Section2- Biological molecules
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
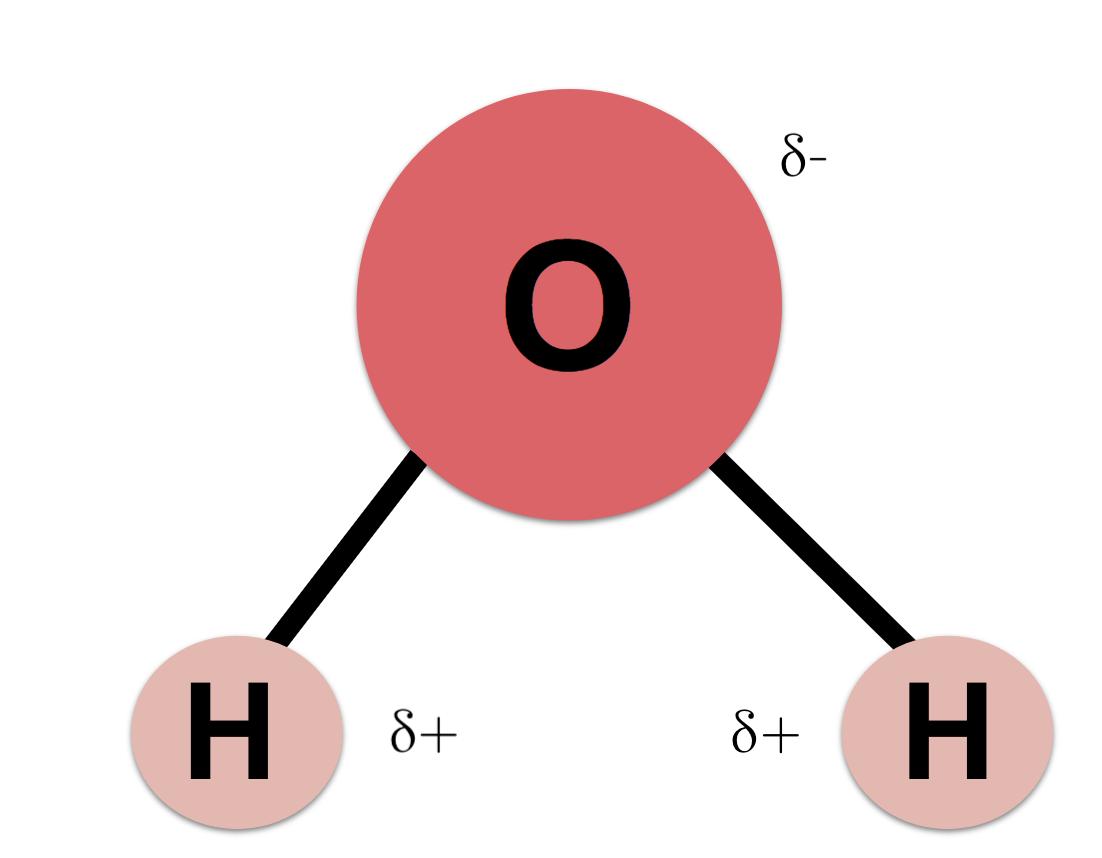
What does dipolar mean?
Two charges
Is water dipolar and if so why?
Yes
It has a +ve and -ve charge
What bond holds together water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds
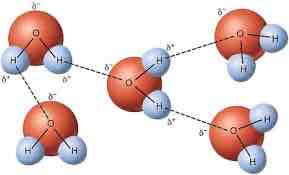
What is cohesion ?
Water molecules being held together
Water+water
What is adhesion?
Water+another molecule
What is high specific heat capacity?
Takes a lot of energy to change temperature
Why is water important?
Reactant- in lots of chemical reactions including hydrolysis
Ice floats- water is less dense when it is solid and forms an insulating layer
Habitat- organisms survive and reproduce in it
Solvent- some substances dissolve in it. Most biological reactions take place in solution (in cytoplasm)
Transports substances- like glucose and oxygen around plants and animals
Temperature control- high specific heat capacity and high latent heat of evaporation
Explain how the temperature of water might affect its ability to hold oxygen
Water is held together by hydrogen bonds
As water cools the distance between water molecules increase
Water can hold more oxygen
How does being a solvent help water molecules?
Being a solvent allows water molecules to attach themselves to other molecules. This allows water to be transported, absorbed and be used in metabolic reactions. Examples of this are water attaching to sodium atoms in blood as a form of transport.
What are the three types of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (one)
Disaccharides (two)
Polysaccharides (many)
Describe the structure of a monosaccharide
Carbon backbone made from 3,4,5 or 6 carbon atoms
One C forms a double bond with an oxygen atom
The other carbons in the chain are bonded to one hydrogen atom(H) or one hydroxyl group(-OH)’
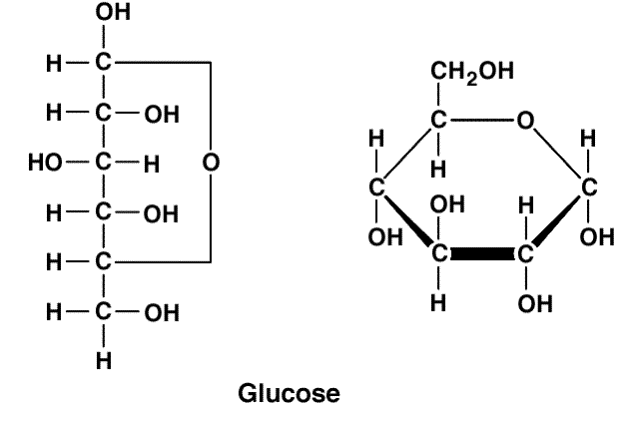
Draw a glucose molecule
What type of ring does a glucose have and what makes it classify as one of these?
Pyranase ring
5 carbon ring with an oxygen
What are the three monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose and galactose
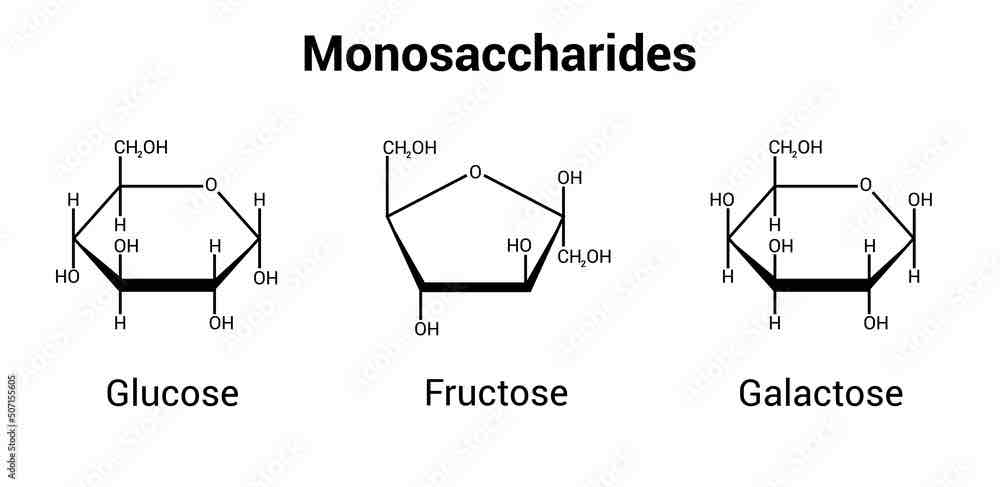
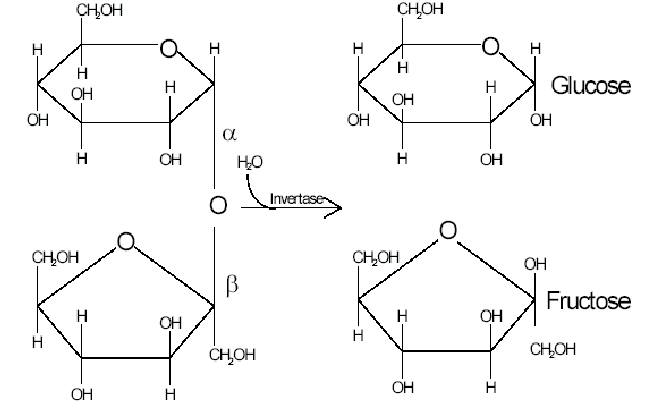
What type of reaction occurs to bind together two glucose molecules?
Condensation reaction
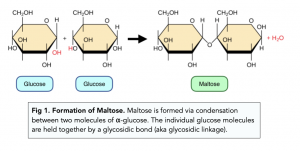
What is removed in a condensation reaction?
Water (H2O)
What bond is formed in a condensation reaction between glucose molecules?
1,4 glycosidic bonds
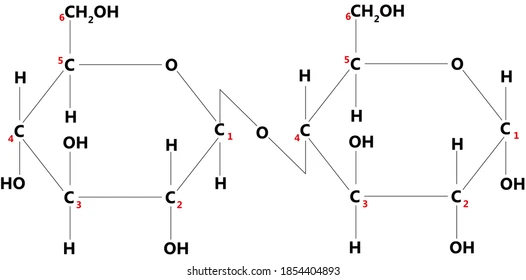
What is made from a condensation reaction?
Made a bigger molecules
Covalent bond is formed
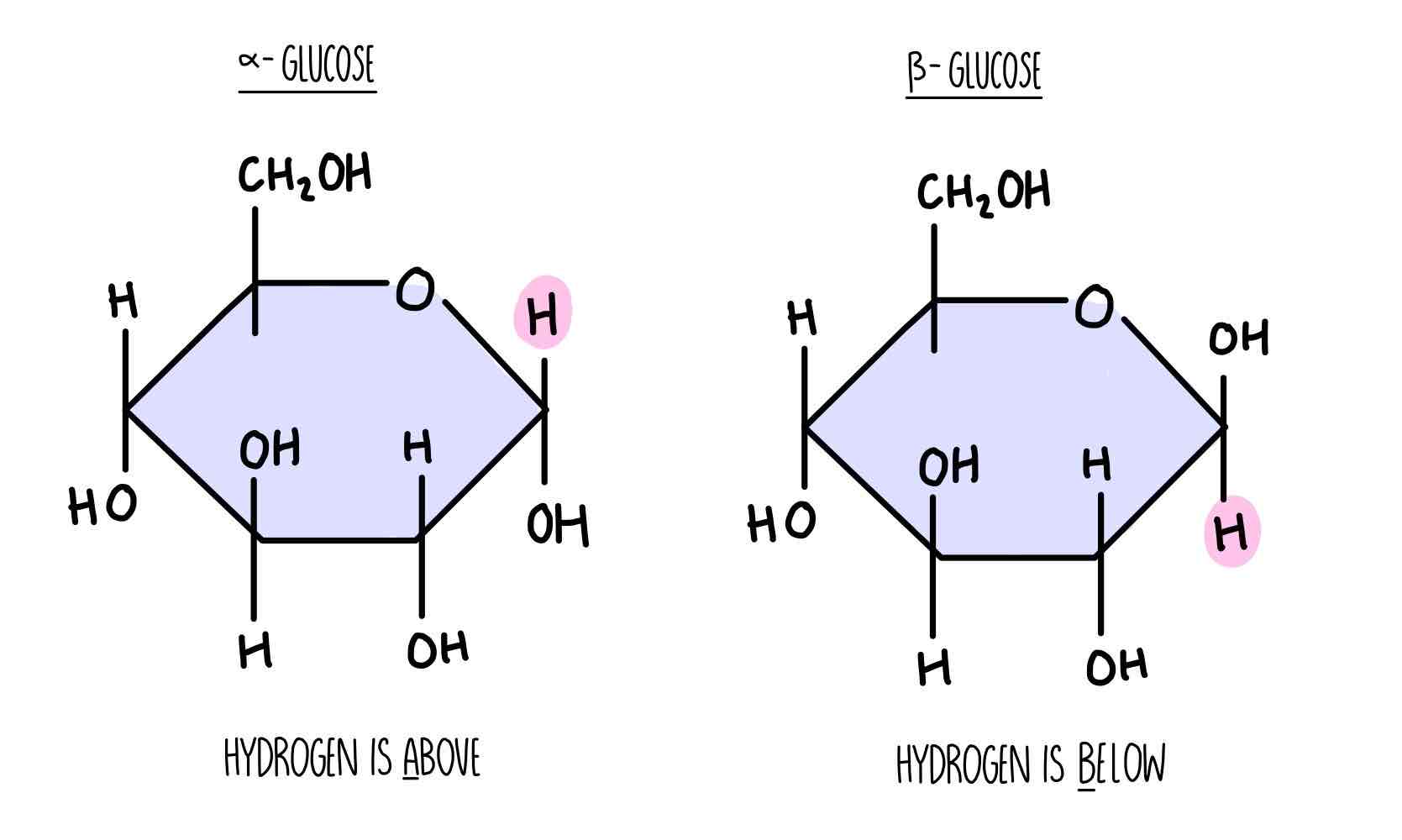
What are the two types of glucoses?
Alpha and beta
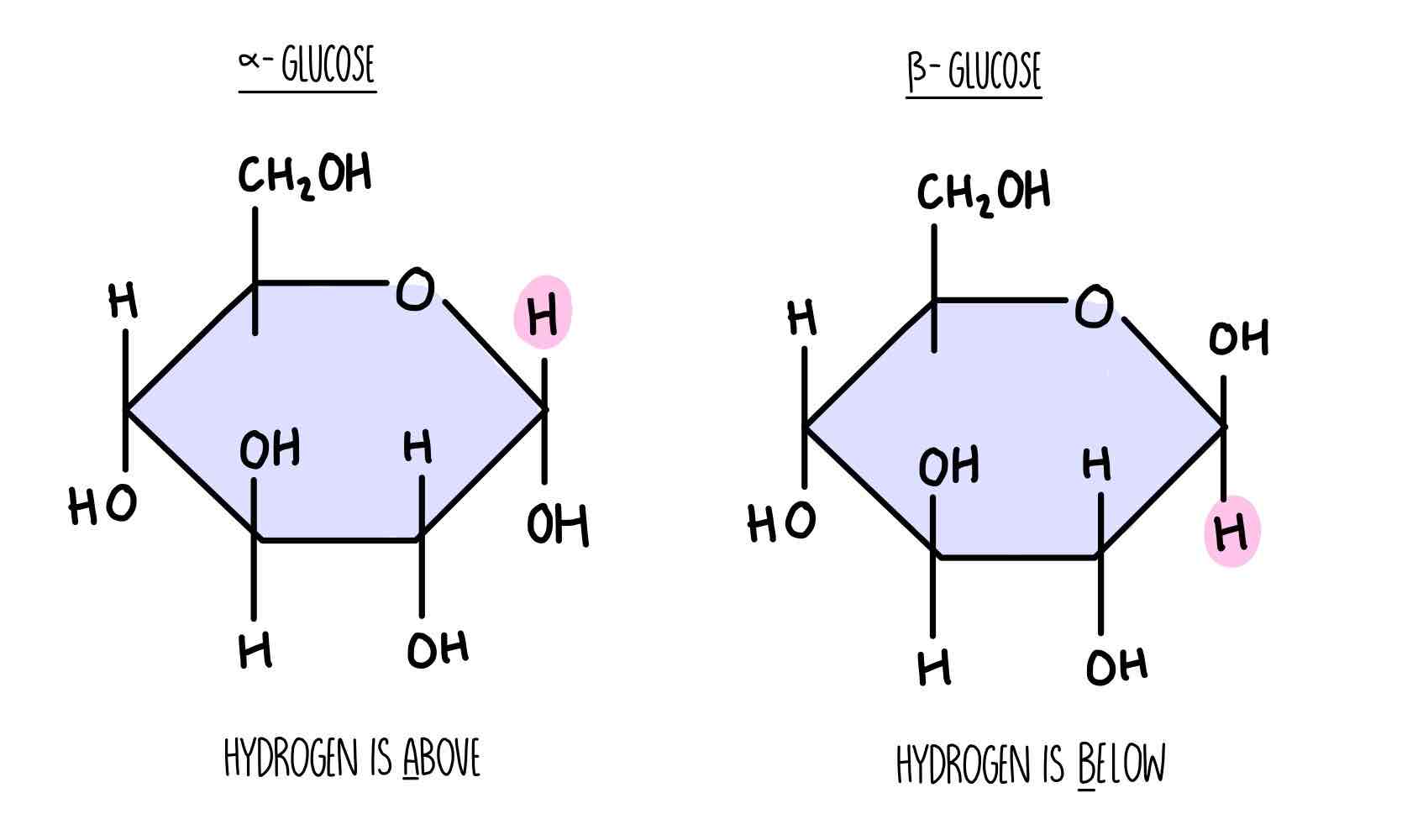
What is isomerism ?
In solution, glucose can take up a number of different shares. Alpha and beta are isomers of each other. They have the same chemical formula but different structural formula. Fructose, glucose and galactose are all isomers
What are disaccharides?
Formed from two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond during a condensation reaction.
What disaccharides do these monosaccharides make?
(Alpha)glucose+(Alpha) glucose =
(Alpha) glucose+(beta) galactose=
(Alpha) glucose+fructose=
Maltose(malt sugar)
Lactose
Sucrose
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
Opposite of condensation
Adding water to break the glycosidic bond to form two monosaccharides j
What type of structure does amylase have?
Coil
What type of shape is amylopectin?
Branching
What shape is Alpha glucose?
Coil shape meaning it is more compact and can fit in more smaller spaces
What type of bond is formed when the bond is branches?
1,6 glycosidic
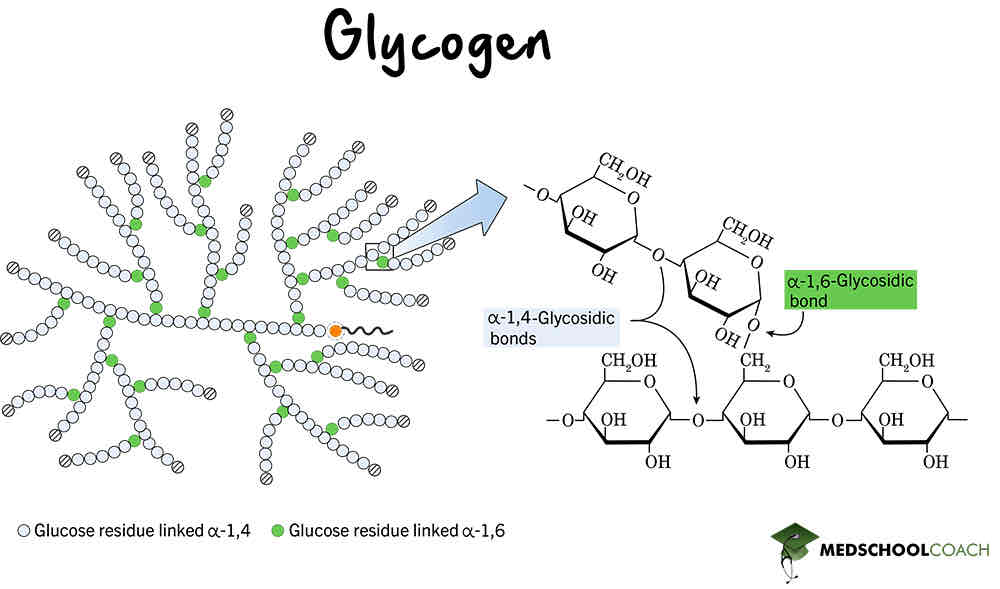
Is glycogen insoluble or soluble ?
Insoluble- doesn’t affect water potential (osmosis)
Glycogen is a polysaccharide of what type of glucose?
Alpha
What are important features of glycogen?
Stored in the liver and muscles in animals
Metabolically inactive so doesn’t use up energy
Has lots of side branches(higher surface are) excellent for fast release of energy
Branches are shorter than starch which allows for quick release of energy
Compact and good for storage
What type of glucose is cellulose made from?
Beta
What are important features of cellulose?
Long straight unbranched chains of Beta glucose
Hydrogen bonds form between the chains forming strong fibres called micro fibrils
Insoluble
Each alternate glucose molecule flips 180degrees to allow hydrogen bonding of the hydroxyl group
Many chains of microfibrils which gives cellulose its stability and mechanical strength

What are the uses of lipids?
Thermal insulation
Buoyancy
Cell membranes
Protection(around vital organs)
Store of energy(adipose fat tissue)
Electrical insulation(insulate nerve cells)
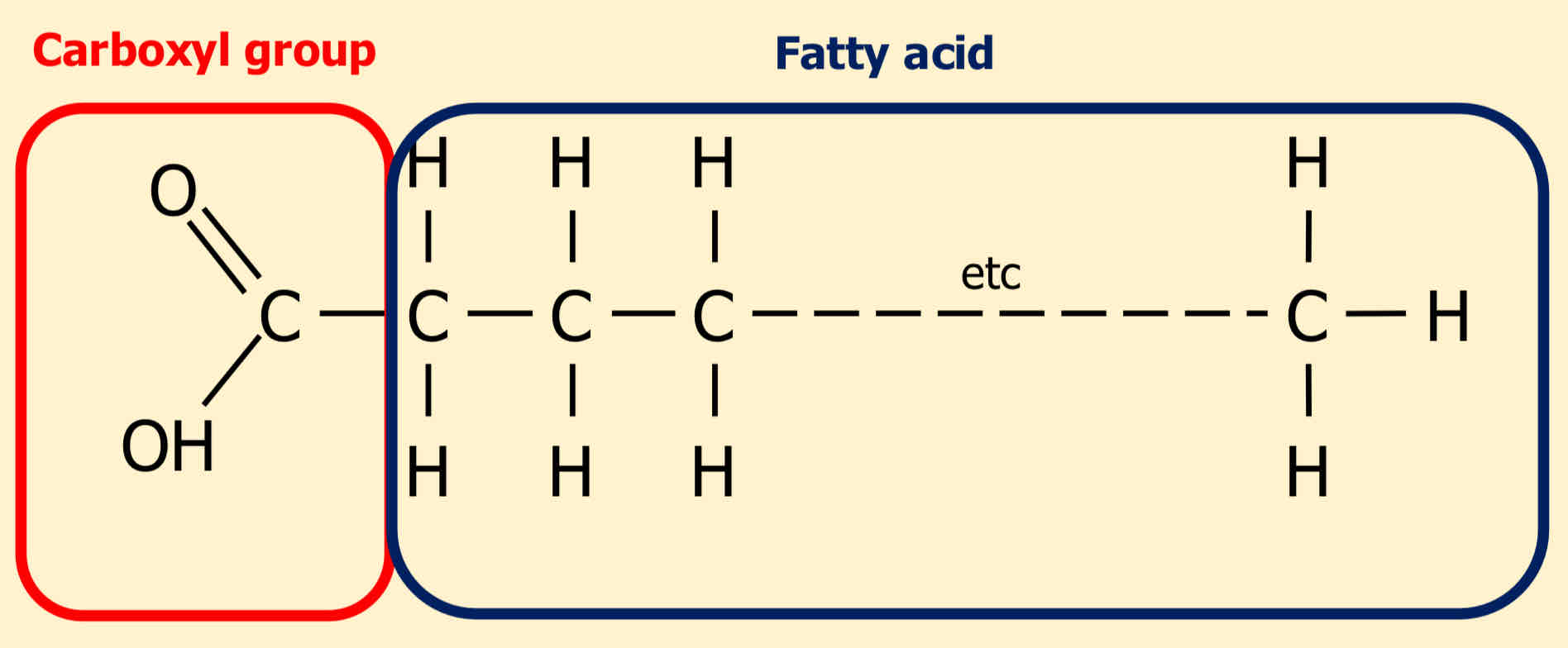
What two components make up a lipid?
Carboxyl group and fatty acid
What does hydrophilic mean?
Water loving
What is hydrophobic?
Water hating
In a lipid, which part is hydrophilic and which is hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic- carboxyl group
Hydrophobic- fatty acid
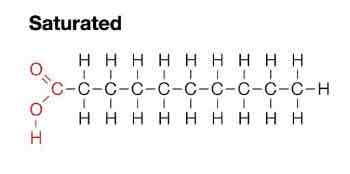
What do saturated fats consist of?
Single carbon bonds
Solid fats
Straight compacted structure
Differ at state at 20degrees
What are unsaturated fats like?
Oils
Double carbon bond
Monounsaturated- has one c=c bond
Polyunsaturated- has more than one c=c bond
Kinked by c=c
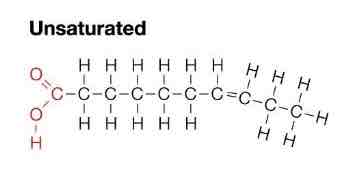
What are phospholipids and triglycerides examples of?
Macromolecule
What two components make up a triglyceride?
Glycerol and fatty acid
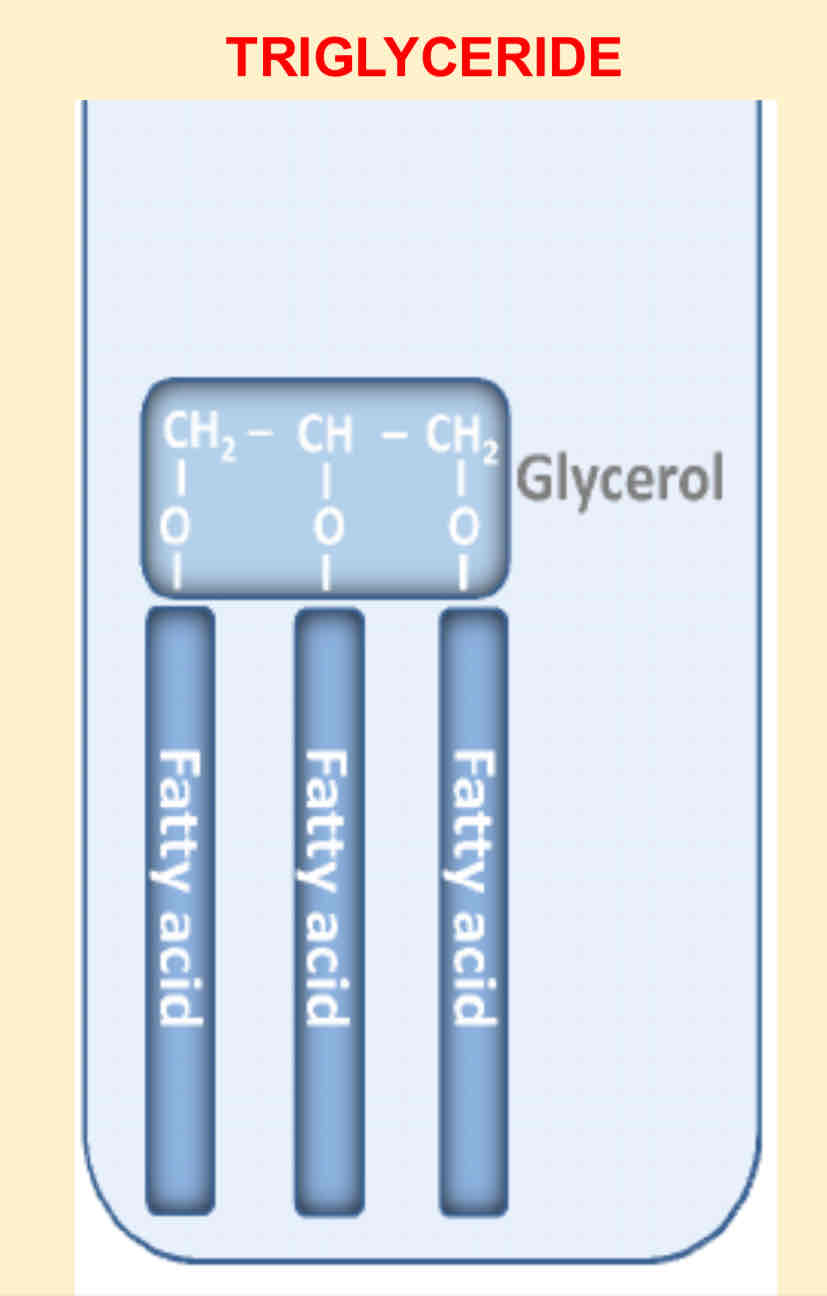
What reaction happens in triglycerides?
Condensation
What bond is formed in a triglyceride?
Ester linkage/bond
Is a triglyceride insoluble or soluble In water?
Insoluble
Due to hydrophobic tail
What are the functions of triglycerides?
Storage of energy( almost twice as much energy is released compared to carbohydrates as hydrogen atom proportion is higher
Acts as thermal insulator
What makes a phospholipid different to a triglyceride?
One of the fatty acids of the triglyceride is substituted by a phosphate group
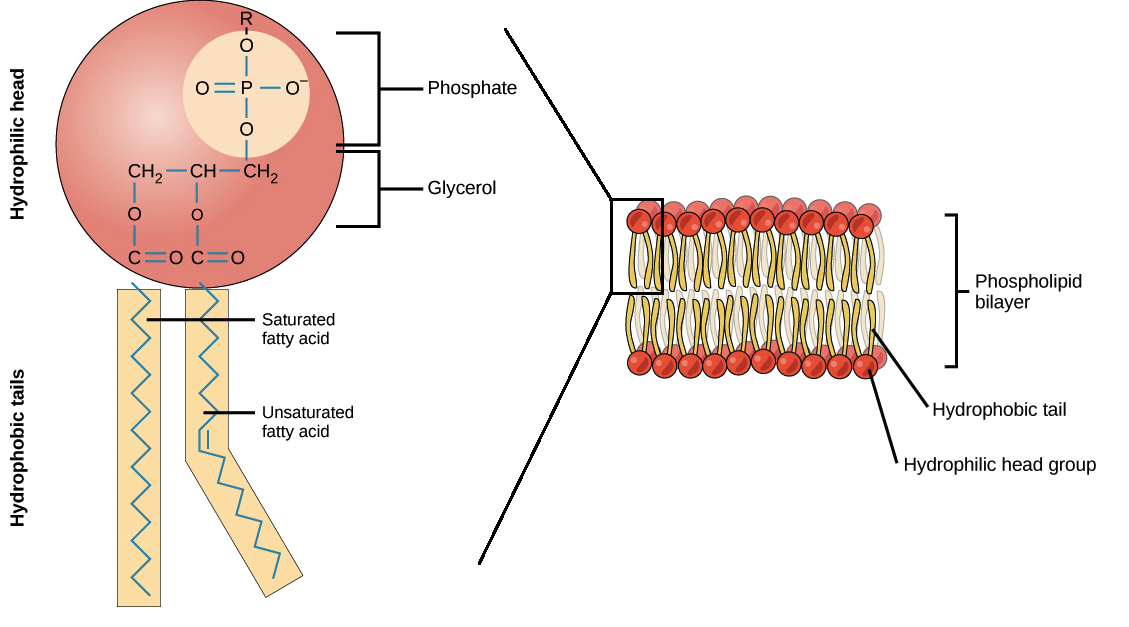
What charge does the phosphate group have in water and how does this compare to fatty acids in water?
A negative charge (attracting the water)
Fatty acids tail are non-polar and repelled by water
Does the heads or tails need to be unsaturated?
Tails
What are the roles of phospholipids?
Cell membranes(also membranes of organelles)
Forms a bilayer with extracellular fluid and cytoplasm
Double bonds in fatty acid tails will increase the fluidity which is beneficial for animals in cold environments
Draw cholesterol
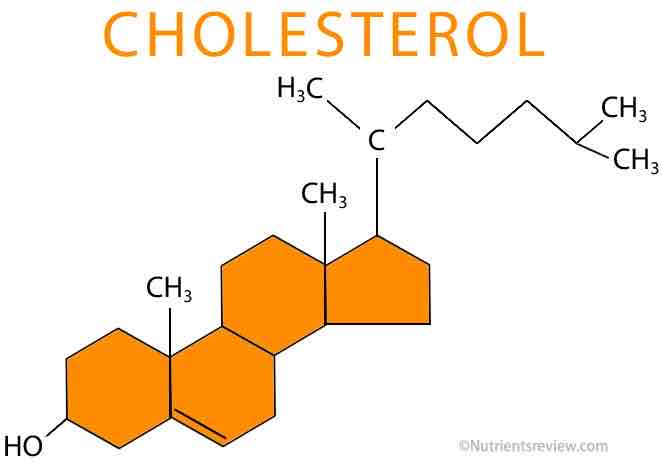
What are some of the features of cholesterol?
Made from four carbon rings with a hydrocarbon tail
The ring has a polar hydroxyl (OH) group
Fits in-between phospholipids and regulates the fluidity of the cell surface membrane
They bind to the hydrophilic tails causing them to pack more closely together=more rigid
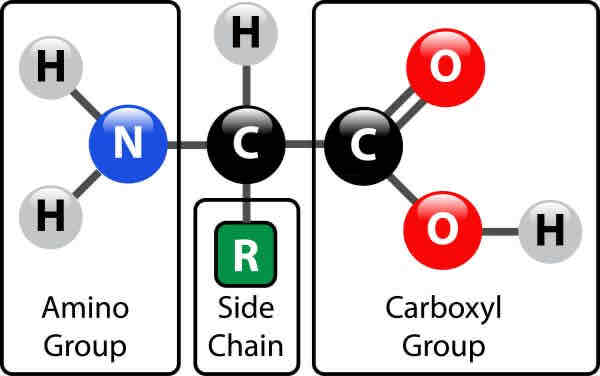
What are proteins made from?
Amino acids
What groups can be found in a protein?
Amine/amino group(-NH2)
Carboxyl group(-COOH)
R group- variable region(1of20)
How do we obtain essential and non essential amino acids?
Essential- nutrition and diet
Non-essential - body makes them
What does amphoteric mean?
The amino acid can act as both an acid and a base
How can the amino group act as a base and then the Carboxyl group as an acid?
Amino group can accept a proton (+H) and act as a base
Carboxyl group can donate a proton and act as an acid
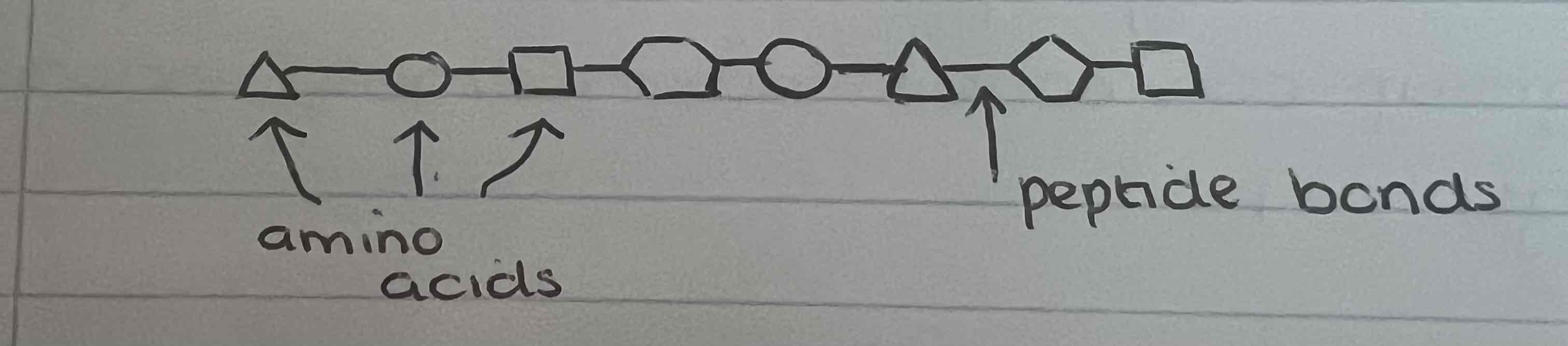
What reaction fuses two amino acids together?
Condensation
What bond is formed between two amino acids?
Peptide bond
What reaction can separate two amino acids?
Hydrolysis
What are the four structures?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
What is the primary structure?
Order, number and sequence of amino acids
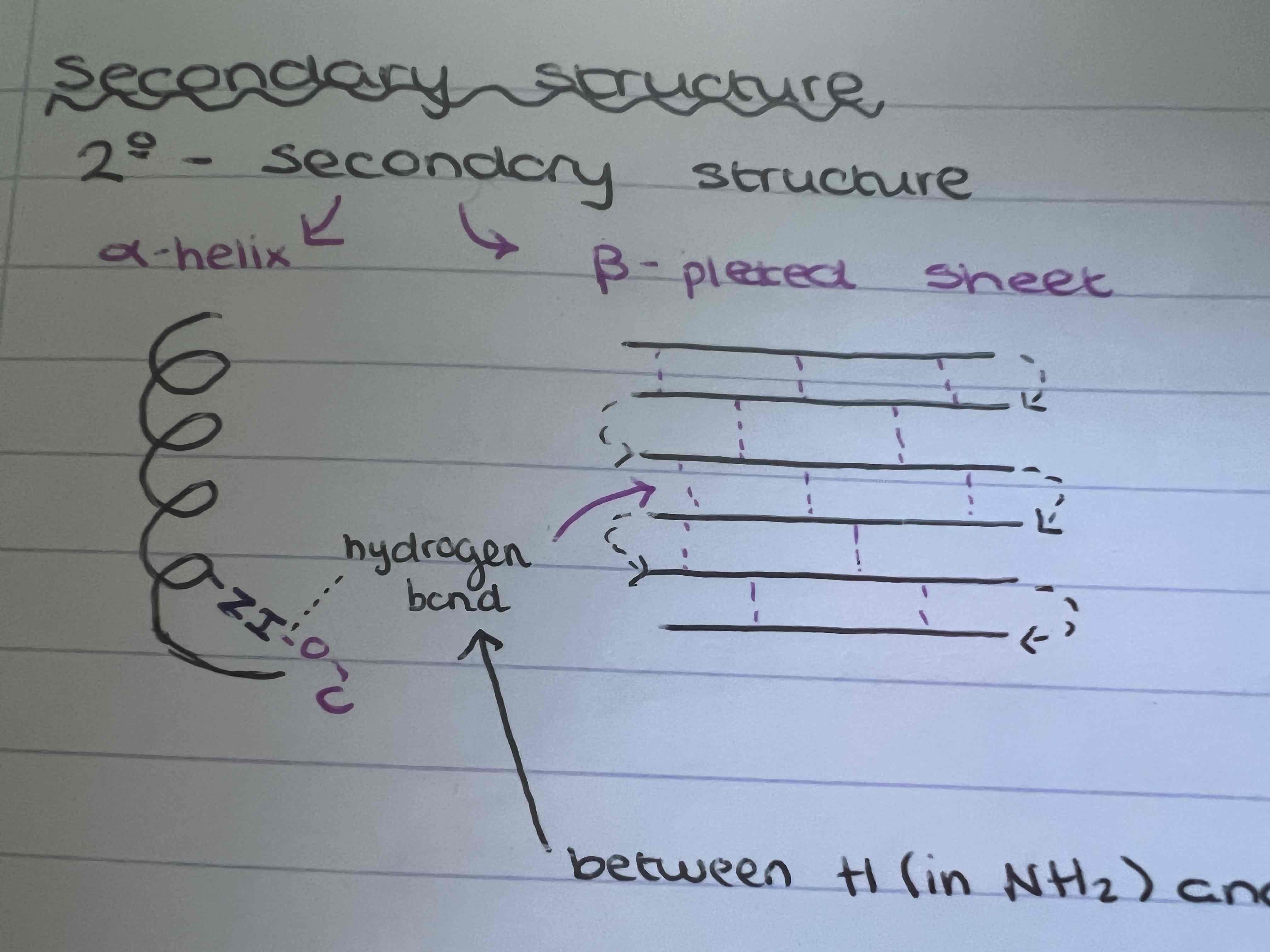
What is the secondary structure?
Either Alpha helix or beta pleated sheets which contain hydrogen bonds
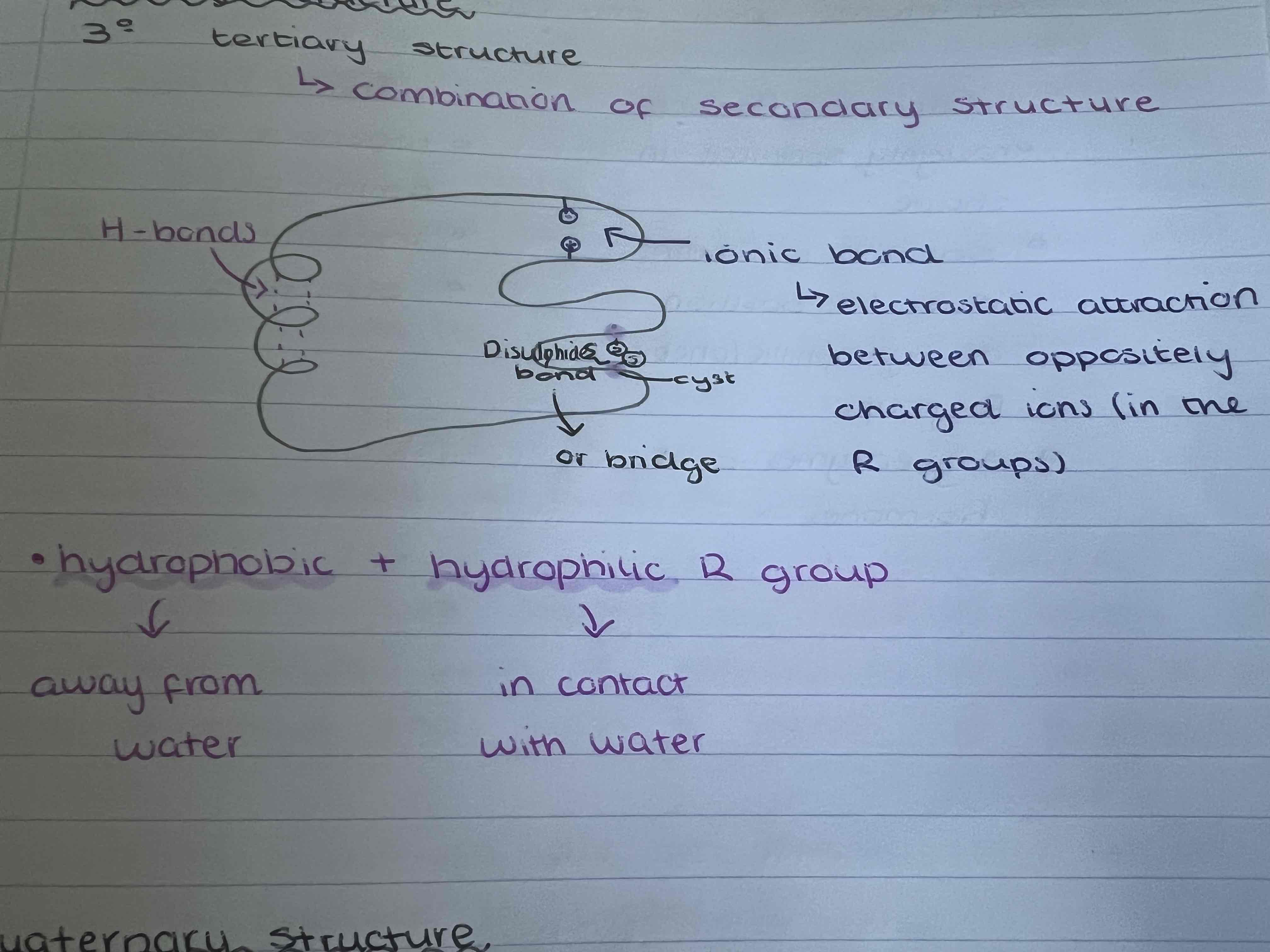
What is the tertiary structure?
Combination of secondary structure
What is quaternary structure?
Arises from a combination of:
A number of different polypeptide chains
Non-protein group (prosthetic group)

What are the two forms of tertiary and quaternary structures?
Globular proteins and fibrous proteins
What are globular proteins like?
roughly spherical in shape
Soluble in water due to position of hydrophilic/phobic R-groups
What are fibrous proteins like?
repetitive sequence of amino acids
Insoluble in water
Structural
What are the three examples of globular protein and give some info on them
Haemoglobin
Made up of two alpha globing and two globin polypeptide chains
Haem group called prosthetic group
Conjugated protein
Insulin
Made of two polypeptide chains
Chains joined by disulphide bonds
Hydrophilic r-groups are on the outside which makes it soluble
Amylase
Catalyses the break down of starch to maltose
Single chain of amino acid with both alpha helix and beta pleated sheet

What are the three examples of fibrous proteins and what are they like?
Collagen
Repeating sequences of amino acids
Each 3rd amino acid is glycine resulting in a left-handed alpha helix shape
Made of 3 polypeptide chains
Hydrogen bonds hold them together
Keratin
Rich in cysteine so lots of disulfide bridges between polypeptide chains
Hydrogen bonds make it very strong
Provides mechanical protection and is also waterproof
Elastin
Cross-linking ans coiling make the structure of elastin strong and flexible
When subjected to stretching the proteins elongate but remain attached to each other
