8. Extracellular Accumulations
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What can accumulate extracellularly?
hyaline substances
amyloid
fibrinoid necross/ change
collagen/ fibrosis
fatty infiltration
gout/psudogout
cholesterol
calcification
heterotopic ossification
_______ substances are homogenous, eosinophilic and translucent appearance to a cellular or extracellular substance
hyaline
proteins are (eosinophilic/ basophilic)
eosinophilic
what are examples of extracellular hyaline structural appearance?
protein in lumen of renal tubules
serum or plasma in blood vessels
collagen fibers
thickened basement membranes
copora amylacea
amyloid was named for its ability to stain with what?
iodine
what is amyloid?
misfolded proteins
unfolded or partially unfolded proteins or peptide fragments capable of self replication
what are 5 causes of an amyloid appearance?
1. Propagation of misfolded proteins that serve as a template for self-replication
2. Accumulation of misfolded precursor peptides as a result of failure of
degradation
3. Genetic mutations that promote misfolding of precursor peptides
4. Protein overproduction from an abnormality in or proliferation of the
synthesizing cell
5. Loss of chaperoning molecules or other components of the protein assembly
process
how do we classify amyloid appearance?
by biochemical identity of its precursor peptide or protein
what is AL amyloidosis?
abnormal plasma cells secrete light chain fragments
AL amyloidosis is considered (primary/ secondary). explain
primary because it is produced by plasma cell dyscarsia or neoplasia
what is AA amyloidosis?
serum amyloid A protein produced by hepatocytes and bound to high density lipoproteins in circulation
it is associated with chronic inflammation
what are the classical sites of amyloid AA?
glomeruli, kidney, liver
AA amyloidosis is considered (primary/ secondary). explain
secondary, not directly produced or associated with another process
T/F: AA amyloidosis can be hereditary
true
We know that the deposition of amyloidosis disrupts and damages tissues. Amyloidosis can be systemic or localized. which is more severe?
systemic, but is independent on site of synthesis
T/F: we will only see localized amyloidosis with disease
false, may see with or without disease as severity depends on biochemical nature of fibrils/ peptide/ oligomer precursors
what is the microscopic appearance of amyloid?
extracellular
homogenous to indistinctly fibrillar, pale eosinophilic, acellular, glassy material
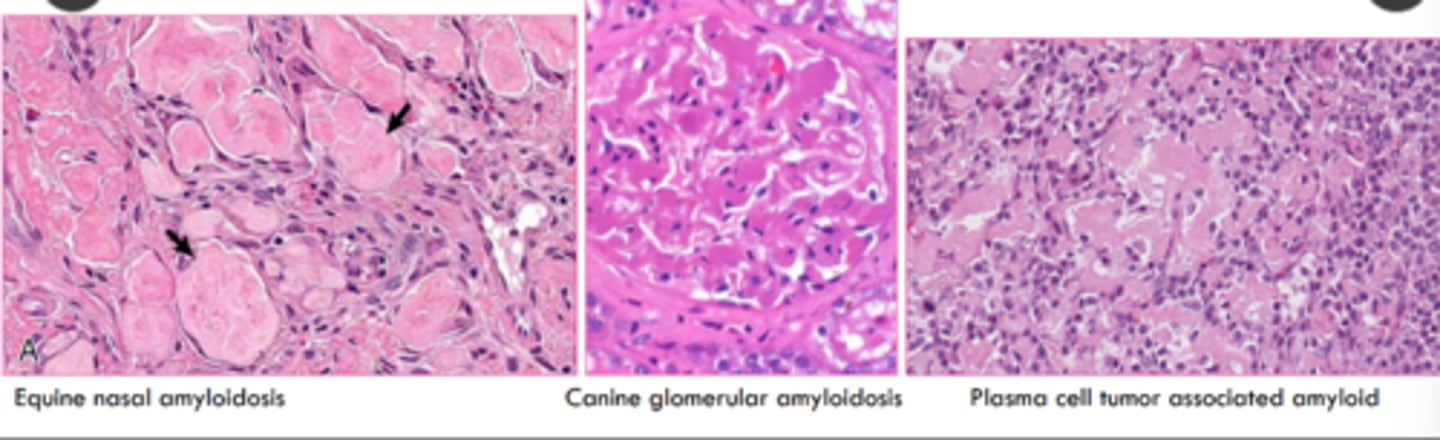
What stain is the 'gold standard' diagnostic for amyloidosis?
congo red stain
___ amyloidosis retains congophilia and apple-green birefringence after pretreatment with potassium permaganate
AL
___ amyloidosis loses congophilia and apple-green birefringence after pretreatment with potassium permaganate
AA
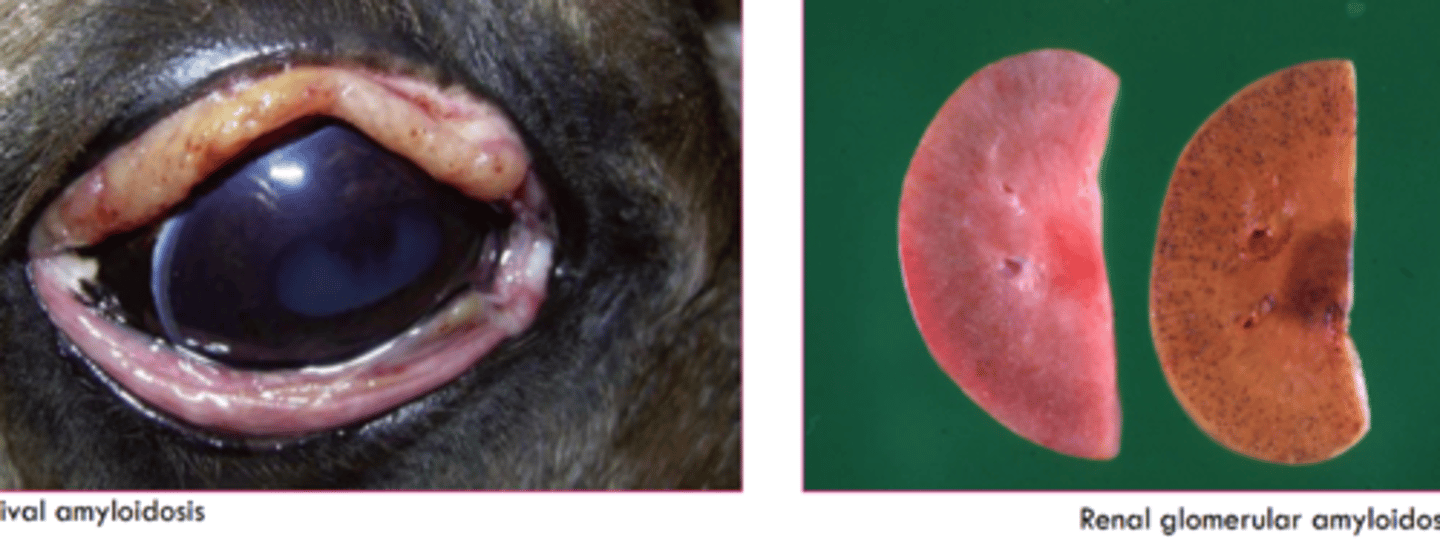
what is the gross appearance of amyloid?
firm, yellow, waxy, coalescing nodular or amorphous deposits
painted with iodine = yellow color then add sulfuric acid -> blue violet
which type of amyloid is associated with this lesion?
Amyloid AA- most common in vet med
has classical locations in renal glomeruli, liver, and spleen
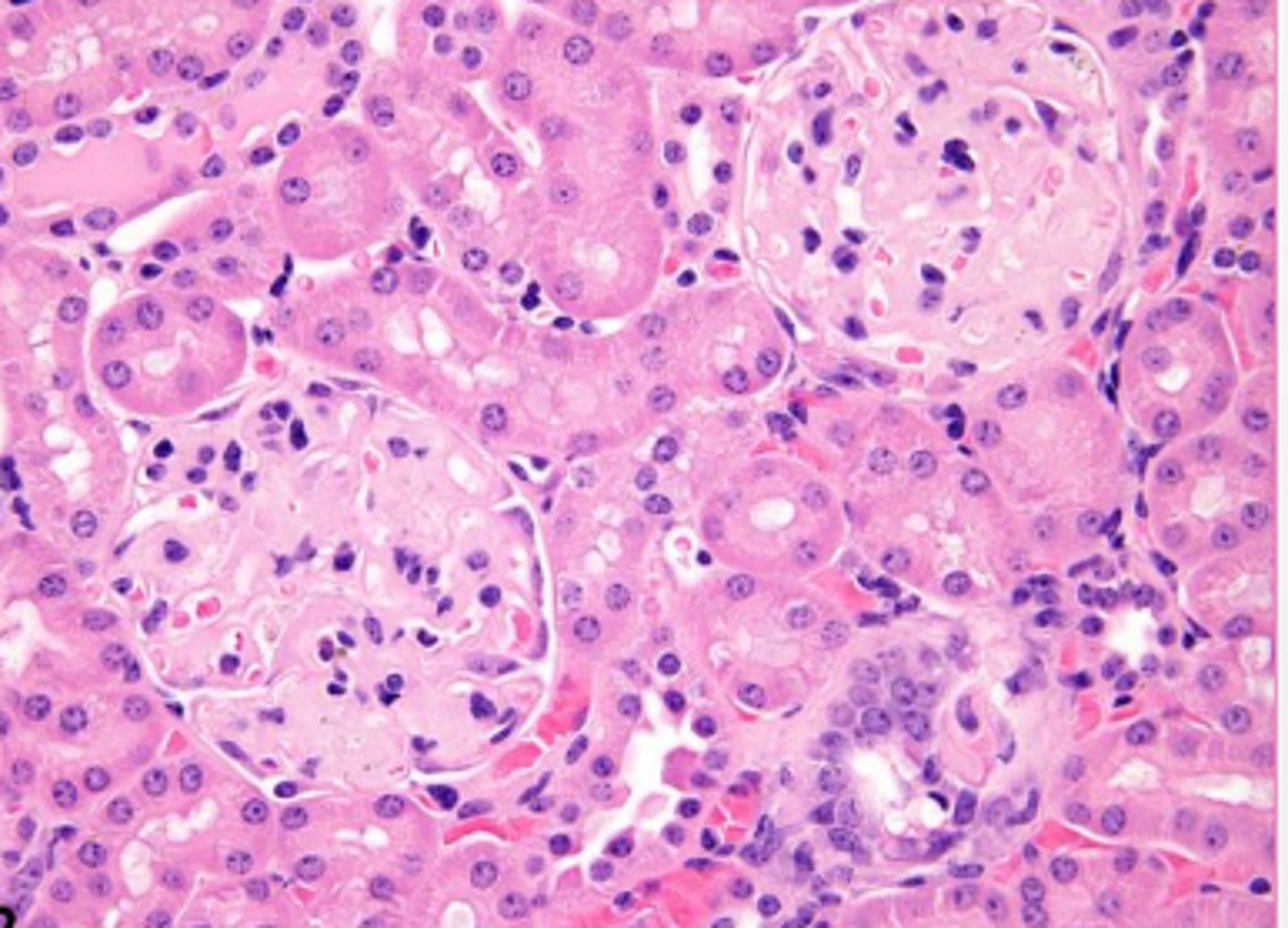
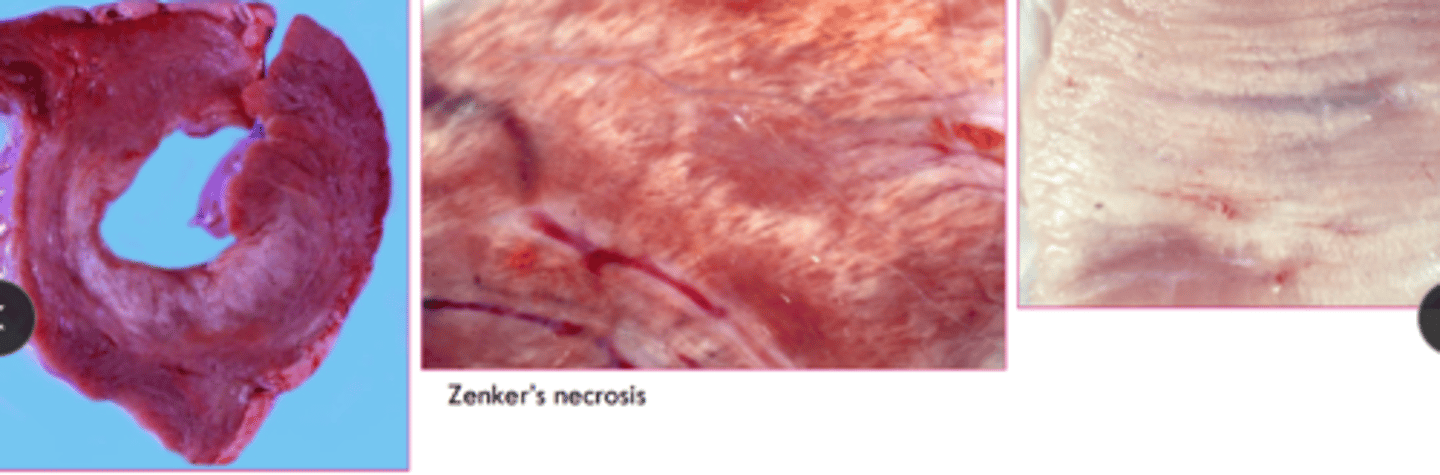
Fibrinoid necrosis/ change is what?
leakage of plasma proteins into vessel wall
fibrinoid necrosis/ change can be seen in response to:
inflammation, infection, trauma, other injury
Fibrosis is excess in _____ collagen in the __________
type I collagen
interstitium
What causes the production of fibrosis?
typically produced by fibroblasts after injury or inflammation
T/F: scarring due to fibrosis may compromise organ functino
true
what is fatty infiltration?
increased in number and or volume of adipocytes in interstitium of organ or tissue
what could cause fatty infiltraiton?
obesity
cardio or skeletal myopathies
atrophied tissue
________ is a deposition of sodium urate crystals in tissues
gout
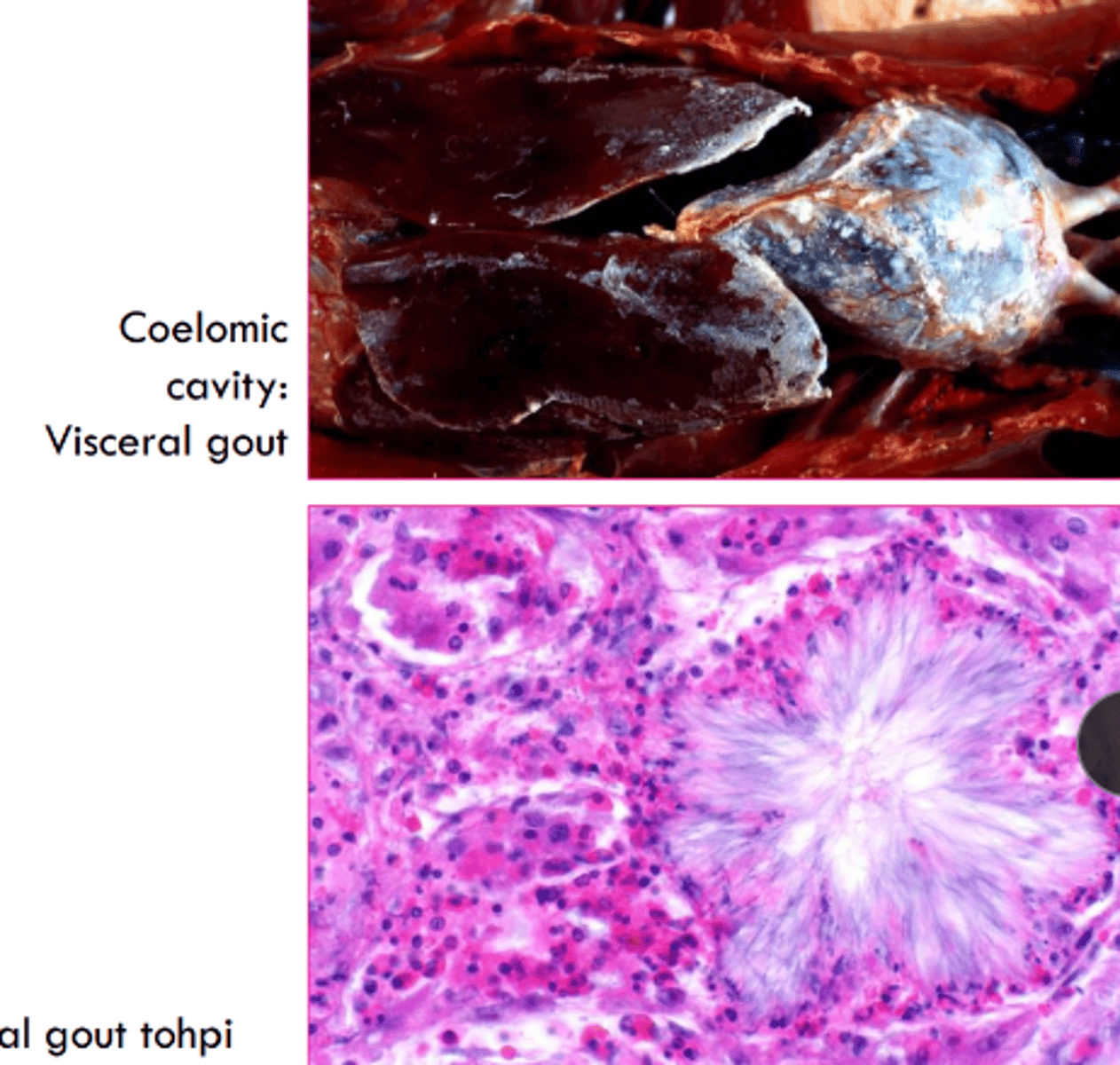
what does gout elicit in primates, birds, and reptiles?
inflammatory response with neutrophils/ heterophils and macrophages
_________ is the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in tissues
pseudogout
T/F: pseudogout is commonly reported in the dog
false, rare
where can cholesterol crystals form?
sites of hemorrhage or necrosis
why may we not see cholesterol after processing?
it dissolves and may leave acicular clefts in histologic section which attracts macrophages
____________ calcification is the deposition of calcium salts in soft tissues
pathologic aka tissues that should not be calcified normally
________ calcification is the result of hypercalcemia aka an imbalance of calcium and phosphorus
metastatic
what are the causes of metastatic calcification?
primary hyperparathyroidism
renal secondary hyperparathyroidism
hypervitaminosisD
paraneoplastic syndromes
where will see metastatic calcification microscopically?
calcium depostition in intima and tunica media of vessels
basement membranes, elastic fibers, collagen fibers
what organs will we see metastatic calcification?
lungs, pleura, endocardium, kidneys, stomach
how will metastatic calcification look microscopically?
subtle basophilic stippling
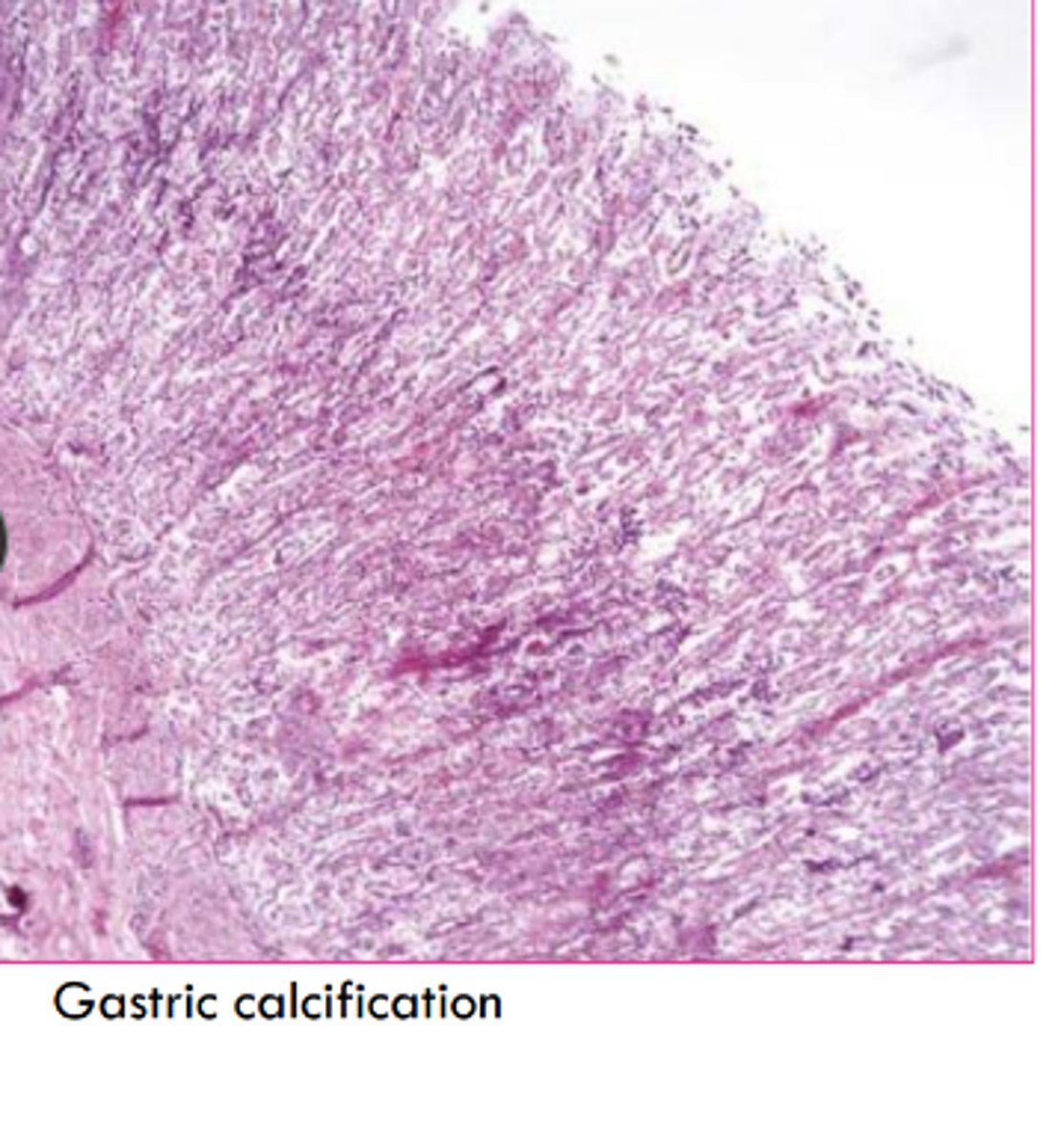
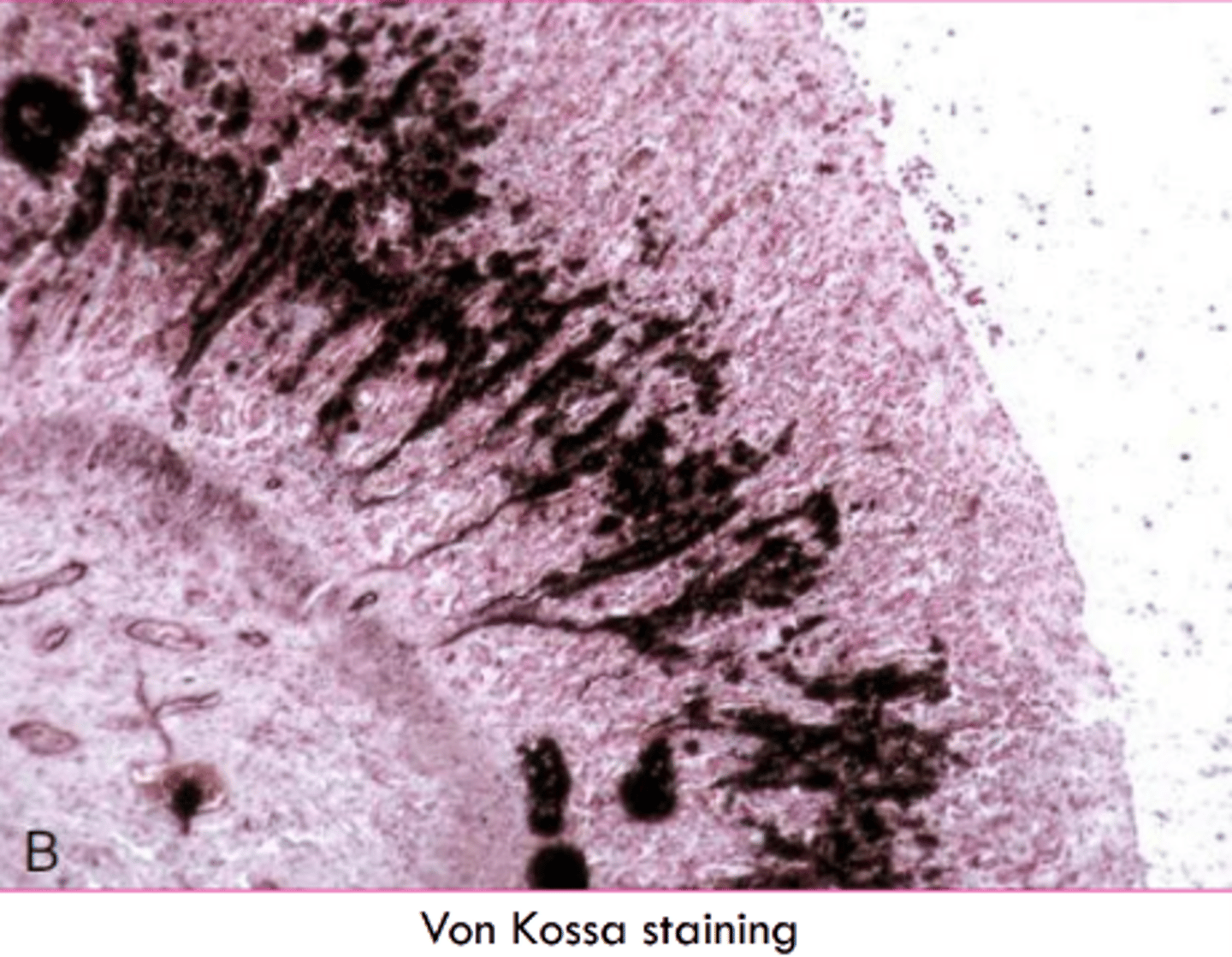
What stain do we use for calcium?
Von Kossa
silver in stain precipitates with calcium salts and stains black
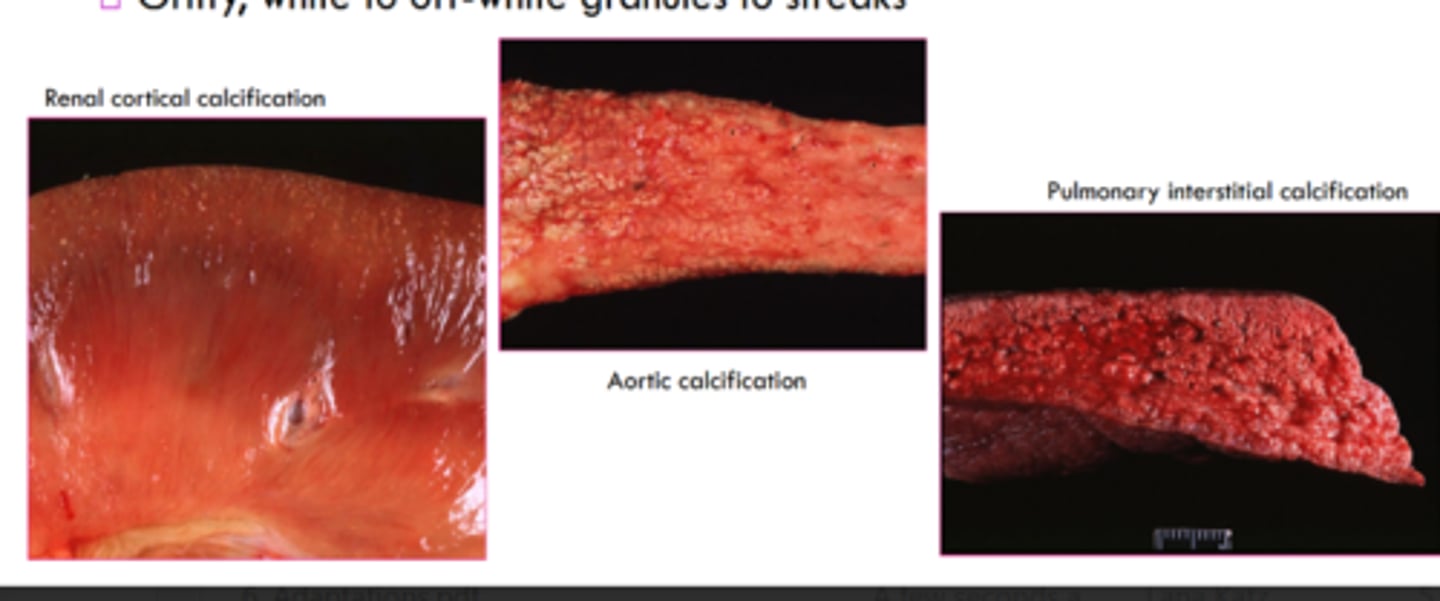
what is the gross appearance of metastatic calcifiction?
gritty, white to off white granules to streaks
_________ calcification is the calcification of dead tissue as part of necrosis
dystrophic
what is dystrophic calcification associated to physiologically?
loss of calcium balance during irreversible cell injury
what are some causes of dystrophic calcificaiton?
necrosis (striated muscle, caseous, fat)
repetitive trauma (calcinosis circumscripta)
what is the microscopic appearance of dystrophic calcification?
initially basophilic stippling in mitochondria which progresses to whole cell and extracellular tissue
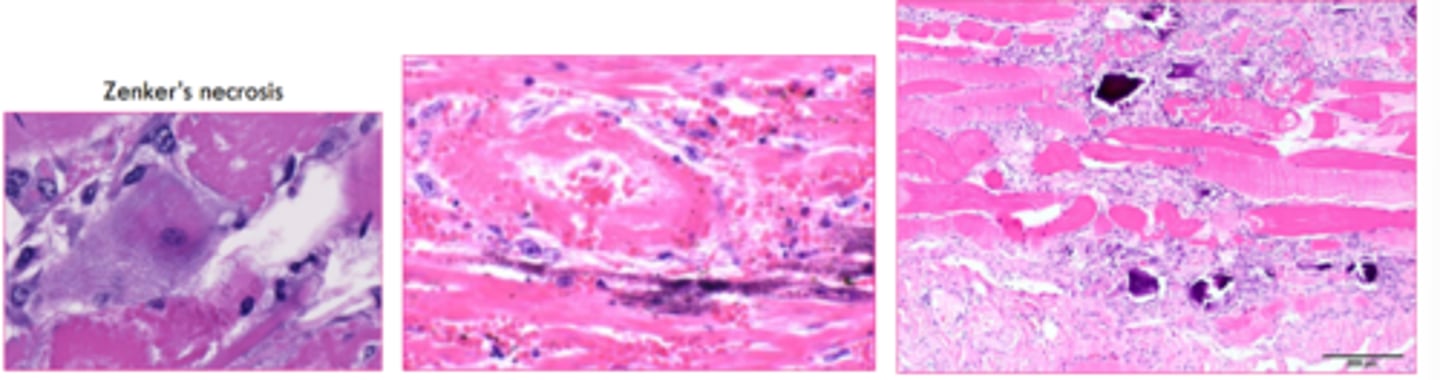
what is the gross appearance of dystrophic calcification?
gritty,, white to off white granules to streaks
to larger calcified nodules
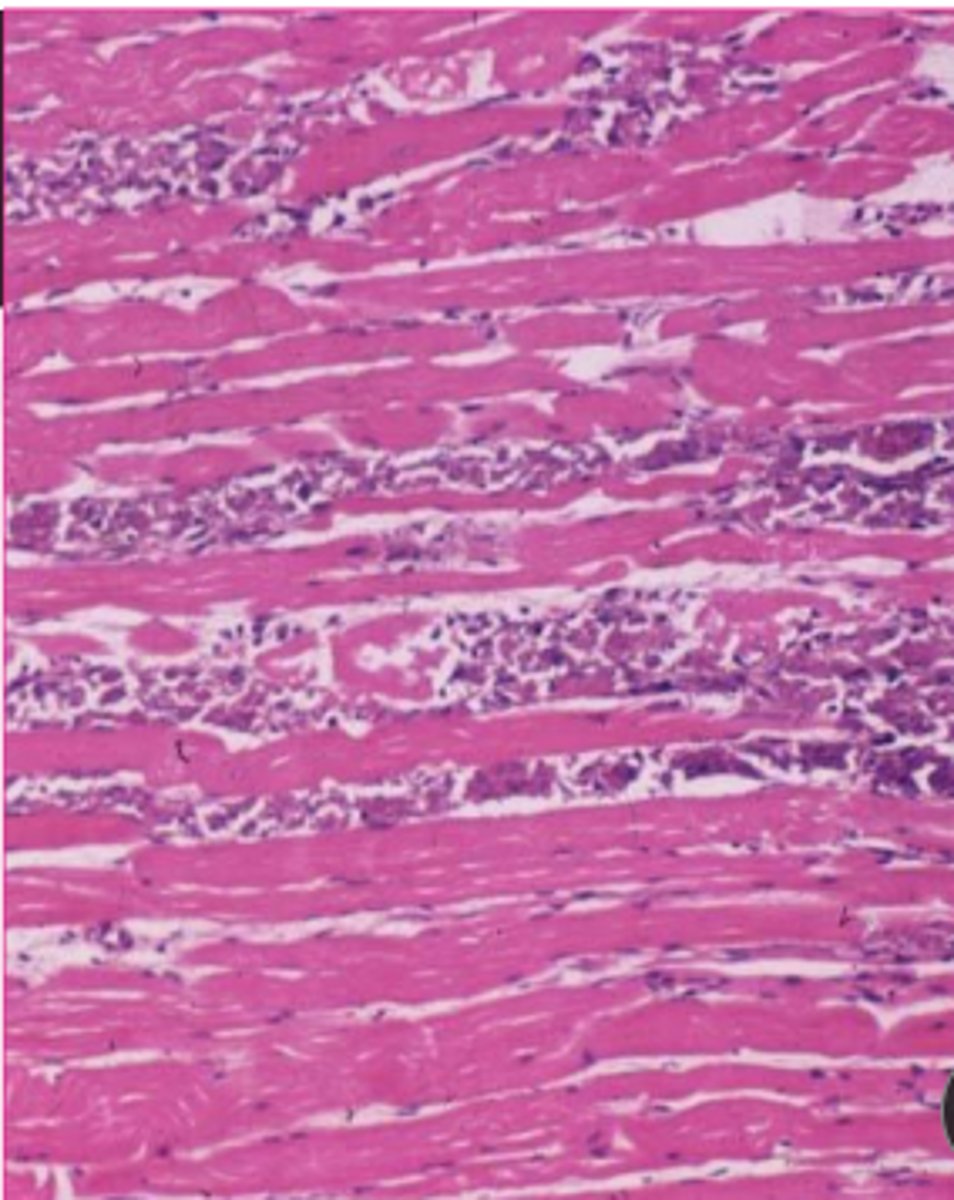
is this metastatic or dystrophic calcification?
dystrophic
______ __________ is the formation of bony tissue at an extra-skeletal site
heterotropic ossification
__________ is deposited by ________ with remodeling and mineralization
osteoid, osteoblasts
T/F: heterotopic ossification can develop into chronic lesions of soft tissue calcificaiotn
true
heterotopic ossification can be an incidental finding where?
in lungs and dura of old dogs