Exam 5 lecture 1
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
exteroceptors
sense stimuli external to the body
interoceptors
sense stimuli int the internal organs
sensory receptor
structure specialized to detect a stimulus
Sense organ
a structure that combines nervous tissue with other tissues that enhance its response to a certain type of stimulus.
Sensory adaptation
if a stimulus is prolonged, neuron firing frequency is lowered down, and you become less aware of a stimulus
thermoreceptors
detect heat or cold
mechanoreceptors
detect physical deformation of plasma membrane or tissue
photoreceptors
detect light
chemoreceptors
Detects chemicals,
odor, taste, and body fluid comp
nociceptors
detect tissue injury and damage
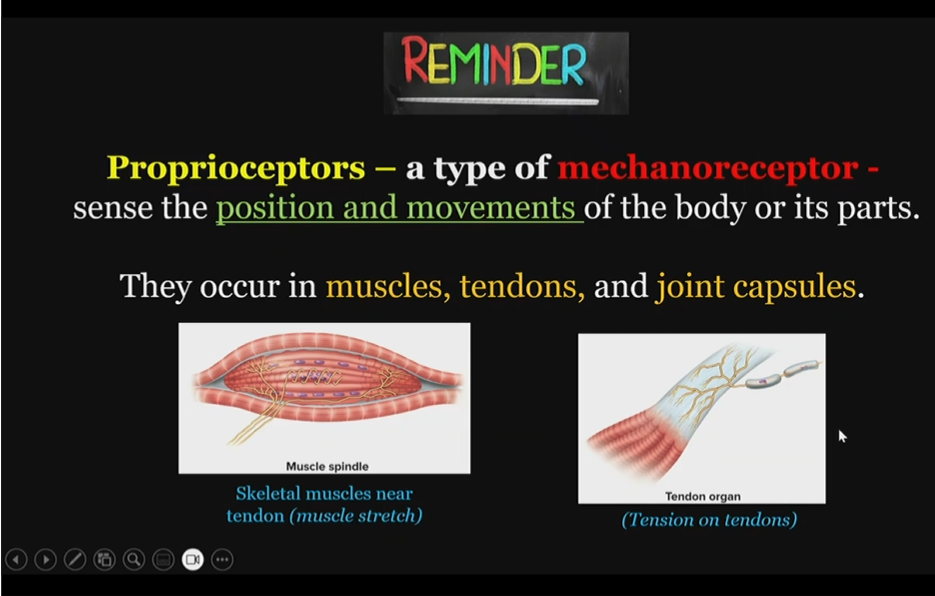
Types of mechanoreceptors
tactile (vibration touch/ pressure)
stretch (proprioceptors)
Tension/pressure change in organs (baroreceptors)
baroreceptors
type of mechanoreceptors
tension/ pressure changes in walls of blood vessels, digestive organs, bladder, and lungs
proprioceptors
type of mechanoreceptors,
detect stretches
Tactile receptors
type of mechanoreceptors,
Vibration/touch/pressure
General senses distribution in body
receptors all over the body
Special senses distribution in body
Limited to the head
5 special senses
smell taste, balance, hearing and vision.
have specialized structures fro detection
General senses
everything that isn’t smell taste, balance, hearing and vision.
touch, pain, and temperature
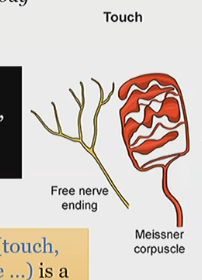
What detects touch?
What are general sense stimuli detected and signaled by?
pseudounipolar neurons

What are special sense stimuli detected and signaled by?
Specialized receptors cells receive signal and the stimulus causes Neuro transmitter release
Transmitts impulse into neurons
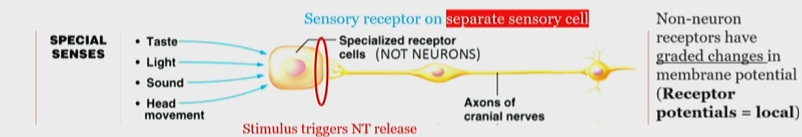
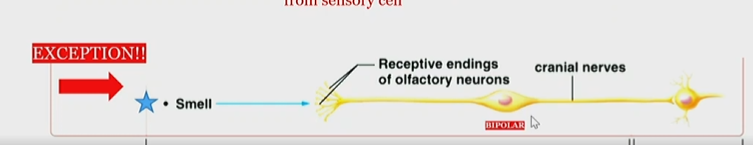
Exception to special sense stimuli detection and signaling rule
smell is received by receptive endings of olfactory neurons
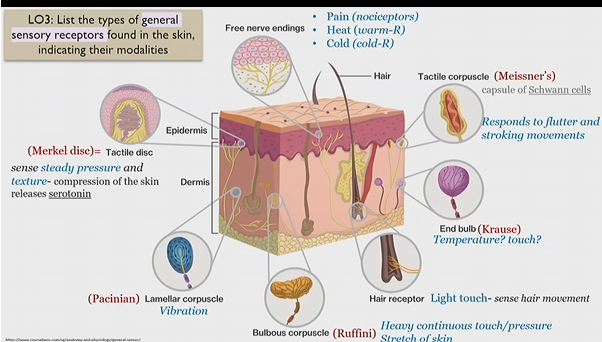
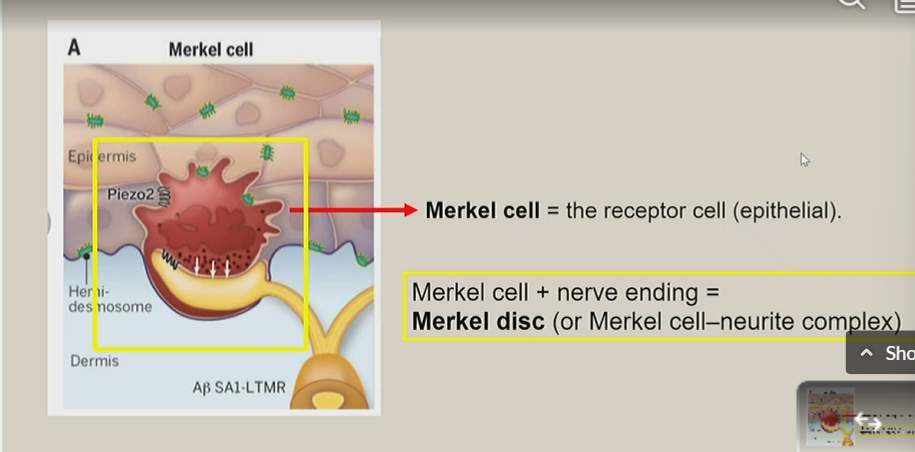
Merkel disc
Tactile disk
general sensory receptor in skin
sense steady pressure and texture
Releases serotonin upon skin compression
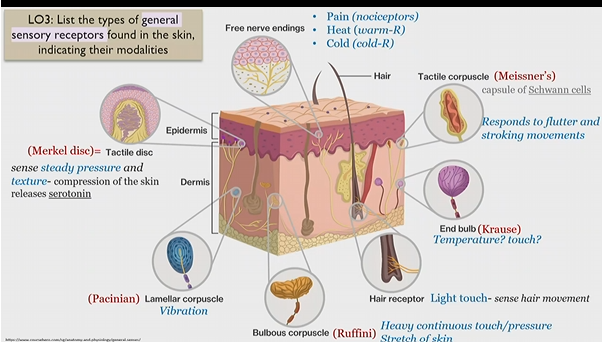
Pacinian corpuscle
lamellar corpuscle
general sensory receptor in skin
senses to vibration
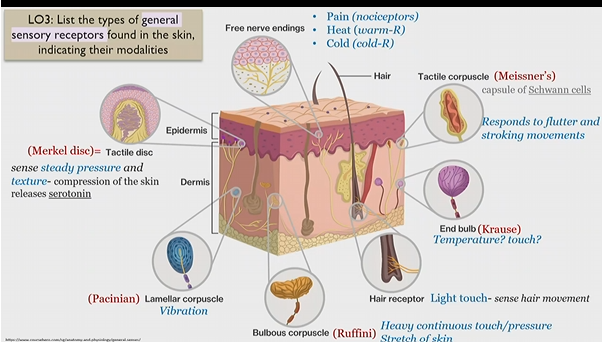
bulbous corpuscle
Ruffini corpuscle
general sensory receptor in skin
senses heavy and continuous touch/pressure
stretch of skin
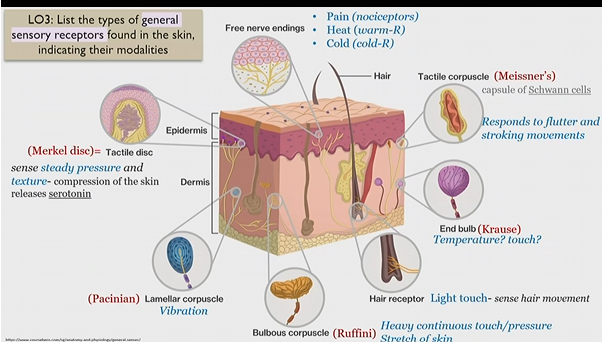
Hair receptor
light touch - sense hair movement

end bulb
krause bulb
general sensory receptor in skin
unknown, possibly temperature and touch
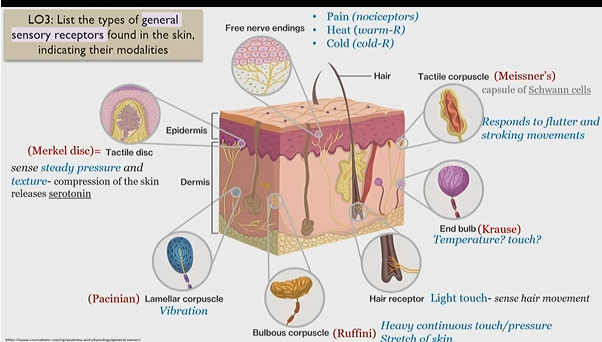
Tactile corpuscle
Meissner’s corpuscle
general sensory receptor in skin
(capsule of schwann cells)
responds to flutter and stroking movements
(massage)
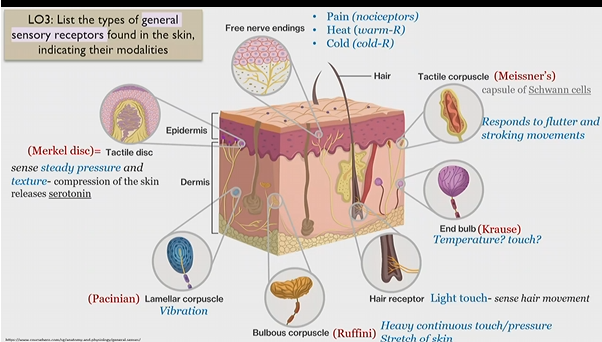
Free nerve endings
general sensory receptor in skin
Pain(nociceptors)
heat (warm-R)
cold (cold-R)
What does the merkel disc consist of?
merkel cell + nerve ending
Some of general sensory receptors have a capsules. What are they made of ?
fibroblasts
collagen fibers
ground substance
glial receptors
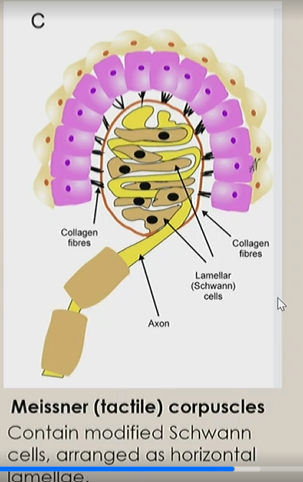
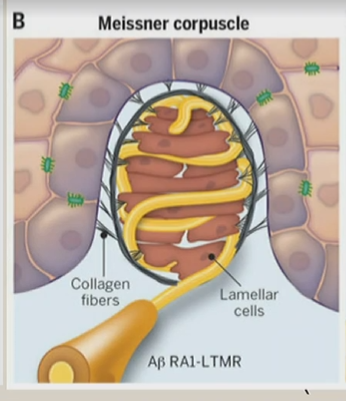
Meissner (tactile) corpuscle
type of surrounding capsule
contain modified Schwann cells, arranged as horizontal lamellae
Pacinian Corpuscle
type of surrounding capsule, has collagen fibers

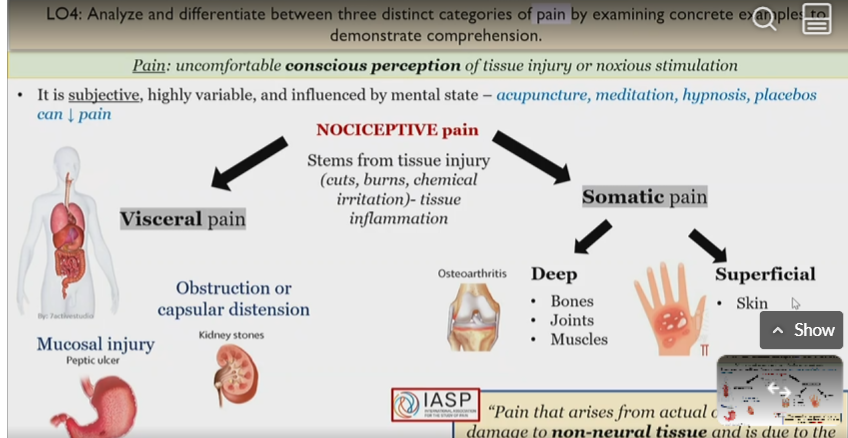
Pain
uncomfortable conscious perception of tissue injury or noxious stimulation
Nociceptive pain
Pain from tissue injury that causes injury inflation
somatic or visceral
Visceral pain
Nociceptive pain
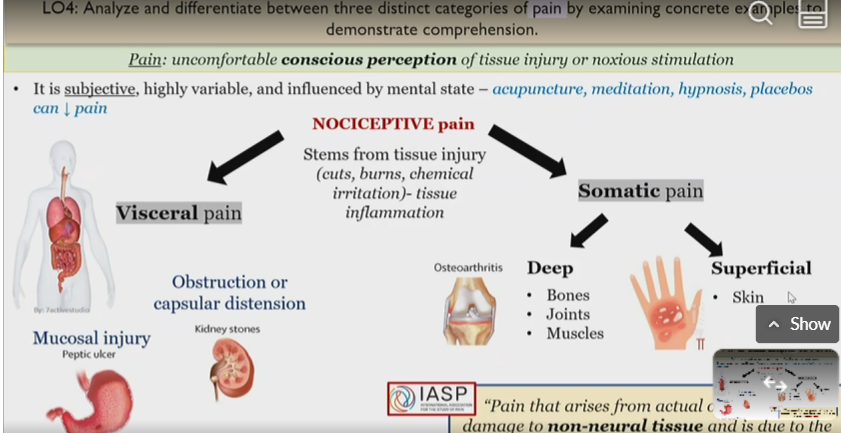
Types of visceral pain
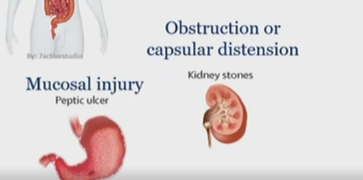
Mucosal injury example
peptic ulcer
type of visceral pain, under nociceptive
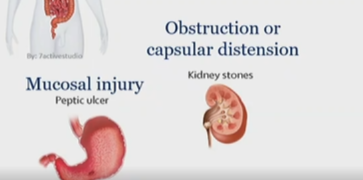
What kind of pain is a petic ulcer injury
mucosal injury
visceral, under nociceptive
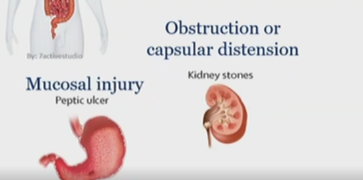
Obstruction or capsular distension example
kidney stone
visceral pain, nociceptive
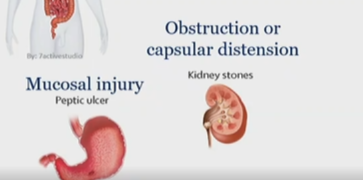
What kind of pain are kidney stones
Obstruction or capsular, visceral pain, nociceptive
Somatic pain
under nociceptive pain
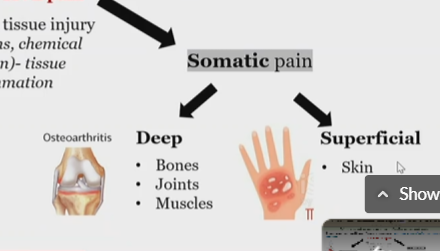
Deep somatic pain
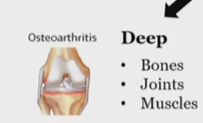
what does osteoarthritis count as
Deep, somatic pain, under nociceptive
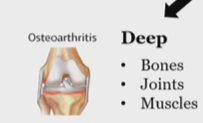
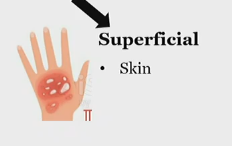
superficial pain
Somatic pain, nociceptive
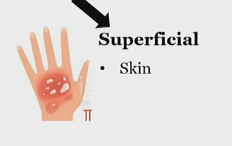
What is skin pain classified as?
Superficial somatic pain, nociceptive
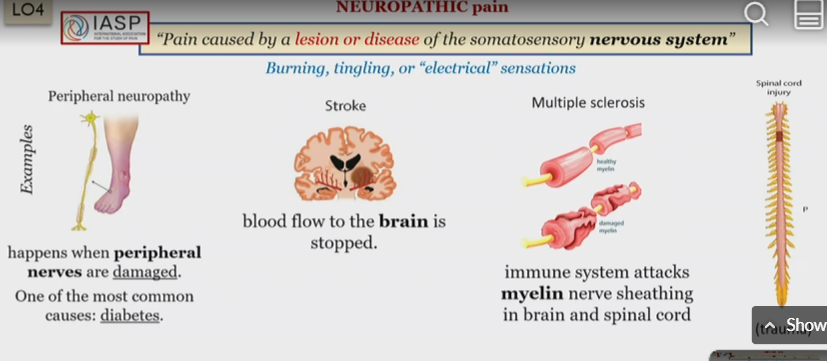
Neuropathic pain
Injury to the nervous system, lesion or disease
Tingling senstations
Types of nociceptive pain
somatic and visceral
What kind of pain is peripheral neuropathy
neuropathic
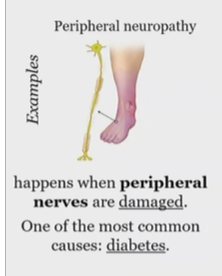
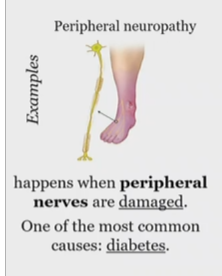
When does peripheral neuropathy happen?
when the peripheral nerves are damaged
What kind of pain is a stroke
messener's corpuscle
When does a stroke happen
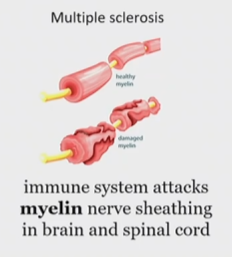
What kind of pain is Multiple sclerosis
Neuropathic pain
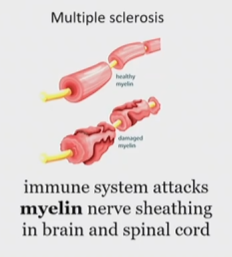
When does multiple sclerosis happen
when the immune system attacks myelin nerve sheathing in brain and spinal cord
What kind of pain is spinal cord injury
Neuropathic
What causes a spinal cord injury
trauma
Nociplastic pain
pain in which neither nociceptors are activated or neuropathy happens. Findings suggest altered nociceptor function
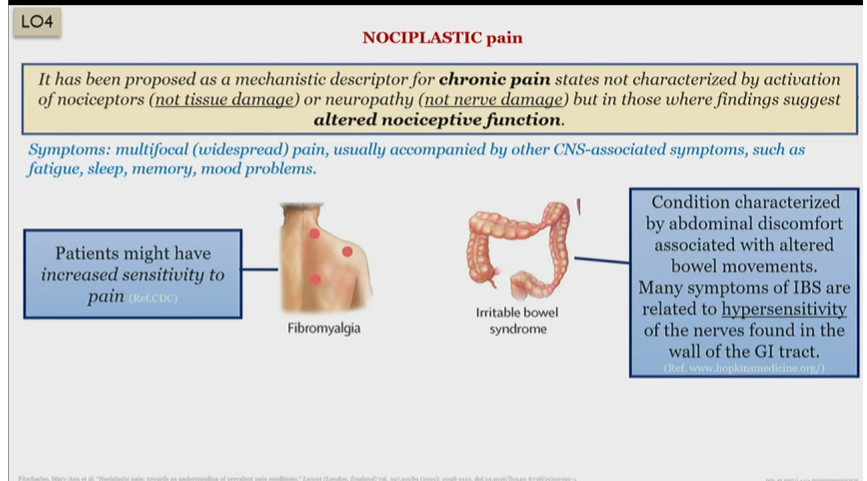
Fibromyalgia pain type
Nociplastic
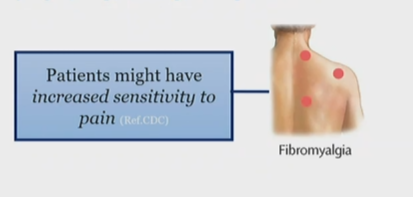
When does fibromyalgia happen?
when patients have increased sensitivity to pain
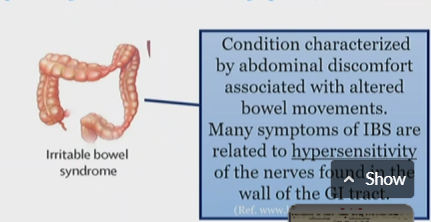
Irritable bowel syndrome pain type
Nociplastic
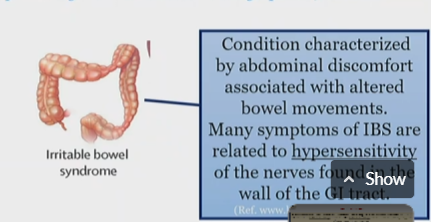
What Is IBS
abdominal discomfort caused due to altered bowel movements
related to hypersensitivity of nerves
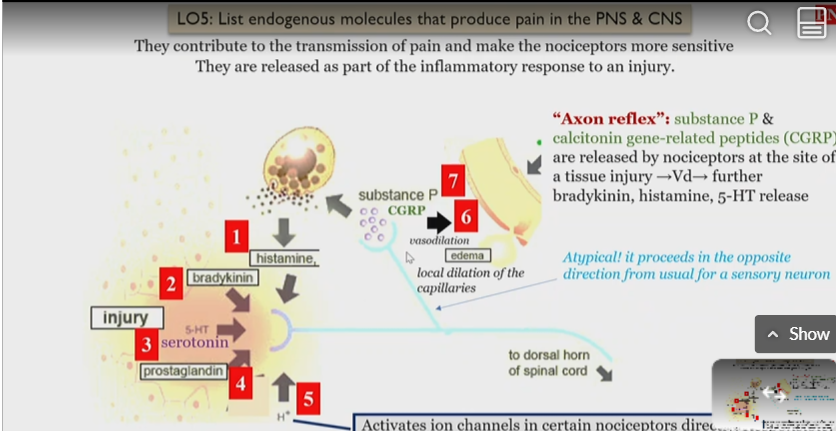
Endogenous molecules that produce pain in PNS and CNS
Release Into Nerve endings:
histamine
bradykinin
serotonin
prostaglandin
protons
Released by the nerves:
Substance P
Calcitonin gene related peptides (CGRP)

Endogenous molecules that produce pain in PNS and CNS released by nerves
Substance P
Calcitonin gene related peptides (CGRP)
Endogenous molecules that produce pain in PNS and CNS released Into Nerve endings:
histamine
bradykinin
serotonin
prostaglandin
protons
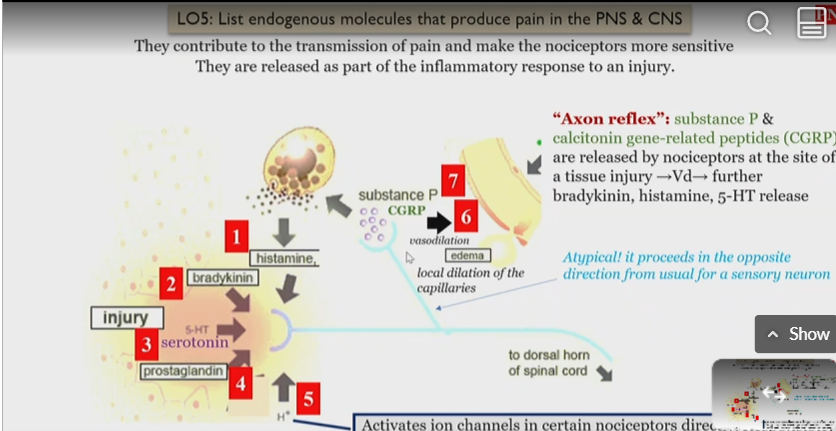
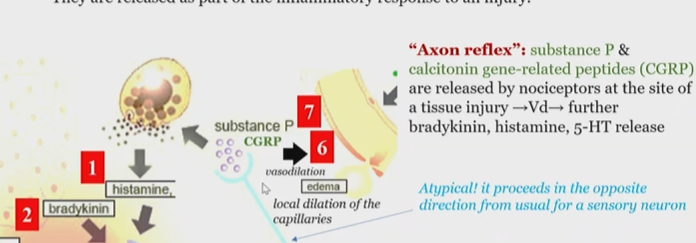
Axon reflex
causes pain in PNS and CNS
substance P and Calcitonin gene related peptides (CGRP) are released by nociceptors at the site of injury and promote
histamine
bradykinin
serotonin
prostaglandin
protons
release
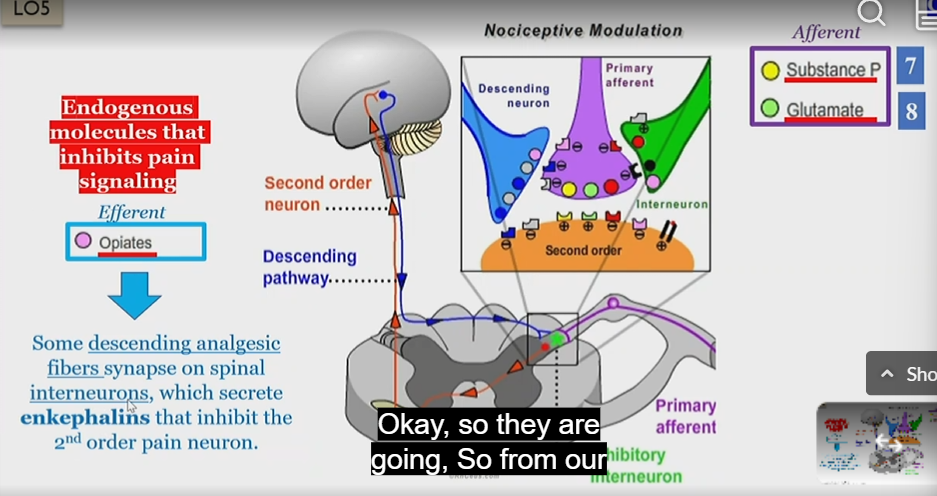
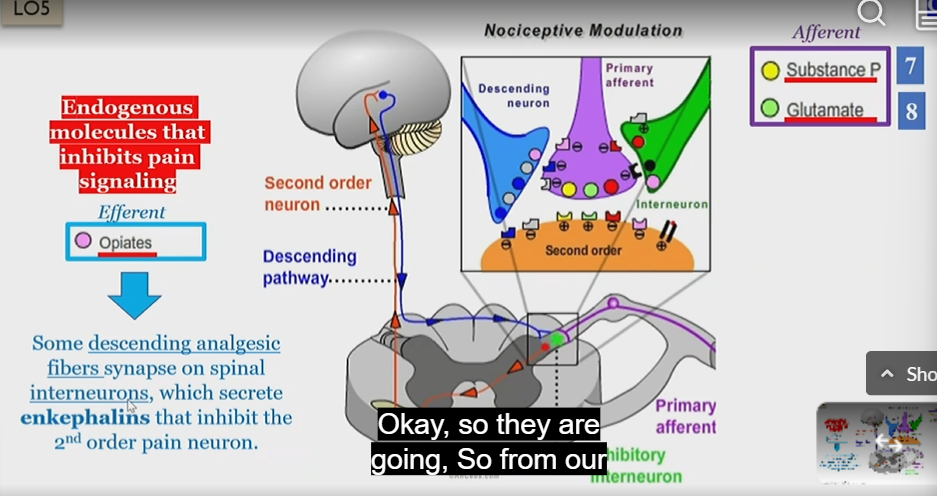
Nociceptive modulation
OPOID RELEASE TO STOP PAIN
IN CNS
Primary afferent neurons move signal from pain stimulus to spinal cord in substancia gelatinosa
Substance P and glutamate are released into second order neurons
The second order pathway connects with the descending efferent pathway which releases opiates into primary afferent neurons
These opiates are then received by the primary afferent neurons, which inhibits the release of substance P and Glutamate
Enkephalins
Opiate that inhibits the 2nd order pain neuron in CNS adaptive modiulation
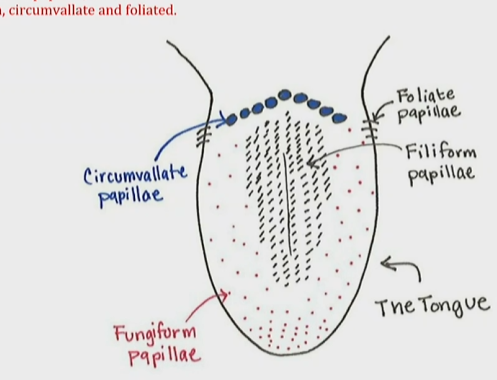
4 different types of papillae
Circumvallate
fungiform
filiform (doesn’t have receptors)
foliate
What papillae doesn’t have receptors?
filiform
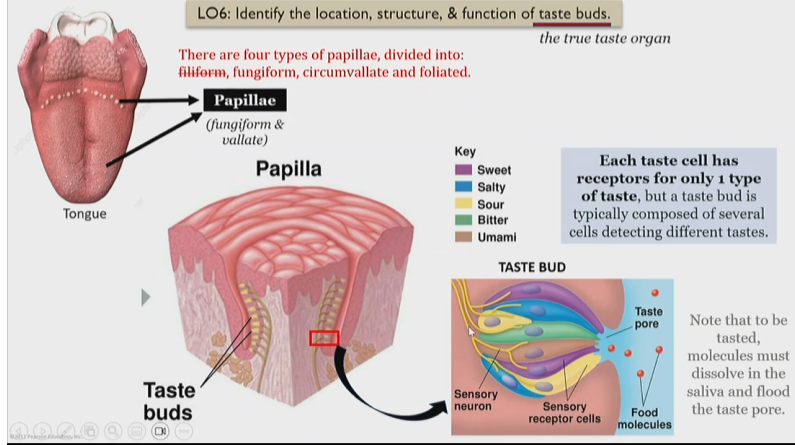
Papilla structure
Inside of papillae there are taste buds, consisting of
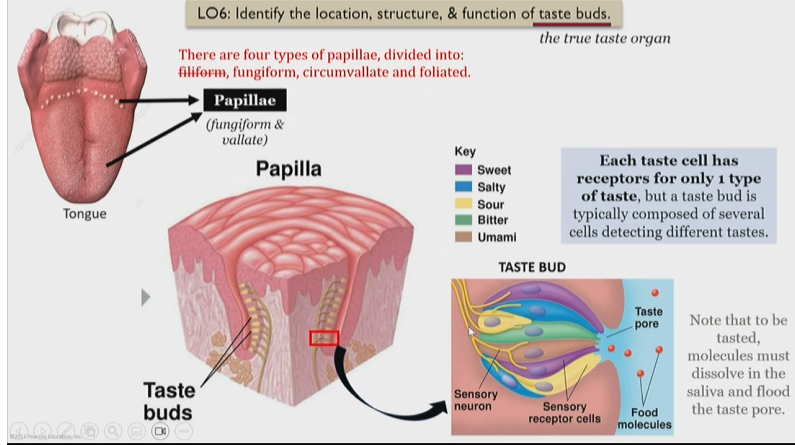
Taste buds
In papillae, groups of taste cells, and each one has receptors for only one type of taste
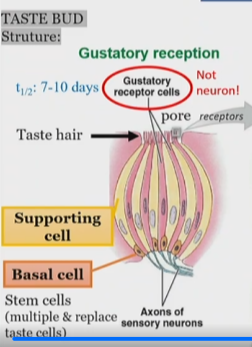
Taste bud structure
Tastants
Chemical stimuli that cause taste
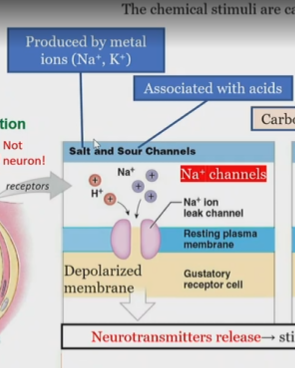
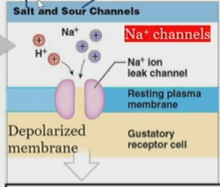
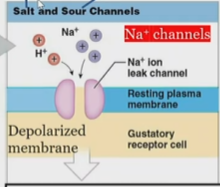
Salt and sour activation of gustatory receptors
On hairs
Ion channels cause a depolarized membrane which release neurotransmitters to stimulate sensory neurons.
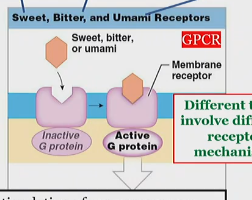
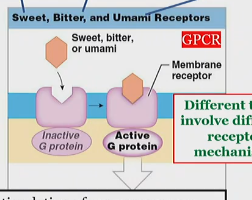
Sweet, bitter, and umami activation of gustatory receptors
On hairs,
Different tastes involve different receptor mechanisms, but typically with G proteins
which release neurotransmitters to stimulate sensory neurons.
Salt activation of gustatory receptors
Produced by metal Ions (Na+ K+)
Sour activation of gustatory receptors
associated with acids
sweet activation of gustatory receptors
associated with carbohydrates
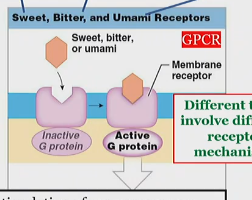
bitter activation of gustatory receptors
associated with spoiled foods and alkaloids
like nicotine and caffeine
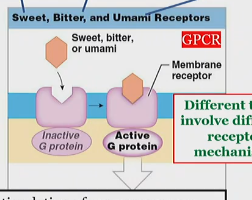
umami activation of gustatory receptors
produced by aas like aspartic and glutamic acids
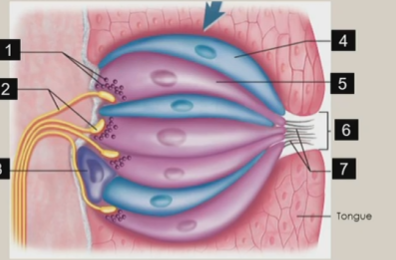
Taste pores
contains taste hairs
CN VII
facial nerve
anterior 2/3 of tongue

CN IX
Glossopharyngeal nerve
posterior 1/3 of tongue
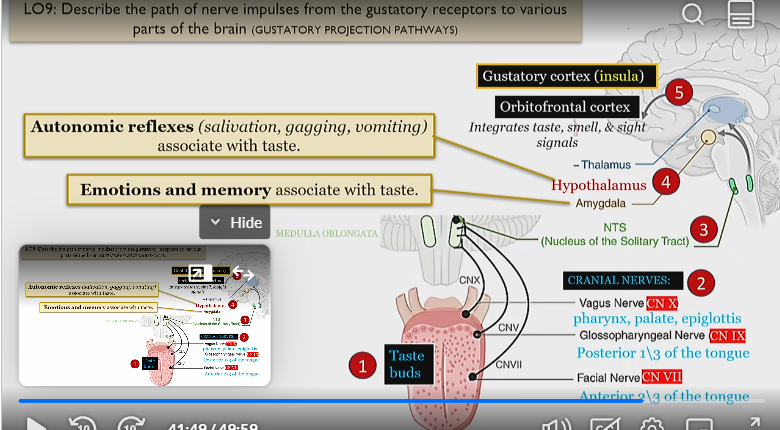
CN X
Vagus nerve
covers pharynx, palate and epiglottis
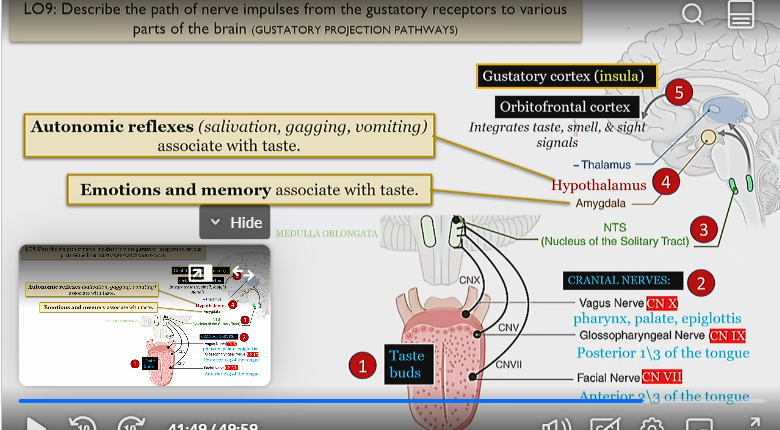
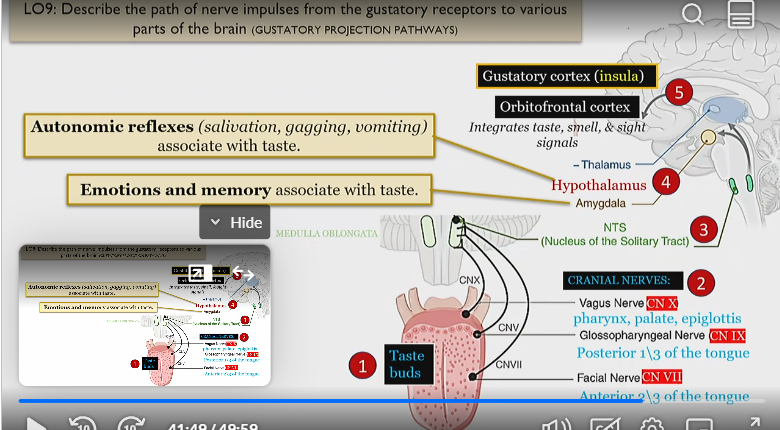
Process of nerve impulses from gustatory receptors to different parts of the brain
Taste buds wire to CN VII, IX, and X.
This information travels to the medulla, in which it travels to the NTS (nucleus of the solitary tract
This then wires to the hypothalamus (which controls autonomic reflexes with taste) like salivating, gagging and vomiting. Also processed by amygdala which controls the emotion and memory of a taste
Then goes to the cortex, in which the gustatory cortex, which processes taste is activated,
as well as the orbitofrontal cortex, which integrates taste smell and sight signals
orbitofrontal cortex
integrates taste smell and sight signals ,
in the cortex, last step of gustatory implementation
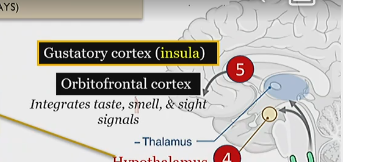
gustatory cortex
processes taste
in the cortex, last step of gustatory implementation
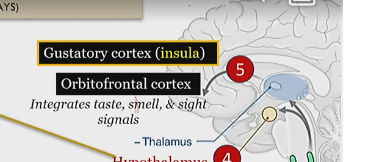
Solitary tract
3rd step of gustatory implementation
series of sensory nuclei that form a vertical column of grey matter in the brainstem

Do taste receptor cells generate Action potentials upon stimulation?
No, they generate receptor portentials
Do plasma membranes of microvilli contain receptor sites that bind selectively with chemicals in saliva?
yes
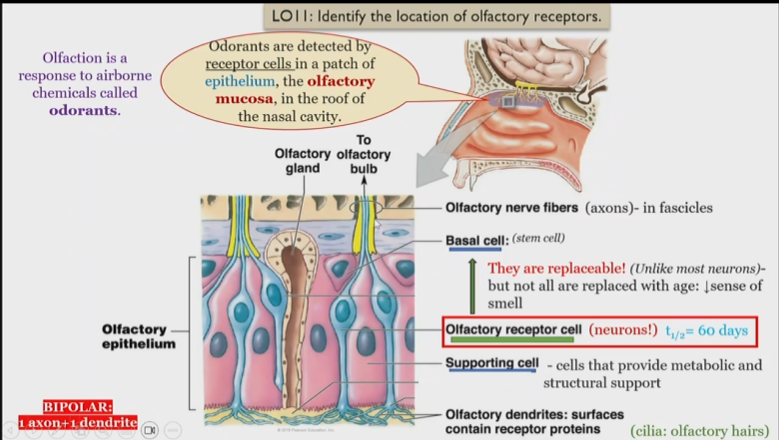
Structure of olfactory system
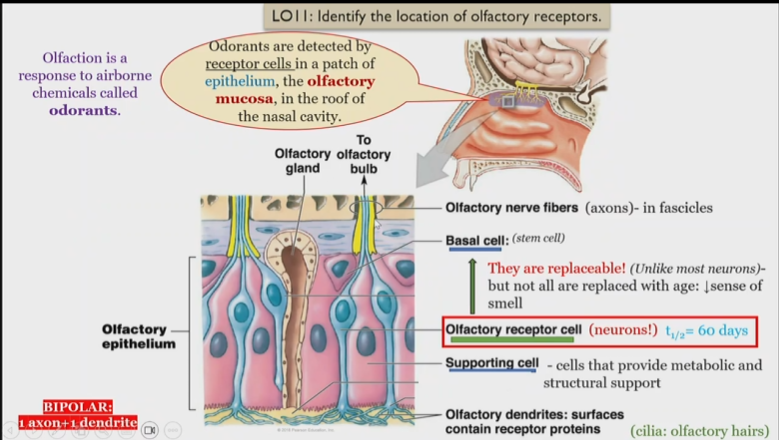
Odorants
detected by receptor cells in the roof of the epithelium of the nasal cavity
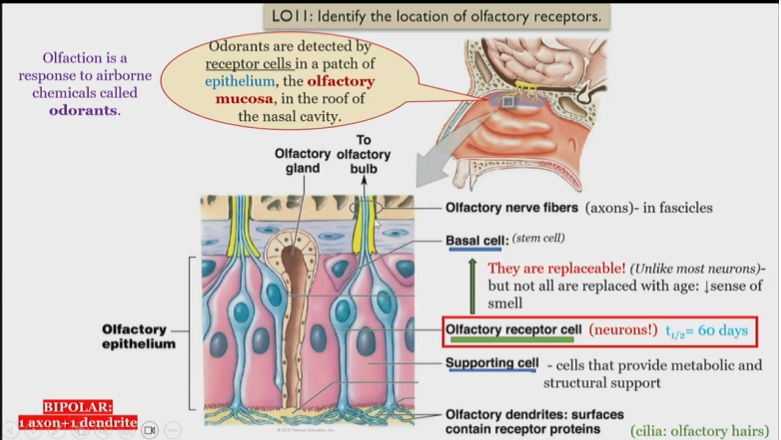
Olfactory dendrites
surfaces contain receptor proteins, detect and send singnals to olfactory receptor cells
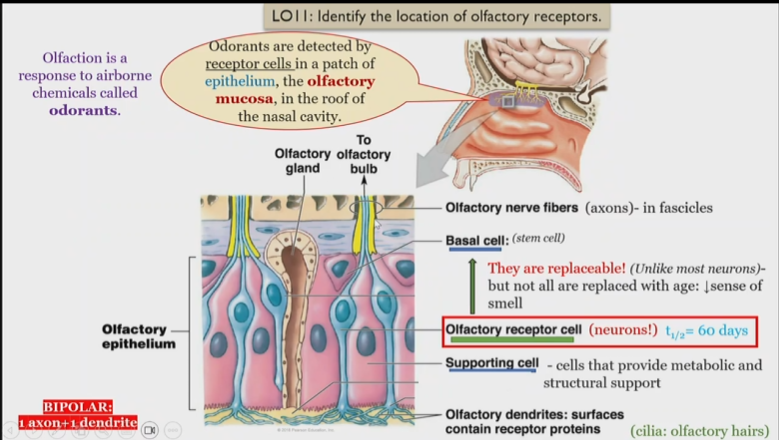
olfactory receptor cells
Neurons, receive information from olfactory dendrites, and send to olfactory nerve fibers
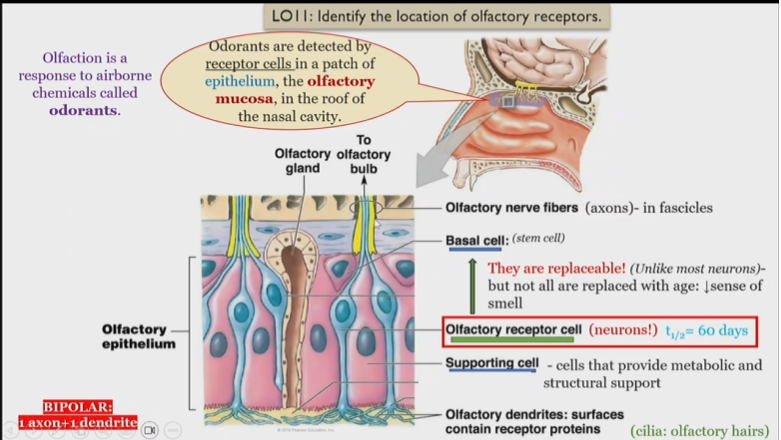
What is unique about olfactory receptor cells
They are replaceable, but not all are replaced with age, leading to a loss of smell
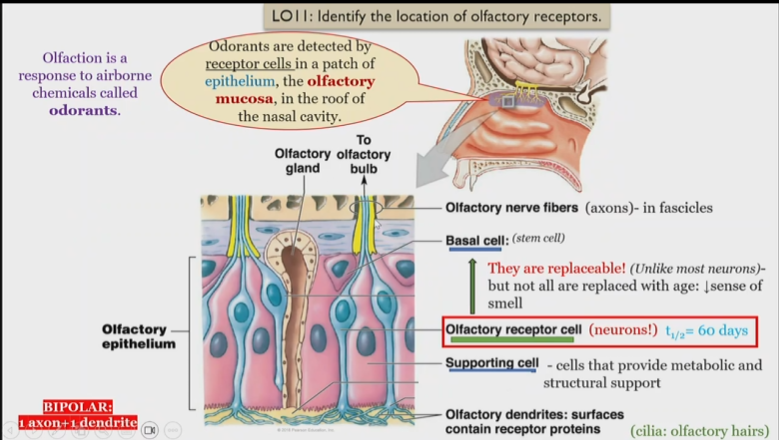
Olfactory nerve fibers
in fascicles, receive information from olfactory receptor cell
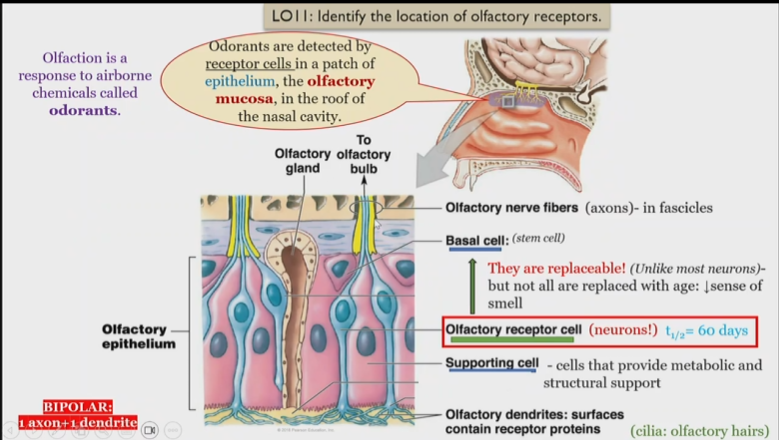
Olfactory fascilces
consists of Olfactory nerve fibers receive information from olfactory receptor cell
as a whole all fascicles make up the olfactory nerve
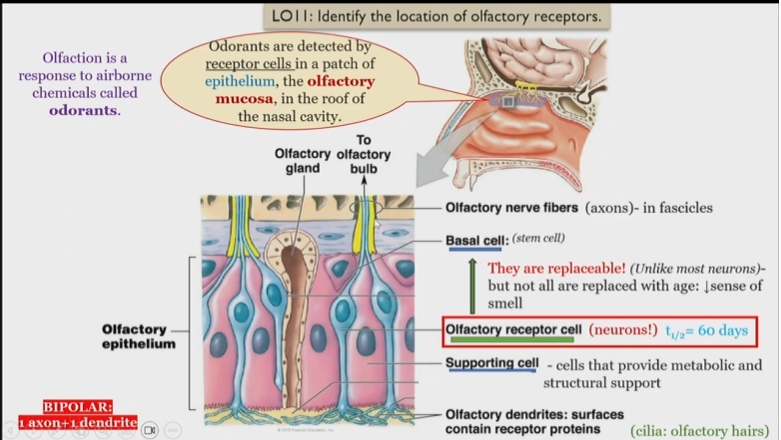
CN I
Olfactory nerve, made of fascicles
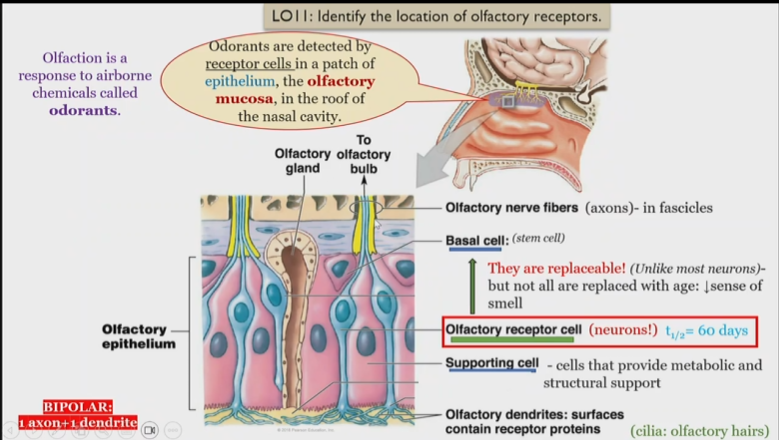
Olfactory epithelium
Consists of basal, olfactory receptor, and supporting cells
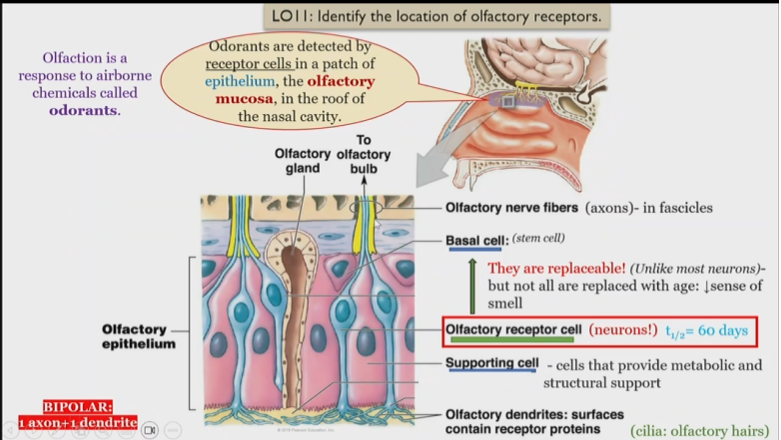
Olfactory mucosa
Contains olfactory dendrites, detect smells