bi 114 - lecture 21
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Gastric mucosa
Mucosa that lines the stomach.
Secretes mucus, bicarbonate, gastric acid, histamine, pepsin, gastin, and more.
Normal oral cavity flora include…
…streptococcus, lactobaccilus, Peptostreptococcus, Veillonella, diptheroid.
Dental plaque begins as what?
Biofilm. The bacteria undergoes metabolism and produces acids that can dissolve tooth enamel.
Dental caries lead to what?
Tooth decay
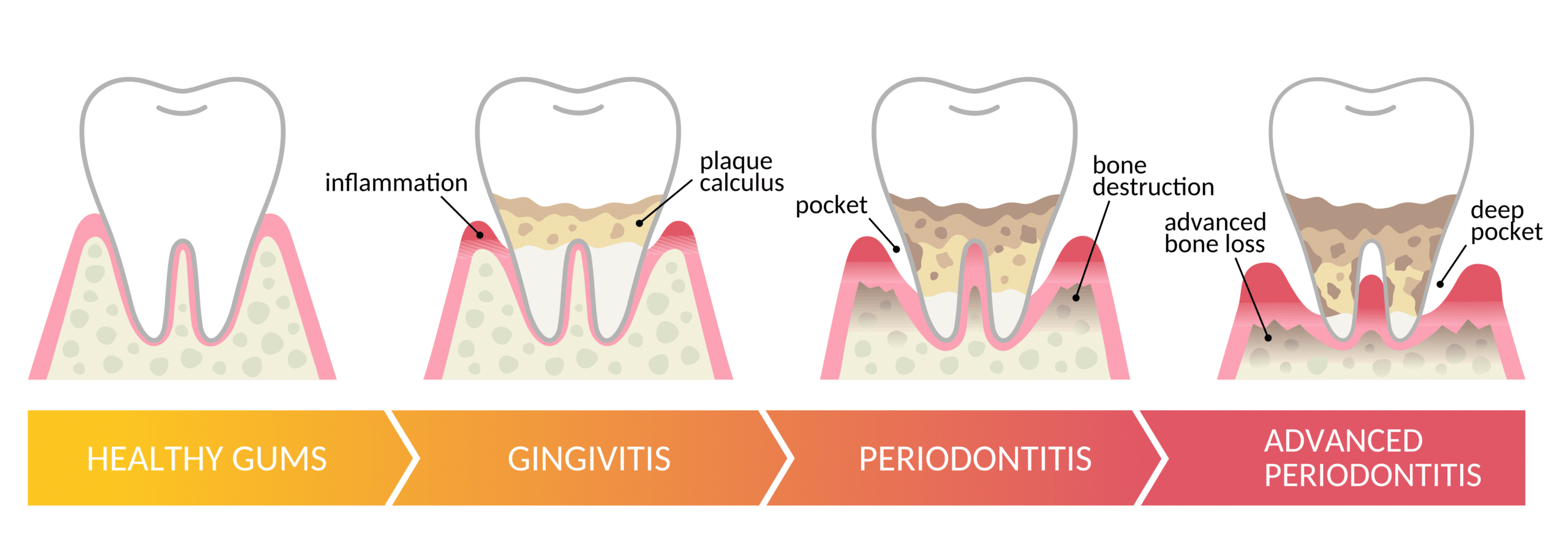
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums
Periodontal disease
Advanced inflammation causing the gums to bleed and pull away from the teeth.
Caused mostly by P. GINGIVALIS
what causes thrush?
this disease is also called oral candidiasis, so it's a FUNGAL disease.
caused by the yeast strain Candida albicans.
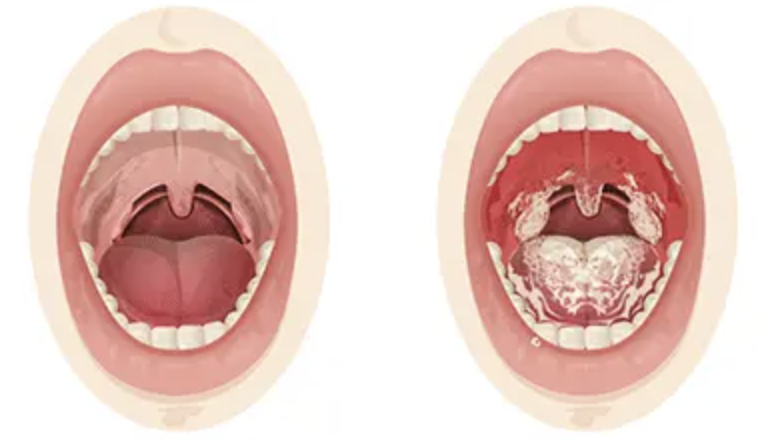
What does thrush look like?
White coating resembling cottage cheese on the tongue and inner cheeks
In whom is thrush usually seen?
Newborns and patients taking antibiotics
How is thrush treated?
Anti-fungal medications, mouthwash, h2o2 as oral rinse
How many categories of diarrhea are there?
4
Osmotic diarrhea
INTESTINAL osmolarity > internal osmolarity, causing water to leave the cells.
Pathogens that prevent nutrient absorption can cause…
…osmotic diarrhea.
Secretory diarrhea
Increased ion secretion causes electrolytes to leave, leading to imbalance.
Pathogens that cause ion secretion cause…
…secretory diarrhea.
Inflammatory diarrhea
Inflammatory cytokines damage mucosal cells and prevent absorption of nutrients and water.
What bacteria are common causes of inflammatory diarrhea?
Shigella and salmonella are common causes of inflammatory diarrhea.
Motility related diarrhea
Food moves too quickly through the intestinal tract and nutrients are not absorbed.
What often causes motility related diarrhea?
Enterotoxins and rotavirus
Gastritis
Inflammation of the stomach lining
Gastroenteritis
Inflammation along the gastrointestinal tract
Enteritis
Inflammation mainly of the small intestine
Enterocolitis
Inflammation of the colon and small intestine
Colitis
Inflammation of the colon
What treats gastritis, gastroenteritis, enteritis, enterocolitis, and colitis?
NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) like ibuprofen
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver caused mostly by the overconsumption of alcohol.
Rotavirus disease
Non-enveloped, segmented dsRNA.
Causes severe, watery diarrhea and vomiting in infants and young children.
How is rotavirus transmitted?
Rotavirus is transmitted via the fecal-oral route
How is rotavirus treated?
Oral rehydration solutions or IV fluid replacement.
Oral Vaccine
what is Norovirus?
genome: Non-enveloped, positive-sense, ssRNA.
causes a sudden onset of symptoms: headache, malaise, and diarrhea.
outbreaks common on cruise ships.
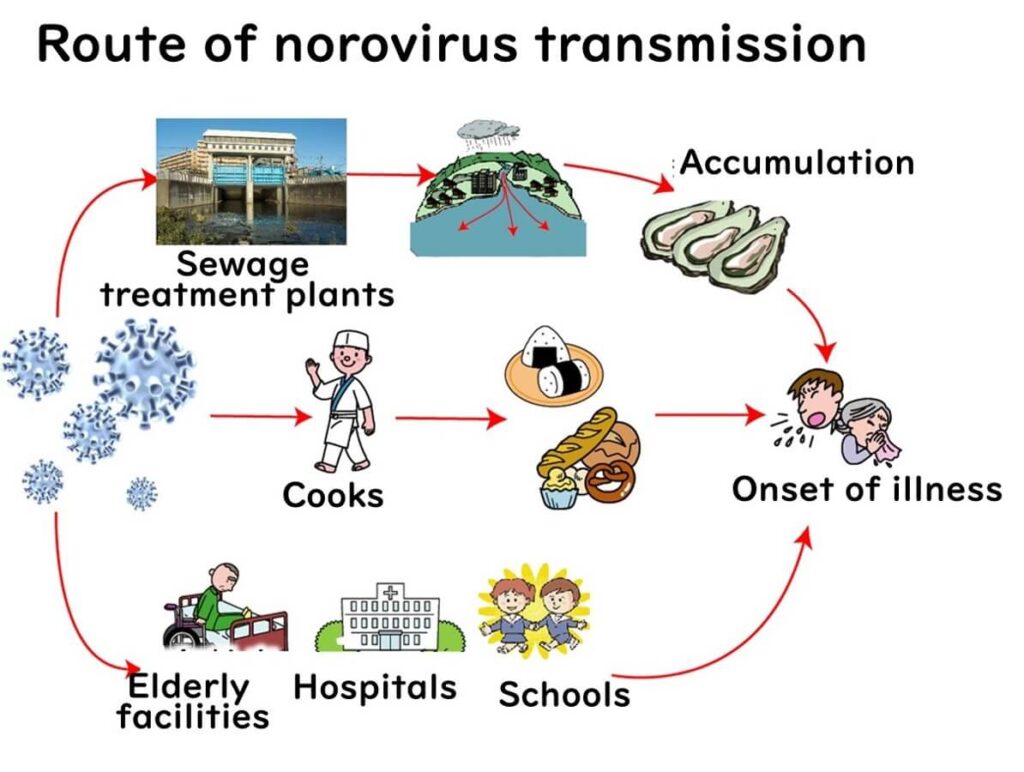
How is norovirus transmitted?
Norovirus is transmitted via the fecal oral route.
How is norovirus treated?
There's no known treatment (NOrovirus = NO Vaccine).
It's recommended to drink plenty of fluids, and do OTC oral rehydration therapy to avoid dehydration.
Hepatitis sometimes results in acute illness followed by chronic disease…
…cirrhosis, leading to liver cancer
Hepatitis A
Infectious hepatitis
Hepatitis B
Serum hepatitis
Mumps is caused by what?
Paramyxovirus, a single stranded RNA virus
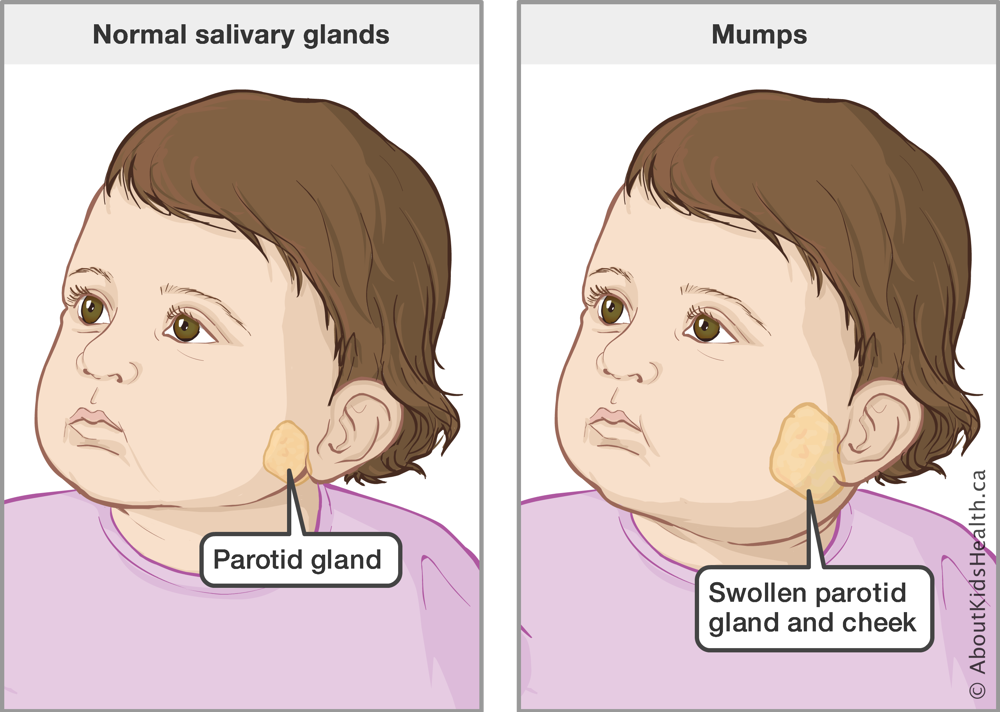
What is mumps?
inflammation of the parotid gland.
highly infectious/self-limiting infection.
Causes massive swelling of parotid glands and can cause harm if swelling of testes occurs.
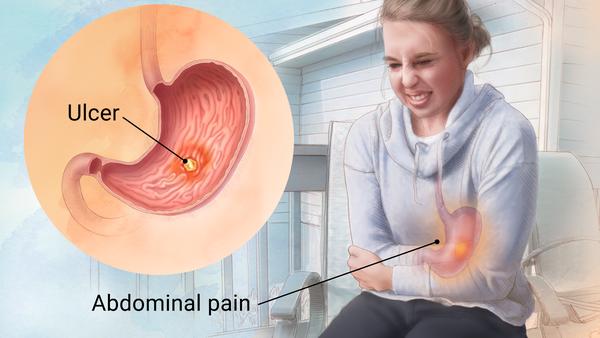
Peptic ulcers are caused by
The gram negative bacteria: Helicobacter pylori
What does Helicobacter pylori produce?
Urease to make ammonia that can neutralize stomach acids.
How are peptic ulcers treated?
Proton pump inhibitors (PPI) therapy with antibiotics. BISMUTH.
Symptoms of peptic ulcers include what?
Dyspepsia, upper abdominal pain, bloating, belching, nausea
E. Coli causes what
Food poisoning, septic shock, meningitis, UTIs, diarrhea
Pathogenesis of E. coli
Colonization of a mucosal site, evasion of host defense, and multiplication and host cell damage
What strain of E Coli causes foodborne illnesses?
O157:H7
Different strains of E. coli produce different…
…toxins
Entertoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Produces Enterotoxins and colonization factors, and causes secretory, watery diarrhea.
Are there any animal reservoirs of Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)?
No, there are no animal reservoirs.
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
pathogenic bacteria whose infection causes a syndrome that is identical to shigellosis, with profuse diarrhea and high fever
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
produces Shiga toxin
causes bloody diarrhea.
In servere cases, can lead to hemolytic uremia syndrome (HUS) and thrombocytopenia purpura.
Shigellosis is caused by what?
Shigella bacteria
How many species of shigella are there?
There are 4 species.
Shigella sonnei
Most common species of shigella in the U.S.
Shigella dysenteriae
Rare in the U.S.
Does shigella have an animal reservoir? How is it transmitted?
shigella has no animal reservoir.
transmitted between humans through fecal-oral route via food/water.
also transmitted through gay sex.
Typhoid fever
Caused by Salmonella typhi.
Associated with food preparation.
Intermittent fever and diarrhea for 1-3 weeks.
NO ANIMAL RESERVOIR
Paratyphoid fever
bacterial infection caused by Salmonella paratyphi.
Non-zoonotic.
Enteric fever.
Enterocolitis is caused by what?
Zoonotic nontyphoidal Salmonella serotypes.
ASSOCIATED W ANIMAL CONTACT.
Short-term illness lasts 6-48 hrs.
Yersiniosis
Bacterial GI disease.
caused by Y. Enterocolitica & Y. Pseudotuberculosis.
transmitted through food/milk/fecal-oral route.
Associated w/ animals
Causes general enteritis lasting up to 2 weeks.
Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. enterocolitica
Cold tolerant, gram negative bacteria
Campylobacter jejuni
Gram-negative, corkscrew-shaped, bipolar flagella.
Causes Campylobacter enterocolitis.
What is the number one cause of diarrhea worldwide?
the bacteria campylobacter jejuni
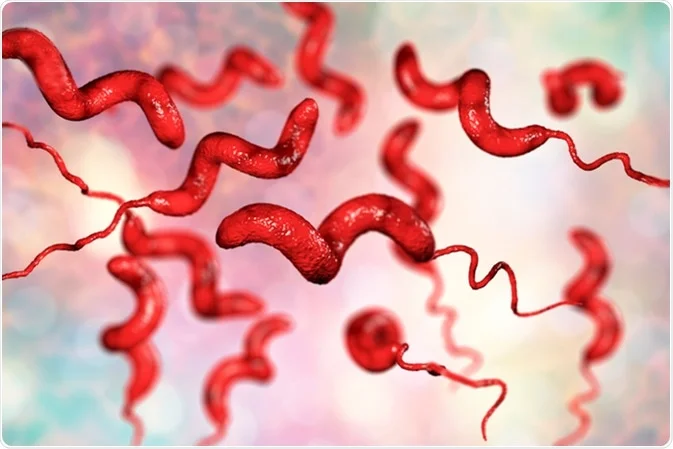
Rarely, Campylobacter jejuni causes an autoimmune disease called…
…guillain barré syndrome.
Cholera is caused by what?
Vibrio cholerae, a gram negative, curved-rod shaped bacteria with a single flagellum. It's transmitted via fecal oral route.
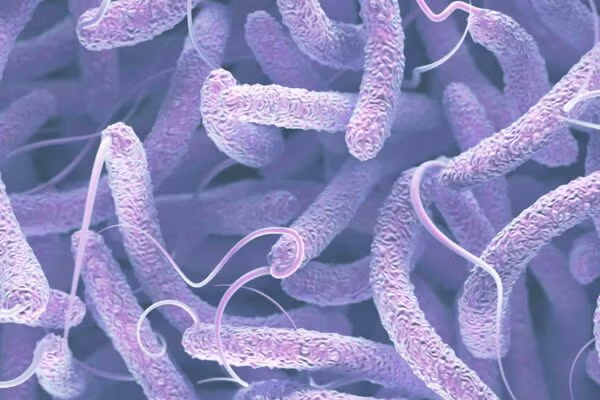
"Rice water stools" are characteristic of what bacteria?
Vibrio cholera (gram negative, faculative anaerobe, rod)
Does vibrio cholera cause fever or bloody stools?
No, it's noninvasive so it doesn't cause fever or blood stools
Is there a vaccine routinely administered for cholera?
No, it's not given in the U.S. at least. But. The Dukoral vaccine is available for travelers.
Listeriosis is caused by what?
Listeria monocytogenes, a gram-positive non spore forming coccobacili bacteria
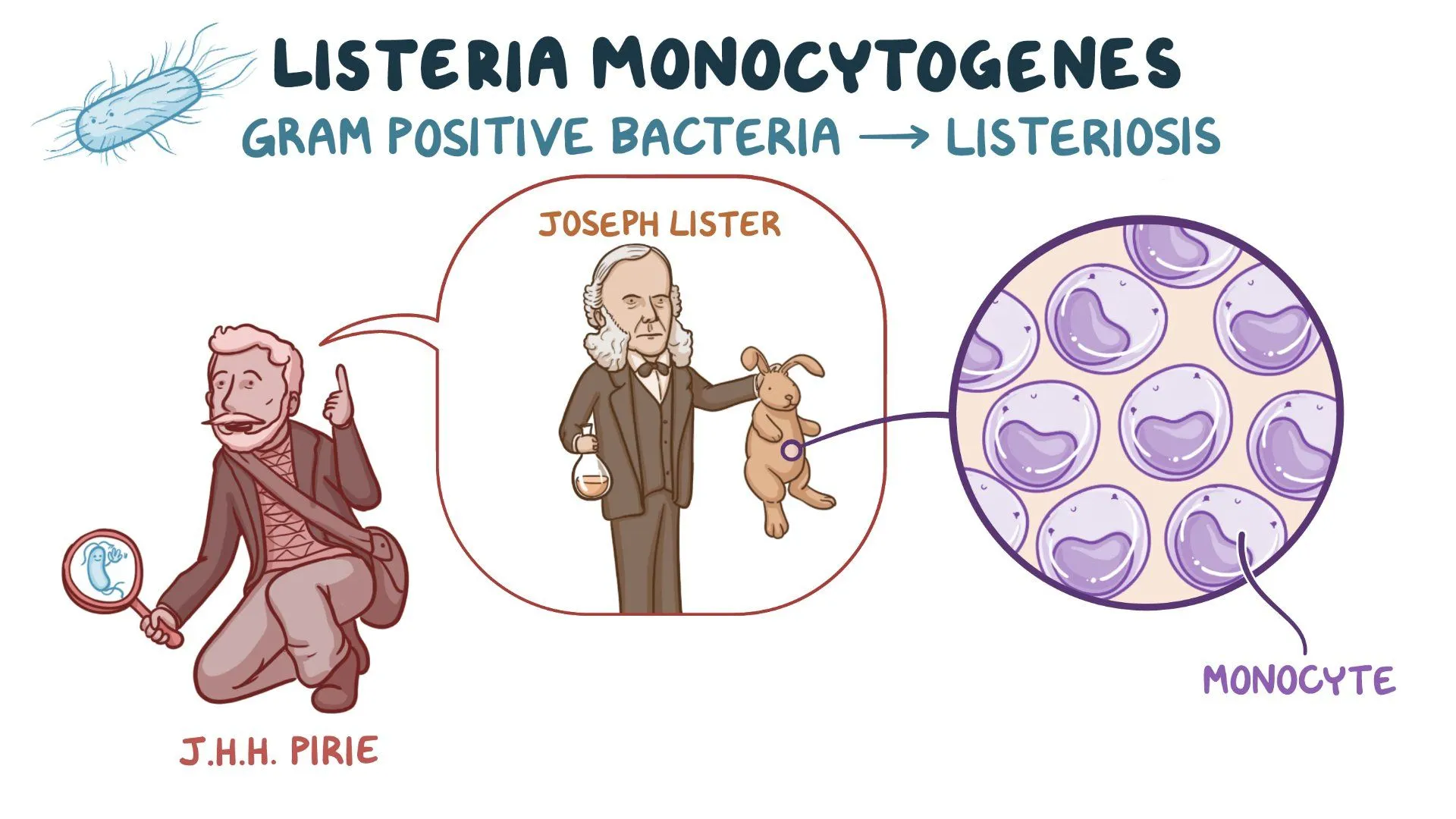
listeriosis
bacteria Listeria monocytogenes.
a foodborne illness.
can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations like pregnant women, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (and severe septicemia).
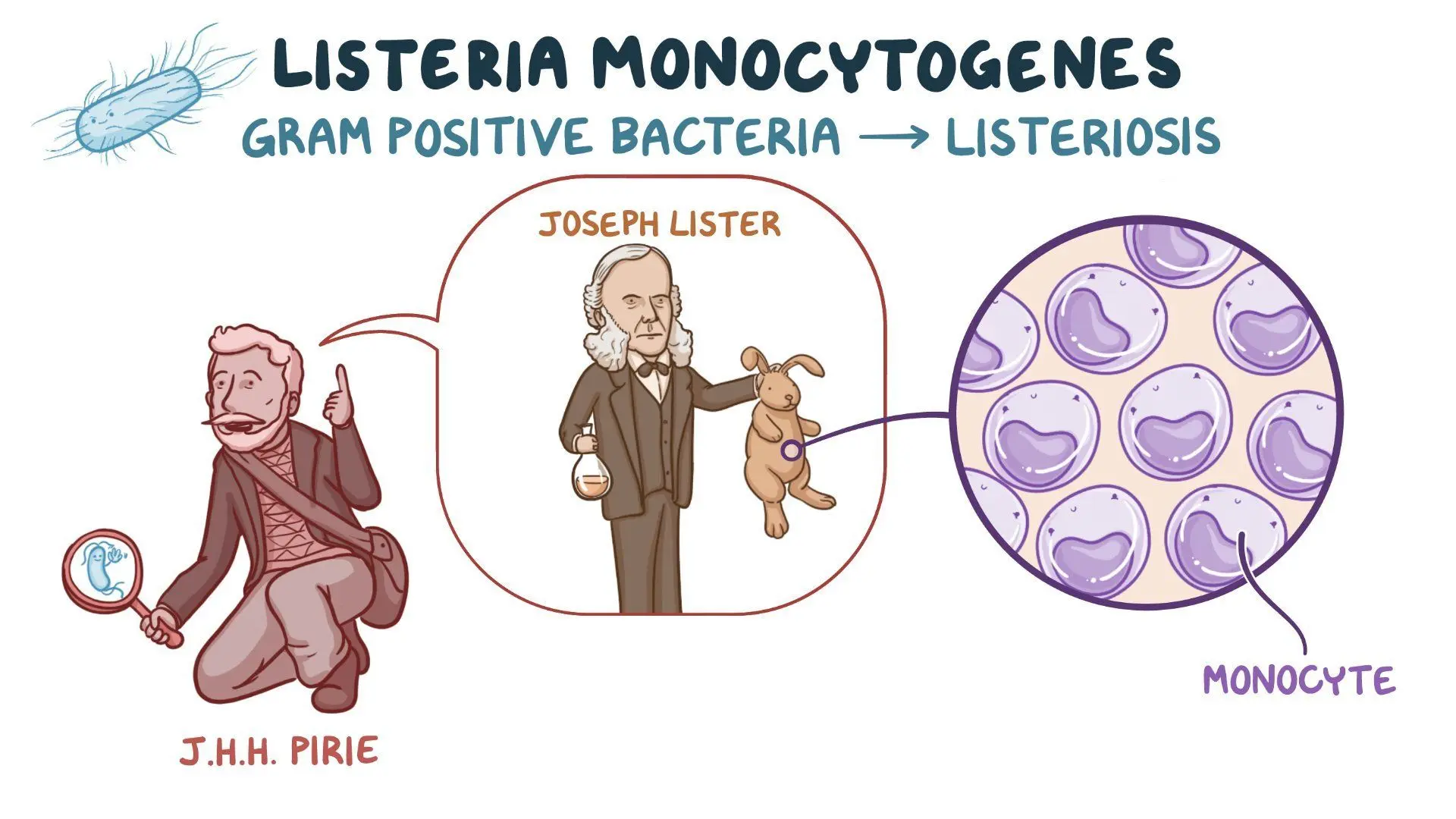
Listeria monocytogenes lives inside…
…macrophages to avoid detection by the immune system
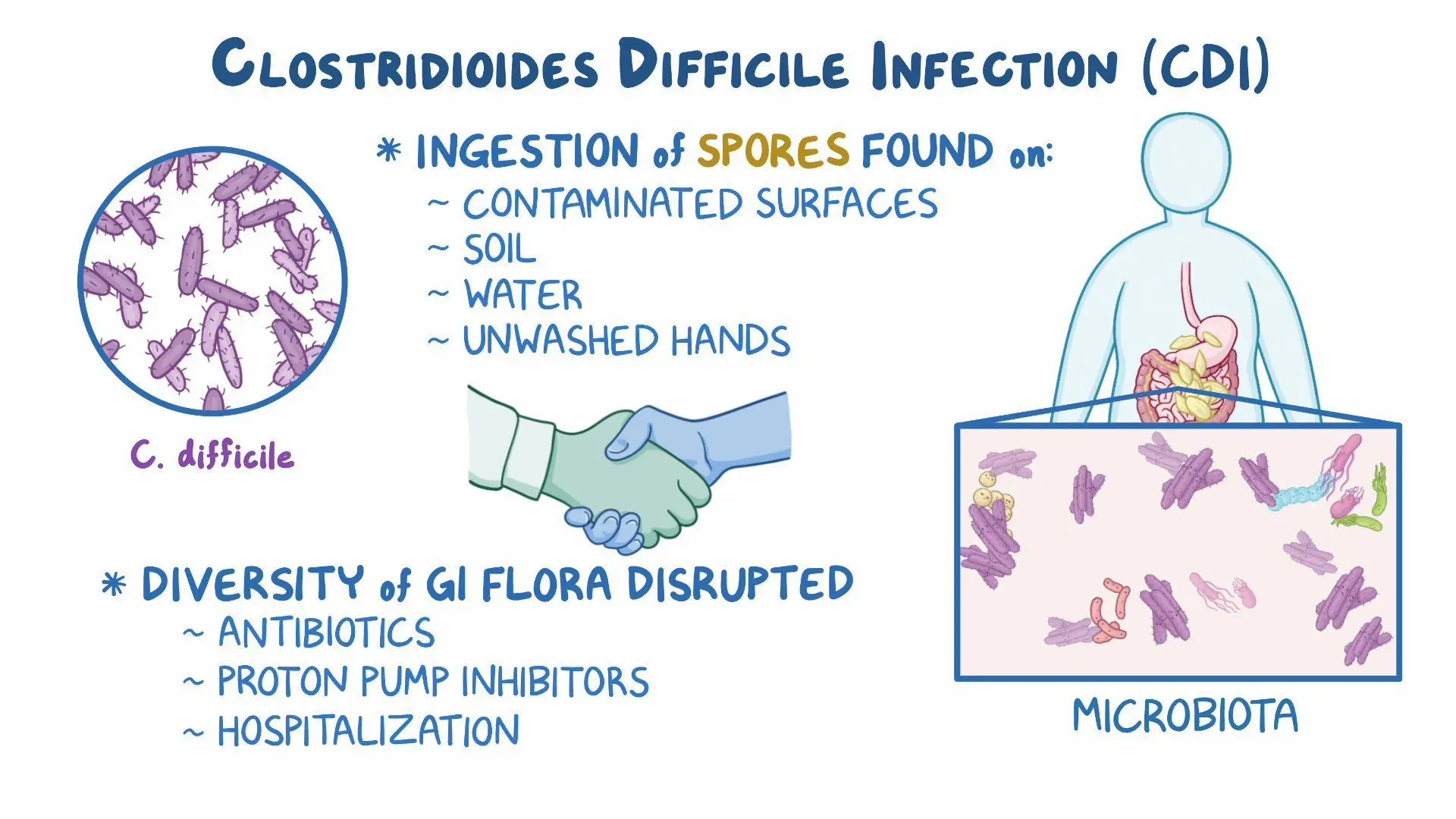
C. difficile
Gram-positive, endospore-forming bacteria.
causes antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis (pseudomembranous colitis).
C difficle prodcues what toxins?
Toxins A & B
What are the drugs of choice for antibiotic associated colitis?
Metronidazole or vancomycin (fecal bacterial treatment is utilized if these antibiotics don't work)
True or false: antibiotic associated colitis is a nosocomial infection.
True, it's a nosocomial infection that occurs due to improper cleaning and disinfection coupled with vulnerable populations
Staphyloccocus aureus
Gram-positive cocci that cause food poisoning and GI infections.
Characterized by a sudden start of nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps.
Symptoms are seen 2-6 hours upon ingestion
True or false: staphylococcal Enterotoxin (SE-B) is heat stable.
True, the staphylococcal Enterotoxin (SE-B) is heat stable.
Giardia lamblia
Flagellated protozoa that causes diarrhea worldwide (associated with freshwater sources).
Cyst -> trophozoite.
Amebic dysentery
protozoan disease.
Invasive diarrhea caused by entamoeba histolytica.
Trophozoites remain in the intestine and organisms can spread to the liver, lungs, or brain.
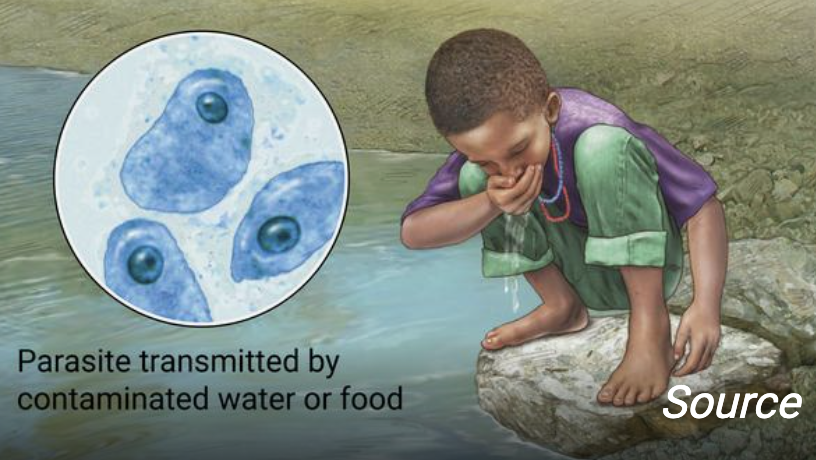
Cryptosporidiosis
Protozoan disease.
Caused by C. hominis and C. paravum.
Contaminated drinking water -> watery diarrhea that lasts 1-2 weeks (self limiting).
Fecal oral route of transmission.
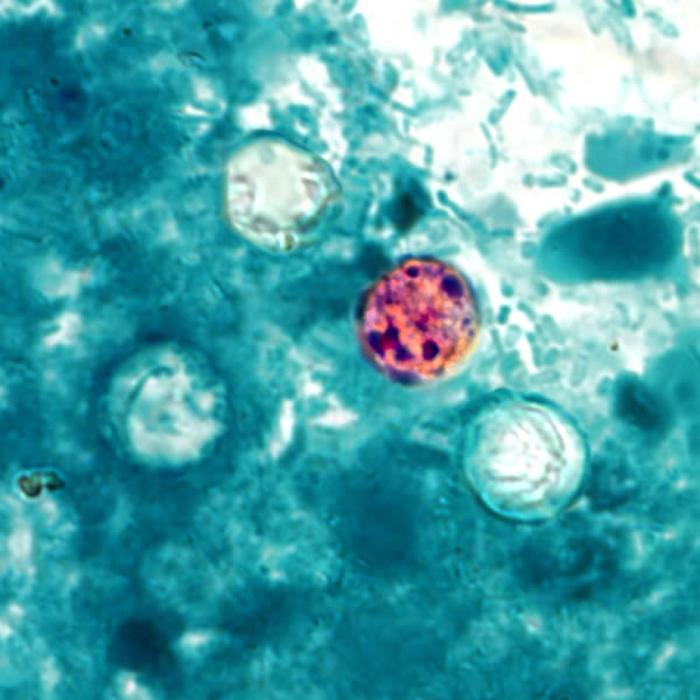
Cyclosporiasis
Protozoan disease.
Caused by Cyclospora cayetanensis.
transmitted through fresh produce/water.
No, the oocysts of cyclosporiasis CANNOT be passed directly by the fecal oral route.
Can the oocysts of cyclosporiasis (the reproductive structures of parasitic protozoa) be passed directly by the fecal oral route?
What helminths cause intestinal distress?
Whip worm, pin worm, and tapeworm
What helminths cause intestinal distress WITH larval migration symptoms?
Hookworms (Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale).
What helminth causes disease with MUSCLE involvement?
Trichinosis
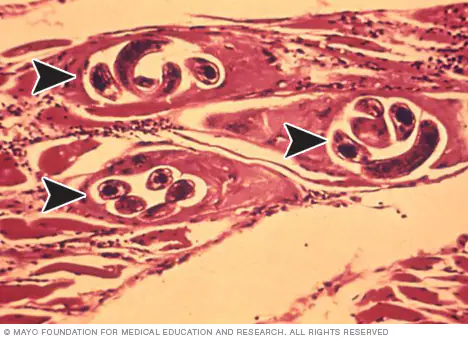
What is the cause of Trichinosis?
Trichinella spiralis (parasite)
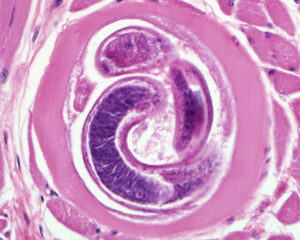
Once larvae are encysted in the muscle, can helminth disease with muscle involvement be cured?
Nope! Encysted larvae = no cure
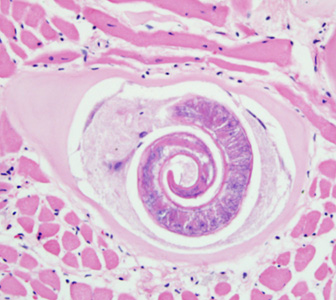
How are helminths (muscle involved) transmitted?
Ingestion of pork or other meat on which cysts of this parasite are embedded
What helminth disease includes liver involvement?
Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis (Bilhazaria)
Helminth infection acquired from contact with water containing infected snails.
Causes itchiness, fever chills, diarrhea, chihuahuas.
Parasitic.
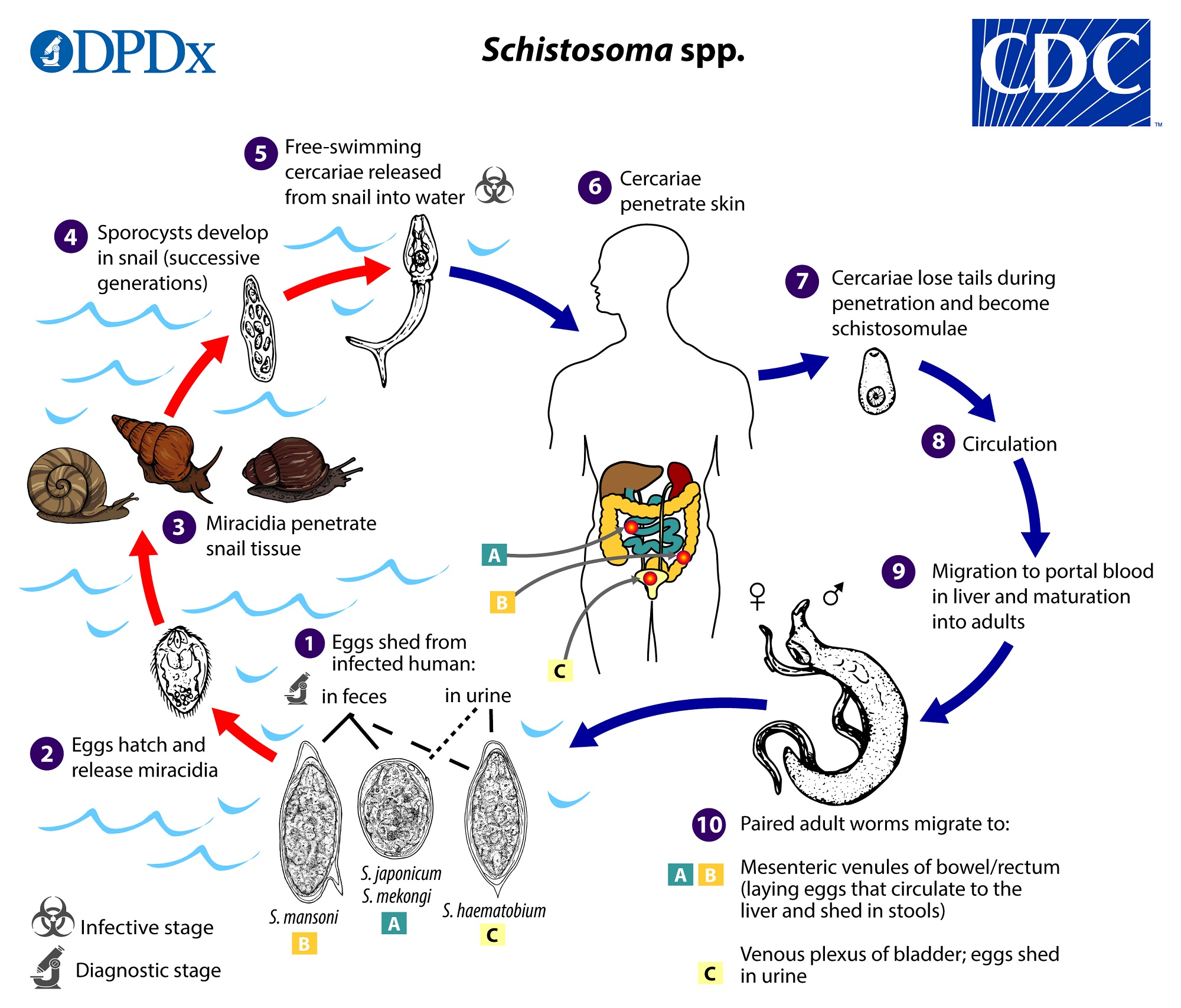
The helminth that causes schistosomiasis is coated in what?
Host blood proteins, which helps it evade the immune system
Schistosoma, Opisthorchis, and Fasciola
What flukes/helminths cause Schistosomiasis?
when does osmotic diarrhea occur?
occurs when the body is unable to absorb enough water and electrolytes, often due to the presence of poorly absorbed solutes in the intestinal lumen
when does secretory diarrhea occur?
occurs when the body actively secretes too much fluid and electrolytes into the intestines, often in response to infections, toxins, or other conditions.