehension
Hippocampus
-Memory
What does a deficit in Wernickes area cause?
Patients can speak but not understand
What are the language centers of the brain?
Brocas area
Wernickes area
Arcuate fasciculus
-Connects Brocas to Wernickes
What does a deficit in the arcuate fasciculus cause?
Cannot repeat what they have been told
What are the parts of the parietal lobe?
Primary sensory cortex
Sensory integration
Spatial coordinate system
What does right sided parietal lobe dysfunction cause?
Neglect
-Denial of the opposite side of space
-Constructional apraxia
--Inability to copy accurately drawings or three-dimensional constructions
What does left sided parietal lobe dysfunction cause?
Right-left disorientation
Acalculia - unable to calculate numbers
What does the occipital cortex do and what does dysfunction there cause?
Primary visual cortex
Lesions can cause homonymous hemianopsia
What does the cerebellum do and what does dysfunction there cause?
Balance and coordination
Mood/emotional regulation
Dysfunction
-Tremors
-Ataxia
What does the basal ganglia do and what does dysfunction there cause?
Regulates motor output
Dysfunction
-Hyperkinetic
-Hypokinetic
What does the thalamus do?
Relay all sensory pathways except olfactory and limbic
Regulate motor function
Maintain consciousness and alertness
What are the parts of the brainstem? What does it do?
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Motor fibers cross in medulla
-R brain controls L limb
What is the motor descending tract from brain to spine?
Corticospinal tract
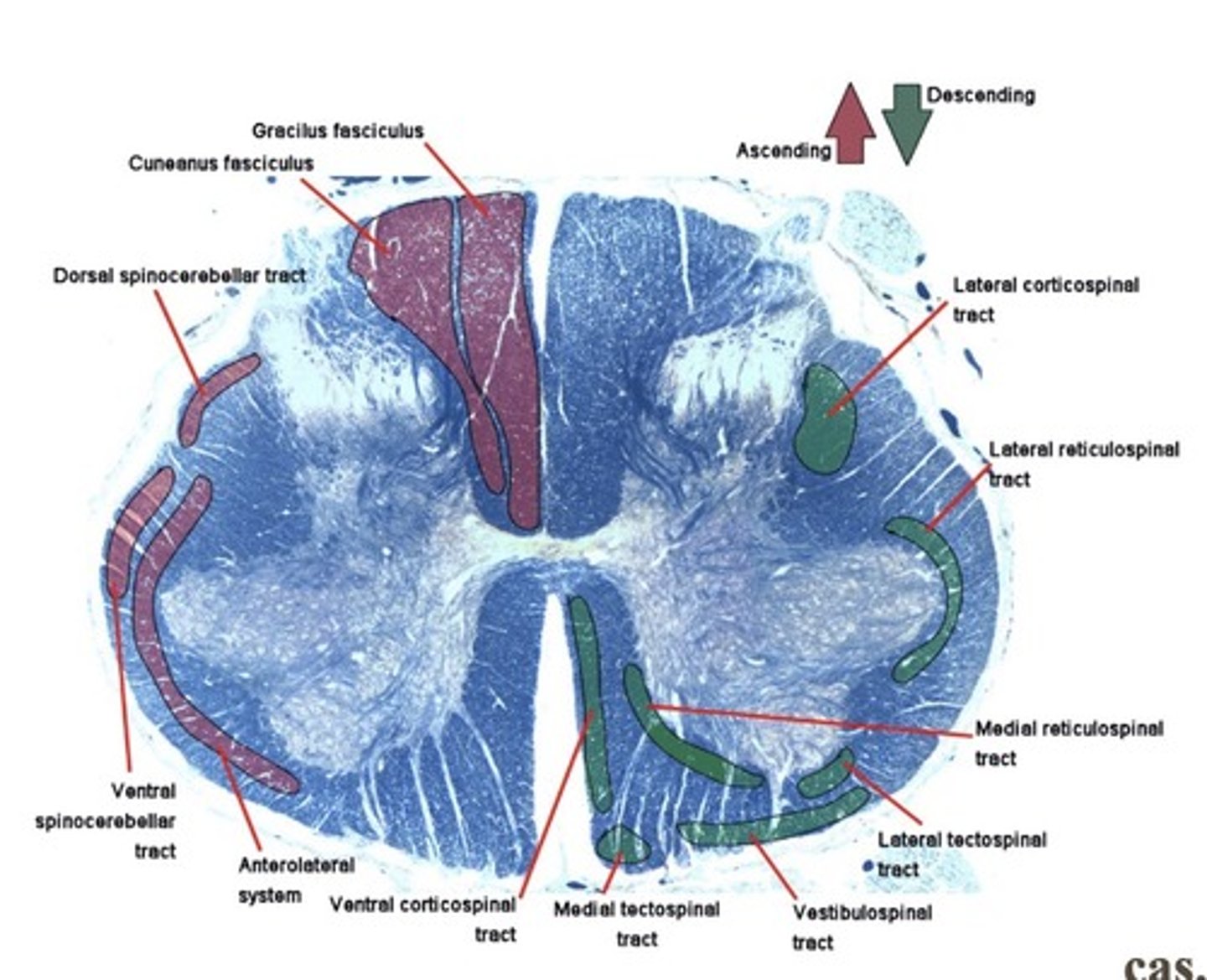
What is a focal lesion?
Limited to a single location
-1 limb/1 part of limb
-1 area of the brain
What is a cortical deficit?
Deficit only in cortex
PNS has no cortical deficits
What are the cortical signs? (5)
Aphasia
Hemineglect
Personality changes
Memory loss
Gaze preference/deviation
Area involved tends to cause multiple symptoms