Centric Relation Position and Criteria for the Optimum Functional Occlusion
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture given on 9/2/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
why do we use centric relation?
it designates the position of the mandible when the condyles are in an orthopedically stable position, it is a physiological and reproducible position, and it is comfortable
why is centric relation not when the condyles are in the most retruded position?
because that can compress the retrodiscal tissue which is highly innervated
why is centric relation not when the condyles are in their most superior position in the articular fossae?
because the superior bone is very thin
why is centric relation not when the condyles are positioned downward and forward on the articular eminences?
because this position increases the activity of the inferior lateral pterygoid muscles which can cause spasms
what is the direction of force of the masseters and the medial pterygoids?
supero-anterior
what is the direction of force of the temporalis?
predominantly straight superior
what is the direction of force of the inferior lateral pterygoids?
anteriorly
what is the most orthopedically stable joint position as dictated by the muscles?
when the condyles are located in their most superoanterior position in the articular fossae, fully seated and resting against the posterior slopes of the articular eminences, with the discs properly interposed
musculoskeletally stable position
same as centric relation
*centric relation
the maxillo-mandibular relationship in which the condyles articulate with the thinnest avascular portion of their respective discs within the TMJ complex, in their anterior-superior positions against the slope of the articular eminences
the mandible is restricted to purely rotary movement
it is a repeatable reference position
it is independent of tooth contact
*in centric relation, can the mandible rotate and translate?
no, it is restricted to purely rotary movement
*t/f centric relation will change every time you ask the patient to find that position?
false- it is a repeatable reference position
*does centric relation depend on tooth contact?
no, it is independent of tooth contact
*t/f often when you find MIP, you also have found CR
false- they rarely coincide in dentate patients
what are synonyms for centric relation position?
centric relation, centric position, centric jaw position
what are synonyms for centric relation record?
centric bite check, centric interocclusal record, centric jaw record, centric jaw relation, jaw releation record
*what is the order for mounting a cast?
take impressions (upper and lower)
take facebow record to mount the upper casts
take interocclusal record to mount the lower cases (if the patient does not have MIP)
interocclusal record
a registration of the positional relationship of the opposing teeth or arches
is CR anterior or posterior to MIP?
posterior
should an interocclusal record for CR made of blue mousse have perforations?
no
should an interocclusal record for MIP made of blue mousse have perforations?
yes
do we always need to taken an interoccusal record?
no, if the casts can be hand articulated to MIP an interocclusal record is not necessary
when should a centric relation record be taken?
when you are working with a complete denture patient, a patient with loss of VDO, or a full mouth rehabilitation
what is a protrusive record used for?
to set condylar inclination for diagnostic purpose
why is it important that teeth do not touch when taking a CR record?
neuromusuclar system acts in a protective manner when the teeth are threatened by damaging contacts
give a brief overview of dawson’s bimanual manipulation technique
recline patient, sit behind patient and point their chin upward, place 4 fingers of each hand on the lower border of the mandible with the smallest finger behind the angle of the mandible (hands should form a C shape), place an upward force on the lower border and the angle of the mandible with the fingers while pressing downward and backward on the chin with your thumb
***when doing dawson’s bimanual manipulation technique, you should place an …
upward force on the lower border and the angle of the mandible with the fingers, while pressing downward and backward on the chin with your thumbs
what is the purpose of the hinging step in dawson’s bimanual manipulation technique?
deactivate the muscles
when hinging the jaw during dawson’s bimanual manipulation technique, how many mm should the movement be, and should the teeth touch?
2-4 mm, NO
give a brief overview of the anterior jig technique
build an anterior jig made of hard acrylic, guide the mandible, ask the patient to close on the posterior teeth, get tooth imprints on the anterior jig, cure, check the tooth imprint and make the surface flat with only one contact on the lower central incisor close to the midline
why does the anterior jig technique work?
the lack of posterior occlusal contact allows the lateral pterygoid to relax because it no longer has to hold the mandible in an anterior or lateral position to avoid posterior contacts
directional force provided by the elevator muscles seats the condyles in a superoanterior position within the fossae
how should the anterior jig contact the teeth?
perpendicularly
what is wrong with an anterior jig that contacts the teeth at a distal incline?
it will deflect the mandible posteriorly, away from CR
what is wrong with an anterior jig that contacts the teeth at a mesial incline?
it will deflect the mandible anteriorly, away from CR
briefly describe the leaf gauge technique
it is the same as the anterior jig except the jig is replaced by a leaf gauge that are all 0.1mm thick
instruct the patient to slide forward and backward and remove leaves one by one until you obtain the 1st contact on the posterior teeth
add more paper to separate the posterior teeth slightly
do we take CR records on all cases?
no
what happens if a patient only has posterior teeth on the left?
activity of the elevator muscles tend to pivot the mandibular using the tooth contacts as a fulcrum
increase in joint force to the left TMJ, decrease in force on the right TMJ
risk of breakdown to the joints and teeth
40 pounds per tooth
what happens if a patient only has their first molars?
with bilateral contacts, mandibular stability and condylar stability
20 pounds per tooth
what happens if a patient has all 8 posterior teeth?
more stabilization
minimal potential damage
10 pounds per tooth
PDL is present between the root of the tooth and acts as?
a natural shock absorber and is capable of converting a destructive force (pressure) into an acceptable force (tension)
do osseous tissues tolerate pressure forces?
no, bones will resorb under prolonged forces however tension (pulling) actually stimulates ossesous formation
what is important about the way PDL fibers are aligned?
vertically directed forces through the long axis (axial loading) can be well accepted and dissipated
vertical forces are ___ accepted by the PDL
well
horizontal forces are ___ accepted by the PDL
not
axial loading
cusp tips contact flat surfaces- the resultant force is directed vertically through the long axes of the teeth, this type of force is accepted well by the PDL
non-axial loading
opposing teeth contact on inclines- the direction of force is not through the long axes of the teeth, instead tipping forces are created that tend to cause compression of certain areas of the PDL, these forces are not effectively dissipated to the bone
t/f with canine guidance, the reduction in elevator muscle activity is much greater than with group function
true (preferrable because it decreases forces to the dental and joint structures)
which tooth is the best suited to accept the horizontal forces that occur during eccentric movements, and why?
canines
because they have the longest and largest roots that are surrounded by dense compact bone which tolerates the forces better than the medullary bone found around posterior teeth
*canine guidance
when the mandible is moved in a right or left laterotrusive excursion, the maxillary and mandibular canines are appropriate teeth to contact and dissipate the horizontal forces while disoccluding or disarticulating the posterior teeth
*if canine guidance is not possible, what is the most desirable group function?
canine, premolars, and sometimes the mesiobuccal cusp of the first molar
*in group function, any laterotrusive contacts more posterior than the mesial portion of the first molar are not desirable because?
the amount of force that can be created as the contact gets closer to the fulcrum (TMJ) increases
anterior guidance
during protrustive movement the anterior teeth can best receive and dissipate the forces
unlike posterior teeth, anteriors are in proper position to accept the forces of eccentric mandibular movements therefore, during protrusion the anterior and not the posterior teeth should contact
the anterior teeth should provide adequate contact or guidance to disarticulate the posteriors
what are some indications for group function?
missing canines, weak canines, implant in the canine position (as shallow as possible, share the occlusal forces),
anterior open bite
class I occlusion with extreme overjet
class II occlusion (canines do not touch and pt rejects orthognathic surgery)
class III occlusion with all lower anterior teeth anterior to the upper teeth
interference
any tooth contact that prevents or hinders harmonious mandibular movements
aka prematurity or deflective occlusal contacts
working side
the side toward which the mandible moves in a lateral excursion
laterotrusive contacts
contacts of teeth made on the side of the occlusion toward which the mandible has moved
non-working side
the side of the mandible that moves toward the medial line in a lateral excursion
mediotrusive contacts
contact of the teeth on the side opposite to the direction of laterotrusion of the mandible, these are undesirable contacts
why can mediotrusive contacts be destructive?
the amount of force they can have and the direction of the force
*which teeth (anterior or posterior) are better for static loading and vertical forces?
posterior teeth
*which teeth (anterior or posterior) are better for dynamic loading and horizontal forces?
anterior teeth
*mutually protected occlusion
posterior teeth function most effectively in stopping the mandible during closure, whereas anterior teeth function most effectively in guiding the mandible closing during eccentric movements
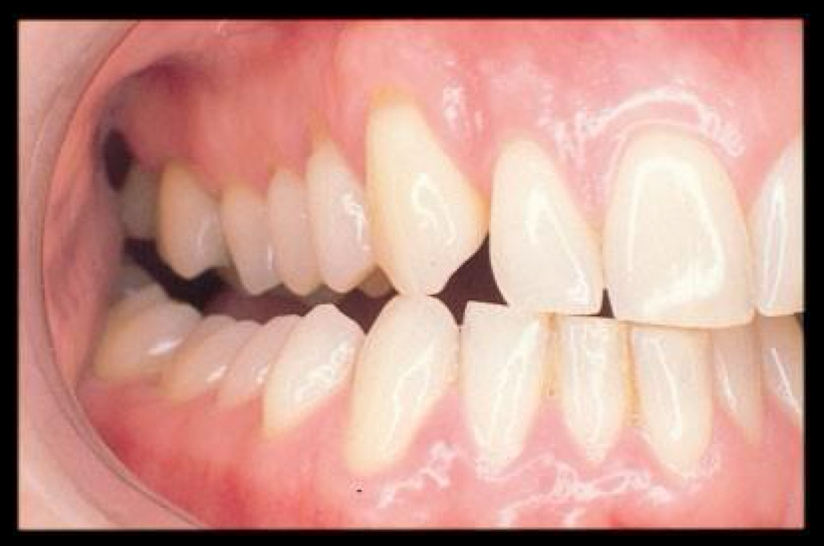
in this image, what are the the laterotrusive contacts?
#6 and #27
*what happens if there is malocclusion in natural dentition?
it may be uneventful for years
*what happens if there is malocclusion with an implant?
crestal bone loss
*what happens if there are non vertical forces in natural dentition?
it is relatively tolerated
*what happens if there are non vertical forces with implants?
it is traumatic to bone
*what load bearing characteristics does natural dentition have?
shock absorbing, stress is distributed
*what load bearing characteristics do implants have?
stress is concentrated at crestal bone
**what are signs of overloading in natural dentition?
PDL thickening, mobility, wear facets, fremitus, pain
**what are signs of overloading in implants?
screw loosening or fracture, abutment fracture, bone loss, implant fracture
*what is the tactile sensitivity of natural dentition?
high (proprioceptive feedback)
*what is the tactile sensitivity of an implant?
low (osseoperception)
where should the contacts be on an implant?
centered, on a 1-1.5 mm flat area
t/f implants should be wider than teeth to accomodate a flat, centered contact
false- they should have a 30-40% smaller / more narrow occlusal table
implants should have ____ contact at heavy bite, and ____ contact at light bite
light, no
t/f implants should have cusps that look just like natural teeth
false- should have flat cusps and shallow occlusal anatomy
can implants have a cantilever?
no or minimal cantilever- dimension larger than the implant diameter can cause cantilever effect
anterior guidance of multiple anterior implants should be as ____ as possible to avoid?
shallow, greater forces on the anterior implants
what should be done if you are doing a canine implant?
use group function and make it as shallow as possible, minimal contact on the cantilever, splinted implants to share the load