8 - Endocrine, Cardiovascular, Immunology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
hormones (put IN the blood)
what are the products of endocrine?
bile, sweat, saliva, semen, breast milk (products end up out of body/diff body cavity)
what are the products of exocrine?
neural
hormonal
humoral
what are the 3 ways of hormone release through systems?
neural hormone release
an action potential causes hormone release (ex: SNS causes epinephrine release)
hormonal (hormone release)
hormones causes the release of TROPIC hormones (ex: ACTH triggers release of hormones from adrenal cortex)
tropic hormones
a class of hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine glands by stimulating growth, secretion, or both.
does NOT act on target tissues to produce a physiological response, but instead act on other endocrine glands
ex: TSH, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), FSH, LH, growth hormone
humoral hormone release
something in the blood, not itself a hormone, causing hormone release (ex: glucose regulate insulin/glucagon)
posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
part of the brain that’s made of nervous system to store + release 2 hypothalamic hormones (oxytocin and ADH)
it’s being controlled by the hypothalamus
hypothalamus
what organ/structure in the brain controls the posterior pituitary?
anterior pituitary (adrenohypophysis)
part of the brain that’s made of nervous system made of gland tissue to secrete 6 major hormones (FLAT PiG)
nervous tissues
posterior pituitary is made up of ______________ (nervous/gland) tissue
gland tissue
anterior pituitary is made up of ______________ (nervous/gland) tissue
FSH
LH
ACTH
TSH
prolactin
growth hormone
what are the 6 hormones that are secreted by anterior pituitary? (FLAT PiG)
neurons produce hormones → transport them down axons and release via action potential into the blood stream
how does the posterior pituitary get hormones to the target organs?
hormone making cells in the hypothalamus → travel to portal veins → anterior pituitary’s own hormone making cells
how does the anterior pituitary get hormones to the target organs?
pressure gradient (forward momentum)
in the arteries, blood moves by _______________ (forward momentum) from high to low pressure area
normal body movement (anything movement that ‘squishes’ the vessel)
in veins, blood moves by _____________ and contains valves
lymphatic system
system that carries lymph to help replenish the loss of fluid as blood travels along capillary bed → carry it back to the heart. also picks up bacteria and pathogens
lymph nodes
concentrated areas of white blood cells (leukocytes) in diff body areas that destroy pathogen/warn immune system
CO, TPR
blood pressure is DIRECTLY related to ______ and ________
peripheral resistance
how hard it is to move blood through the vessels
vasodilation (increase diameter and flow, decrease BP)
vessel lengthens (increase length, increase BP)
what are the factors that increase TPR? (answer has 2, but you know there’s many)
to avoid cardiac tetany (stable, constant contraction for awhile from CONSTANT AP)
why are cardiac action potentials prolonged? (voltage gated Ca2+ channels open longer)
tetany
stable, constant contractions for awhile from constant action potential (good for skeletal cells, bad for cardiac cells)
autoarrhythmic cardiac cells
cardiac cells with higher resting potential (~-40 mV) than cardiac cells, AND the resting potential is unstable → more time in action potential
atrial, ventricular
__________ and __________ muscle cells are NOT connected due to no gap junctions ONLY valves, and therefore need autorhythmic cells
autorhythmic cells (SA node, AV node, purkinje fibers)
how do atrium stimulate action potential to ventricles?
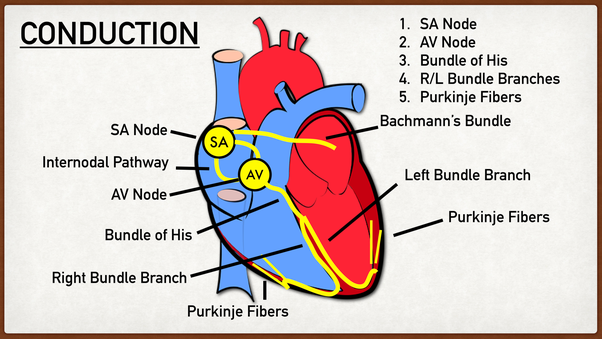
AV node
autorhythmic cells that delay impulse to allow atria to contract BEFORE ventricles

SA node
It is located atop R atrium. ___________ fires first and stimulates AV node in the atria
hematocrit (RBC)
leukocytes (WBC, platelets)
plasma (water, electrolytes, glc, hormones, plasma prots, lipoproteins, etc.)
what are the THREE components of blood?
RBC
what is the component of hematocrit?
WBC and platelets
what are the contents of leukocytes
water, electrolytes, glucose, hormones, plasma proteins, lipoproteins
what are the contents of plasma in blood?
plasma, hemoglobin (Hb), cooperative binding, release O2
when traveling in blood, oxygen… ?
3% dissolves in ___________
97% bound to ______________ in RBCs
hemoglobin has _____________ to O2 → produce sigmoid curve b/w [O2] and % saturated Hb
Hb has the tendency to ____________ O2 instead of keeping it
plasma, hemoglobin, bicarbonate
TISUES CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2CO3 ⇌ H+ + CO3- LUNGS
when traveling in blood, CO2:
7% dissolves in ________
20% dissolves in _________
73% travel as ____________ in plasma
cooperative binding
refers to phenomenon where the binding of a ligand (ex: oxygen) to one binding site on a multimeric protein (ex: Hb) influences the affinity of subsequent binding sites for the same ligand.
lungs are high in O2 → CO3- and H+ high → gets rid of CO2 as its end goal
tissues high in CO2 → converts it to CO3-
explain this:
TISUES CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2CO3 ⇌ H+ + CO3- LUNGS
physical barrier
chemical barrier
cells
what are the 3 types of non-specific defense of the immune system?
physical barrier of the immune system
includes skin, mucus, blood-brain barrier, hair, wax, oils
chemical barrier of the immune system
includes mucus, stomach acid, lysozyme, and histamine
cell defense of the immune system
includes macrophasges, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, NK cells
immunity
specific defense for specific pathogens (energy expensive)
antigen
foreign protein (specific) that triggers an immune response (ex: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein)
antibody
specific protein marker made by the body in response to the antigen
B cells
immune cell that gives humoral (in the blood) immunity by creating antibodies and secrete them into the blood stream + lymph nodes (only ONE type of antibody per ____ cell)
carries an antigen-receptor specific to the antibody it makes on its surface
one type
each B cell makes ___________ (how many) types of antibodies
antigen-receptor
B cells carry a ______________ specific to the antibody it makes on its surface
if an antigen binds to this → activated and clone itself to secrete that antibody
plasma cells
B cells clones from after the pathogenic antigen binds to the antigen-receptor
T cells
immune cells that directs cell-mediated immunity (non-humoral - does not interact with blood)
killer T cell self-receptor
T cell structure that’s used to ID its own body cells
self-receptor
antigen receptor
bacteria must trigger BOTH to induce a reaction from T cells
what are the 2 types of receptors on killer T cells?
killer T cells
helper T cells
what are the 2 types of T cells
helper T cells
type of T cells that secrete chemicals (cytokines) that allow B cells and killer T cells to proliferate (clone themselves)
cytokines
what chemical(s) do helper T cells secrete?
T cells (cell mediated response) + B cells (humoral response)
what is adaptive immunity?
MHC I cells
type of immune cell found on ALL cells and allow cells to display its cell contents on cell surface (does NOT know the difference between normal cell and viral protein)
killer T cells look for MHC I displays on cells to look for viral marker
antigen receptor binds to the top display
self receptor binds to the bottom display
how do killer T cells differentiate between normal and viral contents in the body with regards to MHC I cells?
MHC II cells
immune cells found on B cells and macrophages → allow these cells to display ANYTHING CONSUMED by B cells and macrophages
MHC II
macrophages consume a bacteria → displays the bacteria’s antigens using ______________
then, helper T cells performs receptor mediated endocytosis on ___________ that display the pathogenic antigen
MHC I is found on ALL cells → displays its cell content
MHC II found ONLY on B cells and macrophages → display what they ate
what’s the difference between MHC I and MHC II cells?
primary immune response
1st exposure to antigen that lasts 7-10 days where immune system initiates process of mounting a response to kill the antigen
recognition of antigen (antigen presenting cells present antigen)
activation of lymphocytes (antigen presentation triggers antigen-specific T cells and B cells)
differentiation and effector function (activated T cells differentiate to effector T cells → cytotoxic T cells, helper T cells) (activated B cells differentiate into plasma cells)
antibody production
recognition of antigen (antigen presenting cells present antigen)
activation of lymphocytes (antigen presentation triggers antigen-specific T cells and B cells)
differentiation and effector function (activated T cells differentiate to effector T cells → cytotoxic T cells, helper T cells) (activated B cells differentiate into plasma cells)
antibody production
what are the steps to primary immune response?
to make antibody, activate T cells (killer T and helper T), and memory cells
what are the goals of primary immune response
memory cells
formed by B cells and will be activated if re-exposure occurs → makes antibody and active T cells
antigen, memory cells, primary exposure to the pathogen
vaccines have the proteins that make the specific pathogen’s __________ → trigger an immune response and activate new ______________ without ________________
foreign, self
immune system attacks ____________ antigen, not __________ antigen
self-reactive lymphocytes
type of immune cells that attack its own antigen and cause an autoimmune disease
destruction of self-recognizing B cells - Bone marrow
destruction of self-recognizing T cells - Thymus
how to eliminate self-reactive lymphocytes?