5 DNA sequencing
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what is Sanger sequencing?
a method of determining the sequence of nucleotides in a section of DNA.
what did sanger introduce which allowed us to find the exact DNA composition of the sequence?
dideoxynucleotide - ribonucleotide with removed Oxygen.
it prevents polymerase from adding any more nucleotides to the DNA chain.
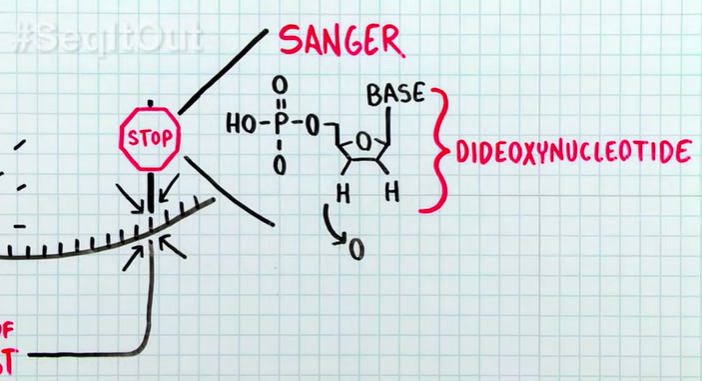
Explain how to isolate a DNA sequence of interest
Primer binds to region of interest.
Polymerase extends primer by adding complementary nucleotides.
Reaction stopped with dideoxynucleotide, preventing further extension.
Specific fluorescent dye used to identify terminated nucleotide.
Extension products vary in length, terminated with dideoxynucleotides.
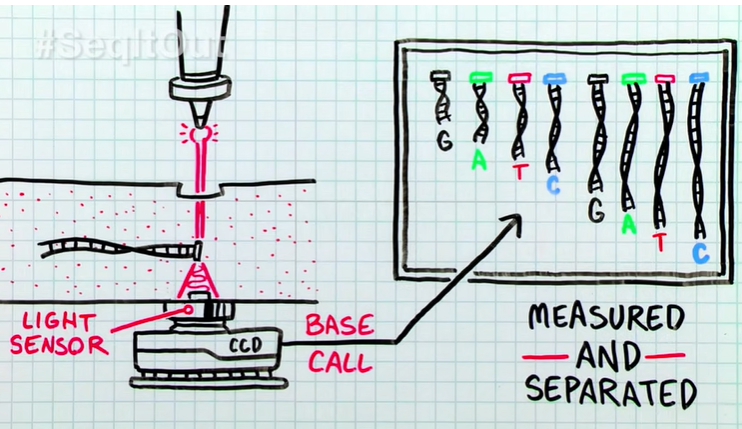
outline how the extension products are separated by capillary electropheresis.
DNA fragments move based on molecular weight.
Laser excites dye-labeled DNA fragments in capillary.
Detected light emissions interpreted by software for base call.
Pool of DNA fragments measured and separated to obtain sequence.
Briefly explain how illumina sequencing works.
it works by simultaneously identifying DNA bases, as each base emits a unique fluorescent signal, and adding them to a nucleic acid chain
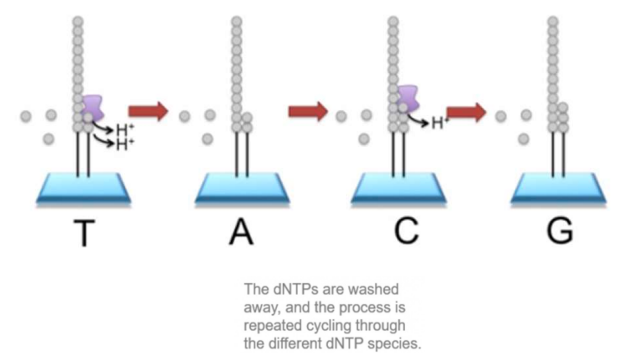
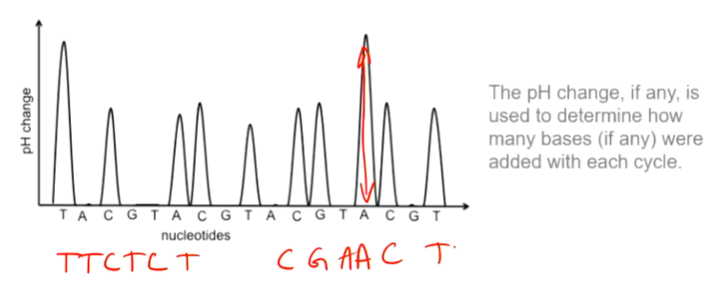
Briefly explain how Ion Torrent sequencing works.
It works by detecting the release of H+ ions as nucleotides are incorporated into a growing DNA strand.
When a nucleotide is added, it releases a H+ ion, which is detected by a sensor.
The sequence of the DNA fragment is determined based on the order in which these ions are released during the sequencing process.
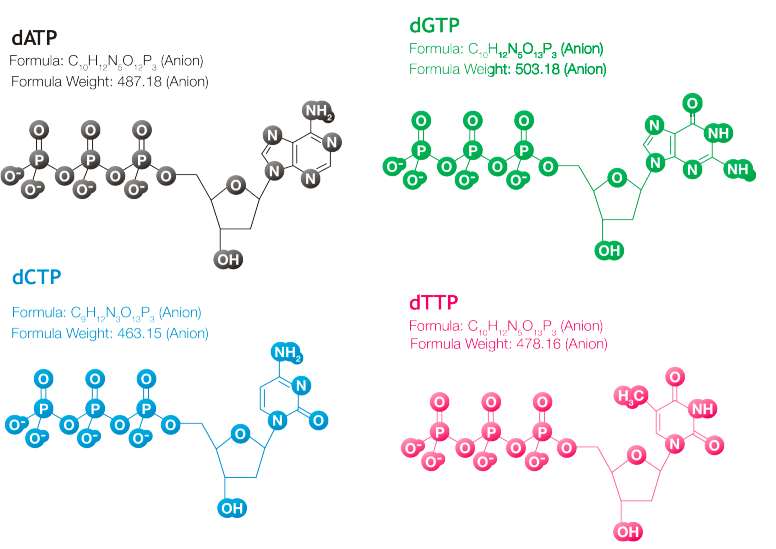
what is dNTP?
deoxynucleotide triphosphate
there are 4 types: adenine (dATP), cytosine (dCTP), guanine (dGTP), and thymine (dTTP)
essentially, __ change is used to determine how many bases were added with each cycle.
pH change.
note: the red is the DNA sequence.
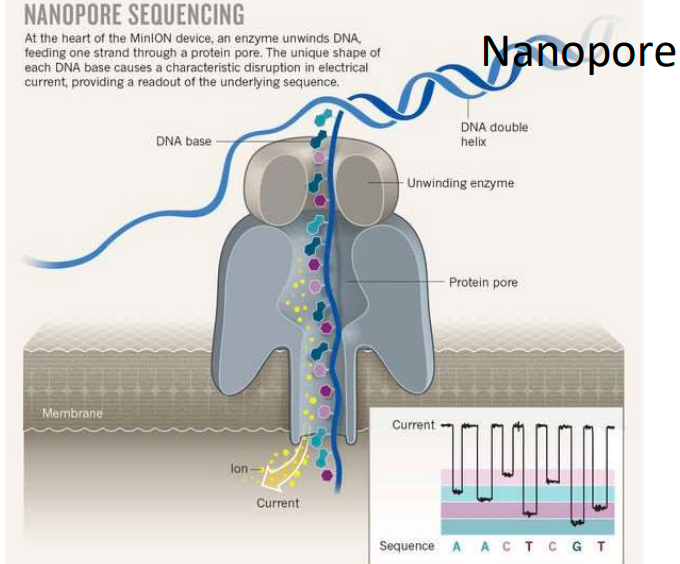
Briefly explain how nanopore sequencing works.
It involves passing DNA through a nanopore & measuring changes in electrical current as individual nucleotides move through the pore. Each nucleotide produces a unique signal, allowing for real-time sequencing of DNA molecules.
summarise the 3 NGS methods.
Illumina (uses fluorescent nucleotides)
Ion Torrent (measures pH change)
Nanopore (uses changes in electrical current through an artificial pore)
what is the purpose of the human genome project
to provide tools to understand:
genetic factors in disease
new strategies for treatment & prevention
what is the purpose of the 100,000 genomes project
to move away from ‘one size fits all’ approach & more towards personalised healthcare.
provides widespread sample of population to understand where variability is within normal (healthy & disease states)
what are medical applications of NGS?
identification of genetic diseases
what are pharma/biotech industry applications of NGS?
new prognostics (predict predisposition to certain diseases)
new diagnostics (see if a patient has a condition or not)
Discovery of new targets for drug design
Design of better medicines of the future