1.2.5 Labour market
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is a factor market
A market for one of the four factors of production – land, labour, capital and enterprise
Where does the supply and demand of labour come from?
Supply of labour: people in households
Demand for labour: businesses.
Derived demand
The demand for labour is dependent on the demand for the final goods and services that they produce
What does the demand curve for labour show
how many workers are hired at a given wage rate
Why does the demand curve for labour slope down?
The higher the wage rate, the fewer workers the firm can afford to hire. Capital substitution will occur. The lower the wage rate the more workers the firm can afford to hire. This will happen in the long run only as capital is fixed in the short run.
The income effect. When wages are higher, firms employ fewer people as they have less income to spend on increasing the workforce.
Picture the demand curve for labour (label the x and y axis)…
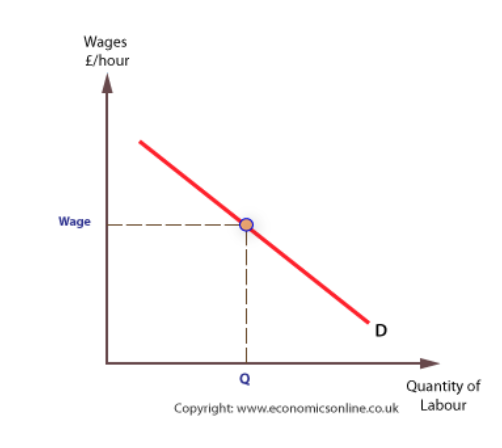
What factors will shift the labour demand curve
The demand for the products/services
Productivity of labour
Substitutes
How does the demand for products/services shift the labour demand curve
If consumers want more of a particular good or service, more firms will want the workers that make the product.
How does the productivity of labour shift the labour demand curve
If workers are more productive, they will be in greater demand. Productivity is influenced by skill levels, education and training, and the use of technology.
How will substitutes shift the labour demand curve
If substitutes such as capital machinery became cheaper or more expensive, the demand curve for labour will shift to the left or right.
Labour of supply
The number of workers willing and able to work, multiplied by the hours they are willing and able to work.
Factors that shift the supply of labour curve
The size of the working population
Migration
Age distribution of population
Retirement age
School leaving age
Female participation
Skills and qualifications
Labour mobility
The size of the working population
The working population is the number of people of working age who are willing and able to work.
Migration
Migrants tend to be of working age, and while the general effect is to increase the supply of labour at all wage rates, migration especially affects supply at lower wage rates.
Age distribution of population
Supply of labour falls if there are a large number of old or young people in the population.
Retirement age
When you reach a certain age and stop working and are eligible for government payouts (pension)
School leaving age
If a country increases the school leaving age, this means children have to stay in education for longer and therefore the supply of labour falls.
Female participation
An increasing number of women have entered the labour force, increasing the supply of labour
Skills and qualifications
If a job requires certain skills and qualifications, this can reduce the labour supply for a given occupation as it represents a barrier to entry
Labour mobility
Immobility of labour is a cause of unemployment and market failure.
Occupational immobility
When workers do not have the right skills to work in the market
E.G. workers made redundant in the steel industry or in heavy engineering may find it difficult to find a new job. They may have specific skills that are not necessarily needed in growing industries which causes a mismatch between the skills on offer from the unemployed and those required by employers looking for workers (called structural unemployment)
This leads to a waste of scarce resources and represents market failure.
Geographical immobility
Barriers that prevent people moving from one area to another to find work.
There are good reasons why geographical immobility might exist:
Family and social ties
The financial costs involved in moving home include the costs of selling a house and removal expenses.
Huge regional variations in house prices lead to a shortage of affordable housing in many areas
The high cost of renting property
Differences in the general cost of living between regions and also between countries
Migration controls e.g. a cap on inward migration
Cultural and language barriers
Human capital
The skills and experience workers have.
Picture a labour market diagram (with x and y axis)
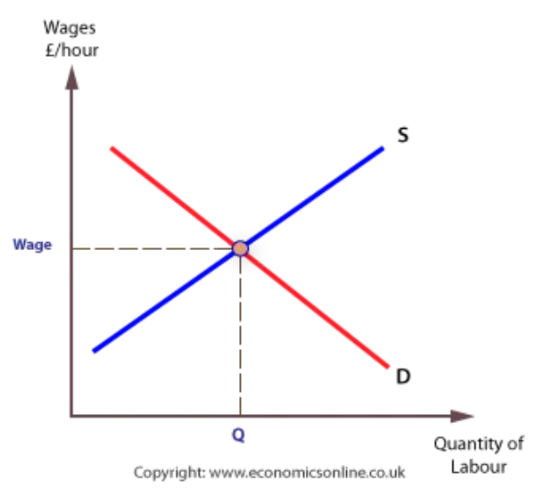
Trade union
Organisations that exist to protect the interests of workers
Main aims of trade unions
Negotiate pay and working conditions with employers
Provide legal protection for members, such as representation in court if an employee is fighting a case against an employer (discrimination in the workplace, for example)
Put pressure on the government to pass legislation that improves the rights of workers
Strike action
Trade unions can encourage strike action (industrial action) if the employer does not agree to making certain changes (e.g. if they do no agree with pay increases). This means workers do not work for a given period of time (withdrawal of labour). Strike action is usually the last resort.
What are the less extreme methods trade unions encourage
“go slow” (work slowly) or “work to rule” (only do the jobs that are specified in the employment contract.