21 - Blood – physiology and functions. Composition and volume of the circulation blood – regulation. Plasma – composition and regulation. Haematocrit. Blood reservoirs
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
sections
function of blood
blood volume
blood resevoirs
what is hematocrit
cause for low haematocrit
cause of high haematocrit
blood regulation
plasm
important proteins in plasms
function of blood
regulates body temp
protection- has leuckocytes, platelets for clots- prevent blood loss
used for internal organs
transport O2 with haemoglobin and nutrients are transported in blood, remove waste CO2----remove waste
nutritive- carries glucose, electrolytes, vitamins, amino acids regulation of
homeostasis of ions and water
blood volume
blood volume is determined by the amount of water and sodium ingested
Blood contains intracellular and extracellular fluid.
45% erythrocytes 55% is plasma
6-8% volume in the body
5-6L in body
blood resevoirs
spleen
liver
skin- veins in adipose tissue under the skin
vein- biggest blood reservoir
the heart and the lungs are not part of the reservoir system, but can be considered blood reservoirs.
do men or women have more RBC
Males have more RBC because they have more testosterone- increases erythropoiesis
what is hematocrit
relationship between volume of erythrocytes and total volume of blood
measures the fraction of the blood that is made up of RBCs.
Males- 0.4-0.5
F- 0.35-0.45
Normal results for children vary, but in general are:
Newborn: 45 to 61%
• Infant: 32 to 42%
cause for low haematocrit (low RBC count)
Haemorrhage
Dehydration
diarrhea/vomiting
Tumor in the hypothalamus
ADH - Alcohol inhibits ADH production
coffee, tea increase urine output
cause of high haematocrit (high RBC count)
Abnormal increase in red blood cells
Low blood oxygen levels (hypoxia)
Scarring or thickening of the lungs
Bone marrow disease that causes abnormal increase in RBCs
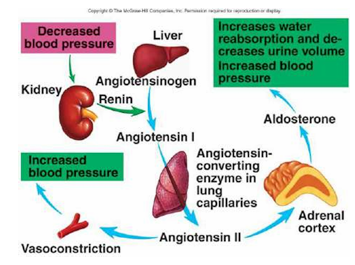
blood regulation
The body releases hormones to correct the blood volume:
ADH (antidiuretic hormone): Increases water reabsorption in kidneys.
Aldosterone: Increases sodium (and water) retention.
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide): Promotes salt and water excretion when blood volume is too high.
Kidney Response:
Kidneys adjust the amount of water and salts reabsorbed or excreted in urine. This helps either conserve or eliminate fluids.Thirst Mechanism:
When blood volume is low, the brain triggers thirst so you drink more water to restore volume.Vasoconstriction or Vasodilation:
Blood vessels can narrow (vasoconstriction) to maintain pressure if blood volume is low, or widen (vasodilation) if volume is high.
plasma
Plasma is the largest component of blood, making up 55%.
High percentage of water
transport medium for blood cells, dissolved nutrients, plasma proteins, etc.
Removes waste from the body.
maintain blood pressure
regulates body temperature.
important proteins in plasms
Albumin-60%
clotting (coagulation) factors
immunoglobulins
fibrinogen
prothrombin